Uk chip designer arm valued 50bn dollars ipo – UK chip designer ARM, valued at a staggering $50 billion, is gearing up for its highly anticipated initial public offering (IPO). This move signifies a pivotal moment for the semiconductor industry, with ARM poised to capitalize on its dominance in the mobile and embedded computing markets.
ARM’s unique architecture, powering billions of devices worldwide, has become a cornerstone of modern technology, and its IPO is expected to send ripples through the global tech landscape.
ARM’s journey began in the 1980s, with a vision to create energy-efficient processors for a range of applications. Its RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computing) architecture revolutionized the industry, offering a more streamlined and efficient approach to chip design. This innovation led to widespread adoption, with ARM processors now powering everything from smartphones and tablets to Internet of Things (IoT) devices and even supercomputers.
ARM’s History and Significance: Uk Chip Designer Arm Valued 50bn Dollars Ipo
ARM, a British chip designer, has emerged as a dominant force in the semiconductor industry, shaping the landscape of modern computing and mobile devices. Its journey from a small startup to a global powerhouse is marked by innovation and a unique architectural approach that has revolutionized the way we interact with technology.
ARM’s Origins and Evolution
ARM’s story begins in 1983 with Acorn Computers, a British company known for its pioneering work in personal computing. The company’s engineers, under the leadership of Hermann Hauser and Sophie Wilson, designed the Acorn RISC Machine (ARM), a revolutionary processor architecture based on the Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) principle.
This architecture, unlike the complex instruction sets used in traditional processors, employed a simpler set of instructions, resulting in faster execution and lower power consumption.In 1990, ARM Holdings was spun off from Acorn Computers, marking the beginning of its independent journey.
The company focused on licensing its processor designs to other semiconductor manufacturers, allowing them to build their own chips based on the ARM architecture. This business model proved incredibly successful, enabling ARM to rapidly expand its reach and influence.
ARM’s Unique Architectural Approach
ARM’s RISC architecture, with its simplicity and efficiency, became a cornerstone of the modern semiconductor industry. Unlike complex instruction set computers (CISC), which use a wide range of instructions to perform tasks, RISC processors rely on a smaller, streamlined set of instructions.
This simplicity translates into faster execution speeds, lower power consumption, and smaller chip sizes, making ARM processors ideal for mobile devices, embedded systems, and a wide range of other applications.
Impact on the Semiconductor Industry
ARM’s impact on the semiconductor industry is undeniable. Its licensing model democratized access to advanced processor technology, enabling a diverse range of companies to develop their own chips based on the ARM architecture. This open approach fostered innovation and competition, driving down costs and accelerating the development of new and powerful processors.
ARM’s Most Successful Processors and Applications
ARM’s success is evident in the widespread adoption of its processors across various industries. Here are some examples of its most successful processors and their applications:
ARM Cortex-A Series
The Cortex-A series is ARM’s flagship processor family, designed for high-performance applications such as smartphones, tablets, and servers. The Cortex-A53 and Cortex-A73 are prominent examples, powering billions of devices worldwide. These processors are known for their exceptional performance, energy efficiency, and scalability, making them ideal for demanding mobile and server workloads.
ARM Cortex-M Series
The Cortex-M series is optimized for microcontrollers, which are embedded processors used in a wide range of devices, from appliances and automotive systems to industrial equipment and medical devices. The Cortex-M3 and Cortex-M4 are popular choices, offering a balance of performance and low power consumption, making them suitable for resource-constrained environments.
ARM Mali Graphics Processors
ARM’s Mali graphics processors are widely used in mobile devices, providing high-quality graphics rendering for games, videos, and other applications. The Mali-T760 and Mali-G72 are examples of powerful graphics processors capable of delivering immersive visual experiences on smartphones and tablets.
The $50 Billion Valuation
ARM’s initial public offering (IPO) at a valuation of $50 billion has sent shockwaves through the tech world. This staggering figure reflects the immense value that investors see in the company’s unique position in the semiconductor landscape.
