Uk does not care about metaverse – UK Doesn’t Care About the Metaverse? This bold statement might seem outlandish, but there’s a grain of truth to it. While other countries are pouring resources into developing the metaverse, the UK seems to be taking a more cautious approach.
The UK government and public are prioritizing other areas of technological advancement, leaving the metaverse to simmer on the back burner.
The UK’s focus on traditional industries like finance and healthcare, coupled with a cautious stance on emerging technologies, has led to a slower adoption of the metaverse compared to other nations. This begs the question: is the UK missing out on a revolutionary opportunity, or is it simply playing the long game?
Understanding the UK’s Perspective

The UK’s approach to the metaverse is currently characterized by a cautious and pragmatic stance. While there is growing interest in the technology’s potential, particularly within the tech industry, there’s a noticeable lack of widespread public excitement or government-led initiatives compared to other nations.
The Current State of Metaverse Adoption in the UK
The UK’s metaverse landscape is still in its early stages. While some companies are experimenting with metaverse applications, particularly in gaming and entertainment, there is no widespread adoption or integration into mainstream sectors. Public awareness of the metaverse remains relatively low, with a significant portion of the population unfamiliar with its concepts and applications.
The UK’s Priorities in Technology and Innovation, Uk does not care about metaverse
The UK government has Artikeld a clear focus on key technological areas, including artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure. While the metaverse is not explicitly mentioned in these priorities, its development could potentially align with these areas. However, there is a potential conflict in resource allocation, as the government may prioritize established technologies with proven economic benefits over emerging technologies like the metaverse.
Comparison with Other Nations
The UK’s approach to the metaverse contrasts with other nations, particularly the US and China, which have shown significant interest and investment in its development. The US, with its large tech companies and venture capital ecosystem, has emerged as a leading player in metaverse development.
China, with its focus on digital transformation and government-led initiatives, is also investing heavily in the metaverse. The UK, in comparison, has been more cautious, with less public and private investment in the technology.
Discover how london based flawless ais true sync tech is a revolutionary approach to film dubbing has transformed methods in this topic.
Economic Considerations
The UK’s stance on the metaverse is a complex one, shaped by a mix of potential economic opportunities and concerns. Understanding the UK’s current economic landscape and its relationship with technology investment is crucial to analyzing the potential impact of the metaverse.
Potential Economic Benefits
The metaverse presents a range of potential economic benefits for the UK.
- Job Creation:The development and maintenance of metaverse technologies, applications, and services are expected to generate numerous new jobs in various sectors, including software development, digital design, content creation, and cybersecurity.
- Economic Growth:The metaverse can stimulate economic growth by fostering innovation, driving investment, and creating new markets. For example, the UK could become a global hub for metaverse development, attracting investment and talent from around the world.
- Enhanced Productivity:The metaverse has the potential to enhance productivity in various industries. For example, virtual collaboration tools could improve teamwork and communication, while virtual training simulations could accelerate skill development.
- New Business Models:The metaverse could create opportunities for new business models, such as virtual commerce, digital experiences, and decentralized platforms. This could lead to the emergence of new industries and revenue streams.
Potential Economic Risks
While the metaverse holds promise, it also presents economic risks for the UK.
- High Investment Costs:Developing and maintaining metaverse infrastructure requires significant investment. The UK needs to ensure it has the necessary resources and incentives to attract and support these investments.
- Job Displacement:The automation and digitization facilitated by the metaverse could lead to job displacement in certain sectors. The UK needs to invest in education and training programs to prepare its workforce for the changing job market.
- Cybersecurity Threats:The metaverse presents new cybersecurity challenges, such as data breaches, identity theft, and malicious attacks. The UK needs to develop robust cybersecurity measures to protect its citizens and businesses.
- Digital Divide:The lack of access to technology and digital skills could exacerbate existing inequalities and create a digital divide within the UK. The government needs to ensure equitable access to the metaverse and digital literacy programs.
The UK’s Current Economic Landscape
The UK’s current economic landscape is characterized by several factors that influence its approach to metaverse investment.
- Post-Brexit Economic Uncertainty:The UK’s exit from the European Union has created economic uncertainty, making businesses more cautious about large-scale investments, including those in emerging technologies like the metaverse.
- Government Focus on Innovation:The UK government has prioritized innovation and technology as key drivers of economic growth. This focus could lead to increased investment in the metaverse and related technologies.
- Strong Technology Sector:The UK has a strong technology sector, with a concentration of tech companies, research institutions, and talent. This provides a foundation for developing and deploying metaverse technologies.
