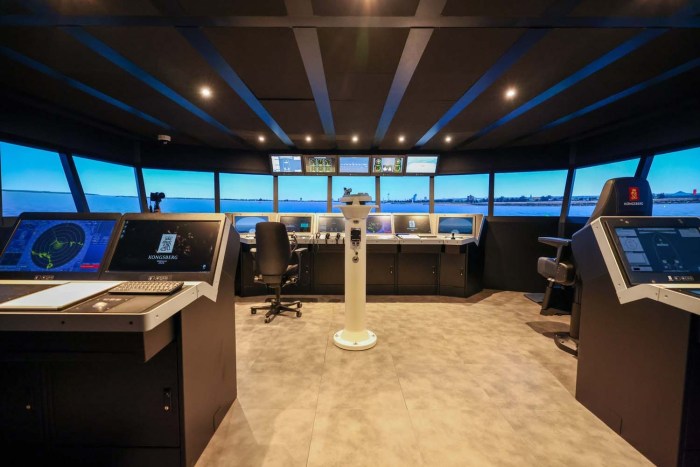
Royal Navy VR tech training warships sets the stage for a fascinating exploration into the future of naval training. Imagine stepping into a virtual world, taking the helm of a destroyer, and navigating complex scenarios, all without leaving dry land.
This is the reality of VR training, and the Royal Navy is leading the charge.
VR technology has revolutionized naval training, offering unparalleled realism and immersion. Sailors can experience the complexities of warship operations, from maneuvering in tight spaces to coordinating with other vessels, all within a safe and controlled environment. This technology is transforming the way the Royal Navy prepares its crews for real-world challenges, enhancing their skills, decision-making abilities, and overall operational readiness.
Introduction to VR Technology in Naval Training
Virtual Reality (VR) technology has revolutionized the way the Royal Navy trains its personnel, offering immersive and interactive experiences that were previously impossible with traditional methods. This technology has evolved significantly over the years, becoming increasingly sophisticated and realistic.
Evolution of VR Technology in Naval Training
The use of VR in naval training has progressed from simple simulations to highly complex and detailed environments. Early applications focused on basic tasks such as navigation and damage control, using rudimentary VR systems. However, with advancements in hardware and software, VR technology has become more powerful and realistic, allowing for more complex and sophisticated training scenarios.
Examples of VR Utilization in the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy has implemented VR technology in various training programs, including:
- Shipboard Navigation and Maneuvering:VR simulators allow trainees to practice navigating complex maritime environments, encountering various weather conditions and other vessels. This experience helps them develop critical decision-making skills and improve their situational awareness.
- Damage Control and Firefighting:VR simulations provide a safe and controlled environment for trainees to practice damage control procedures and firefighting techniques. They can experience realistic scenarios, such as flooding or fires, and learn to react effectively in stressful situations.
- Weapon Systems Training:VR simulations allow trainees to operate various weapon systems, including missiles and guns, without the need for live ammunition. This provides a safe and cost-effective way to train on complex weapon systems and develop proficiency in their operation.
- Maritime Security Operations:VR simulations can be used to train personnel on maritime security operations, such as boarding procedures and counter-piracy tactics. These simulations provide a realistic environment for trainees to practice these skills and develop their understanding of maritime security threats.
Benefits of VR Training
VR training offers several advantages over traditional methods, including:
- Immersive and Interactive Experience:VR provides a highly immersive and interactive training environment, allowing trainees to experience real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled setting. This enhances their learning experience and helps them retain information more effectively.
- Cost-Effectiveness:VR training can be significantly more cost-effective than traditional methods, which often involve expensive equipment, real-world scenarios, and travel costs. VR simulations can be reused multiple times, reducing the overall cost of training.
- Safety and Risk Mitigation:VR training allows trainees to practice dangerous procedures and scenarios in a safe environment, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. This is particularly important for training in hazardous environments such as shipboard operations.
- Flexibility and Accessibility:VR training can be conducted anytime, anywhere, making it more flexible and accessible for trainees. This allows them to learn at their own pace and schedule, improving their overall training efficiency.
- Improved Training Outcomes:Studies have shown that VR training can lead to improved training outcomes, including increased knowledge retention, enhanced skills development, and better decision-making abilities.
VR Training for Warship Operations
Virtual reality (VR) training has become increasingly popular in the Royal Navy, offering a safe and cost-effective way to simulate real-world scenarios and prepare sailors for the demands of operating warships. This technology allows for immersive and realistic training experiences that go beyond traditional classroom settings.
VR Training for Different Warship Types
VR training simulations are tailored to the specific operations and challenges faced by different types of warships. For example, VR training for destroyers might focus on anti-submarine warfare (ASW) tactics, while training for frigates might emphasize surface warfare and air defense.
- Destroyers: VR simulations for destroyers often involve scenarios where crews must identify and track enemy submarines, deploy sonar and torpedoes, and coordinate with other ships and aircraft to conduct ASW operations. These simulations can also include realistic depictions of underwater environments and the challenges of navigating in close proximity to enemy vessels.
- Frigates: VR training for frigates might focus on scenarios where crews must engage enemy surface vessels or aircraft, coordinate with other ships and aircraft to conduct air defense operations, and respond to maritime interdiction missions. These simulations can also include realistic depictions of maritime environments and the challenges of operating in close proximity to enemy vessels.
Scenarios and Challenges Simulated in VR Environments
VR training simulations for warships often involve a wide range of scenarios, including:
- Combat Operations: These simulations allow crews to practice responding to various threats, such as enemy ships, submarines, aircraft, and missiles. They can also involve scenarios where crews must engage in close-quarters combat, fire weapons systems, and maneuver their ships in complex battlefields.
- Navigation and Maneuvering: VR training simulations allow crews to practice navigating in complex maritime environments, including narrow channels, congested ports, and adverse weather conditions. They can also involve scenarios where crews must respond to emergencies, such as engine failures, fires, and flooding.
- Damage Control: VR training simulations allow crews to practice responding to various damage control scenarios, such as fires, flooding, and explosions. They can also involve scenarios where crews must isolate damaged compartments, repair systems, and evacuate personnel.
- Communication and Coordination: VR training simulations allow crews to practice communicating with each other, with other ships and aircraft, and with shore-based command centers. They can also involve scenarios where crews must coordinate their actions to achieve common goals, such as conducting search and rescue operations, responding to humanitarian crises, or enforcing maritime law.
Enhancing Crew Coordination and Decision-Making
VR training has been shown to significantly enhance crew coordination and decision-making. By immersing sailors in realistic scenarios, VR training allows them to experience the pressures and complexities of operating a warship in a safe and controlled environment.
- Improved Communication and Teamwork: VR training simulations encourage crews to communicate effectively and work together to solve problems. This is particularly important in high-pressure situations where quick and accurate decision-making is critical.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: VR training simulations allow crews to develop a better understanding of their surroundings and the actions of other vessels and aircraft. This can help crews to make more informed decisions and react more effectively to threats.
- Increased Confidence and Proficiency: VR training simulations allow crews to practice their skills in a safe and controlled environment, which can help to build their confidence and proficiency. This can lead to better performance in real-world scenarios.
Key VR Technologies Used by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy leverages a diverse array of VR technologies to enhance its training programs, simulating real-world scenarios and fostering crucial skills development. These technologies create immersive and interactive environments that provide a safe and cost-effective platform for training sailors in various aspects of warship operations.
VR Hardware and Software
The Royal Navy employs a range of VR hardware and software systems, each tailored to specific training objectives. The primary components of these systems include:
- VR Headsets: These devices provide immersive visuals, allowing trainees to experience the simulated environment as if they were physically present. The Royal Navy utilizes headsets from various manufacturers, such as Oculus, HTC Vive, and Varjo, each offering different levels of resolution, field of view, and tracking accuracy.
- Motion Tracking Systems: These systems capture the movement of trainees within the VR environment, translating their physical actions into the virtual world. Popular motion tracking technologies include optical tracking systems (like the Vive Trackers) and inertial measurement units (IMUs) integrated into VR headsets.
- Haptic Feedback Devices: These devices provide tactile feedback, enhancing the realism of the training experience by simulating physical sensations. Haptic feedback gloves allow trainees to feel the weight and texture of virtual objects, while haptic feedback suits can simulate the impact of collisions or the force of movement.
Browse the multiple elements of artificial leaf cars sun fuel to gain a more broad understanding.
- VR Software Platforms: The Royal Navy utilizes specialized VR software platforms to create and manage training scenarios. These platforms enable instructors to design realistic simulations, track trainee progress, and provide feedback. Examples of such platforms include Unity, Unreal Engine, and proprietary software developed specifically for naval training.
Comparison of VR Systems
The Royal Navy evaluates VR systems based on factors such as fidelity, immersion, cost, and ease of use.
- Fidelity: The accuracy and realism of the simulated environment are critical for effective training. Higher-fidelity systems, often using advanced graphics engines and physics simulations, provide more realistic experiences.
