Vega rocket europe china smile solar wind space mission – Vega Rocket: Europe, China, and the Smile of Space sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. From the heart of Europe’s space program to the ambitious strides of China’s rocketry, we’ll explore the fascinating journey of the Vega rocket, its role in international collaboration, and the profound impact of the solar wind on space missions.
This journey will take us beyond the technical aspects, delving into the human element of space exploration and the vital role of a positive mindset in overcoming the challenges of venturing into the unknown.
This blog post will unravel the intricacies of space exploration, blending scientific discoveries with the human spirit of adventure. We’ll journey through the history of the Vega rocket, witnessing its evolution from a concept to a vital tool in the European Space Agency’s arsenal.
We’ll then shift our gaze towards China’s rapidly advancing space program, examining its technological prowess and its contributions to the global space community. Along the way, we’ll encounter the powerful and unpredictable force of the solar wind, learning how it shapes our understanding of the cosmos and poses unique challenges for space missions.
Vega Rocket
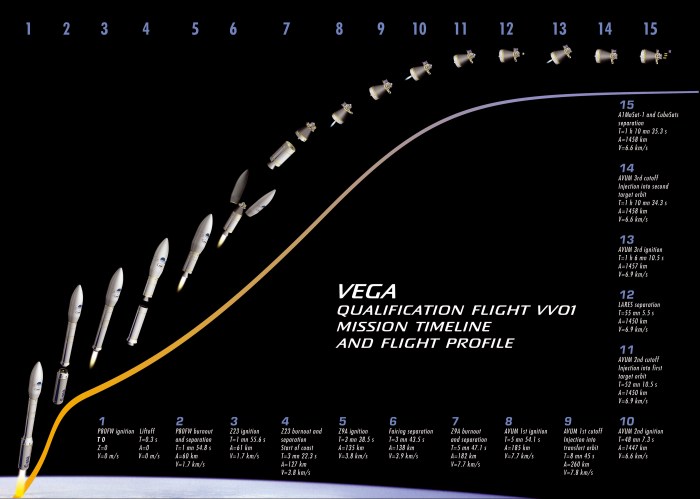
The Vega rocket is a small-lift launch vehicle developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) for launching scientific and technological payloads into low Earth orbit (LEO) and sun-synchronous orbit (SSO). It was conceived as a complement to the larger Ariane family of launch vehicles, offering a cost-effective option for smaller satellites.
History and Development
The Vega program was initiated in 1998, with the goal of developing a versatile and reliable launch vehicle for small satellites. The initial concept involved a three-stage rocket with solid propellants, drawing inspiration from the successful Italian sounding rocket program.
After several years of design and development, the first Vega rocket successfully launched from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana on February 13, 2012.
Technical Specifications and Capabilities
The Vega rocket stands at a height of 30 meters and has a launch mass of 130 tons. It is powered by four solid-propellant stages, each providing a specific thrust and burn time. The first stage is the largest and provides the initial thrust, followed by three smaller stages that progressively increase the rocket’s velocity.The Vega rocket is capable of carrying payloads weighing up to 1.5 tons into LEO and up to 700 kg into SSO.
Its payload fairing has a diameter of 3 meters, allowing for the launch of various types of satellites, including Earth observation, scientific, and technological missions.
Notable Missions
Since its maiden flight in 2012, the Vega rocket has launched numerous successful missions, showcasing its versatility and reliability. Some of the notable missions include:
- PRISMA:An Italian Earth observation mission for hyperspectral imaging of the Earth’s surface.
- LARES:An Italian space mission to study the frame-dragging effect predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
- LISA Pathfinder:A joint ESA-NASA mission to test key technologies for the future space-based gravitational wave observatory, LISA.
- ADM-Aeolus:An ESA mission to measure wind profiles globally, providing valuable data for weather forecasting and climate research.
- Euclid:An ESA mission to study the dark universe, investigating dark matter and dark energy.
Comparison with Other European Launch Vehicles
The Vega rocket complements the larger Ariane family of launch vehicles, providing a cost-effective option for smaller satellites. While Ariane 5 is designed for heavier payloads and geostationary orbit (GEO) missions, Vega caters to the growing market of smaller satellites with LEO and SSO destinations.
