From surplus energy to investment opportunities startups across europe combat fuel poverty – From surplus energy to investment opportunities, startups across Europe are combatting fuel poverty, a growing crisis that affects millions. Fuel poverty, the inability to afford adequate heating and electricity, is a complex issue with deep roots in energy price volatility, low incomes, and inefficient housing.
The consequences are severe, leading to health problems, financial strain, and social isolation. However, innovative startups are rising to the challenge, leveraging surplus energy sources, developing cutting-edge technologies, and creating sustainable solutions that are transforming lives.
These startups are not just addressing the immediate needs of those struggling with fuel poverty but also investing in a more equitable and sustainable energy future for Europe. They are creating a ripple effect, inspiring others to join the movement and contribute to a world where everyone has access to affordable and reliable energy.
Fuel Poverty in Europe: From Surplus Energy To Investment Opportunities Startups Across Europe Combat Fuel Poverty
Fuel poverty is a critical issue affecting millions across Europe, characterized by households struggling to afford adequate heating and energy services. This problem is exacerbated by rising energy prices, stagnant incomes, and inefficient housing, creating a complex web of challenges for individuals and families.
The Extent of Fuel Poverty in Europe
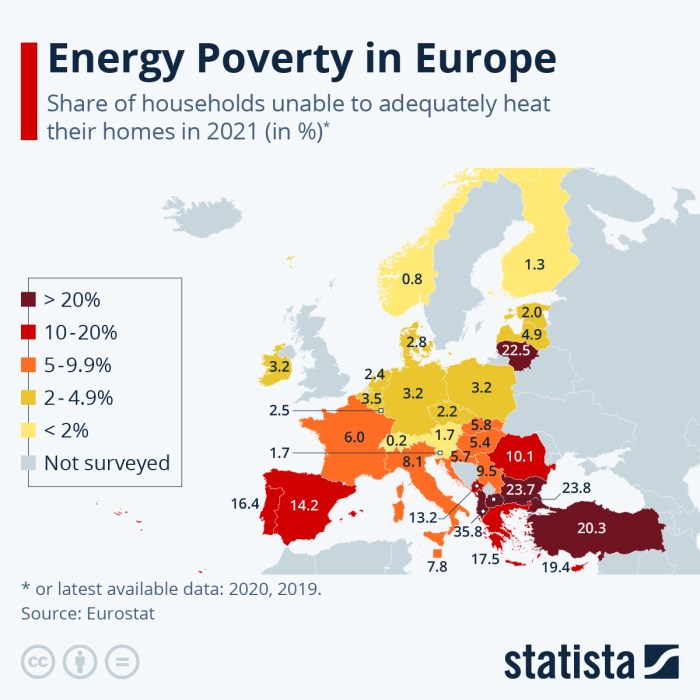
Fuel poverty is a widespread issue across Europe, with varying degrees of severity depending on the country and region. The European Union (EU) defines fuel poverty as a household spending more than 10% of its income on energy. According to Eurostat, in 2020, approximately 54 million people in the EU were living in fuel poverty.
- Eastern Europe:Countries like Bulgaria, Romania, and Latvia have the highest rates of fuel poverty, with over 15% of their populations affected. These countries often have lower incomes and higher energy prices, contributing to the high prevalence of fuel poverty.
- Southern Europe:Southern European countries, including Greece, Spain, and Italy, also face significant fuel poverty challenges. While energy prices may be lower than in Eastern Europe, these countries often have higher unemployment rates and lower incomes, leading to financial strain for many households.
- Northern Europe:Although generally lower, fuel poverty rates are still present in Northern European countries like Finland, Sweden, and Denmark. These countries have higher energy prices and colder climates, contributing to the need for more heating during the winter months.
Causes of Fuel Poverty
Several factors contribute to fuel poverty, creating a complex web of challenges for households struggling to afford adequate heating and energy services.
- Energy Price Volatility:Fluctuations in energy prices, often driven by global market dynamics, can significantly impact household energy bills. Increases in energy prices can disproportionately affect low-income households, pushing them into fuel poverty.
- Low Incomes:Low wages, unemployment, and limited access to social benefits can restrict households’ ability to afford energy. This is particularly prevalent in countries with high levels of income inequality.
- Inefficient Housing:Poorly insulated homes, outdated heating systems, and drafty windows contribute to higher energy consumption and increased energy bills. These issues are often found in older buildings and homes in need of renovation.
Social and Economic Consequences of Fuel Poverty
Fuel poverty has severe social and economic consequences, impacting individuals, families, and communities.
- Health Issues:Cold homes can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and other health complications, particularly among vulnerable groups like the elderly and children.
- Financial Strain:High energy bills can lead to financial hardship, forcing households to cut back on essential expenses like food and healthcare. This can lead to debt, poverty, and social exclusion.
- Social Isolation:Fuel poverty can limit social interaction, as individuals may avoid social gatherings or activities due to concerns about heating costs. This can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Surplus Energy and Investment Opportunities
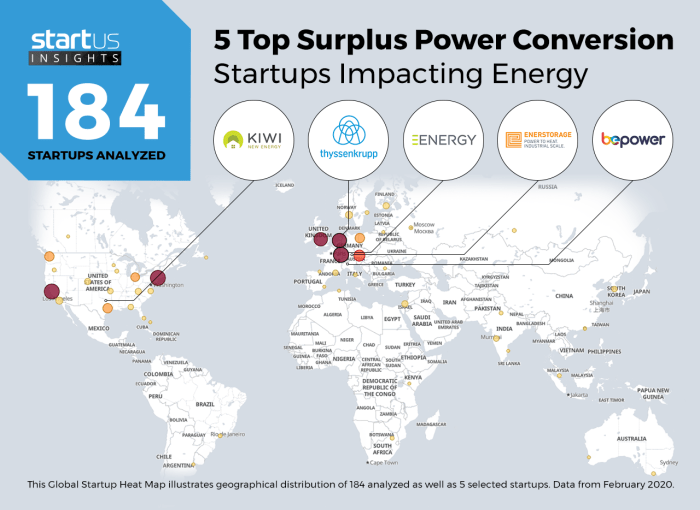
Europe is undergoing a significant energy transition, moving towards a more sustainable and resilient energy system. This shift presents a unique opportunity to address fuel poverty, a pressing issue affecting millions of households across the continent. One key strategy to achieve this is by harnessing surplus energy, the excess energy generated from various sources, and channeling it towards vulnerable communities.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, are becoming increasingly cost-effective and widely accessible. These sources often produce surplus energy, particularly during peak generation periods. For example, solar panels generate the most energy during sunny days, while wind turbines produce more power during strong winds.
This surplus energy can be stored in batteries or used to power homes and businesses in nearby communities.
- Community-owned renewable energy projects: These projects allow local communities to invest in and benefit from renewable energy generation. The surplus energy can be used to power homes and businesses in the community, reducing energy bills and promoting energy independence. An example is the “Energy for All” project in Germany, which has enabled communities to invest in solar power and use the surplus energy to support local residents facing fuel poverty.
- Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms: These platforms allow individuals and businesses to buy and sell excess energy directly from each other. This creates a decentralized energy market where surplus energy can be traded efficiently, providing a more affordable and sustainable energy solution for consumers.
Discover the crucial elements that make europe high tech scramble for better energy storage the top choice.
The “SunShare” platform in the Netherlands allows homeowners with solar panels to sell their excess energy to their neighbors, reducing their energy bills and promoting energy independence.
Energy Efficiency Improvements
Improving energy efficiency in buildings and homes is another crucial aspect of addressing fuel poverty. By reducing energy consumption, households can significantly lower their energy bills and become less vulnerable to energy price fluctuations.
- Smart grids: These systems use advanced technology to optimize energy distribution and consumption, reducing energy waste and improving efficiency. By integrating renewable energy sources and smart grids, surplus energy can be efficiently managed and distributed to homes and businesses, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering energy bills.
- Energy audits and retrofits: These programs help homeowners identify energy-saving opportunities and implement energy-efficient upgrades, such as insulation, efficient appliances, and smart thermostats. These upgrades can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower heating bills, especially for low-income households.
Waste-to-Energy Technologies
Waste-to-energy technologies offer a sustainable way to generate energy while reducing waste. These technologies convert waste into electricity or heat, which can be used to power homes and businesses.
