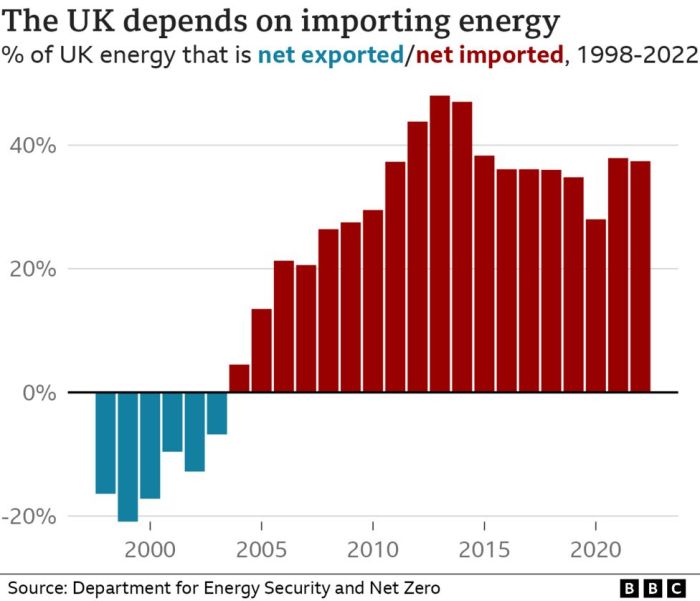
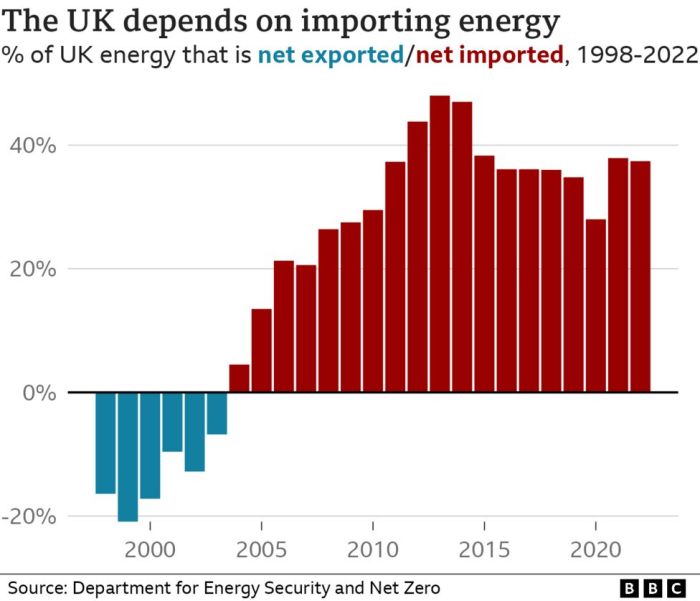
Uk risk lagging behind eu us in clean energy investment race – The UK risks falling behind the EU and US in the clean energy investment race, a concerning trend that could have significant consequences for the nation’s economic competitiveness, environmental sustainability, and energy security. While the UK has made strides in developing renewable energy sources, its investment levels lag behind those of its European and American counterparts.
This gap is fueled by a complex interplay of factors, including policy, market conditions, and public sentiment.
The UK’s current clean energy investment landscape is characterized by a mix of public and private initiatives. The government has set ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, but the private sector has been hesitant to invest at the same scale as in other countries.
This disparity can be attributed to a number of factors, including regulatory uncertainty, financial constraints, and a lack of public support for large-scale energy projects. In contrast, the EU and US have implemented more robust policy frameworks and provided greater financial incentives, encouraging greater private sector participation in clean energy development.
The UK’s Current Clean Energy Investment Landscape
The UK has made significant strides in transitioning to a low-carbon economy, but its clean energy investment lags behind that of the EU and US. While the UK has ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment, achieving these goals requires a substantial increase in investment.
This section will delve into the current state of clean energy investment in the UK, highlighting key sectors and projects, comparing it to other regions, and exploring the reasons behind this lag.
Clean Energy Investment in the UK
The UK’s clean energy investment landscape is characterized by a mix of public and private funding, with a focus on renewable energy sources, energy efficiency, and smart grids. The government has introduced various policies to incentivize clean energy investment, including subsidies, tax breaks, and feed-in tariffs.