Factors Contributing to ARM’s Valuation
The $50 billion valuation is a testament to ARM’s dominant market share, its innovative technology, and its strategic positioning within the rapidly growing semiconductor industry.
- Dominant Market Share:ARM’s architecture powers over 99% of the world’s smartphones, a staggering figure that underscores its dominance in the mobile market. This widespread adoption translates into significant revenue streams and a robust ecosystem of partners.
- Innovative Technology:ARM’s energy-efficient and scalable processor designs have revolutionized the mobile computing landscape. The company continues to innovate, developing advanced technologies like its Armv9 architecture, which is designed to power the next generation of high-performance computing devices.
- Strategic Positioning:ARM occupies a unique position in the semiconductor industry. It doesn’t manufacture chips itself, but licenses its designs to other companies, enabling a wide range of devices to be built using ARM’s technology. This business model provides ARM with a steady stream of licensing fees and a diversified customer base.
- Growth Potential:The demand for semiconductors is expected to continue growing rapidly in the coming years, driven by factors like the proliferation of connected devices, the rise of artificial intelligence, and the increasing adoption of cloud computing. ARM is well-positioned to benefit from this growth, as its technology is essential for powering a wide range of devices.
Benefits and Risks of a High Valuation
A high valuation can be both a blessing and a curse for a company.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of apple event 27 januar .
Benefits
- Strong Financial Position:A high valuation allows ARM to raise significant capital, which can be used to fund research and development, expand into new markets, and make strategic acquisitions.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation:A high valuation reinforces ARM’s position as a leading innovator in the semiconductor industry, enhancing its brand reputation and attracting top talent.
- Access to New Opportunities:A strong financial position opens doors to new opportunities, allowing ARM to invest in emerging technologies and expand its reach into new markets.
Risks
- Pressure to Perform:Investors will expect ARM to deliver strong financial performance to justify its high valuation. Failure to meet these expectations could lead to a decline in the company’s stock price.
- Competition:The semiconductor industry is highly competitive, and ARM faces competition from other companies developing their own processor architectures. A decline in ARM’s market share could negatively impact its valuation.
- Economic Downturn:A global economic downturn could negatively impact demand for semiconductors, potentially hurting ARM’s financial performance and its valuation.
Comparison to Other Semiconductor Companies
ARM’s $50 billion valuation is significantly higher than that of many other prominent semiconductor companies. For example, Intel, the world’s largest chipmaker, has a market capitalization of around $150 billion. However, it’s important to note that Intel’s business model is different from ARM’s, as Intel designs, manufactures, and sells its own chips.
ARM’s valuation reflects the unique value proposition it offers to the semiconductor industry. Its licensing model, coupled with its dominant market share and innovative technology, makes it a highly attractive investment for investors.
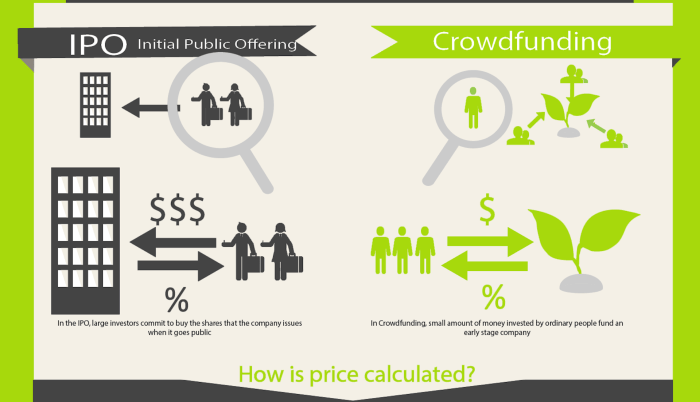
The IPO and Market Impact

ARM’s highly anticipated IPO is set to be a pivotal event for the semiconductor industry, potentially reshaping the landscape and influencing the trajectory of future innovations. The IPO is expected to generate significant interest from both investors and industry players, as it offers a unique opportunity to participate in the growth of a company at the heart of the technological revolution.
