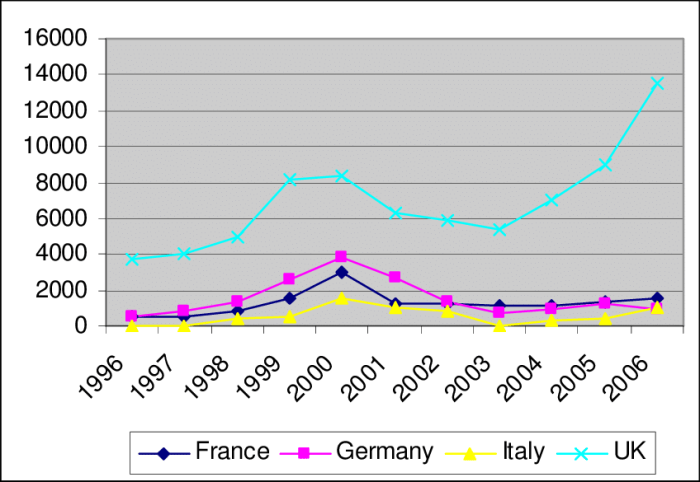
* europe most depressed year vc exit value – Europe’s Most Depressed Year: VC Exit Value Impact takes center stage as we delve into a complex economic landscape. This period, marked by challenging economic conditions, has significantly impacted the value of venture capital exits in Europe. We’ll explore how global economic trends, geopolitical events, and industry shifts have shaped this downturn and its lasting effects on the European venture capital ecosystem.
The year in question saw a confluence of factors that converged to create a perfect storm for venture capital exits. The global economic slowdown, coupled with political instability in certain regions, created a climate of uncertainty and risk aversion.
This led to a decrease in investor appetite for new ventures and a significant drop in valuations for existing companies. As a result, venture capitalists found themselves facing a challenging landscape, navigating through a period of reduced liquidity and compressed exit multiples.
Europe’s Economic Landscape
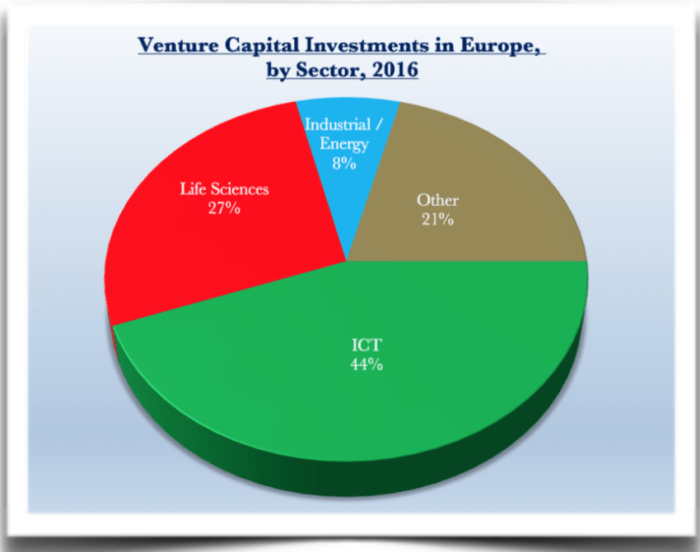
Europe’s economic landscape has been shaped by a confluence of factors in recent years, leading to a period of both challenges and opportunities. The continent has faced a complex interplay of global economic trends, geopolitical events, and internal structural changes.
Global Economic Trends
Global economic trends have played a significant role in shaping Europe’s economic performance. The 2008 global financial crisis had a profound impact on European economies, leading to a period of recession and austerity measures. The subsequent recovery was uneven, with some countries experiencing faster growth than others.
The rise of emerging markets, particularly in Asia, has also had an impact on European economies, both in terms of competition and trade. The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated economic challenges, leading to widespread lockdowns and supply chain disruptions. The global economic slowdown and rising inflation have also presented significant challenges for European economies.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events have also had a significant impact on European economies. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has disrupted energy markets and led to increased inflation. The UK’s decision to leave the European Union (Brexit) has also created uncertainty and economic disruption.
The rise of populism and nationalism in some European countries has also contributed to political instability and economic uncertainty.
Impact on Key Industries and Sectors
The European economy is characterized by a diverse range of industries and sectors. The impact of global economic trends and geopolitical events has been felt across various sectors, including:
- Energy:The conflict in Ukraine has led to a surge in energy prices, particularly for natural gas. This has had a significant impact on households and businesses, as well as on the competitiveness of energy-intensive industries.
- Manufacturing:The global economic slowdown and supply chain disruptions have impacted manufacturing activity in Europe. Some sectors, such as automotive and aerospace, have been particularly affected.
- Tourism:The COVID-19 pandemic had a devastating impact on the tourism industry in Europe. While tourism has recovered somewhat, it still faces challenges, including the ongoing threat of new virus variants and the rising cost of travel.
- Technology:The European technology sector has experienced strong growth in recent years. However, it faces competition from global tech giants and challenges in attracting investment.
Venture Capital Activity in Europe
Europe’s venture capital (VC) landscape has witnessed a remarkable transformation in recent years, evolving from a relatively nascent market to a global powerhouse. The rise of innovative startups, coupled with supportive government policies and a growing pool of experienced investors, has fueled this growth.
Key Factors Driving Venture Capital Activity in Europe, * europe most depressed year vc exit value
The surge in VC activity in Europe is driven by a confluence of factors:
- A Thriving Startup Ecosystem:Europe is home to a burgeoning ecosystem of innovative startups across various sectors, including technology, healthcare, and consumer goods. These startups are attracting significant VC attention due to their disruptive potential and innovative solutions.
- Government Support:Governments across Europe are actively promoting VC investment through initiatives such as tax breaks, grants, and programs designed to support early-stage companies. These policies create a favorable environment for VC firms to invest in European startups.
- Growing Pool of Experienced Investors:The emergence of experienced VC investors, both domestic and international, has contributed to the maturity of the European VC market. These investors bring expertise, networks, and capital to support the growth of promising startups.
- Favorable Regulatory Environment:Europe’s regulatory environment has become increasingly conducive to VC investment, with initiatives aimed at simplifying fundraising and streamlining regulatory processes for startups. This has made it easier for VC firms to deploy capital in European companies.
Major Venture Capital Funds and Investors Active in Europe
Several prominent VC funds and investors are actively shaping the European VC landscape:
- Index Ventures:A leading global VC firm with a strong presence in Europe, Index Ventures has backed successful startups such as TransferWise, Wise, and GoCardless. They focus on early-stage technology companies.
- Accel:A global VC firm with a long history of investing in successful technology companies, Accel has offices in London and Berlin. They have backed companies like Spotify, UiPath, and Deliveroo.
- Atomico:Founded by Skype co-founder Niklas Zennström, Atomico is a VC firm focused on European technology startups. They have invested in companies like Wise, Supercell, and Stash.
- Balderton Capital:A European VC firm with a focus on early-stage technology companies, Balderton Capital has backed companies such as Skyscanner, LoveFilm, and Betfair.
- European Investment Fund (EIF):The EIF is a public financial institution that supports VC investment in Europe through various programs and initiatives. They play a crucial role in fostering early-stage innovation.
Performance of Venture Capital Investments in Europe
The performance of VC investments in Europe has been impressive in recent years.
- Increased Deal Activity:The number of VC deals in Europe has increased significantly in recent years, indicating a growing appetite for investment in European startups.
- Higher Valuation:European startups are attracting higher valuations, reflecting the strong investor confidence in the region’s innovative potential.
- Successful Exits:There have been several notable exits in the European VC market, including IPOs and acquisitions, demonstrating the potential for strong returns on VC investments.
Venture Capital Exits in Europe
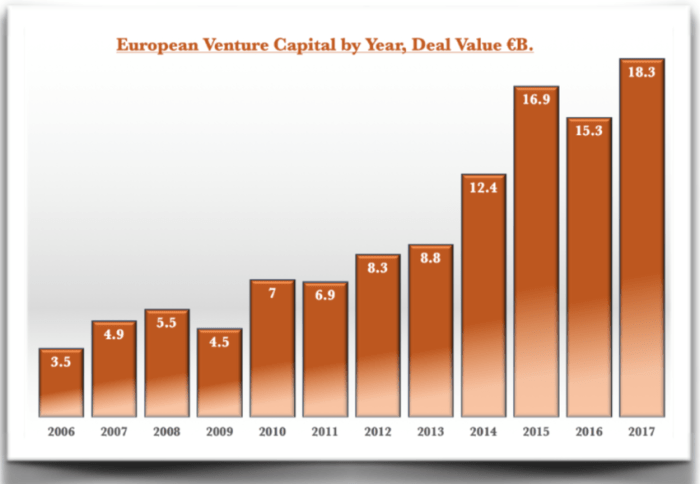
Venture capital exits are the ultimate goal for venture capitalists (VCs) and their portfolio companies. They represent the realization of the investment made in a company and the potential for significant returns. Understanding the different types of exits, the factors influencing their value, and the trends in exit activity is crucial for both investors and entrepreneurs in the European VC ecosystem.
Types of Venture Capital Exits
Venture capital exits occur when investors realize their investment in a portfolio company. These exits can take several forms, each with its own characteristics and potential benefits.
