Biotech startup targets genes treat skin diseases sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The field of dermatology is witnessing a revolutionary shift, with biotech startups emerging as key players in the quest for groundbreaking treatments for skin diseases.
These companies are leveraging the power of gene editing and gene therapy to target the root causes of these conditions, offering hope for millions suffering from debilitating skin disorders.
Gene editing technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas9, are enabling scientists to precisely modify genes involved in skin disease development. This precision allows for targeted therapies that can address the underlying genetic defects, potentially leading to long-lasting cures. This innovative approach holds immense promise for treating a wide range of skin diseases, from rare genetic disorders to common conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
The Rise of Biotech Startups in Dermatology
The field of dermatology is experiencing a surge in innovation, driven by the increasing prevalence of skin diseases and the emergence of groundbreaking technologies. Biotech startups are at the forefront of this revolution, developing novel therapies that target the underlying causes of skin conditions, offering hope for millions affected by these debilitating diseases.
The Growing Market for Innovative Skin Disease Treatments
The global skin disease treatment market is expanding rapidly, fueled by several factors. The rising prevalence of skin conditions, including acne, eczema, psoriasis, and skin cancer, is a significant driver of market growth. Additionally, the increasing awareness of skin health and the demand for effective treatments are contributing to the market’s expansion.
The market is expected to reach a value of over $50 billion by 2028, presenting a substantial opportunity for biotech startups to develop and commercialize innovative therapies.
The Role of Gene Editing and Gene Therapy in Dermatology
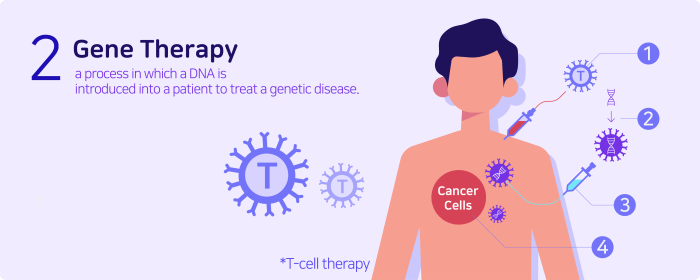
Gene editing and gene therapy are revolutionizing the treatment of skin diseases by addressing the root cause of these conditions at the genetic level. Gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 allow for precise modifications of genes, correcting genetic defects that lead to skin diseases.
Gene therapy, on the other hand, involves delivering therapeutic genes to cells to replace or supplement defective genes, offering a long-term solution for genetic skin disorders.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of ev charging startup vool funding scale production optimise grid usage through case studies.
Challenges and Opportunities for Biotech Startups in Dermatology
Biotech startups in dermatology face several challenges, including:
- High development costs: Developing new therapies requires significant investment in research, clinical trials, and manufacturing.
- Regulatory hurdles: Obtaining regulatory approval for new therapies can be a lengthy and complex process.
- Competition from established players: The dermatology market is dominated by large pharmaceutical companies, creating intense competition for startups.
Despite these challenges, there are numerous opportunities for biotech startups in dermatology:
- Growing market demand: The increasing prevalence of skin diseases and the unmet needs of patients create a strong demand for innovative treatments.
- Advances in technology: The development of gene editing and gene therapy technologies provides new tools for developing effective therapies.
- Government support: Governments are increasingly investing in research and development of new therapies for skin diseases.
Targeting Specific Genes for Skin Disease Treatment: Biotech Startup Targets Genes Treat Skin Diseases
The field of dermatology is witnessing a revolution with the emergence of gene-based therapies. These innovative treatments offer a targeted approach to address the root cause of various skin diseases by directly modifying the genes involved. By understanding the intricate mechanisms of gene therapy and the different gene editing technologies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the transformative potential of this field.
Examples of Skin Diseases Targeted by Gene Therapy
Gene therapy holds promise for treating a wide range of skin diseases, from genetic disorders to inflammatory conditions. Here are some examples:
- Epidermolysis bullosa (EB):This group of inherited disorders causes fragile skin that blisters easily. Gene therapy aims to correct the genetic defects responsible for EB, potentially leading to improved skin strength and reduced blistering.
- Ichthyosis:This group of disorders causes dry, scaly skin. Gene therapy is being explored to address the underlying genetic mutations that cause ichthyosis, potentially leading to improved skin hydration and reduced scaling.
- Psoriasis:This chronic autoimmune disease causes red, scaly patches on the skin. Gene therapy is being investigated to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation, potentially leading to improved skin appearance and reduced symptoms.
- Alopecia areata:This autoimmune disorder causes hair loss. Gene therapy is being explored to target immune cells and promote hair regrowth, potentially leading to restored hair follicles and hair growth.