Hypothetical Scenario: Economic Impact of a Fully Developed Metaverse
Imagine a future where the metaverse is fully developed and integrated into daily life in the UK. In this scenario, the economic impact would be profound.
- Increased Productivity:Virtual collaboration tools would significantly enhance productivity across industries, leading to increased economic output and job creation.
- New Industries:The metaverse would create new industries, such as virtual tourism, digital fashion, and virtual entertainment, generating new revenue streams and employment opportunities.
- Economic Growth:The UK’s economy would experience significant growth, driven by the metaverse’s impact on productivity, innovation, and investment.
- Social and Cultural Impact:The metaverse would also have a profound impact on social interactions, cultural expression, and education, leading to changes in how people work, learn, and socialize.
Social and Cultural Implications
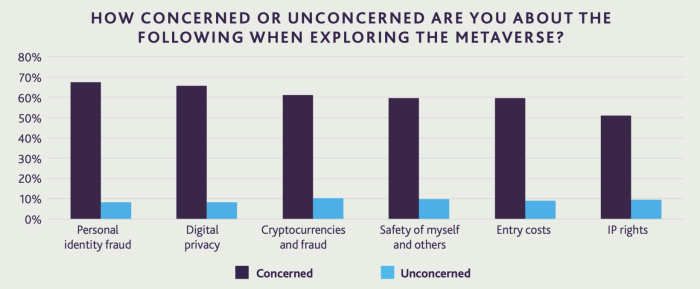
The metaverse’s potential impact on the UK extends beyond economic considerations, delving into the realm of social and cultural implications. The interconnected nature of the digital and physical worlds raises questions about accessibility, privacy, and digital inequality, all of which could shape the UK’s social fabric.
Accessibility and Digital Inequality
The metaverse’s accessibility is crucial for its widespread adoption. However, digital inequality, characterized by disparities in access to technology and digital skills, poses a significant challenge. The UK already faces challenges with digital inclusion, and the metaverse could exacerbate these inequalities.
- Limited access to high-speed internet:Reliable internet access is essential for engaging with the metaverse. Areas with limited broadband infrastructure or high internet costs could experience a digital divide, hindering their participation.
- Cost of equipment:The metaverse requires specialized hardware, such as VR headsets and high-performance computers, which can be expensive. This could exclude individuals and communities with limited financial resources.
- Digital literacy:Navigating the metaverse requires digital skills, such as navigating virtual environments, understanding digital currency, and interacting with avatars. Lack of digital literacy could hinder participation, creating a gap between tech-savvy users and those less familiar with digital technologies.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The metaverse raises significant privacy and security concerns. The collection and use of personal data in virtual environments raise questions about user control and potential misuse.
- Data collection:Companies operating in the metaverse could collect vast amounts of user data, including their movements, interactions, and preferences. This data could be used for targeted advertising, profiling, and potentially even manipulation.
- Cybersecurity threats:The metaverse presents new avenues for cyberattacks, such as identity theft, data breaches, and virtual property theft. Ensuring robust security measures is crucial to protect users from these threats.
- Virtual identity and anonymity:The metaverse allows users to create avatars and assume virtual identities, blurring the lines between real and digital identities. This raises concerns about anonymity and the potential for misuse, such as harassment or illegal activities.
Impact on Existing Social Structures and Communities
The metaverse could transform how people interact and form communities, potentially impacting existing social structures.
- New forms of social interaction:The metaverse provides new avenues for social interaction, allowing users to connect with people from all over the world, regardless of physical location. This could foster new communities and relationships, but it could also lead to a decline in face-to-face interactions.
- Virtual communities and identity:The metaverse could create virtual communities based on shared interests, values, or identities. These communities could provide a sense of belonging and support, but they could also lead to the formation of echo chambers and reinforce existing social divisions.
- Impact on real-world relationships:The metaverse could potentially impact real-world relationships, as individuals spend more time interacting in virtual environments. This could lead to social isolation and a decline in face-to-face interactions, particularly for those who rely heavily on the metaverse for social connection.
Addressing Social Challenges
The metaverse also presents opportunities to address social challenges in the UK. Its immersive and interactive nature can be used to create new ways of engaging with social issues and promoting positive change.
- Education and training:The metaverse can provide immersive learning experiences, making education more engaging and accessible. This could be particularly beneficial for students with learning disabilities or those who struggle with traditional classroom settings.
- Healthcare and mental health:The metaverse can be used to develop virtual therapy sessions, provide support for mental health conditions, and offer interactive health education programs.
- Social inclusion and accessibility:The metaverse can create virtual spaces where people with disabilities or those facing social isolation can connect and participate in activities. This can promote social inclusion and combat loneliness.
