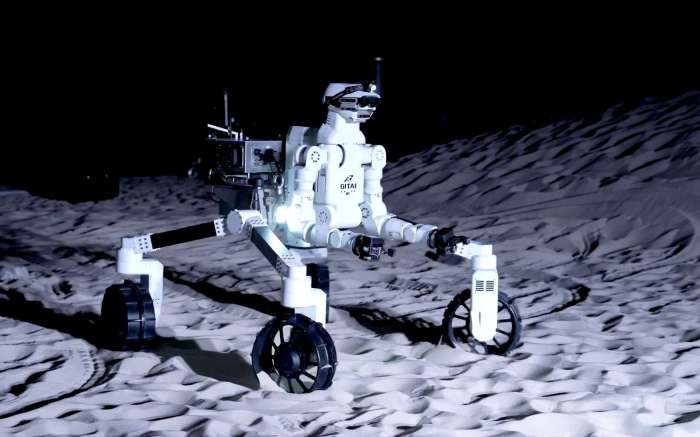
Robot squad could be next big thing lunar exploration – Robot Squad: The Future of Lunar Exploration? This intriguing question is sparking a wave of excitement within the scientific community and beyond. As we push the boundaries of space exploration, the idea of deploying a team of robots to the Moon is becoming increasingly feasible and appealing.
The potential benefits are vast, ranging from groundbreaking scientific discoveries to the establishment of lunar infrastructure, all while minimizing the risks associated with human spaceflight.
Imagine a team of robots, each equipped with specialized skills and tools, working together to map the lunar surface, collect samples, and even build structures. This is the vision that is driving the development of robotic lunar exploration, and it’s a vision that holds the promise of unlocking new frontiers in our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
The Rise of Robotic Exploration

The Moon, our celestial neighbor, has always captivated humanity’s imagination. While dreams of human lunar colonies may still be far off, the era of robotic exploration is in full swing. With advancements in technology and a growing understanding of the Moon’s potential, robotic missions are becoming increasingly sophisticated and ambitious.
Advantages of Robotic Exploration
The use of robots offers several significant advantages over sending human astronauts to the Moon. Robots are more cost-effective, as they require less complex life support systems and can operate for longer durations. Furthermore, robots can be deployed to hazardous environments that are too dangerous for humans, such as craters and deep canyons.
They can also perform tasks that are physically demanding or repetitive, freeing up human astronauts for more critical scientific endeavors.
Existing Robotic Lunar Missions
Several robotic missions have already provided invaluable insights into the Moon’s geology, composition, and history.
- The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO), launched in 2009, has mapped the lunar surface in unprecedented detail, providing data on its topography, composition, and potential resources.
- The GRAIL mission, consisting of two spacecraft named Ebb and Flow, mapped the Moon’s gravity field, revealing insights into its internal structure and evolution.
- The Chang’e-5 mission, conducted by China in 2020, successfully collected lunar samples and returned them to Earth, marking a significant milestone in lunar exploration.
Robot Squad Capabilities

Imagine a team of robotic explorers, each equipped with specialized tools and capabilities, working in unison to unlock the mysteries of the Moon. This is the vision behind a robot squad, a group of autonomous or semi-autonomous robots designed to work collaboratively in challenging environments like the lunar surface.
Notice best google review ever for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
These squads can revolutionize lunar exploration by extending human reach, overcoming limitations, and accelerating scientific discoveries.
Types of Robots in a Lunar Robot Squad
The robots in a lunar squad would be diverse, reflecting the range of tasks required for lunar exploration. Each robot would be designed with specific capabilities and functionalities, contributing to the overall success of the mission.
- Sample Collection Robots:These robots would be equipped with advanced drilling and sampling systems, allowing them to collect lunar regolith, rock samples, and ice. These samples would provide valuable insights into the Moon’s geological history, composition, and potential for resource extraction.
- Terrain Mapping Robots:Equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR sensors, and ground-penetrating radar, these robots would map the lunar surface in detail, creating 3D models and identifying potential landing sites, resource deposits, and areas of scientific interest.
- Infrastructure Construction Robots:These robots would be capable of constructing lunar habitats, research stations, and communication infrastructure. They could be equipped with robotic arms, 3D printing technology, and other advanced tools to build structures using lunar materials.
- Mobile Base Stations:These robots would serve as mobile command centers, providing communication relays, power distribution, and data processing for the rest of the robot squad. They could be equipped with advanced communication systems, energy storage, and computing capabilities.
Communication and Coordination Challenges, Robot squad could be next big thing lunar exploration
The success of a lunar robot squad depends heavily on the ability of the robots to communicate and coordinate their actions effectively. The harsh lunar environment poses unique challenges to communication, including:
- Signal Attenuation:The Moon’s lack of atmosphere and presence of dust can significantly attenuate radio signals, making reliable communication difficult.