These policies have spurred growth in renewable energy generation, particularly in offshore wind, solar, and onshore wind.
- Offshore Wind:The UK is a global leader in offshore wind, with over 10 GW of installed capacity. The government has set ambitious targets for offshore wind deployment, aiming to reach 40 GW by 2030. This growth is driven by large-scale projects like Dogger Bank Wind Farm, which is expected to be the world’s largest offshore wind farm upon completion.
- Solar:Solar power has witnessed significant growth in the UK, driven by declining costs and government support. The UK has over 13 GW of installed solar capacity, primarily from rooftop installations and utility-scale solar farms. However, recent policy changes, such as the removal of feed-in tariffs for new solar installations, have slowed down growth in this sector.
- Onshore Wind:Onshore wind is another key renewable energy source in the UK, with over 14 GW of installed capacity. However, onshore wind development has faced challenges due to public opposition and planning restrictions. Despite these challenges, the UK government has committed to supporting onshore wind development, recognizing its potential to contribute to the country’s clean energy goals.
Comparison with the EU and US
The UK’s clean energy investment pales in comparison to that of the EU and US. The EU has committed to a Green Deal, aiming for climate neutrality by 2050, and has significantly increased its investment in clean energy technologies. The US, under the Biden administration, has also made clean energy a top priority, with significant investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, and electric vehicle infrastructure.The UK’s clean energy investment is characterized by a lower scale and a different focus compared to the EU and US.
While the UK has made significant progress in offshore wind, its investment in other renewable energy sources, such as solar and onshore wind, lags behind. Additionally, the UK has been slower to adopt policies promoting energy efficiency and smart grid technologies.
Reasons for Lagging Investment
Several factors contribute to the UK’s lagging clean energy investment.
- Policy Uncertainty:Frequent policy changes and a lack of long-term policy certainty have created uncertainty for investors. The UK government has shifted its approach to clean energy support multiple times, which has discouraged long-term investment.
- Market Conditions:The UK’s energy market is characterized by high energy prices and a complex regulatory environment. These factors make it challenging for clean energy projects to compete with traditional fossil fuel-based power generation.
- Public Sentiment:Public sentiment towards clean energy projects, particularly onshore wind, has been mixed. Concerns about visual impact and potential environmental impacts have hindered the development of some projects.
Challenges and Opportunities for the UK: Uk Risk Lagging Behind Eu Us In Clean Energy Investment Race
The UK faces a number of challenges in attracting and retaining clean energy investment, which could hinder its progress towards a sustainable future. These challenges are interconnected and require a comprehensive approach to address them effectively.
Regulatory Hurdles
The UK’s regulatory environment has been identified as a key challenge for clean energy investors. Complex and evolving regulations can create uncertainty and increase costs for businesses, making the UK less attractive compared to other markets with more streamlined and predictable regulatory frameworks.
- Permitting Process:The lengthy and complex permitting process for renewable energy projects can significantly delay development and increase costs. Streamlining the permitting process and providing clear guidance on regulatory requirements could attract more investment.
- Grid Connection:Connecting new renewable energy projects to the grid can be challenging due to limited grid capacity and complex connection processes. Addressing grid constraints and simplifying connection procedures would be crucial to facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources.
- Policy Stability:Frequent changes in government policies and support mechanisms can create uncertainty for investors, discouraging long-term commitments. Establishing a stable and predictable policy framework would provide investors with the confidence needed to make significant investments in the UK’s clean energy sector.
Financial Constraints
The UK’s clean energy sector faces financial constraints, including limited access to capital and high costs associated with developing and deploying clean energy technologies.
- Access to Capital:Attracting private investment in clean energy projects can be challenging due to perceived risks and long-term payback periods. Expanding access to capital through innovative financing mechanisms and government-backed investment schemes could address this issue.
- High Project Costs:The high cost of developing and deploying clean energy technologies, particularly in areas like offshore wind and hydrogen production, can make projects less attractive to investors. Developing cost-effective technologies and exploring new business models could make clean energy projects more financially viable.
Find out further about the benefits of switzerland bans violent games that can provide significant benefits.
Technological Barriers
While the UK has a strong research and development capacity in clean energy technologies, there are still technological challenges that need to be overcome to achieve widespread adoption.
