Tech companies spend 113m lobbying eu policies – Tech companies spend €113 million lobbying EU policies, a staggering sum that underscores the influence these giants wield in shaping European regulations. This figure represents a significant portion of the overall lobbying expenditure in the EU, raising questions about the balance of power between tech giants and policymakers.
The tech industry’s lobbying efforts are directed at a wide range of policies, from data privacy and competition to artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. Their influence extends beyond individual companies, impacting the entire tech ecosystem and ultimately shaping the digital landscape of Europe.
The Scale of Tech Lobbying in the EU
The tech industry’s influence on EU policy is significant, as evidenced by the €113 million spent on lobbying in 2022. This figure highlights the industry’s commitment to shaping regulations that affect its operations and future.
The Significance of €113 Million
The €113 million spent on lobbying by tech companies in 2022 represents a substantial portion of the overall EU lobbying spending. While exact figures for total lobbying spending are difficult to obtain due to the complex nature of the industry, estimates suggest that the tech sector’s contribution is significant.
This signifies the industry’s determination to influence policy decisions that impact its interests.
Comparison with Other Industries, Tech companies spend 113m lobbying eu policies
Tech companies are not the only industry heavily involved in lobbying EU policies. The financial services, pharmaceutical, and energy sectors also dedicate significant resources to influencing regulations. However, the tech industry’s rapid growth and its influence on various aspects of modern life have made it a major player in the lobbying landscape.
Top Tech Lobbying Contributors
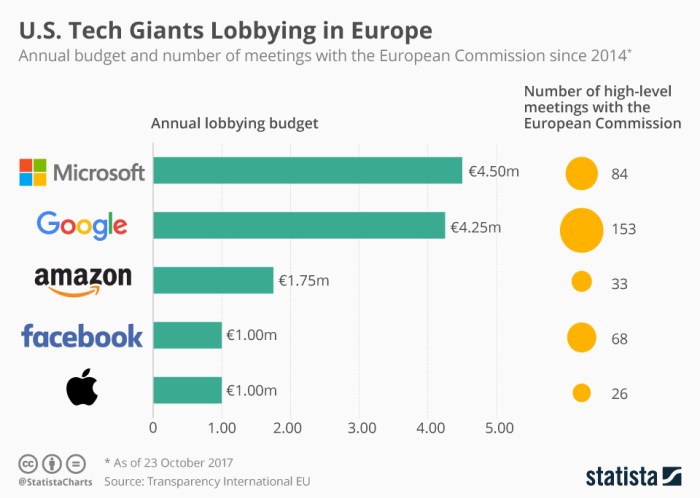
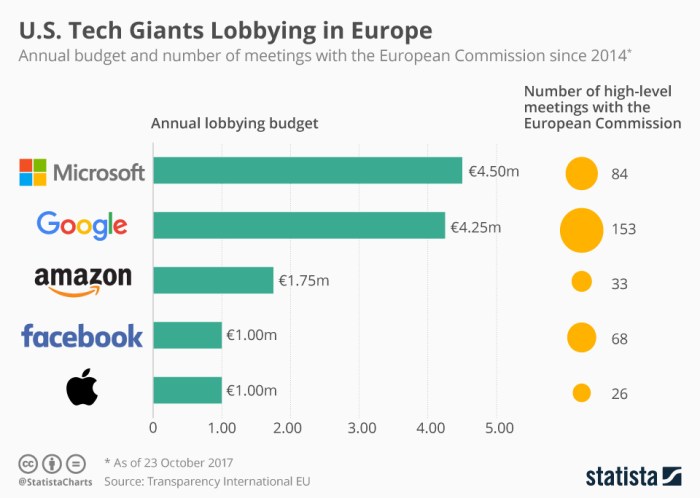
A breakdown of the top tech companies contributing to the €113 million lobbying expenditure reveals a concentration of influence among the industry giants. The top contributors include:
- Google: Google is known for its extensive lobbying efforts, focusing on areas such as digital advertising, data protection, and antitrust regulations. Their lobbying activities aim to ensure a favorable regulatory environment for their business model.
