Uk sensitive tech china cyberespionage – UK Sensitive Tech: China’s Cyberespionage Threat has become a pressing issue, raising concerns about national security and economic stability. The UK, with its advanced aerospace, defense, and telecommunications sectors, is a prime target for cyberespionage, particularly from China. China’s motives are multifaceted, ranging from economic gain and technological advancement to political influence.
This complex interplay of technology, geopolitics, and national interests demands a thorough understanding of the risks and potential solutions.
The vulnerabilities of these sectors stem from the interconnected nature of modern technology and the reliance on digital infrastructure. China’s sophisticated cyberespionage operations, often employing malware, hacking, and social engineering techniques, pose a significant threat to the UK’s sensitive data and intellectual property.
The consequences of a successful cyberespionage attack could be devastating, impacting national security, economic competitiveness, and international relations.
The UK’s Sensitive Technology Landscape
The UK boasts a thriving technological landscape, with several sectors heavily reliant on sensitive technologies. These sectors are vital for national security, economic prosperity, and international competitiveness. However, their reliance on advanced technologies also makes them vulnerable to cyberespionage.
Vulnerable Sectors and Technologies
The UK’s sensitive technology landscape encompasses several sectors that are crucial to national security and economic growth. These sectors rely on advanced technologies that are attractive targets for cyberespionage. Here are some of the key sectors and technologies:
- Aerospace and Defense:This sector relies on cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced materials, sensors, and communication systems. Cyberespionage could compromise sensitive data, including design plans, production processes, and operational procedures, potentially impacting national security and defense capabilities.
- Telecommunications:The telecommunications sector is essential for communication, data transmission, and network infrastructure. Cyberespionage could disrupt critical communication networks, steal sensitive data, or compromise network security, potentially impacting national security, economic activity, and public safety.
- Energy and Utilities:This sector relies on critical infrastructure, including power grids, pipelines, and water treatment facilities. Cyberespionage could disrupt energy production and distribution, leading to widespread power outages, supply chain disruptions, and economic damage.
- Financial Services:The financial sector relies on sensitive data and financial transactions. Cyberespionage could steal financial data, compromise financial systems, and disrupt market operations, potentially leading to significant economic losses and instability.
- Healthcare:The healthcare sector relies on sensitive patient data, medical devices, and research and development. Cyberespionage could compromise patient privacy, disrupt healthcare services, and hinder medical innovation, potentially impacting public health and safety.
Vulnerabilities to Cyberespionage
The UK’s sensitive technology sectors face numerous vulnerabilities to cyberespionage. These vulnerabilities arise from the complex and interconnected nature of modern technology, the reliance on digital networks, and the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks.
- Network Security:The reliance on interconnected networks creates opportunities for cyberespionage actors to gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data. Weak network security measures, such as outdated software, inadequate firewalls, and lack of proper encryption, can make these networks vulnerable to exploitation.
Discover more by delving into apple event 27 januar further.
- Human Error:Human error, such as clicking on malicious links, opening infected attachments, or failing to follow security protocols, can create entry points for cyberespionage actors. Phishing campaigns, social engineering, and other tactics exploit human vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive systems.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities:The global nature of supply chains creates opportunities for cyberespionage actors to compromise systems and data through third-party vendors and suppliers. Compromised software, hardware, or services can provide backdoors for attackers to gain access to sensitive information.
- Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness:Insufficient cybersecurity awareness among employees and lack of proper training can leave organizations vulnerable to cyberespionage. Employees may not be aware of potential threats, security best practices, or how to identify and report suspicious activity.
Economic and National Security Implications
Successful cyberespionage attacks on UK sensitive technology can have significant economic and national security implications.
- Economic Disruption:Cyberespionage attacks can disrupt critical infrastructure, supply chains, and financial markets, leading to economic losses, job losses, and reduced productivity. For example, a successful cyberattack on the UK’s energy sector could cause widespread power outages, disrupting businesses, transportation, and essential services.
- National Security Risks:Cyberespionage attacks can compromise sensitive military and intelligence data, potentially impacting national security and defense capabilities. For example, a cyberattack on the UK’s defense sector could steal classified information, disrupt military operations, or compromise weapon systems.
- Loss of Competitive Advantage:Cyberespionage attacks can steal intellectual property, trade secrets, and research data, potentially giving competitors an unfair advantage and harming the UK’s economic competitiveness. For example, a cyberattack on a UK aerospace company could steal designs for new aircraft, potentially benefiting a foreign competitor.
- Erosion of Public Trust:Cyberespionage attacks can erode public trust in the government and businesses, potentially impacting public confidence in digital services and technologies. For example, a cyberattack on a UK bank could lead to data breaches and financial losses, eroding public trust in the financial system.