- Limited Bandwidth:The available bandwidth for communication between Earth and the Moon is limited, which restricts the amount of data that can be transmitted in real-time.
- Time Delays:Communication between Earth and the Moon takes approximately 1.3 seconds, creating significant time delays for commands and data transmission.
Addressing Communication and Coordination Challenges
To overcome these challenges, researchers are developing innovative solutions, including:
- Advanced Communication Systems:Using lasers for communication can overcome signal attenuation and provide higher bandwidth compared to radio waves.
- Autonomous Decision-Making:Robots can be programmed with advanced algorithms to make decisions autonomously, reducing reliance on real-time communication with Earth.
- Collaborative Robotics:Robots can communicate and coordinate with each other using local networks, enabling them to share information and make decisions as a team.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):AI can play a crucial role in optimizing communication and coordination. AI-powered robots can learn from their experiences, adapt to changing environments, and make decisions in real-time.
Technological Advancements for Lunar Robots: Robot Squad Could Be Next Big Thing Lunar Exploration
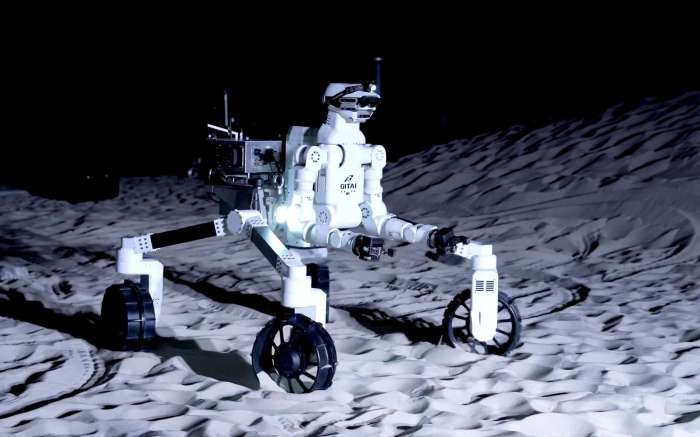
The Moon’s harsh environment poses significant challenges for robots. To ensure their effective operation, significant technological advancements are needed to overcome these obstacles. These advancements encompass various fields, including robotics, artificial intelligence, and power sources.
Overcoming the Challenges of Extreme Temperatures, Radiation, and Dust
The Moon’s surface experiences extreme temperature variations, ranging from scorching hot during the lunar day to frigid cold during the lunar night. Additionally, the lack of a substantial atmosphere leaves robots exposed to harmful solar radiation. Lunar dust, composed of fine, abrasive particles, can cause wear and tear on robotic components.
- Temperature Control Systems:Robots must be equipped with advanced thermal control systems to regulate their internal temperatures. These systems can utilize insulation, heat sinks, and active cooling mechanisms to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Radiation Shielding:To protect against harmful radiation, robots will need specialized shielding materials. These materials can be integrated into the robot’s design or used as protective layers for sensitive components.
- Dust Mitigation Strategies:Engineers are developing strategies to minimize the impact of lunar dust on robots. These strategies include using dust-resistant materials, incorporating dust-removal mechanisms, and designing robots with sealed compartments to protect internal components.
Advancements in AI, Robotics, and Power Sources
To overcome these challenges, advancements in AI, robotics, and power sources are crucial.
- Autonomous Navigation and Decision-Making:Robots operating on the Moon will require advanced AI algorithms for autonomous navigation and decision-making. These algorithms will enable them to navigate complex terrain, avoid obstacles, and make informed decisions in real-time.
- Enhanced Mobility and Dexterity:Lunar robots will need enhanced mobility and dexterity to traverse the Moon’s diverse terrain. This includes developing advanced locomotion systems, such as wheels, tracks, or hopping mechanisms, and incorporating dexterous manipulators for tasks like sample collection and scientific experiments.
- Power Source Solutions:The Moon’s lack of a readily available power source presents a challenge. Researchers are exploring various power solutions, including solar panels, radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs), and fuel cells, to provide sustained energy for lunar robots.
Scientific and Commercial Applications
A robot squad on the Moon could revolutionize our understanding of the lunar environment and unlock a plethora of commercial opportunities. These robotic explorers can conduct scientific research, extract resources, and establish infrastructure, all while pushing the boundaries of human ingenuity.
Scientific Objectives
A robot squad can conduct various scientific experiments on the Moon, leading to groundbreaking discoveries in several fields.
- Lunar Geology and Geochemistry:Robots equipped with advanced sensors and drilling tools can analyze lunar rocks and soil, providing insights into the Moon’s formation, evolution, and internal structure. This data can shed light on the early history of the solar system.
- Lunar Water Ice Exploration:Robots can search for and analyze water ice deposits at the lunar poles, which could be a valuable resource for future human settlements and fuel production.
- Lunar Atmosphere and Exosphere Research:Robots can study the thin lunar atmosphere and exosphere, providing data on the composition, dynamics, and interaction with the solar wind. This research can contribute to our understanding of space weather and its effects on the Moon and Earth.
- Astrobiology Research:Robots can search for signs of past or present life on the Moon, including biosignatures in rocks and soil. This research could reveal if the Moon ever harbored life or if it could potentially support life in the future.
Commercial Applications
The Moon holds significant commercial potential, with resources and infrastructure that could support future human settlements and space exploration.
- Resource Extraction:Robots can mine and process resources like helium-3, a potential fuel source for fusion reactors, and rare earth elements, which are essential for electronics and other technologies. These resources could be used to support future lunar settlements or transported back to Earth.
- Infrastructure Development:Robots can construct lunar bases, research stations, and other infrastructure, using materials extracted from the Moon. This infrastructure could support future human missions, scientific research, and commercial activities.
- Space Tourism:Robots can help develop lunar tourist destinations, including hotels, restaurants, and other amenities. This could generate revenue and stimulate interest in space exploration.
Benefits for Humanity
Lunar exploration by robot squads can bring numerous benefits to humanity, including:
- Scientific Advancement:Robots can gather valuable data that can advance our understanding of the Moon, the solar system, and the universe. This knowledge can lead to breakthroughs in various fields, including physics, geology, and astrobiology.
- Technological Innovation:Developing robots capable of operating in the harsh lunar environment can drive technological innovation, leading to advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and other fields. These advancements can benefit humanity in various ways, including healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation.
- Economic Growth:Lunar exploration can create new industries and jobs, boosting the economy and providing opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. This economic growth can contribute to societal progress and improve living standards.
- Inspiration and Education:Robots exploring the Moon can inspire future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. This can help address the global need for skilled workers in these fields.
Ethical Considerations and Future Outlook
The deployment of robot squads to the Moon raises important ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed. These considerations extend beyond the technical aspects of robotic exploration and delve into the potential consequences of our actions on a celestial body that holds scientific and cultural significance.
Ethical Considerations in Lunar Robotics
The use of robots for lunar exploration presents a unique set of ethical challenges. It is crucial to ensure that our robotic endeavors are conducted responsibly and sustainably, minimizing any potential harm to the lunar environment. Here are some key ethical considerations:
- Environmental Protection: The Moon’s surface is a pristine environment, and it is essential to minimize the impact of our robotic missions. This includes avoiding contamination with Earth-based organisms and managing waste responsibly.
- Data Ownership and Access: The data collected by robotic missions is a valuable resource that should be shared equitably with the scientific community and the public. Transparency and open access to data are crucial for fostering collaboration and advancing scientific understanding.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: As robots become more sophisticated, they may be granted greater autonomy in decision-making. Establishing clear ethical guidelines for robotic behavior is crucial to ensure that their actions align with human values and principles.
- Cultural Sensitivity: The Moon holds cultural and spiritual significance for various cultures around the world. It is essential to approach lunar exploration with sensitivity and respect for these diverse perspectives.
Potential Risks and Challenges
The deployment of robot squads on the Moon presents a number of potential risks and challenges that must be carefully considered and mitigated. These include:
- Technical Malfunctions: Robots are complex machines that can experience malfunctions. The harsh lunar environment, including extreme temperatures and radiation, can increase the risk of technical failures. Redundancy and robust design are crucial for ensuring mission success.
- Communication Disruptions: Maintaining reliable communication with robotic missions on the Moon is essential for monitoring their progress and controlling their operations. Interruptions in communication, caused by factors such as solar flares or technical issues, can pose significant challenges.
- Safety of Astronauts: While robot squads are intended to reduce the risks for human explorers, they can also pose potential safety hazards. For example, a malfunctioning robot could collide with a human astronaut or release harmful substances.
- Environmental Impact: The deployment of robot squads on the Moon can have unintended environmental consequences. For example, the robots could disturb lunar dust, which can affect the delicate balance of the lunar ecosystem.
Future Outlook: Advancements and Timelines
The future of lunar exploration with robot squads holds immense potential for scientific discovery and technological advancement. Here are some key areas of expected progress:
- Enhanced Robotics Capabilities: Robots are expected to become more sophisticated, with improved mobility, dexterity, and autonomy. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning will enable robots to perform increasingly complex tasks and adapt to unforeseen challenges.
- Improved Communication Technologies: Advancements in communication technologies, such as laser communication and quantum communication, will enhance the reliability and speed of data transmission from the Moon to Earth. This will enable real-time monitoring and control of robotic missions.
- Sustainable Lunar Infrastructure: The development of sustainable lunar infrastructure, such as power generation systems and 3D printing facilities, will support long-term robotic exploration and enable the establishment of a permanent lunar base.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: International collaboration and partnerships will be crucial for accelerating progress in lunar robotics. Sharing resources, expertise, and data will enable the development of more sophisticated robotic systems and accelerate scientific discovery.