Shell investment in renewable biogas is wonderfully worrisome – Shell’s investment in renewable biogas is wonderfully worrisome. On the one hand, it’s a welcome sign that a major oil and gas company is embracing cleaner energy sources. The potential for biogas to replace fossil fuels and reduce greenhouse gas emissions is undeniable.
But on the other hand, Shell’s involvement raises concerns about greenwashing and the potential for unintended environmental consequences.
This investment presents a complex dilemma. Is Shell genuinely committed to a sustainable future, or is this just a calculated move to maintain its market share and appease growing public pressure for climate action? The answer is far from simple, and exploring the implications of this investment is crucial for understanding the future of renewable energy.
Shell’s Renewable Biogas Investment
Shell’s recent investment in renewable biogas is a significant development in the energy sector. It signifies a major shift towards a more sustainable future, with the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and provide a cleaner energy source.
Benefits of Shell’s Renewable Biogas Investment
The investment in renewable biogas presents numerous benefits for both Shell and the environment.
- Diversification of Energy Portfolio:Shell’s investment in renewable biogas diversifies its energy portfolio, reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and enhancing its sustainability profile.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint:Biogas production from organic waste can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. Shell’s investment contributes to a cleaner energy system.
- New Revenue Streams:The growing demand for renewable energy sources creates new revenue streams for Shell, potentially leading to long-term financial stability.
- Enhanced Brand Image:Investing in renewable biogas enhances Shell’s image as a responsible and environmentally conscious company, attracting environmentally conscious consumers.
Potential Risks and Challenges
While Shell’s renewable biogas investment offers significant benefits, it also presents potential risks and challenges.
- High Initial Investment Costs:Developing and deploying biogas infrastructure requires substantial upfront investments, which may pose a financial risk for Shell.
- Limited Availability of Feedstock:The availability of suitable organic waste for biogas production can be a challenge, particularly in regions with limited waste management infrastructure.
- Technological Advancements:The biogas industry is rapidly evolving, with advancements in technology constantly emerging. Shell needs to adapt and invest in new technologies to remain competitive.
- Regulatory Landscape:Government policies and regulations surrounding renewable energy can be complex and subject to change, creating uncertainty for investors like Shell.
Comparison with Other Renewable Energy Investments
Shell’s renewable biogas investment aligns with the broader trend of major corporations investing in renewable energy sources. For example, companies like BP, Total, and ExxonMobil have invested in solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies. However, Shell’s focus on biogas distinguishes it from other companies, leveraging a unique technology with potential for significant environmental impact.
Biogas as a Sustainable Energy Source: Shell Investment In Renewable Biogas Is Wonderfully Worrisome
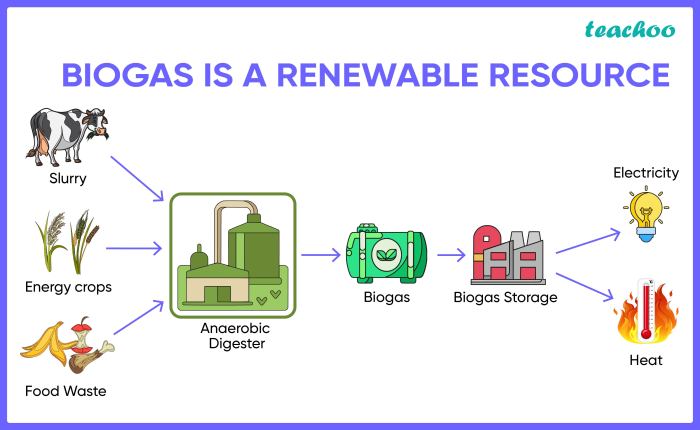
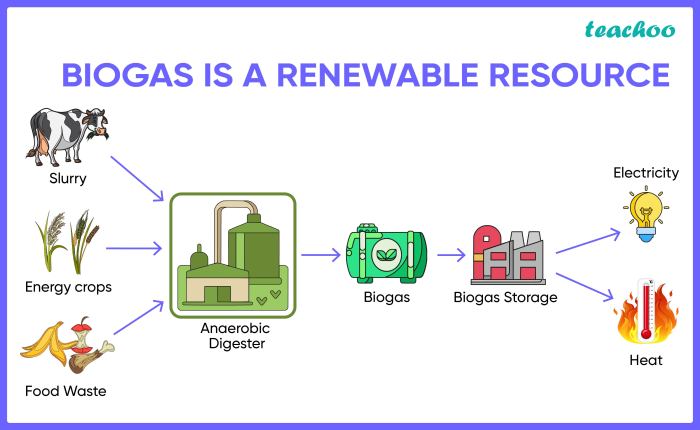
Biogas, a renewable energy source derived from the breakdown of organic matter, is gaining increasing attention as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. It offers a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote energy independence.
Biogas Production
Biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion, a natural process where microorganisms break down organic matter in the absence of oxygen. This process occurs in specialized digesters, where organic waste materials, such as food scraps, agricultural residues, and animal manure, are mixed with water and kept in controlled conditions.
During anaerobic digestion, the microorganisms convert the organic matter into biogas, primarily composed of methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Environmental Benefits of Biogas
Biogas offers significant environmental benefits compared to traditional fossil fuels:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions:Biogas production and use can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, primarily methane, which is a potent greenhouse gas. This is because the methane released during the breakdown of organic matter is captured and used as fuel, preventing it from escaping into the atmosphere.
- Renewable and Sustainable:Biogas is a renewable energy source, meaning it can be replenished naturally. The organic waste used for biogas production is readily available and can be continuously replenished, making it a sustainable energy solution.
- Waste Management:Biogas production offers a solution for managing organic waste, diverting it from landfills and reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal. By converting organic waste into biogas, we can minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills, where it decomposes and releases harmful greenhouse gases.
Economic Feasibility of Biogas Production
Biogas production can be economically viable, particularly in regions with abundant organic waste resources. The economic feasibility depends on factors such as:
- Cost of Organic Waste:The availability and cost of organic waste are crucial factors in determining the economic feasibility of biogas production. Regions with readily available and affordable organic waste resources have a greater potential for economic success.
- Digester Size and Technology:The size and technology of the digester play a significant role in the cost of biogas production. Smaller-scale digesters may be more suitable for individual farms or communities, while larger-scale digesters are more suitable for industrial applications.
- Government Incentives:Government incentives, such as tax breaks and subsidies, can make biogas production more economically attractive. These incentives can encourage investment in biogas technology and promote the development of the biogas industry.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biogas Production
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Renewable and sustainable energy source | Requires significant initial investment in digester technology |
| Reduces greenhouse gas emissions | Can be affected by variations in organic waste quality and quantity |
| Improves waste management | May require specialized technical expertise for operation and maintenance |
| Potential for local economic development | Limited scalability in some regions due to limited organic waste availability |
Shell’s Role in the Energy Transition
Shell, a global energy giant, is actively engaged in transitioning towards a low-carbon future. This transition is driven by the urgent need to address climate change and meet the growing demand for cleaner energy sources. Shell’s strategy for achieving this involves a multi-pronged approach, encompassing investments in renewable energy, carbon capture and storage, and energy efficiency initiatives.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of matter launches world smart home day iot connected devices that is effective.
Renewable Biogas in Shell’s Energy Transition Strategy, Shell investment in renewable biogas is wonderfully worrisome
Renewable biogas plays a significant role in Shell’s energy transition strategy. It is a clean and sustainable source of energy that can be used to generate electricity, heat, and transportation fuels. Shell’s investments in renewable biogas are part of its broader commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting a circular economy.
By leveraging its expertise in gas infrastructure and technology, Shell aims to accelerate the development and deployment of renewable biogas solutions.
Shell’s Commitment to Renewable Energy Compared to Other Oil and Gas Companies
Shell has made significant strides in its commitment to renewable energy compared to other major oil and gas companies. The company has set ambitious targets for reducing its carbon footprint and increasing its renewable energy portfolio. For instance, Shell aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, a goal that is aligned with the Paris Agreement.
However, Shell’s commitment to renewable energy is still being scrutinized by environmental groups and investors who are calling for a faster and more decisive shift away from fossil fuels.
Timeline of Shell’s Investments in Renewable Energy
Shell’s investments in renewable energy have increased significantly over the past decade. Here’s a timeline of key investments:
- 2013:Shell invests in the construction of a large-scale solar farm in California.
- 2016:Shell acquires First Utility, a UK-based renewable energy supplier.
- 2017:Shell invests in the development of a wind farm in the Netherlands.
- 2019:Shell announces its ambition to become a net-zero emissions company by 2050.
- 2020:Shell invests in a bioenergy plant in Brazil.
- 2021:Shell acquires a stake in a solar energy company in India.
The Worrisome Aspects of Shell’s Investment
While Shell’s investment in renewable biogas presents a positive step towards a greener future, it’s essential to acknowledge the potential negative aspects that accompany this transition. While the company’s efforts to diversify its portfolio and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels are commendable, concerns remain regarding the environmental, ethical, and social implications of large-scale biogas production.
Potential Negative Environmental Impacts
The production of biogas, while renewable, can have significant environmental consequences if not carefully managed. The large-scale cultivation of crops for anaerobic digestion, a common method of biogas production, can lead to land-use changes, deforestation, and biodiversity loss. This can disrupt ecosystems and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- Land Use Changes:Large-scale biogas production requires significant land for cultivating energy crops. This can lead to deforestation, habitat fragmentation, and the displacement of local communities. The conversion of natural ecosystems, such as forests, into agricultural land can also release significant amounts of carbon dioxide, exacerbating climate change.
- Water Consumption:Biogas production can be water-intensive, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions. The cultivation of energy crops requires substantial water resources, potentially leading to water scarcity and conflicts with other water users, such as agriculture and human consumption.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions:While biogas itself is a renewable energy source, the production process can still contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. For example, the transportation and processing of feedstock, as well as the anaerobic digestion process itself, can release methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Shell’s Involvement
Shell’s long history as a major oil and gas company raises ethical concerns regarding its involvement in the renewable energy sector. Some argue that Shell’s entry into the renewable energy market is driven by a desire to maintain its market dominance and control over energy resources, rather than a genuine commitment to sustainability.
- Greenwashing:There is a risk that Shell’s investment in biogas could be used as a tool for greenwashing, creating a perception of environmental responsibility while continuing to invest heavily in fossil fuels. This could mislead consumers and policymakers, hindering genuine efforts to transition to a truly sustainable energy system.
- Lack of Transparency:There are concerns about the lack of transparency in Shell’s renewable energy investments. Critics argue that the company has not been forthcoming about its plans for biogas production, including the potential environmental and social impacts. This lack of transparency raises questions about the company’s commitment to ethical and responsible practices.
- Conflicts of Interest:Shell’s continued involvement in the fossil fuel industry creates potential conflicts of interest in its renewable energy ventures. The company’s financial interests in oil and gas production could incentivize it to prioritize these activities over renewable energy development.
Potential for Greenwashing
Shell’s investment in biogas could contribute to greenwashing if the company does not simultaneously reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and invest in truly sustainable energy solutions. Critics argue that Shell’s investment in biogas is a strategic move to maintain its market share and control over energy resources, rather than a genuine commitment to sustainability.
- Misleading Marketing:Shell could use its biogas investments to promote a misleading image of environmental responsibility, while continuing to invest heavily in fossil fuels. This could mislead consumers and policymakers, hindering genuine efforts to transition to a truly sustainable energy system.
- Focus on Biogas as a “Silver Bullet”:There is a risk that Shell could focus solely on biogas as a solution to its environmental challenges, neglecting other renewable energy sources and sustainable practices. This could limit the potential for a truly diversified and sustainable energy system.
- Lack of Accountability:Shell’s biogas investments could be used to deflect attention from the company’s ongoing fossil fuel activities, making it less accountable for its environmental and social impacts.
The Future of Renewable Biogas
The renewable biogas market is poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for sustainable energy sources and supportive government policies. The technology offers a promising solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance energy security, and contribute to a circular economy.
Market Growth and Potential
The global renewable biogas market is expected to witness substantial growth in the coming years. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the market is projected to reach USD 62.4 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 12.8% during the forecast period.
This growth is attributed to factors such as increasing government support for renewable energy, rising concerns about climate change, and growing demand for sustainable energy solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities for Renewable Biogas Technology
The development and deployment of renewable biogas technology face several challenges and opportunities:
Challenges
- High Initial Investment Costs:Establishing biogas plants requires significant upfront capital investments, making it challenging for small-scale producers to enter the market.
- Limited Feedstock Availability:Access to consistent and reliable feedstock, such as agricultural waste and manure, is crucial for biogas production. However, feedstock availability can be a challenge, especially in urban areas.
- Technological Advancements:Ongoing research and development are essential to improve biogas production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the technology’s environmental performance.
Opportunities
- Government Incentives and Policies:Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote the development and adoption of renewable biogas, including subsidies, tax breaks, and feed-in tariffs.
- Integration with Other Renewable Energy Sources:Biogas can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to create a more resilient and sustainable energy system.
- Emerging Technologies:Advancements in biogas technology, such as anaerobic digestion and gas upgrading, are enabling the production of high-quality biogas that can be used for various applications, including transportation and electricity generation.
Role of Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the future of renewable biogas. Supportive policies can accelerate market growth by providing incentives for biogas production, establishing clear regulations for feedstock sourcing and waste management, and promoting research and development in the sector.