- Initial Public Offering (IPO):This is the most traditional and widely recognized exit route. An IPO involves listing a company’s shares on a public stock exchange, allowing investors to buy and sell them freely. IPOs offer the potential for significant returns but are often a complex and time-consuming process.
- Trade Sale:In a trade sale, a company is sold to another company, typically a larger and more established player in the same industry. Trade sales can provide a quick and efficient exit for investors, and the acquiring company often benefits from acquiring valuable technology, market share, or talent.
- Merger:A merger occurs when two companies combine to form a single entity. Mergers can be a strategic exit option for companies looking to expand their reach or gain access to new markets.
- Acquisition:Similar to a trade sale, an acquisition involves one company buying another. However, in an acquisition, the acquiring company typically takes full ownership of the acquired company, while in a trade sale, the acquired company may retain some independence.
- Secondary Sale:In a secondary sale, investors sell their shares in a company to other investors, typically institutional investors or private equity firms. This type of exit allows investors to realize their investment without the company going public or being acquired.
- Debt Financing:Some companies choose to exit by taking on debt financing, using the proceeds to pay back investors. This option can be attractive to companies that are profitable but lack the resources for growth through equity financing.
Factors Influencing the Value of Venture Capital Exits
The value of a venture capital exit is influenced by a range of factors, including:
- Company Performance:The most important factor determining exit value is the company’s performance. Strong revenue growth, profitability, and a solid track record of execution all contribute to a higher valuation.
- Market Conditions:The overall economic climate and market conditions can significantly impact exit valuations. In a strong economy with robust investor appetite, exits are likely to be more successful and command higher prices.
- Competition:The level of competition in the market for the company’s products or services can influence its value. If there are many similar companies vying for the same customers, the exit value may be lower.
- Strategic Value:The strategic value of a company to potential acquirers can significantly influence its exit value. Companies with unique technologies, strong brand recognition, or a large customer base are often more attractive to buyers.
- Negotiation Skills:The negotiation skills of both the company and the investors play a crucial role in determining the final exit price. A strong negotiating team can secure a favorable deal for all parties involved.
Trends in Venture Capital Exit Activity in Europe
Venture capital exit activity in Europe has been steadily increasing in recent years, driven by several factors, including:
- Growth of the European Tech Ecosystem:The rise of successful tech companies in Europe has attracted significant investor interest, leading to increased exit activity.
- Increased Availability of Capital:European VCs have access to more capital than ever before, fueling investment in high-growth companies and increasing the number of potential exit opportunities.
- Strategic Acquisitions:Large multinational corporations are increasingly looking to acquire European tech companies to gain access to innovative technologies and new markets.
Notable Venture Capital Exits in Europe
- Spotify (IPO, 2018):The Swedish music streaming service went public in 2018, becoming one of the most successful European tech IPOs in recent years.
- Wise (formerly TransferWise) (IPO, 2021):The UK-based international money transfer service went public in 2021, raising over £1 billion in its IPO.
- Deliveroo (IPO, 2021):The UK-based food delivery platform went public in 2021, despite a challenging market environment.
- Checkout.com (Acquisition by a consortium of investors, 2022):The UK-based payments company was acquired by a consortium of investors, including private equity firms and venture capital firms, in a deal valued at over $15 billion.
- GoCardless (Acquisition by Bain Capital, 2022):The UK-based direct debit payment platform was acquired by private equity firm Bain Capital in a deal valued at over $1 billion.
The Impact of Economic Downturns on Venture Capital Exits
Economic downturns can have a significant impact on venture capital exits, often leading to lower valuations and fewer successful exits. The decline in investor confidence, reduced market liquidity, and increased risk aversion during such periods can make it challenging for companies to secure favorable exit terms.
The Effect of Economic Conditions on Venture Capital Exit Values
Economic conditions directly influence the value of venture capital exits. When the economy is strong, investors are more willing to take on risk, leading to higher valuations for companies seeking exits. However, during economic downturns, investor sentiment shifts towards risk aversion, resulting in lower valuations.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring promising european startup audio analytic devoured by meta.
This is because investors anticipate lower future earnings potential and a greater likelihood of business failures in a weakened economy.
The Role of Government Policies in Venture Capital Exits
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the venture capital landscape, influencing the flow of capital, the availability of talent, and the overall attractiveness of the investment environment. These policies can directly impact the success of venture capital exits, as they affect the regulatory environment, the availability of funding, and the overall economic climate.
Impact of Government Regulations on Venture Capital Exits
Government regulations can significantly impact the process of venture capital exits. Regulations governing mergers and acquisitions, securities offerings, and tax laws can influence the timing, structure, and feasibility of exit strategies. For example, stringent regulations surrounding initial public offerings (IPOs) can make it more challenging and costly for startups to go public, potentially discouraging exits through this route.