- Anaerobic digestion: This process breaks down organic waste in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used to generate electricity or heat. This technology can be particularly beneficial in reducing reliance on fossil fuels and providing a sustainable source of energy for rural communities.
- Incineration: This technology burns waste at high temperatures, generating heat and electricity. While incineration has environmental concerns, it can be a viable option for waste management and energy generation, particularly in urban areas with limited land for waste disposal.
Investment Opportunities in the Energy Sector
The energy sector is undergoing a major transformation, driven by the need to address climate change and energy security. This presents significant investment opportunities for companies and individuals looking to contribute to a more sustainable and equitable energy future.
- Renewable energy infrastructure: Investing in renewable energy projects, such as solar farms, wind farms, and hydroelectric plants, can provide a steady stream of returns while contributing to a cleaner energy system.
- Energy efficiency technologies: Investing in companies developing energy-efficient technologies, such as smart grids, energy management systems, and building insulation materials, can offer significant returns and help reduce energy consumption.
- Waste-to-energy solutions: Investing in waste-to-energy technologies, such as anaerobic digestion and incineration plants, can help reduce waste and generate clean energy.
- Community energy projects: Investing in community-owned renewable energy projects can provide social and environmental benefits while offering a potential return on investment.
Examples of Successful Startups and Initiatives
Several startups and initiatives across Europe have successfully leveraged surplus energy to address fuel poverty.
- The “Energy for All” project in Germany: This project has enabled communities to invest in solar power and use the surplus energy to support local residents facing fuel poverty. The project has demonstrated the potential of community-owned renewable energy projects to address energy affordability and create social impact.
- The “SunShare” platform in the Netherlands: This platform allows homeowners with solar panels to sell their excess energy to their neighbors, reducing their energy bills and promoting energy independence. The platform has created a decentralized energy market where surplus energy can be traded efficiently, providing a more affordable and sustainable energy solution for consumers.
Startups Combatting Fuel Poverty
Fuel poverty, a pressing issue across Europe, has spurred the emergence of innovative startups developing solutions to address this critical challenge. These startups are leveraging technology and creative business models to empower individuals and communities, offering them access to affordable and sustainable energy sources.
Startup Solutions to Fuel Poverty
These startups are tackling fuel poverty through various approaches, utilizing technology and innovative business models to provide affordable and sustainable energy solutions. Here are some notable examples:
- Energy Efficiency Solutions:Some startups focus on improving energy efficiency in homes, reducing energy consumption, and lowering energy bills. For example, “Sense” (UK) uses smart sensors to identify and reduce energy waste in homes, enabling users to save money on their energy bills.
- Renewable Energy Access:Other startups focus on providing access to renewable energy sources, particularly for those living in off-grid areas or lacking access to traditional energy infrastructure. “SunCulture” (Kenya) offers solar-powered irrigation systems to farmers in developing countries, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and increasing their income.
- Community-Based Energy Solutions:Several startups are developing community-based energy solutions, empowering local communities to manage and control their energy resources. “Etopia” (UK) develops and installs community-owned renewable energy projects, enabling local communities to generate and share clean energy.
Comparison of Startup Approaches, From surplus energy to investment opportunities startups across europe combat fuel poverty
Here’s a table comparing different startup approaches to combat fuel poverty:
| Startup | Target Audience | Technology Used | Impact on Fuel Poverty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sense (UK) | Households | Smart sensors, data analytics | Reduced energy consumption, lower energy bills |
| SunCulture (Kenya) | Farmers in developing countries | Solar-powered irrigation systems | Increased access to clean energy, improved agricultural productivity |
| Etopia (UK) | Local communities | Renewable energy technologies, community ownership models | Increased access to clean energy, reduced energy costs, community empowerment |
Challenges Faced by Startups
Startups tackling fuel poverty face several challenges in scaling their solutions:
- Funding:Securing sufficient funding to develop and deploy their solutions is a major hurdle. Many startups rely on venture capital, grants, and social impact investments, but accessing these funds can be challenging.
- Regulation:Navigating complex regulatory frameworks and obtaining necessary permits can be time-consuming and costly.
- Market Penetration:Reaching a large enough customer base to achieve significant impact can be difficult. This requires effective marketing strategies and partnerships with local organizations.