Technological Challenges and Opportunities: Uk Does Not Care About Metaverse

The metaverse, a burgeoning digital realm, presents both technological hurdles and exciting opportunities for the UK. While the UK has a strong foundation in digital technology, specific challenges need to be addressed to ensure its successful integration into the metaverse.
Technical Challenges Facing Metaverse Development in the UK
The UK faces several technical challenges in its pursuit of a thriving metaverse. These challenges stem from the need for robust infrastructure, interoperability between platforms, and addressing data privacy and security concerns.
- Infrastructure:Building a metaverse requires significant computing power, high-speed internet connectivity, and advanced hardware. The UK needs to invest in upgrading its existing infrastructure to support the demands of the metaverse. This includes expanding fiber optic networks, improving 5G coverage, and developing data centers with sufficient capacity.
- Interoperability:The metaverse is not a single platform but a collection of interconnected virtual worlds. Interoperability, the ability for different platforms to seamlessly communicate and share data, is crucial for its success. The UK needs to encourage the development of open standards and protocols to facilitate interoperability between metaverse platforms.
- Data Privacy and Security:The metaverse collects vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy and security. The UK needs to establish robust data protection regulations and develop innovative solutions to ensure user privacy and data security in the metaverse.
Potential Areas for UK Leadership in Metaverse Technology
Despite the challenges, the UK has the potential to become a global leader in metaverse technology. The UK’s strengths in research and development, its vibrant tech sector, and its commitment to innovation position it well to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the metaverse.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):The UK has a strong AI research community and is well-positioned to develop AI-powered applications for the metaverse, such as realistic avatars, intelligent virtual assistants, and immersive experiences.
- Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR):The UK has a thriving AR/VR industry, with companies developing cutting-edge hardware and software. This expertise can be leveraged to create immersive metaverse experiences.
- Blockchain Technology:The UK has a strong blockchain ecosystem, with expertise in decentralized applications and digital asset management. Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent systems for managing virtual assets and identities in the metaverse.
Role of UK Research and Development Institutions
The UK’s research and development institutions play a crucial role in shaping the future of the metaverse. These institutions are at the forefront of technological innovation and are developing the foundational technologies that will underpin the metaverse.
- Universities:UK universities are leading research in areas such as AI, AR/VR, and blockchain, which are essential for the metaverse. They are also educating the next generation of metaverse developers and researchers.
- Research Institutes:Research institutes such as the Alan Turing Institute and the National Physical Laboratory are conducting cutting-edge research in areas relevant to the metaverse. They are also collaborating with industry to translate research into real-world applications.
Alternative Priorities
The UK’s apparent disinterest in the metaverse might be a reflection of its prioritization of other pressing issues and potential future opportunities. While the metaverse presents intriguing possibilities, the UK government and its citizens may be focusing their attention on more immediate and tangible concerns, such as the ongoing economic recovery, climate change, and the development of crucial technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and quantum computing.
Prioritizing Traditional Economic Growth
The UK’s economy has been facing significant challenges in recent years, including the impact of Brexit and the COVID-19 pandemic. The government’s primary focus is likely on stimulating economic growth, creating jobs, and attracting investment. In this context, investing in traditional sectors like manufacturing, finance, and technology development, which offer more immediate and tangible returns, might be considered a more prudent approach.
Addressing Climate Change
Climate change is a global crisis, and the UK has set ambitious targets for reducing its carbon emissions. The government is likely to prioritize investments in renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and green technologies. These efforts require significant resources and attention, potentially diverting focus from the metaverse.
Investing in AI and Quantum Computing
AI and quantum computing are considered crucial technologies of the future, with the potential to revolutionize various industries. The UK government has recognized their importance and has been investing heavily in research and development in these areas. The potential economic and societal benefits of these technologies are vast, making them a strong contender for prioritization.
A Hypothetical Policy Framework
A balanced policy framework for the UK’s technology sector should consider the following:* Prioritizing research and development:Investing in fundamental research in areas like AI, quantum computing, and biotechnology is crucial for long-term innovation.
Supporting emerging technologies
While the metaverse might not be a top priority, exploring its potential and supporting the development of related technologies, like virtual and augmented reality, is essential.
Addressing societal challenges
Investing in technologies that address societal challenges, such as climate change, healthcare, and education, is vital for long-term well-being.
Building a skilled workforce
The UK needs to invest in education and training programs to ensure a skilled workforce for the future, capable of working with emerging technologies.
Promoting responsible innovation
It is crucial to develop ethical frameworks and regulations for emerging technologies to mitigate potential risks and ensure responsible development.
The UK’s technology policy should be guided by a balanced approach that prioritizes both immediate economic needs and long-term innovation.