Key Players and Interests in the IPO
The ARM IPO is attracting a diverse range of investors, each with their own motivations and expectations. These include:
- Traditional Investors:Institutional investors like mutual funds and hedge funds are seeking to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on the potential growth of the semiconductor industry. They are primarily interested in the financial returns of the IPO and the long-term prospects of ARM.
- Tech Giants:Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon are major customers of ARM’s technology and are likely to invest in the IPO to secure access to ARM’s intellectual property and future innovations. They are also interested in gaining influence within the company and shaping its future direction.
- Semiconductor Companies:Chip manufacturers such as Qualcomm, Samsung, and TSMC are heavily reliant on ARM’s architecture and will be closely watching the IPO to understand the implications for their own businesses. They are likely to invest to secure a stake in ARM’s future and potentially gain leverage in negotiations.
- Venture Capitalists:VC firms that have invested in ARM over the years will be looking to cash out on their investments and reap the rewards of their early support. They will be seeking to maximize their returns and potentially gain access to future investment opportunities in the semiconductor sector.
Potential Outcomes of a Successful vs. Unsuccessful IPO
The success or failure of ARM’s IPO will have significant implications for the semiconductor market, affecting the dynamics of competition, innovation, and investment.
| Outcome | Successful IPO | Unsuccessful IPO |
|---|---|---|
| Valuation | High valuation, reflecting strong market confidence in ARM’s future. | Low valuation, indicating investor skepticism about ARM’s growth prospects. |
| Investment | Attracts significant investment, fueling ARM’s growth and expansion. | Limited investment, hindering ARM’s ability to compete and innovate. |
| Competition | Increases ARM’s competitive edge, enabling it to invest in new technologies and attract talent. | Reduces ARM’s competitive advantage, making it vulnerable to rivals. |
| Innovation | Encourages innovation and development of new technologies, driving the semiconductor industry forward. | Slows down innovation and hinders the development of new chip architectures. |
| Market Share | Expands ARM’s market share, solidifying its position as a dominant force in the semiconductor industry. | Limits ARM’s market share, reducing its influence and impact. |
ARM’s Competitive Landscape

ARM’s IPO has sparked much discussion about its competitive position in the chip design industry. While ARM is a dominant player, it faces stiff competition from various companies with their own strengths and strategies.
Key Competitors
ARM’s key competitors include companies that design and manufacture chips, those that license their own intellectual property, and those that develop software and tools for chip design. These competitors can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Chip Design and Manufacturing Companies:Companies like Intel, Qualcomm, AMD, and Nvidia are major players in the chip design and manufacturing space. They develop their own chip architectures and compete directly with ARM in various market segments, particularly in high-performance computing and mobile devices.
- IP Licensing Companies:Companies like Imagination Technologies and MIPS Technologies license their own processor architectures to chip manufacturers. These companies compete with ARM in the market for licensing intellectual property.
- Software and Tools Developers:Companies like Cadence Design Systems, Synopsys, and Mentor Graphics develop software and tools used in chip design. These companies play a crucial role in the chip design ecosystem and can influence the adoption of different architectures.
Comparison of Strengths and Weaknesses
Comparing ARM’s strengths and weaknesses against its competitors is crucial to understanding its competitive advantage.
- ARM’s Strengths:
- Widely adopted architecture:ARM’s architecture is widely adopted in various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices. This widespread adoption gives ARM a significant advantage in terms of market share and ecosystem support.
- Energy efficiency:ARM’s architecture is known for its energy efficiency, which is particularly important for mobile and embedded devices. This advantage allows ARM to compete effectively in power-constrained environments.
- Licensing model:ARM’s licensing model allows chip manufacturers to customize and optimize its architecture for specific applications. This flexibility attracts a wide range of customers and fosters innovation.
- Strong ecosystem:ARM has a robust ecosystem of partners, including software developers, tool providers, and chip manufacturers. This ecosystem supports the development and deployment of ARM-based devices.
- ARM’s Weaknesses:
- Limited control over manufacturing:ARM licenses its architecture to other companies, giving it limited control over the manufacturing process. This can lead to variations in chip performance and quality.
- Competition in high-performance computing:ARM faces strong competition from companies like Intel and AMD in the high-performance computing market. ARM’s architecture is not as widely adopted in high-performance applications as it is in mobile and embedded devices.
- Dependence on licensing revenue:ARM’s revenue is largely dependent on licensing fees. This can make the company vulnerable to changes in the market or economic conditions.
Impact of the IPO on Competitive Position
ARM’s IPO is expected to have a significant impact on its competitive position.
- Increased visibility and market capitalization:The IPO will increase ARM’s visibility in the market and provide it with greater access to capital. This could help ARM invest in research and development, expand its product portfolio, and acquire new technologies.
- Enhanced ability to compete:The IPO will provide ARM with more financial resources to compete with larger companies like Intel and Qualcomm. This could allow ARM to invest in areas where it currently lags behind, such as high-performance computing.
- Potential for strategic partnerships:The IPO could attract new strategic partners to ARM, potentially leading to new product development opportunities and market expansion.
Future of ARM
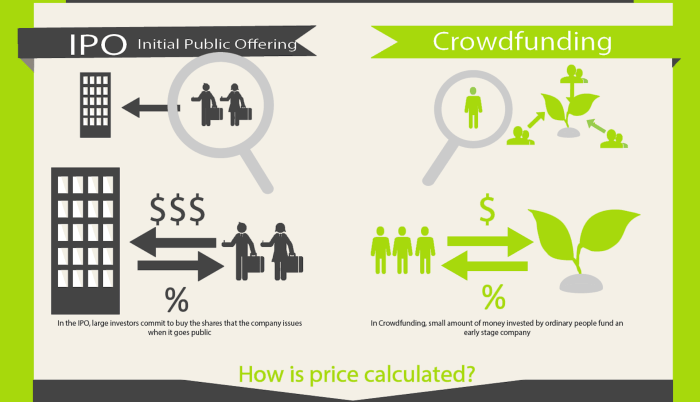
ARM’s successful IPO marks a new chapter for the company, positioning it to capitalize on the expanding semiconductor landscape. With its dominant market share in mobile devices, ARM is poised to expand its reach into new markets, driving future growth.
Growth Potential and Strategic Direction
ARM’s future growth potential is driven by several key factors. The company’s dominance in the mobile market, coupled with its expansion into emerging technologies like automotive, IoT, and AI, presents significant opportunities for revenue growth. ARM’s licensing model, which allows chipmakers to use its designs and pay royalties, ensures a recurring revenue stream, making it less susceptible to cyclical market fluctuations.
The company is strategically investing in research and development to enhance its existing technologies and develop new ones, further solidifying its position as a leader in the semiconductor industry.
Challenges and Opportunities, Uk chip designer arm valued 50bn dollars ipo
While ARM enjoys a dominant market position, it faces challenges in the years to come. The increasing complexity of semiconductor design and the emergence of new competitors, particularly in the automotive and AI markets, present hurdles for ARM. However, these challenges also represent opportunities for growth and innovation.
ARM’s commitment to developing advanced technologies, such as its scalable, energy-efficient processors, positions it well to address these challenges and capitalize on emerging trends.
Potential Milestones and Key Events
ARM’s future is likely to be marked by several key milestones and events. The company will continue to expand its reach into new markets, including automotive, IoT, and AI, while also strengthening its position in existing markets like mobile devices.
ARM is expected to invest heavily in research and development, particularly in areas such as energy efficiency, performance, and security. The company may also consider strategic acquisitions to expand its portfolio of technologies and enter new markets. These milestones will be driven by factors such as technological advancements, market trends, and competition.