- Microsoft: Microsoft, another tech giant, invests heavily in lobbying to influence EU policies on cloud computing, cybersecurity, and intellectual property rights. Their lobbying activities are designed to shape regulations that benefit their cloud computing platform and software products.
- Amazon: Amazon’s lobbying efforts are focused on issues related to e-commerce, competition, and taxation. They actively engage in lobbying to ensure a favorable regulatory environment for their online retail operations.
- Meta: Meta, formerly Facebook, engages in lobbying to influence EU regulations on data privacy, online content moderation, and competition. Their lobbying activities aim to shape regulations that allow them to operate effectively in the EU digital market.
- Apple: Apple’s lobbying efforts are concentrated on issues related to intellectual property rights, privacy, and antitrust regulations. Their lobbying activities aim to protect their brand, products, and business model in the EU.
EU Policies Targeted by Tech Lobbying
The tech industry’s influence on European policymaking is undeniable. Lobbying efforts, particularly those aimed at shaping EU regulations, are extensive and multifaceted. This section delves into key EU policies that tech companies actively lobby and the reasons behind their engagement.
Data Protection and Privacy
Tech companies are deeply involved in lobbying efforts surrounding EU data protection and privacy regulations, particularly the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Their concerns stem from the potential impact these regulations could have on their business models, which often rely on collecting and utilizing user data.
- Data Portability:Tech companies often advocate for more flexible data portability rules, allowing them to transfer user data more easily across platforms and jurisdictions. This would facilitate cross-border operations and potentially enable them to leverage user data more effectively.
- Data Retention:Lobbying efforts also focus on data retention requirements. Tech companies may push for shorter retention periods or more lenient guidelines for data storage, arguing that excessive retention can lead to unnecessary costs and administrative burdens.
- Data Security:While data security is a key concern for users, tech companies may lobby for more flexible data security standards, arguing that stringent requirements can hinder innovation and limit their ability to develop new technologies.
These policies have significant implications for the tech industry. The GDPR has led to increased compliance costs for companies and has prompted a shift towards more privacy-focused practices. However, it has also empowered users and fostered a more data-conscious environment.
Competition and Antitrust
Tech companies actively lobby on EU competition and antitrust policies, aiming to influence regulations that could affect their market dominance and business practices.
- Market Definition:Tech companies may argue for broader market definitions that encompass a wider range of services and products, potentially diluting their market share and reducing the likelihood of antitrust scrutiny.
- Mergers and Acquisitions:Lobbying efforts also extend to merger and acquisition regulations. Tech companies may seek to influence the approval process for acquisitions, arguing that certain mergers are beneficial to consumers and contribute to innovation.
- Antitrust Enforcement:Tech companies may lobby for more lenient antitrust enforcement, arguing that certain regulations can stifle innovation and discourage investment.
EU competition policies have a direct impact on the tech industry’s ability to grow and expand. The European Commission has taken a more assertive stance in recent years, investigating and imposing fines on tech giants for antitrust violations. These actions have created uncertainty and potential challenges for tech companies operating in the EU.
Digital Taxation
The EU’s digital taxation policies are a major point of contention for tech companies. These policies aim to ensure that tech companies contribute their fair share of taxes in the EU, even if their physical presence in the region is limited.
- Tax Base:Tech companies may lobby for narrower tax bases, arguing that current proposals are too broad and unfairly target their businesses.
- Tax Rates:Lobbying efforts may focus on lowering tax rates or seeking exemptions from certain taxes, arguing that high tax burdens can discourage investment and innovation.
- Tax Avoidance:Tech companies may lobby for more flexible tax avoidance rules, arguing that current regulations are overly restrictive and hinder their ability to optimize their tax liabilities.
EU digital taxation policies are designed to ensure a level playing field and prevent tax avoidance by tech companies. However, these policies can create significant financial burdens for tech companies and may influence their investment decisions.
Platform Regulation
The EU’s platform regulation proposals aim to address concerns about the power and influence of large online platforms, including those owned by tech companies. These proposals cover areas such as content moderation, algorithmic transparency, and the protection of user data.
- Content Moderation:Tech companies may lobby for more flexible content moderation rules, arguing that strict regulations can stifle freedom of expression and hinder their ability to manage user-generated content.
- Algorithmic Transparency:Lobbying efforts may focus on limiting the scope of algorithmic transparency requirements, arguing that disclosing detailed information about their algorithms could compromise their competitive advantage and expose them to intellectual property theft.
- Interoperability:Tech companies may lobby for more lenient interoperability rules, arguing that mandatory interoperability can create technical challenges and hinder innovation.
EU platform regulations have the potential to reshape the online landscape and impact the way tech companies operate. These regulations aim to promote fairness, transparency, and user protection but could also lead to increased compliance costs and regulatory burdens for tech companies.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of be my eyes app uses openai gpt 4 help visually impaired.
Methods and Strategies of Tech Lobbying: Tech Companies Spend 113m Lobbying Eu Policies
Tech companies employ a wide range of methods to influence EU policymaking. Their lobbying strategies are multifaceted, encompassing direct engagement with policymakers, public relations campaigns, and strategic alliances. These methods aim to shape the regulatory landscape in favor of their business interests.
Direct Lobbying
Tech companies engage in direct lobbying by interacting with policymakers, including Members of the European Parliament (MEPs), national government officials, and EU Commission staff. This direct engagement takes various forms:
- Meetings and briefings:Tech companies organize meetings and briefings with policymakers to present their views on specific policy proposals. These meetings allow them to directly advocate for their interests and address concerns raised by policymakers.
- Lobbying groups and associations:Tech companies often join lobbying groups and associations that represent their sector’s interests. These groups provide a platform for collective lobbying efforts and allow companies to leverage their combined resources and influence.
- Expert testimony:Tech companies often provide expert testimony to parliamentary committees or EU Commission hearings. This allows them to present their technical expertise and shape the policy debate from a technical perspective.
- Contributions to policy consultations:The EU Commission often conducts public consultations on policy proposals. Tech companies actively participate in these consultations by submitting written contributions that Artikel their views and recommendations.
Public Relations Campaigns
Tech companies also engage in public relations campaigns to influence public opinion and create a favorable environment for their policy goals. These campaigns often involve:
- Media relations:Tech companies cultivate relationships with journalists and media outlets to ensure positive coverage of their activities and policies. They often issue press releases, organize media events, and provide expert commentary to shape public perception.
- Social media campaigns:Tech companies leverage social media platforms to engage with the public and build support for their policy positions. They often use social media to amplify their messages, mobilize supporters, and counter negative narratives.
- Public awareness campaigns:Tech companies may launch public awareness campaigns to highlight the benefits of their technologies and promote their policy agenda. These campaigns can take various forms, including advertising, educational initiatives, and community outreach programs.
Strategic Alliances
Tech companies often forge strategic alliances with other stakeholders to strengthen their lobbying efforts. These alliances can involve:
- Industry coalitions:Tech companies join industry coalitions that represent their sector’s interests. These coalitions allow companies to pool resources, coordinate lobbying activities, and amplify their collective voice.
- Cross-sector partnerships:Tech companies may form partnerships with organizations from other sectors, such as academia, think tanks, or civil society groups. These partnerships allow companies to leverage the expertise and networks of their partners to advance their policy objectives.
Effectiveness of Lobbying Strategies
The effectiveness of tech lobbying strategies in shaping EU policy outcomes is a complex issue. While tech companies have significant resources and influence, they face a range of challenges, including:
- Transparency and accountability:The EU has implemented transparency rules for lobbying activities, but concerns remain about the effectiveness of these rules in ensuring accountability and preventing undue influence. The lack of transparency can make it difficult to assess the impact of lobbying on policy outcomes.
- Competing interests:Tech companies are not the only actors lobbying on EU policies. They face competition from other industries, civil society groups, and national governments, all of which have their own interests and agendas.
- Public scrutiny:Tech companies face increasing public scrutiny and criticism over their lobbying activities. This scrutiny can limit their ability to influence policy decisions and may lead to negative public perception.
Transparency and Accountability in Tech Lobbying
The influence of tech companies on EU policymaking is a topic of growing concern, particularly in light of the significant financial resources these companies invest in lobbying activities. Transparency and accountability are crucial for ensuring that EU policy decisions are made in the best interests of citizens and not solely influenced by the interests of powerful tech companies.
Transparency in Tech Lobbying
Transparency in tech lobbying refers to the degree to which information about lobbying activities is publicly available. This includes details about the lobbyists involved, the issues they are advocating for, and the amount of money spent on lobbying efforts. A high level of transparency allows for greater public scrutiny and accountability, enabling citizens and policymakers to understand the influence of tech lobbying on EU policymaking.
However, the level of transparency in tech lobbying within the EU is currently a matter of debate.
- The EU Transparency Register, a voluntary system for registering lobbyists, provides some information about lobbying activities. However, it has been criticized for its limitations, including the fact that registration is not mandatory and that the information provided is often incomplete.
- There are also concerns about the lack of transparency surrounding the use of “revolving doors” between the tech industry and EU institutions. This refers to individuals who move between positions in the tech industry and EU institutions, potentially bringing with them biases and conflicts of interest.
Concerns Regarding the Influence of Tech Lobbying
There are several potential concerns regarding the influence of tech lobbying on EU policymaking.
- One concern is that tech companies may use their lobbying efforts to influence EU policy in ways that benefit their own interests, even if those interests are not aligned with the public good. This could lead to policies that favor large tech companies at the expense of smaller businesses, consumers, or civil liberties.
- Another concern is that tech lobbying may undermine the democratic process by creating an uneven playing field between powerful tech companies and ordinary citizens. This could lead to policies that are not representative of the will of the people.
The Role of Public Scrutiny and Accountability
Public scrutiny and accountability are essential for ensuring that tech lobbying does not undermine the democratic process.
- Media investigations, citizen advocacy groups, and academic researchers play a crucial role in exposing and scrutinizing tech lobbying activities. This can help to bring attention to potential conflicts of interest and raise public awareness about the influence of tech companies on EU policymaking.
- EU policymakers also have a responsibility to ensure that tech lobbying does not unduly influence policy decisions. This includes strengthening transparency requirements for lobbyists, implementing conflict of interest rules, and engaging in public consultations to gather a broad range of perspectives on policy issues.
The Broader Context of Tech Lobbying
The issue of tech lobbying in the EU doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s intertwined with global trends and the approaches of other major economies. Understanding this broader context is crucial for grasping the complexities and implications of tech lobbying in Europe.
Comparison with Other Major Economies
The EU’s approach to tech lobbying can be compared with that of other major economies, revealing both similarities and differences. The US, for instance, has a long-standing tradition of lobbying, with a robust legal framework regulating it. However, concerns about transparency and influence have also emerged in the US, leading to calls for reforms.
In contrast, China’s tech sector is largely controlled by the government, with lobbying playing a less prominent role. However, Chinese tech companies are increasingly active in lobbying efforts in other countries, including the EU.
Global Trends in Tech Lobbying
Global trends in tech lobbying are characterized by a growing influence of tech giants on policymaking worldwide. This is driven by factors such as the rapid growth of the tech sector, its increasing economic importance, and the complex challenges it poses to policymakers.
For instance, the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to increased lobbying efforts by tech companies to shape regulations in this area. Another notable trend is the increasing use of sophisticated lobbying tactics, including the deployment of in-house lobbyists, the use of third-party organizations, and the cultivation of relationships with policymakers.
Potential Future of Tech Lobbying in the EU
The future of tech lobbying in the EU is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including the ongoing evolution of the tech sector, the EU’s regulatory agenda, and the public’s perception of tech lobbying. The EU is likely to continue to face pressure from tech companies to shape regulations in their favor.
However, there is also a growing awareness of the potential risks associated with excessive tech lobbying, leading to calls for greater transparency and accountability. The EU may also consider adopting new regulations to address the challenges posed by tech lobbying, such as stricter disclosure requirements or limits on lobbying activities.