Key Features and Benefits of the Vega Rocket
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Solid-propellant stages | Reliable and cost-effective propulsion system |
| Versatile payload capacity | Capable of launching a wide range of satellites |
| High launch frequency | Provides frequent access to space for small satellites |
| Proven track record | Demonstrated reliability and success in numerous missions |
China’s Space Program and Rocketry
China’s space program has undergone a remarkable transformation in recent decades, evolving from a modest beginning to a global powerhouse in space exploration. This ascent has been fueled by significant advancements in rocket technology, a strategic commitment to national development, and a growing ambition to assert its presence in the final frontier.
Advancements in China’s Space Program and Rocket Technology
China’s space program has witnessed a remarkable surge in technological capabilities, particularly in rocketry. This progress has been driven by a focused national strategy and significant investments in research and development.
Get the entire information you require about dutch startup shell floating offshore solar north sea on this page.
- Long March Rocket Family:The backbone of China’s space program, the Long March series of rockets, has evolved significantly. The program boasts a wide range of rockets, from the Long March 2F, used for crewed missions, to the powerful Long March 5, capable of launching heavy payloads into geostationary orbit.
These rockets have successfully launched numerous satellites, space stations, and probes, contributing to China’s growing space infrastructure.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles:China is actively pursuing the development of reusable launch vehicles (RLVs), aiming to reduce the cost of space access. In 2020, China successfully tested its first reusable RLV, the “Zhuque-2,” showcasing its commitment to developing cutting-edge technologies.
- Advanced Propulsion Systems:China has made strides in developing advanced propulsion systems, including high-performance liquid-propellant engines and solid-propellant boosters. These advancements enable more powerful and efficient launches, expanding the capabilities of its space program.
Role of Chinese Rockets in National and International Missions
Chinese rockets play a crucial role in supporting both national and international space missions.
- National Missions:Chinese rockets have launched numerous satellites for communication, navigation, Earth observation, and scientific research. These missions have significantly enhanced China’s capabilities in various sectors, contributing to national development and security. For instance, the Beidou Navigation Satellite System, a rival to the American GPS system, was launched using Chinese rockets.
- International Collaborations:China has actively engaged in international collaborations, launching satellites for other countries and participating in joint space missions. This demonstrates its willingness to share its expertise and contribute to the global space community. Examples include launching satellites for the United Nations and participating in the International Space Station (ISS) program.
Comparison of Chinese Rockets with European Counterparts
China’s rocket technology has progressed significantly, narrowing the gap with its European counterparts. While Europe has a longer history in space exploration, China has demonstrated rapid development and innovation.
- Performance:In terms of performance, Chinese rockets, particularly the Long March 5, have achieved comparable capabilities to European rockets like the Ariane 5. Both rocket families are capable of launching heavy payloads into geostationary orbit.
- Cost:China’s space program is known for its cost-effectiveness, offering competitive launch services compared to European providers. This has made Chinese rockets attractive to international customers seeking affordable access to space.
- Ambition:China’s space program is characterized by its ambition and strategic vision. While Europe focuses on collaborative missions, China has embarked on independent missions, including lunar exploration and Mars exploration, showcasing its commitment to pushing the boundaries of space exploration.
Future Plans and Ambitions of China’s Space Program
China’s space program has ambitious plans for the future, aiming to solidify its position as a leading space power.
- Lunar Exploration:China has set its sights on establishing a permanent lunar base, conducting robotic and crewed missions to the Moon. This includes plans to collect lunar samples, build scientific outposts, and potentially extract resources from the Moon.
- Mars Exploration:China has successfully landed a rover on Mars, demonstrating its capability for deep-space exploration. Future plans include sending more missions to Mars, potentially involving sample return and establishing a Mars base.
- Space Station Development:China is currently operating its own space station, the Tiangong Space Station, and plans to expand its capabilities in the coming years. The station will serve as a platform for scientific research, technology development, and international collaborations.
Timeline of Significant Milestones in China’s Space Exploration History
- 1970:China launches its first satellite, Dong Fang Hong I, marking the beginning of its space program.
- 1975:China launches its first crewed spacecraft, Shenzhou 5, sending astronaut Yang Liwei into orbit, making China the third country to achieve human spaceflight.
- 2003:China successfully launches its first lunar probe, Chang’e 1, marking the beginning of its ambitious lunar exploration program.
- 2013:China lands its first rover, Yutu, on the Moon, becoming the third country to achieve a soft landing on the lunar surface.
- 2019:China launches Chang’e 4, the first spacecraft to land on the far side of the Moon.
- 2020:China launches its first Mars rover, Tianwen-1, successfully landing on Mars and sending a rover to explore the Martian surface.
- 2021:China completes the construction of its Tiangong Space Station, marking a significant milestone in its ambition to establish a permanent presence in space.
The Solar Wind and Its Impact on Space Missions
The solar wind, a constant stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun, plays a significant role in the environment surrounding Earth and throughout the solar system. This constant flow of energy and particles can have both beneficial and detrimental effects on space missions, posing challenges that engineers and scientists must carefully consider.
The Nature and Origin of the Solar Wind
The solar wind originates from the Sun’s corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere. The corona is heated to millions of degrees Celsius, causing the particles within it to gain enough energy to escape the Sun’s gravitational pull. These particles, primarily protons and electrons, are propelled outward at speeds ranging from 250 to 750 kilometers per second, forming a continuous stream of charged particles known as the solar wind.
Effects of the Solar Wind on Spacecraft and Astronauts
The solar wind’s charged particles can interact with spacecraft and astronauts in various ways.
- Radiation Damage:The energetic particles can penetrate spacecraft shielding and damage sensitive electronics, affecting their performance and lifespan. This can lead to malfunctions, data loss, or even complete system failure.
- Surface Charging:The solar wind can cause the buildup of static electricity on spacecraft surfaces, leading to electrical discharges or interference with sensitive instruments.
- Health Risks:Astronauts exposed to prolonged periods of solar wind radiation are at increased risk of radiation sickness, cancer, and other health issues.
Challenges Posed by the Solar Wind for Space Missions
The solar wind presents several challenges for space missions:
- Communication Disruptions:The solar wind can interfere with radio signals, disrupting communication between Earth and spacecraft.
- Navigation Errors:The solar wind’s charged particles can affect spacecraft navigation systems, leading to inaccurate position determination.
- Mission Delays:Solar wind events, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), can pose significant risks to astronauts and spacecraft, potentially leading to mission delays or even cancellations.
Technologies and Strategies to Mitigate Solar Wind Effects
Engineers and scientists have developed various technologies and strategies to mitigate the effects of the solar wind:
- Shielding:Spacecraft are designed with radiation shielding to protect sensitive electronics and astronauts from harmful radiation.
- Redundancy:Critical systems are often designed with redundancy, allowing for backup systems in case of failure.
- Space Weather Monitoring:Constant monitoring of the solar wind’s activity allows for early warnings of potential threats, enabling mission planners to take appropriate precautions.
- Solar Wind Prediction:Sophisticated models and simulations help predict solar wind events and their potential impact on spacecraft and astronauts.
- Adaptive Mission Planning:Mission plans are often flexible and adaptable to accommodate changing space weather conditions.
Solar Wind Events and Their Consequences
The table below summarizes various types of solar wind events and their potential consequences:
| Solar Wind Event | Description | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Flares | Sudden bursts of energy and radiation from the Sun’s surface. | Radio blackouts, satellite malfunctions, increased radiation exposure for astronauts. |
| Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) | Large expulsions of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun’s corona. | Geomagnetic storms, power grid disruptions, satellite failures, auroral displays. |
| Solar Energetic Particle (SEP) Events | High-energy particles accelerated by solar flares or CMEs. | Radiation damage to spacecraft, health risks for astronauts. |
Space Mission Success and Collaboration: Vega Rocket Europe China Smile Solar Wind Space Mission
The history of space exploration is a testament to the power of international collaboration. From the early days of the Cold War to the present, nations have joined forces to push the boundaries of human knowledge and understanding of the cosmos.
Examples of Successful International Collaborations
Successful international collaborations in space exploration are numerous and demonstrate the benefits of working together. Here are some prominent examples:
- International Space Station (ISS):This iconic orbiting laboratory is a prime example of international collaboration. A joint project of the United States, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency (ESA), the ISS has been continuously inhabited since 2000 and has hosted hundreds of astronauts from various countries.
The ISS has facilitated groundbreaking research in various fields, including biology, physics, and astronomy.
- Hubble Space Telescope:This revolutionary telescope, launched in 1990, is a product of collaboration between NASA and the ESA. The Hubble Telescope has provided us with stunning images of the universe, revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos, and made significant contributions to our understanding of dark matter, black holes, and the age of the universe.
- Cassini-Huygens Mission:This ambitious mission, launched in 1997, explored Saturn and its moons. It was a joint effort of NASA, the ESA, and the Italian Space Agency. The mission’s discoveries included the confirmation of liquid water on Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons, and the observation of methane lakes on Titan, another of Saturn’s moons.