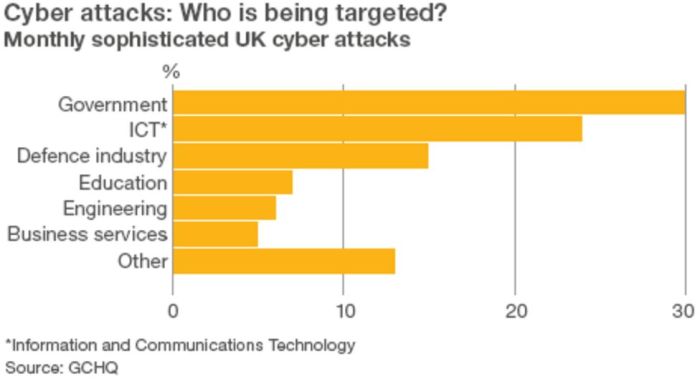
China’s Cyberespionage Activities
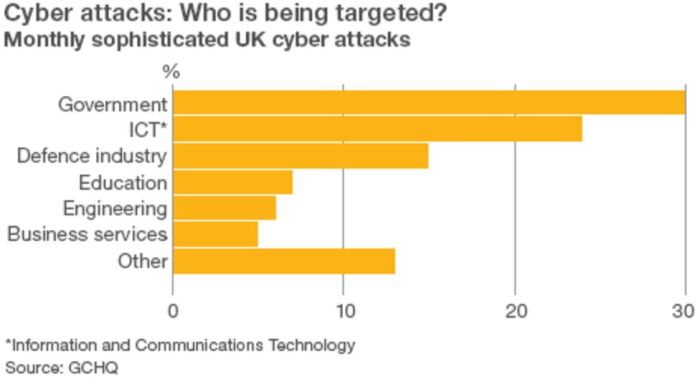
China’s cyberespionage activities have been a source of concern for many countries, particularly in recent years. The Chinese government has been accused of engaging in a range of activities aimed at stealing intellectual property, compromising sensitive information, and gaining strategic advantage over its rivals.
These activities have raised significant concerns about the security of sensitive technologies and the potential for disruption to global stability.
History of Chinese Cyberespionage
The history of Chinese cyberespionage is intertwined with the country’s rapid economic and technological development. In the early days of the internet, China focused on building its own infrastructure and catching up to the West. However, as China’s economic ambitions grew, so too did its interest in acquiring foreign technology and expertise.
- Early 2000s:The first notable incidents of Chinese cyberespionage emerged in the early 2000s. Targets included US companies, research institutions, and government agencies. These attacks often focused on stealing intellectual property related to aerospace, defense, and energy sectors.
- 2010s:Chinese cyberespionage activities intensified in the 2010s, with high-profile attacks on major companies like Google, Sony, and Lockheed Martin. These attacks often involved sophisticated malware and hacking techniques aimed at stealing large amounts of data.
- 2020s:In recent years, Chinese cyberespionage has become increasingly sophisticated, targeting not only traditional industries but also emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and biotechnology.
Motivations for Chinese Cyberespionage
China’s motivations for cyberespionage are complex and multifaceted, but they can be broadly categorized into three main areas:
- Economic Gain:China’s economic growth has been driven by its ability to acquire and adapt foreign technology. Cyberespionage allows China to gain access to cutting-edge research, designs, and manufacturing processes, which can be used to develop its own industries and products.
- Political Influence:China’s cyberespionage activities are also motivated by a desire to gain political influence and undermine its adversaries. By stealing sensitive information and disrupting critical infrastructure, China can weaken its rivals and advance its own geopolitical goals.
- Technological Advancement:China is striving to become a global leader in technology. Cyberespionage provides a means to acquire the knowledge and expertise needed to accelerate its technological development and catch up to the West.
Methods and Techniques
Chinese cyberespionage operations often involve a combination of methods and techniques, including:
- Malware:Chinese hackers develop and deploy sophisticated malware to gain access to target systems and steal data. Examples include the notorious “Stuxnet” worm, which targeted Iranian nuclear facilities.
- Hacking:Chinese hackers use a variety of hacking techniques, including exploiting vulnerabilities in software, using social engineering to trick victims into giving up their credentials, and launching denial-of-service attacks to disrupt critical systems.
- Social Engineering:Chinese hackers often use social engineering techniques to manipulate individuals into revealing sensitive information or granting access to their systems. This can involve phishing emails, fake websites, or impersonating trusted individuals.
The UK’s Response to Chinese Cyberespionage: Uk Sensitive Tech China Cyberespionage
The UK has recognized the growing threat posed by Chinese cyberespionage and has taken a number of steps to counter it. These measures include strengthening cybersecurity policies and regulations, enhancing international cooperation, and increasing public awareness.
Cybersecurity Policies and Regulations
The UK has implemented a range of cybersecurity policies and regulations to mitigate the risks of cyberespionage. These include the National Cyber Security Strategy (NCSS), which Artikels the UK’s approach to cybersecurity, and the Cyber Security Act 2017, which provides a legal framework for cybersecurity.
The NCSS emphasizes the importance of collaboration, resilience, and deterrence in addressing cyber threats. The Cyber Security Act 2017 introduces mandatory reporting requirements for certain organizations and provides powers for the government to take action against cyber threats.
Effectiveness of Policies and Regulations
The effectiveness of the UK’s cybersecurity policies and regulations in mitigating the risks of Chinese cyberespionage is a complex issue. While these measures have undoubtedly improved the UK’s cybersecurity posture, they are not without limitations. One challenge is the difficulty of attributing cyberattacks to specific actors, particularly in cases of state-sponsored cyberespionage.
Another challenge is the constant evolution of cyber threats, requiring continuous adaptation of policies and regulations.
International Cooperation
The UK has recognized the importance of international cooperation in combating cyberespionage. It actively participates in multilateral forums such as the G7 and NATO, sharing intelligence and coordinating joint operations. The UK also has bilateral partnerships with other countries, including the US, Canada, and Australia, to exchange information and collaborate on cyber security initiatives.
The UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) works closely with international partners to share threat intelligence and best practices, and to coordinate responses to cyber incidents.
Examples of UK-China Cyberespionage Cooperation
The UK has participated in a number of joint initiatives with China on cybersecurity, including the China-UK Cybersecurity Dialogue, which aims to promote cooperation on cyber security issues. However, these efforts have been complicated by concerns over Chinese cyberespionage activities.
Public Awareness
The UK government has taken steps to raise public awareness of cyber threats, including the importance of cybersecurity hygiene and the risks of cyberespionage. This includes public campaigns, educational programs, and the publication of guidance materials.
Technological and Strategic Implications
The UK’s vulnerability to cyberespionage is amplified by the rapid advancements in technology, which have significantly increased the sophistication and reach of cyberattacks. These advancements, coupled with China’s growing cyber capabilities, pose significant challenges to the UK’s national security, economic competitiveness, and international relations.
Technological Advancements
The evolution of cyberespionage techniques has been driven by technological advancements in several key areas. These advancements have enabled attackers to conduct more targeted, stealthy, and impactful operations.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI is being increasingly used in cyberespionage for tasks such as identifying targets, automating attacks, and analyzing large volumes of data. AI-powered tools can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of cyberespionage campaigns, enabling attackers to target specific individuals or organizations with greater precision.
- Quantum Computing:Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize cryptography, potentially breaking current encryption methods used to protect sensitive information. This could significantly impact the UK’s ability to safeguard its critical infrastructure and sensitive data from cyberespionage.
- Zero-Day Exploits:These are vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to developers and security researchers. Exploiting these vulnerabilities allows attackers to gain unauthorized access to systems before security patches are available. The development and use of zero-day exploits are a major concern for cybersecurity, as they can enable attackers to bypass traditional defenses.
Strategic Implications for the UK
Cyberespionage poses a multifaceted threat to the UK, impacting its national security, economic competitiveness, and international relations.
- National Security:Cyberespionage can compromise critical infrastructure, such as power grids, telecommunications networks, and financial systems. This can disrupt essential services, undermine national security, and potentially lead to significant economic losses.
- Economic Competitiveness:Cyberespionage can steal intellectual property, trade secrets, and sensitive business information, which can give foreign competitors an unfair advantage in the global marketplace. This can erode the UK’s economic competitiveness and hinder its ability to innovate and create jobs.
- International Relations:Cyberespionage can strain relations between countries, especially when it is perceived as an act of aggression. This can lead to diplomatic tensions, sanctions, and even military confrontations.
Countermeasures and Solutions, Uk sensitive tech china cyberespionage
To mitigate the risks of cyberespionage, the UK needs to adopt a comprehensive approach that includes improved cybersecurity defenses, intelligence gathering, and diplomatic efforts.
- Enhanced Cybersecurity Defenses:The UK government and private sector need to invest in robust cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and security awareness training. This will help to prevent cyberattacks and detect malicious activity early on.
- Intelligence Gathering:The UK intelligence agencies need to actively monitor and analyze cyber threats, including those originating from China. This will help to identify potential targets, understand the motives of attackers, and develop effective countermeasures.
- Diplomatic Efforts:The UK government needs to engage in diplomatic efforts to address cyberespionage with China. This includes raising concerns about cyberattacks, promoting international norms of responsible state behavior in cyberspace, and collaborating with other countries to address the issue.