Similarly, regulations regarding mergers and acquisitions can impact the attractiveness of acquisitions as an exit strategy.
Government Initiatives to Support Venture Capital Activity
Governments around the world have implemented various initiatives to foster venture capital activity and support the growth of startups. These initiatives aim to create a more favorable environment for venture capital exits by providing financial incentives, reducing regulatory burdens, and promoting innovation.Here are some common government initiatives:
- Tax Incentives:Governments may offer tax breaks or deductions for venture capital investments, making it more attractive for investors to allocate capital to startups. These incentives can also encourage angel investors and seed-stage funding, ultimately supporting the growth of startups and increasing the potential for successful exits.
- Government-backed Funds:Governments may establish venture capital funds or provide funding to existing funds, increasing the availability of capital for startups. This can be particularly beneficial in early-stage companies, where access to funding can be challenging.
- Research and Development Grants:Government grants for research and development can help startups innovate and develop valuable technologies, increasing their potential for success and ultimately improving their chances of a successful exit.
- Simplified Regulatory Processes:Governments can streamline regulatory processes for startups, reducing the administrative burden and making it easier for companies to navigate the legal and regulatory landscape. This can be particularly beneficial for startups seeking to expand internationally or raise capital through IPOs.
Examples of Government Policies Influencing Venture Capital Exits
Several government policies have directly impacted venture capital exits, both positively and negatively.
- The JOBS Act in the United States:The Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (JOBS Act) of 2012 eased regulations for small businesses seeking to raise capital through IPOs. This act aimed to increase the number of startups going public, potentially leading to more successful exits for venture capital investors.
- The European Union’s Investment Fund:The European Union’s Investment Fund provides venture capital funding and support to startups across Europe. This initiative aims to foster innovation and create a more favorable environment for venture capital activity, potentially leading to more successful exits for European startups.
The Future of Venture Capital Exits in Europe: * Europe Most Depressed Year Vc Exit Value
Europe’s venture capital landscape is undergoing a dynamic transformation, with exits playing a pivotal role in the ecosystem’s health and growth. As the region navigates economic uncertainties and technological advancements, understanding the future trends in venture capital exits becomes crucial for investors, entrepreneurs, and policymakers alike.
Emerging Technologies’ Impact on Venture Capital Exits
The emergence of disruptive technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping the venture capital landscape, significantly influencing exit strategies.
- AI-powered companies, for instance, are attracting significant investment, leading to faster growth and potential for quicker exits through acquisitions or initial public offerings (IPOs).
- Blockchain technology is revolutionizing industries, creating opportunities for exits through mergers and acquisitions (M&A) or tokenization of assets.
- The IoT is driving innovation in various sectors, creating new avenues for exits through strategic partnerships or acquisitions by established players seeking to leverage this technology.
These emerging technologies are not only driving innovation but also creating new exit avenues, making it crucial for venture capitalists to adapt their strategies and invest in companies with strong technological foundations.
The Role of Innovation and Entrepreneurship in Shaping Future Exits
Innovation and entrepreneurship are the driving forces behind venture capital exits. Europe’s thriving startup ecosystem, fueled by a wave of young, ambitious entrepreneurs, is creating a pipeline of promising companies ripe for exits.
- The rise of deep-tech startups, focusing on areas like biotechnology, quantum computing, and advanced materials, is attracting significant investment, potentially leading to large exits through IPOs or acquisitions by established players.
- The growing focus on sustainability and social impact is driving the emergence of startups addressing environmental and social challenges, creating opportunities for exits through impact-driven investments or partnerships with corporations seeking to align with these values.
The continued emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship will be critical in shaping the future of venture capital exits in Europe, as it fosters the creation of high-growth companies with strong exit potential.
Challenges and Opportunities Facing Venture Capital Exits in Europe
Despite the promising outlook, venture capital exits in Europe face certain challenges and opportunities.
- One of the primary challenges is the limited availability of public markets for exits, particularly for early-stage companies. This often leads to a reliance on M&A, which can be more time-consuming and less lucrative than IPOs.
- Another challenge is the regulatory environment, which can sometimes be complex and hinder the growth of startups, potentially affecting their exit potential.
- However, Europe also presents significant opportunities for venture capital exits. The increasing availability of capital from both domestic and international investors, coupled with the growing number of promising startups, creates a fertile ground for exits.
- Moreover, the rise of alternative exit options, such as secondary markets and private equity buyouts, provides additional avenues for investors to realize returns.
Navigating these challenges and capitalizing on opportunities will be crucial for the success of venture capital exits in Europe.