Benefits of International Cooperation
International cooperation in space exploration brings numerous benefits:
- Shared Resources and Expertise:Collaboration allows nations to pool resources, share expertise, and leverage each other’s strengths, reducing individual costs and increasing efficiency. This is particularly crucial for expensive missions like space exploration.
- Enhanced Scientific Progress:Collaboration fosters a global scientific community, promoting knowledge exchange and accelerating scientific progress. Diverse perspectives and expertise from different nations contribute to a richer understanding of the universe.
- Strengthened International Relations:Space exploration serves as a platform for diplomacy and cooperation, fostering positive relationships between nations. It promotes a sense of shared purpose and global citizenship.
Challenges and Complexities of International Cooperation
While international collaboration in space exploration is highly beneficial, it also presents challenges:
- Coordination and Communication:Coordinating complex space missions involving multiple nations requires meticulous planning, clear communication, and effective coordination. Cultural differences and varying priorities can complicate these efforts.
- Political and Economic Considerations:International space collaborations are often influenced by political and economic factors. Funding disputes, national priorities, and geopolitical tensions can impact the success of missions.
- Technological Differences:Different nations have different technological capabilities and standards. Integrating these technologies into a single mission can be challenging and require compromises and adaptations.
The Role of Diplomacy and Communication
Effective diplomacy and communication are essential for successful international space collaborations:
- Building Trust and Consensus:Diplomatic efforts are crucial for establishing trust and building consensus among participating nations. This involves open dialogue, mutual understanding, and the ability to address concerns and resolve disputes.
- Clear Communication and Coordination:Clear communication channels and well-defined roles and responsibilities are essential for coordinating complex missions. This includes sharing data, information, and progress reports, as well as resolving technical issues.
- Long-Term Vision and Commitment:Successful international space collaborations require a long-term vision and commitment from all participating nations. This involves consistent funding, sustained political support, and a shared commitment to achieving common goals.
Key International Space Partnerships and Achievements, Vega rocket europe china smile solar wind space mission
| Partnership | Achievements |
|---|---|
| NASA (United States) and ESA (Europe) | Hubble Space Telescope, International Space Station, Cassini-Huygens Mission, James Webb Space Telescope |
| NASA (United States) and Roscosmos (Russia) | International Space Station, Soyuz spacecraft, Space Shuttle-Mir Program |
| JAXA (Japan) and ESA (Europe) | BepiColombo mission to Mercury, International Space Station, Hayabusa asteroid sample return mission |
| ISRO (India) and ESA (Europe) | Chandrayaan-1 lunar mission, Mars Orbiter Mission, Gaganyaan human spaceflight program |
The Significance of a Smile in Space Exploration
In the vast expanse of space, where the challenges of isolation, stress, and danger are ever-present, a smile holds profound significance for astronauts. It is not just a facial expression but a symbol of resilience, camaraderie, and a positive mindset that is essential for navigating the demanding conditions of space exploration.
The Importance of a Positive Mindset and Teamwork in Space Missions
Space missions are inherently complex and risky endeavors that require a high level of coordination, communication, and problem-solving skills. A positive mindset is crucial for astronauts to effectively handle the immense pressures of space travel. A positive attitude fosters a collaborative environment where team members are more likely to support each other, communicate openly, and find solutions to unforeseen challenges.
This collaborative spirit is vital for mission success, as astronauts rely on each other for their safety and well-being.
The Impact of Stress and Isolation on Astronauts and Their Mental Health
Space missions are inherently stressful, with astronauts constantly exposed to extreme conditions, limited resources, and the potential for unforeseen emergencies. The isolation of space travel can also take a toll on astronauts’ mental health, leading to feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression.
The lack of social interaction, the constant monitoring of vital signs, and the confinement of the spacecraft can all contribute to psychological strain.
Stories of Astronauts Who Have Maintained a Positive Attitude During Challenging Missions
Despite the challenges, many astronauts have demonstrated remarkable resilience and maintained a positive attitude during their missions. For example, during the Apollo 13 mission, the crew faced a life-threatening crisis when an oxygen tank exploded. Despite the dire situation, the astronauts remained calm, focused, and resourceful, working together to improvise solutions and bring the crew safely back to Earth.
This story illustrates the importance of a positive mindset in overcoming adversity and highlights the power of teamwork in space exploration.