- Immersion: The sense of presence and engagement within the VR environment is crucial for effective learning. Factors such as field of view, resolution, and haptic feedback contribute to the overall immersion of the training experience.
- Cost: The cost of VR systems can vary significantly, depending on the hardware and software components used. The Royal Navy balances cost considerations with the need for effective and realistic training.
- Ease of Use: The user-friendliness of VR systems is essential for both trainees and instructors. Simple interfaces and intuitive controls facilitate a seamless training experience.
Role of VR Technologies in Training
VR technologies play a crucial role in enhancing the effectiveness and realism of naval training by providing a safe and controlled environment for practicing critical skills:
- Motion Tracking: Motion tracking allows trainees to interact with the virtual environment in a natural and intuitive way, simulating real-world movements. This is essential for training tasks such as navigation, weapon handling, and damage control.
- Haptic Feedback: Haptic feedback provides a sense of physical presence and realism, enhancing the learning experience by simulating the weight, texture, and forces involved in various tasks.
- Immersive Visuals: High-fidelity visuals create an immersive environment that allows trainees to experience realistic scenarios and develop situational awareness.
Impact of VR Training on Naval Readiness
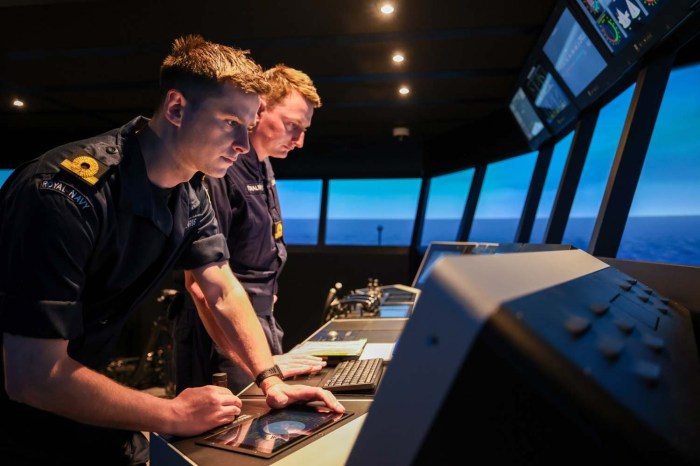

VR training has revolutionized naval training, significantly improving crew proficiency and operational readiness. It provides a safe, cost-effective, and highly realistic environment for sailors to learn and practice critical skills, enhancing their preparedness for real-world scenarios.
Improved Crew Proficiency
VR training offers a unique opportunity to enhance crew proficiency by providing immersive, interactive, and repetitive training experiences. Sailors can practice complex procedures, navigate challenging environments, and react to unexpected situations in a safe and controlled virtual environment. This repeated exposure to various scenarios helps them develop muscle memory and automaticity, leading to faster and more accurate responses during real-world operations.
Enhanced Operational Readiness, Royal navy vr tech training warships
VR training significantly contributes to enhanced operational readiness by allowing sailors to practice critical skills and procedures in a realistic and dynamic environment. They can experience various scenarios, from routine tasks to complex emergencies, without the risks and costs associated with traditional training methods.
This hands-on experience in a virtual setting allows them to develop situational awareness, decision-making skills, and teamwork, preparing them for real-world challenges.
Cost-Effectiveness of VR Training
VR training offers significant cost savings compared to traditional training methods. It eliminates the need for expensive real-world assets, such as warships and aircraft, for training purposes. The virtual environment allows for cost-effective replication of various scenarios and equipment, reducing the overall training expenses.
Moreover, VR training can be conducted on-demand, eliminating the need for dedicated training schedules and reducing travel costs.
“The Royal Navy is committed to exploring and implementing innovative technologies to enhance training and operational readiness. VR training has emerged as a game-changer, providing a safe, cost-effective, and highly realistic environment for our sailors to develop essential skills and prepare for real-world scenarios.”
Admiral [Name], Royal Navy
Case Studies Demonstrating the Effectiveness of VR Training
Several case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of VR training in enhancing naval readiness. For instance, the Royal Navy’s use of VR training for submarine operations has shown significant improvements in crew proficiency and operational readiness. Sailors trained in a virtual environment exhibited faster reaction times and better decision-making skills during simulated emergencies.Another case study involves the use of VR training for aircraft carrier operations.
The training program allowed sailors to practice complex procedures, such as landing aircraft on the carrier deck, in a safe and controlled environment. The results indicated a significant reduction in errors and improved crew coordination during simulated operations.
Cost-Effectiveness of VR Training Compared to Traditional Methods
VR training offers significant cost savings compared to traditional training methods. A study by the [Name of Institution] found that VR training for naval operations could reduce training costs by up to 50%. This cost-effectiveness stems from the ability to replicate complex scenarios and equipment in a virtual environment, eliminating the need for expensive real-world assets.
“VR training is a cost-effective and efficient solution for naval training. It allows us to provide our sailors with the necessary skills and experience in a safe and controlled environment, while significantly reducing training costs.”
[Name], Director of Training, Royal Navy
Future of VR in Naval Training: Royal Navy Vr Tech Training Warships
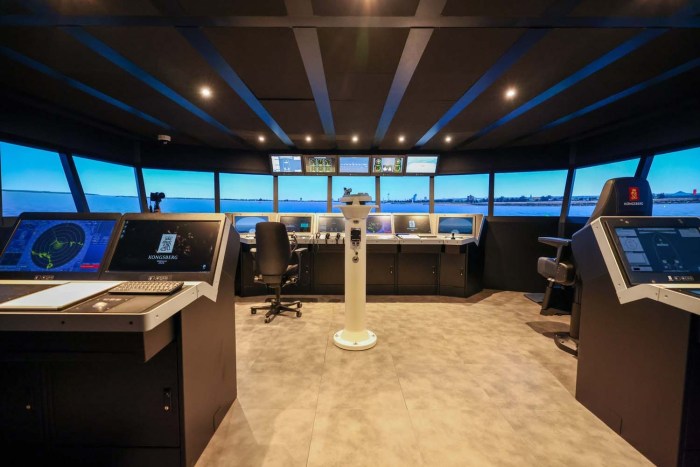

The Royal Navy’s adoption of VR training marks a significant step toward a more efficient and effective training paradigm. As VR technology continues to evolve, the future of naval training promises even more immersive, realistic, and adaptable experiences. This section delves into the emerging VR technologies and their potential applications in naval training, explores the challenges and opportunities in expanding VR training programs, and Artikels a vision for the future of VR-enabled naval training.
Emerging VR Technologies and Their Potential Applications
The rapid advancements in VR technology are opening up new possibilities for naval training. Here are some emerging technologies and their potential applications:
- Haptic Feedback: This technology provides realistic tactile sensations, allowing trainees to feel the force of a weapon recoil or the weight of a steering wheel. This enhanced realism improves motor skills development and muscle memory.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can be integrated into VR simulations to create more dynamic and challenging training scenarios. AI-powered adversaries can adapt to trainee actions, providing a more realistic and unpredictable learning environment.
- Mixed Reality (MR): MR blends the real and virtual worlds, allowing trainees to interact with virtual objects in a real-world environment. This technology can be used to simulate complex tasks, such as repairing equipment or navigating a ship in a real-world setting.
- Biometric Monitoring: Integrating biometric sensors into VR headsets can track physiological responses like heart rate and perspiration, providing insights into trainee stress levels and cognitive load. This data can be used to optimize training scenarios and identify areas where trainees need additional support.
Challenges and Opportunities in Expanding VR Training Programs
While the potential of VR in naval training is immense, there are challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful implementation:
- Cost and Accessibility: Implementing VR training programs requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and training facilities. Making VR training accessible to all personnel, regardless of their location or rank, is crucial.
- Data Security and Privacy: VR training involves collecting and storing sensitive data about trainees, including their performance and physiological responses. Robust data security measures and clear privacy policies are essential to protect this information.
- Integration with Existing Training Systems: VR training programs must seamlessly integrate with existing training systems and curricula to avoid disruption and ensure that trainees receive a comprehensive and cohesive learning experience.
Vision for the Future of VR-Enabled Naval Training
The future of VR-enabled naval training envisions a fully immersive and personalized learning experience that equips sailors with the skills and knowledge necessary to operate effectively in a dynamic and complex maritime environment. Here are some key elements of this vision:
- Personalized Training Pathways: VR training can be tailored to individual learning styles and skill levels, providing personalized training pathways that optimize learning outcomes.
- Collaborative Training Environments: VR can facilitate collaborative training scenarios, allowing trainees to work together in virtual teams to solve complex problems and develop teamwork skills.
- Real-World Applications: VR training can be used to simulate real-world scenarios, including combat operations, shipboard emergencies, and maritime law enforcement. This hands-on experience prepares sailors for real-world challenges.
- Continuous Learning and Assessment: VR training can be integrated with continuous learning and assessment systems, providing feedback and insights into trainee performance throughout their careers.