Startups ai data centre energy use big tech – Startups, AI, data centers, and big tech are all intertwined in a complex web of innovation and energy consumption. The rise of artificial intelligence has fueled a surge in demand for powerful computing resources, driving the construction of massive data centers that require vast amounts of energy.
This creates a critical dilemma: how can we harness the potential of AI while minimizing its environmental impact?
This blog post delves into the energy use challenges facing AI startups, exploring the unique demands of AI workloads, the environmental impact of data centers, and the role of big tech in shaping the future of AI and energy consumption.
We’ll also discuss potential solutions and innovations that could help us create a more sustainable future for AI.
The Rise of AI in Startups
The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies by startups is surging across various industries. AI’s ability to automate tasks, analyze data, and provide insights is transforming how startups operate, innovate, and scale. This trend is driven by the increasing availability of affordable AI tools, the growing volume of data, and the need for startups to compete in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
AI Applications in Startups
AI is being implemented in a wide range of applications by startups, driving innovation and efficiency across various industries. These applications can be categorized into:
- Customer Experience Enhancement:AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are transforming customer service, providing instant support and personalized interactions. These tools can handle routine inquiries, gather customer feedback, and even predict customer needs, leading to improved satisfaction and loyalty.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:Startups are leveraging AI to analyze vast amounts of data, identifying trends, patterns, and insights that can inform strategic decisions. This includes market research, competitor analysis, and customer behavior analysis, leading to more informed product development, marketing campaigns, and business strategies.
- Process Automation:AI-powered automation tools are streamlining repetitive tasks, freeing up time and resources for startups to focus on strategic initiatives. This includes automating administrative tasks, data entry, and even coding, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Product Development and Innovation:AI is playing a significant role in product development and innovation, enabling startups to create more personalized, intelligent, and efficient products. This includes AI-powered design tools, predictive maintenance systems, and personalized recommendation engines, leading to enhanced customer experiences and competitive advantages.
Examples of Startups Using AI
- Grammarly:This startup uses AI to provide real-time grammar and spelling suggestions, improving writing quality and productivity.
- X.ai:This startup uses AI to schedule meetings, automating the process and saving time for busy professionals.
- Clara Labs:This startup uses AI to manage personal assistants, handling scheduling, travel arrangements, and other administrative tasks.
- DeepMind:This startup, acquired by Google, is developing AI algorithms for various applications, including game playing, protein folding, and medical diagnosis.
Data Center Demands of AI Startups: Startups Ai Data Centre Energy Use Big Tech

The rapid rise of AI in startups has brought about a significant shift in data center demands. Unlike traditional workloads, AI models require immense computational power and storage capacity, leading to unique energy requirements and infrastructure challenges.
Energy Consumption of AI Workloads
Training and deploying AI models demands substantial computational power, leading to increased energy consumption. The process of training a large language model, for example, can consume millions of kilowatt-hours, comparable to the annual energy consumption of thousands of households.
The energy efficiency of AI workloads is crucial, particularly for startups with limited resources.
- Model Size and Complexity:Larger and more complex AI models require more computational resources, leading to higher energy consumption. For instance, the training of GPT-3, a large language model, is estimated to have consumed 1,287 megawatt-hours, enough to power 100,000 homes for a day.
- Data Volume:Training AI models on vast datasets significantly increases energy consumption. As AI models become more sophisticated, the amount of data required for training continues to grow.
- Training Time:The time required to train AI models can vary significantly depending on the model’s complexity and the size of the dataset. Longer training times contribute to increased energy consumption.
Scaling Data Centers for AI Startups
Scaling data centers to accommodate the demands of AI-powered startups presents unique challenges. The high computational requirements of AI workloads necessitate specialized hardware and infrastructure, which can be costly and difficult to manage.
Startups need to carefully consider their data center needs and choose solutions that are scalable, efficient, and cost-effective.
- Compute Power:AI workloads require high-performance computing (HPC) capabilities, often utilizing specialized GPUs and TPUs. Scaling data centers to support these demands can be expensive and complex.
- Storage Capacity:AI models often require massive amounts of data for training and inference. Data centers must have sufficient storage capacity to accommodate these needs, including both on-premises and cloud-based solutions.
- Cooling Infrastructure:The high energy consumption of AI workloads generates significant heat, requiring robust cooling systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Data centers need to invest in efficient cooling solutions to prevent equipment failures and ensure performance.
Infrastructure and Hardware Considerations
AI-driven businesses need to consider specific infrastructure and hardware components to optimize performance and efficiency. These include:
- GPUs and TPUs:Graphics processing units (GPUs) and tensor processing units (TPUs) are specialized hardware designed for accelerating AI workloads. They offer significant performance gains compared to traditional CPUs, but they also come with higher energy consumption.
- Networking:High-speed networking is essential for AI workloads, enabling rapid data transfer between different components within the data center. Startups need to invest in robust networking infrastructure to support the demands of AI applications.
- Software and Frameworks:AI applications rely on specialized software and frameworks, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Keras. These frameworks provide tools for building, training, and deploying AI models, and they can impact energy consumption and performance.
Energy Consumption and Sustainability in AI
The rapid rise of AI has brought about transformative advancements in various industries, but it has also raised concerns about its environmental impact, particularly the energy consumption of data centers that power AI operations. As AI startups continue to emerge and scale their operations, it is crucial to address the energy demands and explore sustainable solutions to mitigate the environmental footprint of this burgeoning technology.
Examine how good developers need good negotiation skills heres some tips can boost performance in your area.
Data Center Energy Consumption, Startups ai data centre energy use big tech
Data centers are the backbone of AI, housing the massive computing power required for training and running AI models. However, these centers consume significant amounts of energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The energy consumption of a data center depends on factors such as the size of the facility, the type of hardware used, and the workload it processes.
AI workloads, with their complex algorithms and large datasets, often require more computational resources than traditional applications, leading to increased energy demands.
Big Tech’s Role in AI and Data Centers
Big tech companies, including giants like Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook, play a pivotal role in shaping the AI landscape. Their vast resources, expertise, and data sets have fueled the development of powerful AI models and applications, transforming various industries.
However, this dominance comes with significant implications for the energy consumption of AI data centers, raising critical ethical considerations.
Impact on Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of AI data centers is a significant concern, and Big Tech companies are major contributors to this issue. The immense computational power required to train and run complex AI models demands substantial energy, leading to a substantial carbon footprint.
This impact is further amplified by the continuous growth of AI applications and the increasing size and complexity of data centers.
- Data Center Expansion:Big Tech companies are constantly expanding their data center infrastructure to accommodate the growing demands of AI, leading to increased energy consumption. For example, Microsoft has invested billions of dollars in building new data centers around the world, while Google has a vast network of data centers powering its AI services.
- Training AI Models:Training large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 requires enormous computational power and energy. A study by OpenAI estimated that training GPT-3 consumed the equivalent energy of 126 homes for a year.
- Powering AI Services:Running AI-powered services like search engines, facial recognition, and virtual assistants requires constant processing power, contributing to ongoing energy consumption. The energy used to power these services is often overlooked but contributes significantly to the overall energy footprint of AI.
Ethical Considerations
The energy consumption associated with AI development and use raises significant ethical concerns. While AI offers numerous benefits, its impact on the environment cannot be ignored.
- Sustainability:The growing energy demands of AI data centers must be addressed through sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources and optimizing energy efficiency. Failure to do so could exacerbate climate change and contribute to environmental degradation.
- Accessibility and Equity:The high energy consumption of AI can create a digital divide, making it inaccessible to those in regions with limited access to clean energy. This could perpetuate existing inequalities and limit the benefits of AI to certain populations.
- Transparency and Accountability:Big Tech companies must be transparent about their energy consumption and take responsibility for the environmental impact of their AI operations. This includes disclosing data on energy use, adopting sustainable practices, and collaborating with stakeholders to develop responsible AI guidelines.
Future Trends in AI and Data Center Energy
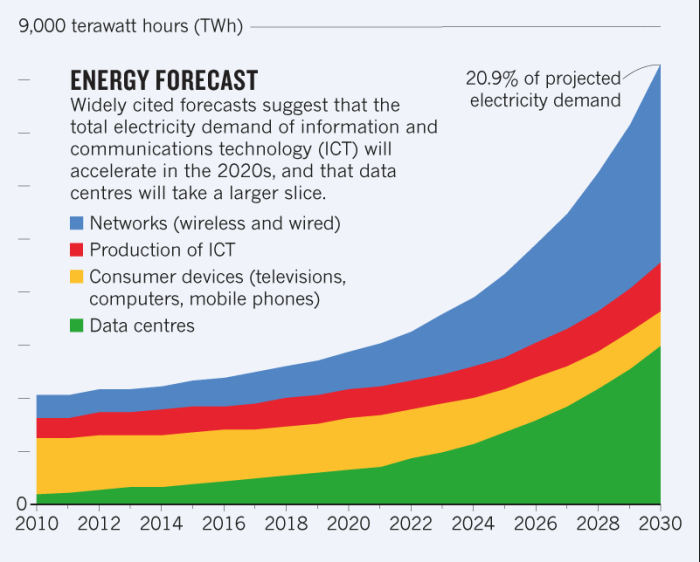
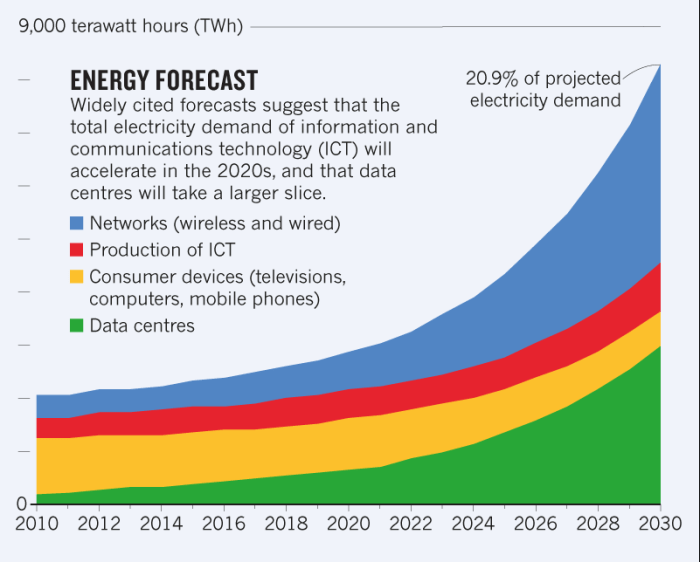
The insatiable appetite of AI for data processing power is driving a surge in data center energy demand. This demand is expected to grow exponentially in the coming years as AI applications become more sophisticated and widespread. This raises critical questions about the future of data center energy consumption and the need for sustainable solutions.
AI Adoption and Data Center Energy Demand
The rapid adoption of AI across various industries will significantly impact data center energy demand. As AI algorithms become more complex and data sets grow larger, the computational power required to train and run these models will increase proportionally.
This trend is already evident in the exponential growth of data center infrastructure globally.
- The global data center market is projected to reach $350 billion by 2026, fueled by the increasing adoption of AI and cloud computing. (Source: Statista)
- The energy consumption of data centers is expected to double by 2025, driven by the growth of AI, big data analytics, and cloud computing. (Source: International Energy Agency)
Innovations in Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
To address the growing energy demand of AI and data centers, innovative solutions are being developed to improve energy efficiency and leverage renewable energy sources. These solutions are critical to ensure the sustainability of AI and its associated infrastructure.
- Advanced Cooling Technologies:Data centers are exploring innovative cooling technologies like liquid immersion cooling and air-side economizers to reduce energy consumption. These technologies can significantly improve cooling efficiency and reduce the reliance on traditional air conditioning systems.
- Dynamic Power Management:Dynamic power management techniques are being implemented to optimize power consumption based on real-time workloads. This allows data centers to adjust power usage according to demand, reducing energy waste during periods of low activity.
- Renewable Energy Integration:Data centers are increasingly integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into their operations. This transition to renewable energy can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future for AI.
Technological Advancements and their Impact on AI Energy Consumption
The rapid pace of technological advancements is constantly influencing the energy consumption patterns of AI. The following table highlights some key technological advancements and their potential impact on AI energy consumption: