Space startup open comos climate change satellites – Space startups, like Open Cosmos, are leading the charge in combating climate change with innovative satellite technology. This new wave of companies is leveraging advancements in space exploration to develop cutting-edge solutions for monitoring our planet’s health. By deploying satellites equipped with sophisticated sensors, they are providing valuable data to scientists and policymakers, enabling them to understand and address the pressing issues of climate change.
The impact of these startups extends far beyond data collection. They are developing new ways to analyze and interpret satellite data, unlocking insights that can drive climate action. From tracking deforestation to monitoring sea levels, these startups are contributing to a more sustainable future by empowering us with the knowledge and tools necessary to make informed decisions.
The Rise of Space Startups
The space industry is undergoing a dramatic transformation, fueled by the emergence of a new breed of companies: space startups. These innovative ventures are challenging traditional aerospace giants and redefining the possibilities of space exploration and commercialization.
Key Drivers of Growth
The surge in space startups can be attributed to several key factors:
- Advancements in Technology:The development of smaller, more powerful, and affordable technologies, such as CubeSats and miniaturized sensors, has made it easier and cheaper to launch and operate spacecraft. This has opened up opportunities for startups to enter the market with innovative solutions.
- Reduced Launch Costs:The emergence of private launch providers, such as SpaceX and Blue Origin, has significantly reduced the cost of launching payloads into space. This has made it more financially feasible for startups to access space and pursue their ambitious projects.
- Increased Investor Interest:Investors are increasingly recognizing the potential of the space industry, drawn by the promise of high returns and the transformative potential of space-based technologies. This influx of capital has provided startups with the resources they need to grow and scale their operations.
Prominent Space Startups
The space startup landscape is diverse, with companies focusing on a wide range of applications:
- Planet Labs:This company operates a constellation of small satellites that provide high-resolution Earth imagery, used for applications such as agriculture monitoring, disaster response, and urban planning.
- Spire Global:Spire develops and operates nanosatellites for space-based weather forecasting, maritime tracking, and other applications.
- Rocket Lab:Rocket Lab provides launch services for small satellites, offering a more affordable and flexible alternative to traditional launch providers.
- Astra:Astra focuses on developing and launching small-lift rockets, targeting the growing market for small satellite deployments.
- Virgin Orbit:Virgin Orbit offers air-launched space launches, providing a more convenient and cost-effective method for deploying small satellites.
Open Cosmos
Open Cosmos is a leading space startup that has carved a niche for itself in the burgeoning NewSpace industry. It operates a unique business model that makes space technology accessible to a wider range of organizations, contributing significantly to the democratization of space.
Open Cosmos’s Business Model
Open Cosmos has adopted a “space-as-a-service” model, which allows businesses and organizations to access and leverage space technology without having to invest heavily in their own infrastructure. They offer a range of services that cater to diverse needs, making space technology more affordable and accessible.
Open Cosmos’s Services, Space startup open comos climate change satellites
Open Cosmos provides a comprehensive suite of services that encompass the entire satellite lifecycle, from development and launch to data analytics and operations.
- Satellite Development:Open Cosmos specializes in developing custom-built nanosatellites tailored to specific client requirements. These satellites are designed for various applications, including Earth observation, telecommunications, and scientific research.
- Launch Services:Open Cosmos offers launch services for its nanosatellites, leveraging partnerships with established launch providers to ensure reliable and cost-effective access to space.
- Data Analytics:Open Cosmos provides data analytics services to help clients extract meaningful insights from the data collected by their satellites. They offer a range of tools and techniques to process, analyze, and interpret satellite data, enabling clients to make informed decisions.
Open Cosmos’s Projects and Impact
Open Cosmos has been involved in numerous successful projects that have had a positive impact on various industries.
- Earth Observation:Open Cosmos has developed satellites for Earth observation applications, providing valuable data for environmental monitoring, disaster management, and agriculture. For instance, their satellites have been used to monitor deforestation rates in the Amazon rainforest, providing crucial data for conservation efforts.
- Telecommunications:Open Cosmos has developed nanosatellites for telecommunications applications, providing connectivity to remote areas and underserved populations. Their satellites have been used to establish communication networks in disaster zones, enabling relief efforts and communication channels.
- Scientific Research:Open Cosmos has developed satellites for scientific research, providing data for various studies, including atmospheric research, climate monitoring, and astrophysics. Their satellites have been used to collect data on atmospheric composition, enabling researchers to better understand climate change and its impact.
Climate Change and Satellites
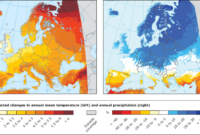
Satellites play a crucial role in monitoring and understanding climate change. They provide a unique perspective from space, allowing us to observe Earth’s systems on a global scale and over long periods. This data is essential for tracking changes in our planet’s atmosphere, oceans, and land, and for understanding the causes and impacts of climate change.
Atmospheric Analysis
Satellites are equipped with instruments that measure various atmospheric parameters, including:
- Greenhouse gas concentrations:Satellites can detect and measure the concentration of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere. This data helps scientists understand the sources and sinks of these gases and track their changes over time.
- Temperature profiles:Satellites measure temperature at different altitudes in the atmosphere, providing insights into changes in the Earth’s energy balance and the role of greenhouse gases in trapping heat.
- Cloud cover and precipitation:Satellites monitor cloud formation, movement, and precipitation patterns, providing crucial data for understanding climate models and predicting weather events.
These measurements help scientists understand the complex interactions within the atmosphere and how they are affected by human activities and natural processes.
Sea Level Monitoring
Satellites equipped with radar altimeters measure the distance between the satellite and the sea surface. This data allows scientists to track changes in sea level over time.
- Global sea level rise:Satellite data has revealed a consistent trend of rising sea levels, attributed to the expansion of ocean water due to warming and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets.
- Regional variations:Satellites also detect regional variations in sea level, which can be influenced by factors like ocean currents, gravity, and land subsidence.
Understanding these changes is critical for coastal communities facing the risks of flooding and erosion.
Deforestation Tracking
Satellites can monitor land cover changes, including deforestation, by capturing images of the Earth’s surface.
- Forest loss mapping:Satellites provide high-resolution images that allow scientists to map deforestation patterns, identify areas of forest loss, and track the rate of deforestation.
- Deforestation drivers:Satellite data can help identify the drivers of deforestation, such as agricultural expansion, logging, and wildfires, providing insights for developing conservation strategies.
Monitoring deforestation is essential for mitigating climate change, as forests play a vital role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Expand your understanding about career in ai make sure you have 8 skills with the sources we offer.
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Satellite data is crucial for developing effective climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- Greenhouse gas emissions monitoring:Satellite data helps track emissions from various sources, enabling policymakers to develop strategies for reducing emissions and transitioning to cleaner energy sources.
- Climate modeling:Satellite data is used to improve climate models, providing more accurate predictions of future climate change and its impacts.
- Adaptation planning:Satellite data helps assess the vulnerability of communities to climate change impacts, such as sea level rise and extreme weather events, enabling them to develop effective adaptation strategies.
By providing a comprehensive understanding of climate change, satellite data empowers decision-makers to take informed actions to address this global challenge.
Satellite Data for Climate Action
Satellites are powerful tools for monitoring and understanding our planet, providing crucial data to address the urgent challenge of climate change. They offer a global perspective, capturing data across vast areas, and providing insights into various aspects of the Earth’s climate system.
Types of Satellite Data and Applications
Satellite data provides a comprehensive view of Earth’s systems, enabling us to monitor and understand climate change impacts. Different types of data serve specific purposes in addressing climate change. Here’s a breakdown of key data types, their sources, resolutions, and applications:
| Data Type | Source | Resolution | Key Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Imagery | Landsat, Sentinel-2 | 10-30 meters | Monitoring deforestation, land cover changes, agricultural practices, and urban expansion. Assessing the impact of climate change on vegetation and ecosystems. |
| Thermal Infrared Imagery | MODIS, VIIRS | 1 km | Measuring surface temperatures, identifying heat islands, monitoring wildfires, and assessing the impact of climate change on sea ice and glaciers. |
| Radar Imagery | Sentinel-1, RADARSAT-2 | 10-30 meters | Monitoring sea level rise, mapping ice sheets and glaciers, detecting land subsidence, and assessing the impact of climate change on coastal areas. |
| Atmospheric Data | AIRS, IASI | 1 km | Monitoring greenhouse gas concentrations, measuring atmospheric temperature and humidity, and tracking the movement of pollutants. |
| Oceanographic Data | Jason-3, Sentinel-3 | 1 km | Measuring sea surface temperature, monitoring ocean currents, and assessing the impact of climate change on marine ecosystems. |
The Future of Space Startups and Climate Change: Space Startup Open Comos Climate Change Satellites

The burgeoning space startup ecosystem is poised to play a pivotal role in addressing the urgent challenge of climate change. With innovative technologies and a fresh perspective, these companies are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in Earth observation, atmospheric monitoring, and climate modeling.
Challenges and Opportunities for Space Startups
Space startups face unique challenges and opportunities in the climate change domain. These companies must navigate the complex regulatory landscape, secure funding for high-risk ventures, and develop robust partnerships with established players in the climate sector.
- Funding Challenges:Space startups often require significant capital investments to develop and launch their satellites. Securing funding can be challenging, particularly for early-stage companies. This is especially true in the climate change sector, where the return on investment may be long-term and uncertain.
- Regulatory Complexity:The space industry is subject to a complex web of regulations, both national and international. Space startups must navigate these regulations to ensure their operations comply with legal requirements and environmental standards.
- Data Access and Integration:Space startups are generating massive amounts of data, which needs to be processed, analyzed, and integrated with existing climate datasets. This presents significant challenges in terms of data management, storage, and processing capabilities.
- Collaboration and Partnerships:To achieve meaningful impact, space startups need to collaborate with governments, research institutions, and other stakeholders in the climate sector. This requires building strong partnerships and fostering open data sharing.
Potential Future Trends and Innovations
Space startups are at the forefront of developing innovative technologies that can contribute to climate action.
- Advanced Earth Observation:High-resolution satellites equipped with advanced sensors can provide detailed insights into the Earth’s changing environment. These insights can be used to monitor deforestation, track greenhouse gas emissions, and assess the impact of climate change on ecosystems.
- Climate Modeling and Prediction:Space startups are developing sophisticated climate models that incorporate satellite data to improve our understanding of climate patterns and predict future climate scenarios. These models can inform policy decisions and help us prepare for the impacts of climate change.
- Climate Mitigation Technologies:Space startups are exploring technologies for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or mitigating the effects of climate change. These technologies include space-based solar power, carbon capture and storage, and geoengineering solutions.