Mechanisms of Action of Gene-Based Therapies for Skin Diseases
Gene therapy for skin diseases primarily works by delivering therapeutic genes to target cells in the skin. This delivery can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Viral vectors:These are modified viruses that can carry therapeutic genes into cells. They are often used in gene therapy because they can efficiently deliver genes to target cells.
- Non-viral vectors:These include liposomes, nanoparticles, and other delivery systems that can encapsulate therapeutic genes and deliver them to target cells.
Once the therapeutic gene is delivered to target cells, it can:
- Replace a faulty gene:In cases of genetic disorders, gene therapy can replace a faulty gene with a functional copy, potentially correcting the underlying cause of the disease.
- Modulate gene expression:Gene therapy can be used to increase or decrease the expression of specific genes, potentially influencing the activity of certain proteins and pathways involved in skin disease development.
- Introduce new genes:Gene therapy can introduce new genes into cells to provide a therapeutic function, such as producing a protein that can inhibit inflammation or promote skin repair.
Gene Editing Technologies in Dermatology, Biotech startup targets genes treat skin diseases
Gene editing technologies offer precise tools for modifying the genetic code of cells. These technologies are revolutionizing the field of dermatology by providing new avenues for treating skin diseases.
- CRISPR-Cas9:This technology uses a guide RNA molecule to target specific DNA sequences and a Cas9 enzyme to cut the DNA at the desired location. This allows for the insertion, deletion, or modification of specific genes, potentially correcting genetic defects or modulating gene expression.
- TALENs:These are protein-based gene editing tools that can be designed to target specific DNA sequences. They can be used to introduce double-strand breaks in DNA, allowing for gene editing or gene silencing.
- ZFNs:These are zinc finger proteins that can be engineered to bind to specific DNA sequences. They can be used to introduce double-strand breaks in DNA, allowing for gene editing or gene silencing.
Comparison of Gene Editing Technologies
| Technology | Mechanism | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| CRISPR-Cas9 | Guide RNA-directed Cas9 enzyme for DNA cleavage | Highly efficient, versatile, and relatively easy to use | Potential for off-target effects, ethical concerns about unintended consequences |
| TALENs | Protein-based DNA binding and cleavage | High specificity, relatively easy to design | More complex to design and produce compared to CRISPR-Cas9 |
| ZFNs | Zinc finger proteins for DNA binding and cleavage | High specificity, well-characterized | More complex to design and produce compared to CRISPR-Cas9 and TALENs |
The Biotech Startup Landscape in Dermatology
The field of dermatology is experiencing a rapid transformation, driven by the emergence of innovative biotech startups focused on developing gene-based therapies for skin diseases. These companies are leveraging cutting-edge technologies to target specific genes responsible for various skin conditions, offering hope for more effective and personalized treatments.
Notable Biotech Startups in Dermatology
The emergence of biotech startups in dermatology is a testament to the growing demand for novel and targeted therapies for skin diseases. These companies are employing a diverse range of technologies, from gene editing to cell therapy, to address the underlying genetic causes of skin conditions.
Here is a table showcasing some of the notable biotech startups in dermatology, highlighting their target diseases, technologies, and stages of development:
| Company Name | Target Disease | Technology | Stage of Development |
|---|---|---|---|
| Casma Therapeutics | Epidermolysis Bullosa | Gene Editing | Clinical Trials |
| Verve Therapeutics | Atopic Dermatitis | Gene Editing | Preclinical Trials |
| Orphazyme | Ichthyosis | Enzyme Replacement Therapy | Approved |
| Evelo Biosciences | Psoriasis | Microbiome Modulation | Clinical Trials |
Clinical Trials and Regulatory Considerations
Navigating the complex landscape of clinical trials and regulatory approvals is a crucial step for biotech startups developing gene-based therapies for dermatological conditions. These therapies offer immense potential, but their development requires rigorous testing and adherence to strict regulatory guidelines.
Challenges in Conducting Clinical Trials for Gene Therapies in Dermatology
Clinical trials for gene therapies in dermatology present unique challenges compared to traditional drug development. The targeted nature of gene therapies requires careful patient selection and monitoring to ensure efficacy and safety. Additionally, the long-term effects of gene modification need to be assessed, which necessitates extensive follow-up studies.
- Patient Recruitment and Retention:Identifying patients with specific genetic mutations and recruiting them for clinical trials can be challenging. Furthermore, maintaining patient retention throughout the trial is crucial for obtaining meaningful data.
- Dosage and Delivery:Determining the optimal dosage and delivery method for gene therapy is critical. This involves considering factors such as the size and location of the target area, the type of gene being delivered, and the potential for off-target effects.
- Long-Term Safety and Efficacy:Gene therapies have the potential for long-term effects, both positive and negative. Monitoring patients for long-term safety and efficacy is essential to ensure the therapy’s long-term viability.
- Measuring Clinical Outcomes:Assessing the effectiveness of gene therapy in dermatology can be challenging. The clinical endpoints used to measure treatment success need to be carefully chosen and validated to ensure they accurately reflect the therapeutic benefits.
Examples of Ongoing Clinical Trials for Gene Therapies Targeting Skin Diseases
Several clinical trials are underway for gene therapies targeting various skin diseases, showcasing the growing interest in this field.
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB):Companies like are developing gene therapies for DEB, a rare genetic skin disorder characterized by fragile skin and blistering. These trials aim to deliver genes that encode for missing or defective proteins involved in skin structure and function.
- Psoriasis:Gene therapies targeting specific pathways involved in psoriasis, such as the IL-23 pathway, are being investigated in clinical trials. These therapies aim to modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis.
- Alopecia Areata:Gene therapies targeting the immune system are being explored for the treatment of alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss. These therapies aim to suppress the immune response that attacks hair follicles.
Regulatory Landscape for Gene Therapy in Dermatology
The regulatory landscape for gene therapy in dermatology is evolving rapidly. Regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe, are working to establish clear guidelines for the development and approval of gene therapies.
- Pre-Clinical Studies:Rigorous pre-clinical studies are required to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of gene therapies before they can be tested in humans. These studies typically involve animal models and in vitro experiments.
- Clinical Trial Design:Clinical trials for gene therapies must adhere to specific design criteria, including patient selection, dosage, and endpoints. Regulatory agencies provide guidance on the design and conduct of clinical trials.
- Post-Marketing Surveillance:Even after approval, gene therapies are subject to post-marketing surveillance to monitor their long-term safety and efficacy. This includes collecting data from patients who have received the therapy and conducting follow-up studies.
The Future of Gene-Based Therapies in Dermatology
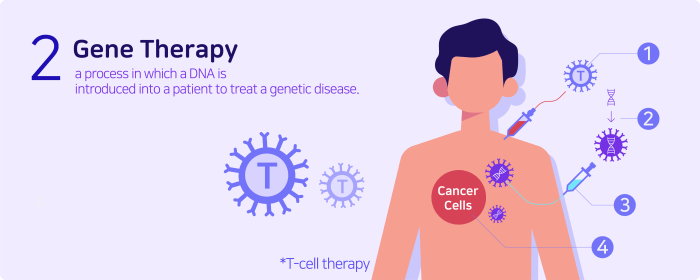
The field of gene therapy is rapidly evolving, and its potential applications in dermatology are vast. Gene therapy offers the promise of targeted and durable treatments for a wide range of skin diseases, from rare genetic disorders to common conditions like psoriasis and acne.
Potential Future Applications of Gene Therapy in Dermatology
Gene therapy holds immense potential for treating various skin conditions. Here are some potential future applications:
- Treating Genetic Skin Disorders:Gene therapy can directly address the underlying genetic defects responsible for many inherited skin diseases. For example, it could be used to correct the gene mutations causing epidermolysis bullosa, a group of rare, debilitating skin disorders characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily.
- Targeting Inflammatory Skin Diseases:Gene therapy could be used to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation in conditions like psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and lupus. This could involve delivering genes that suppress inflammatory pathways or enhance immune tolerance.
- Promoting Skin Regeneration:Gene therapy could be used to stimulate skin cell growth and repair, aiding in the treatment of wounds, burns, and other skin injuries. This could involve delivering genes that encode growth factors or other proteins that promote tissue regeneration.
- Treating Skin Cancer:Gene therapy could be used to target cancer cells specifically, either by delivering genes that induce cell death or by enhancing the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Risks Associated with Gene Editing in Skin Diseases
While gene therapy holds immense promise, it also raises ethical considerations and potential risks:
- Off-target Effects:Gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, can sometimes target unintended genes, leading to unforeseen consequences. Careful research and rigorous safety testing are essential to minimize off-target effects.
- Long-Term Effects:The long-term effects of gene editing are not yet fully understood. It’s crucial to monitor patients treated with gene therapy for potential side effects that may emerge over time.
- Accessibility and Equity:Ensuring equitable access to gene therapy is essential. The high cost of developing and administering these treatments could create disparities in healthcare access.
- Germline Editing:Gene editing that alters the germline (sperm or egg cells) could have implications for future generations. Ethical debates surround the use of germline editing, as it could lead to unintended consequences for future offspring.
The Potential Impact of Gene-Based Therapies on the Future of Dermatology
Gene-based therapies have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of skin diseases. They offer the possibility of:
- Personalized Medicine:Gene therapy can be tailored to the specific genetic makeup of each patient, offering more targeted and effective treatments.
- Long-Term Solutions:Gene therapy has the potential to provide durable and long-lasting treatments, reducing the need for frequent or lifelong medication.
- Improved Quality of Life:By addressing the underlying causes of skin diseases, gene therapy could significantly improve the quality of life for patients suffering from these conditions.