- Energy Storage:Developing cost-effective and reliable energy storage solutions is crucial for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS):CCS technologies play a critical role in decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors, such as heavy industry and power generation. The UK needs to accelerate the development and deployment of CCS technologies to achieve its net-zero targets.
- Hydrogen Production:Green hydrogen production, using renewable energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, is a promising clean energy source. However, scaling up hydrogen production and distribution infrastructure requires significant investment and technological advancements.
Opportunities for Accelerated Clean Energy Investment
Despite the challenges, the UK has significant opportunities to accelerate clean energy investment and become a global leader in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- Emerging Technologies:The UK can capitalize on its strengths in research and development to foster innovation in emerging clean energy technologies, such as advanced battery storage, next-generation solar panels, and sustainable biofuels.
- Market Trends:The growing global demand for clean energy technologies presents a significant market opportunity for UK businesses. Leveraging this demand by developing and exporting clean energy solutions can boost economic growth and create new jobs.
- International Collaborations:The UK can collaborate with other countries to share best practices, develop joint research projects, and attract international investment in clean energy projects.
Policy Recommendations for the UK

The UK faces a significant challenge in attracting and retaining clean energy investment. To bridge the gap and accelerate the transition to a low-carbon economy, a comprehensive policy framework is crucial. This framework should focus on enhancing the investment environment, addressing regulatory barriers, and fostering collaboration between the public and private sectors.
Tax Incentives
Tax incentives play a vital role in incentivizing private investment in clean energy projects. These incentives can be structured to target specific technologies or project phases, ensuring maximum impact.
- Enhanced Investment Tax Relief:Extending the existing Investment Tax Relief scheme to cover a broader range of clean energy technologies, including renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture and storage, would encourage investment in these sectors.
- Accelerated Depreciation:Allowing for faster depreciation of clean energy assets would reduce the upfront capital costs for investors, making projects more financially attractive. This would encourage investment in technologies with longer payback periods, such as large-scale solar or offshore wind farms.
- Tax Credits for Renewable Energy Production:Introducing tax credits for renewable energy producers would provide direct financial support, boosting profitability and encouraging further investment in renewable energy generation.
Regulatory Reforms
Streamlining and simplifying regulatory processes is crucial for attracting investment in clean energy.
- Faster Permitting Processes:Reducing the time and complexity associated with obtaining permits for clean energy projects would make the UK more attractive to investors. Streamlining the permitting process and leveraging digital tools could significantly reduce delays.
- Clarity on Grid Connection:Providing clear and predictable guidelines for connecting renewable energy projects to the grid would reduce uncertainty and encourage investment in renewable energy generation.
- Stable Policy Framework:Establishing a stable and predictable policy framework for clean energy, with clear long-term targets and consistent support mechanisms, would provide investors with the confidence needed to commit to long-term projects.
Public-Private Partnerships
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can unlock significant investment in clean energy infrastructure. PPPs allow for the sharing of risks and rewards between the public and private sectors, leveraging the expertise and resources of both.
- Green Infrastructure Funds:Establishing dedicated green infrastructure funds, with public and private sector participation, would provide a source of long-term capital for large-scale clean energy projects. These funds could focus on specific sectors, such as offshore wind or energy storage.
- Public Procurement:Utilizing public procurement to prioritize clean energy solutions would create a market for innovative technologies and stimulate private sector investment in these areas.
- Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration:Facilitating knowledge sharing and collaboration between public and private sector actors would accelerate innovation and improve the efficiency of clean energy projects.
Economic and Environmental Benefits, Uk risk lagging behind eu us in clean energy investment race
Implementing these policy recommendations would not only boost clean energy investment but also deliver significant economic and environmental benefits.
- Job Creation:The clean energy sector is a major job creator. By attracting investment, the UK can create new jobs in manufacturing, construction, operation, and maintenance of clean energy infrastructure.
- Reduced Energy Costs:Increased investment in renewable energy can help reduce the UK’s reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower energy costs for consumers and businesses.
- Reduced Carbon Emissions:Shifting to clean energy sources would significantly reduce the UK’s carbon footprint, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Energy Security:By diversifying energy sources, the UK can enhance its energy security and reduce its dependence on volatile global energy markets.
Global Context of Clean Energy Investment
The UK’s clean energy investment landscape is not only influenced by domestic policies but also by global trends and strategies. Understanding the approaches taken by other major players, such as the EU and US, provides valuable insights into the international context of clean energy investment.
Comparative Analysis of EU and US Clean Energy Investment Strategies
The EU and US have distinct approaches to clean energy investment, each with its strengths and weaknesses.
- EU:The EU’s strategy focuses on a comprehensive approach with ambitious targets for renewable energy deployment and energy efficiency improvements. Its flagship program, the Green Deal, aims to achieve climate neutrality by 2050. Key strengths include a robust regulatory framework, strong financial instruments, and a commitment to cross-border collaboration.
However, challenges include bureaucratic complexities and the need for further investment in innovative technologies.
- US:The US approach emphasizes market-driven solutions and technological innovation. Its recent infrastructure investments, including the Inflation Reduction Act, provide significant financial incentives for clean energy projects. Strengths include a large domestic market and a strong tradition of technological innovation.
However, the US faces challenges in terms of policy consistency and the need for more comprehensive climate action.
The Role of International Cooperation and Collaboration
International cooperation is crucial for accelerating global clean energy investment. Joint initiatives can help overcome barriers such as financing gaps, technology transfer challenges, and policy misalignment.
- International Energy Agency (IEA):The IEA plays a significant role in promoting global energy security and clean energy transitions. It provides data, analysis, and policy recommendations to governments and industry stakeholders.
- International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA):IRENA focuses on promoting renewable energy deployment and fostering international cooperation. It provides technical assistance, capacity building programs, and knowledge sharing platforms.
Global Trends in Clean Energy Technology and Finance
Global trends in clean energy technology and finance are shaping the investment landscape.
- Declining Costs of Renewable Energy:The cost of renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind, has significantly declined in recent years, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. This trend is driving investment in renewable energy projects worldwide.
- Emergence of Green Finance:The growth of green finance, including green bonds and sustainable investment funds, is providing new sources of capital for clean energy projects. These financial instruments are attracting investors who seek to align their investments with environmental and social goals.
Case Studies of Successful Clean Energy Investments
Successful clean energy investments serve as valuable models for future projects, demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of various technologies and approaches. By examining these case studies, the UK can gain insights into best practices, overcome challenges, and identify opportunities for replicating success within its own clean energy landscape.
Successful Clean Energy Projects in the UK, EU, and US
The following table presents case studies of successful clean energy projects in the UK, EU, and US, highlighting their key features, challenges, and lessons learned.
| Project Name | Location | Technology | Investment Size | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| London Array Offshore Wind Farm | UK | Offshore wind | £1.5 billion | – Generates enough electricity to power 500,000 homes.
|
| Horns Rev 3 Offshore Wind Farm | Denmark | Offshore wind | €1.2 billion | – Generates enough electricity to power 425,000 homes.
|
| Ivanpah Solar Power Facility | US | Concentrated solar power | $2.2 billion | – Generates enough electricity to power 140,000 homes.
|
Key Lessons Learned from Case Studies
These case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities associated with successful clean energy investments:
- Government Support:Strong government policies, including financial incentives and regulatory frameworks, are crucial for attracting investment and mitigating risk.
- Technology Advancement:Continuous innovation in clean energy technologies is essential for driving down costs and improving efficiency.
- Community Engagement:Successful projects involve robust community engagement, ensuring local acceptance and support.
- Risk Management:Effective risk management strategies are necessary to address uncertainties associated with clean energy investments.
- Collaboration:Partnerships between governments, businesses, and research institutions foster innovation and knowledge sharing.
Implications for Future Clean Energy Investment in the UK
The UK can leverage these case studies to inform its future clean energy investment decisions:
- Prioritize Offshore Wind:The UK has significant potential for offshore wind development, as demonstrated by the London Array project.
- Invest in Solar Power:The success of the Ivanpah facility highlights the viability of large-scale solar power projects in the UK.
- Promote Innovation:The UK should invest in research and development to advance clean energy technologies, particularly in areas like energy storage and smart grids.
- Strengthen Policy Framework:The government should create a clear and supportive policy framework that encourages private investment in clean energy.
- Engage Communities:Future projects should prioritize community engagement and ensure local benefits.