- Sustainability:Ensuring long-term financial sustainability and creating a sustainable business model is crucial for startups to thrive and continue to address fuel poverty.
Policy and Regulatory Landscape
Navigating the policy and regulatory landscape is crucial for startups tackling fuel poverty in Europe. Existing frameworks present both opportunities and challenges for these innovative ventures. Understanding the current landscape and identifying potential policy recommendations can foster an environment conducive to their growth and impact.
Current Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
The European Union (EU) has implemented various policies to address energy poverty, including the Energy Poverty Observatory, the Energy Efficiency Directive, and the Renewable Energy Directive. These initiatives aim to promote energy efficiency, renewable energy sources, and affordable energy access.
However, these policies often focus on broader energy issues and may not adequately address the specific needs of startups tackling fuel poverty. For example, the Energy Efficiency Directive encourages energy efficiency improvements in buildings, but it may not sufficiently address the specific challenges faced by low-income households with older, poorly insulated homes.
Policy Recommendations for a More Favorable Environment
To create a more favorable environment for startups tackling fuel poverty, several policy recommendations can be considered:
- Targeted Funding Programs:Establishing dedicated funding programs specifically for startups developing innovative solutions to address fuel poverty would provide crucial financial support for research, development, and deployment. These programs could include grants, loans, and equity investments.
- Regulatory Sandbox Programs:Creating regulatory sandbox programs would allow startups to test their solutions in a controlled environment, reducing regulatory hurdles and accelerating the development and deployment of innovative solutions.
- Data Accessibility:Improving data accessibility for startups would allow them to better understand the needs and challenges of fuel-poor households. This could include access to energy consumption data, socioeconomic data, and building stock information.
- Public Procurement:Incorporating a “social value” element into public procurement processes could incentivize the adoption of solutions that address fuel poverty. This would allow startups to showcase their solutions and gain valuable market access.
Government and Private Sector Partnerships
Government and private sector partnerships play a vital role in supporting the development and deployment of innovative solutions to address fuel poverty.
- Public-Private Partnerships:Government agencies can partner with private sector companies to develop and implement pilot projects that test and validate the effectiveness of innovative solutions.
- Incubator and Accelerator Programs:Government-supported incubator and accelerator programs can provide startups with access to mentorship, funding, and networking opportunities.
- Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration:Facilitating knowledge sharing and collaboration between startups, government agencies, and private sector companies can foster innovation and accelerate the development of effective solutions.
The Future of Energy Access and Affordability
The future of energy access and affordability in Europe is a complex landscape, shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, policy changes, and evolving social trends. The rise of renewable energy sources, smart grids, and energy efficiency technologies offers significant potential to improve energy access and affordability, while challenges such as the need for infrastructure upgrades, regulatory frameworks, and social equity remain.
Impact of Emerging Technologies and Trends
Emerging technologies and trends are poised to significantly impact energy access and affordability in Europe. The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, coupled with advancements in energy storage technologies, promises to enhance energy independence and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
Smart grids, with their ability to optimize energy distribution and manage demand, will play a crucial role in ensuring efficient energy utilization and reducing energy waste. Furthermore, the development of energy efficiency technologies will contribute to lowering energy consumption and costs for households and businesses.
Role of Startups in Shaping the Future
Startups are playing an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of energy access and affordability in Europe. Their agility and innovative approaches are driving the development of disruptive technologies and business models in the energy sector. Startups are actively developing solutions for decentralized energy generation, smart grids, energy storage, and energy efficiency.
These innovations are not only making energy more accessible but also contributing to the creation of a more sustainable and resilient energy system. Examples include:
- Sunroof Energy, a Dutch startup, develops solar panel solutions for residential and commercial buildings, making renewable energy accessible to a wider audience.
- GridX, a German startup, provides software solutions for managing and optimizing energy grids, enabling more efficient energy distribution and reduced energy waste.
- Power Ledger, an Australian startup, develops blockchain-based solutions for peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to buy and sell energy directly from each other.
Potential Scenarios for the Future
The future of energy access and affordability in Europe is a dynamic landscape influenced by a range of factors. The following table Artikels potential scenarios for the future, considering technological advancements, policy changes, and social trends: