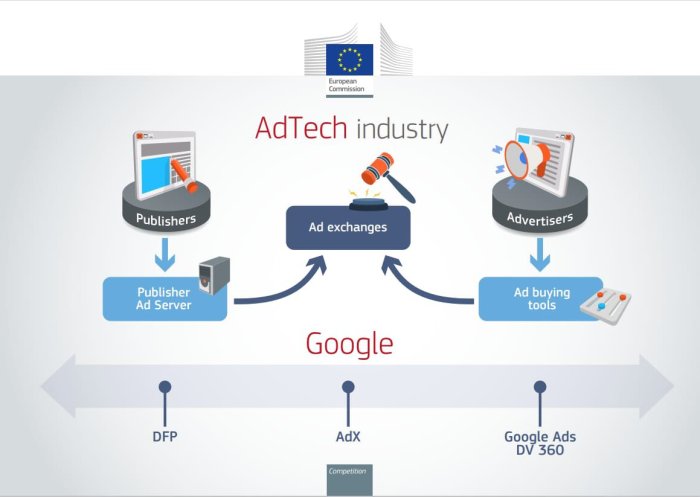
The Rationale Behind Antitrust Concerns
Plans to stop tech giants buying smaller rivals threaten future innovations – The idea of antitrust laws regulating the tech giants’ mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is gaining traction, and for good reason. While tech giants claim that acquisitions fuel innovation, many argue that these deals stifle competition and harm consumers in the long run.
The potential negative consequences of these mergers raise serious concerns about market dominance and stifled innovation.
Historical Examples of Antitrust Actions Against Tech Giants
Antitrust actions against tech giants have a long history. In the late 1990s, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) filed an antitrust lawsuit against Microsoft, alleging that the company was abusing its monopoly power in the operating system market. The lawsuit ultimately resulted in a settlement that forced Microsoft to make changes to its business practices, including making its operating system compatible with competing browsers.
In 2011, Google was accused of antitrust violations for favoring its own services in search results. The European Commission (EC) fined Google €2.42 billion in 2017 for violating antitrust rules. The EC found that Google had used its dominance in the search market to give an unfair advantage to its own shopping comparison service.These historical examples demonstrate the importance of antitrust enforcement in ensuring a fair and competitive marketplace.
However, the rapid pace of technological innovation presents new challenges for antitrust regulators.
Arguments for and Against Government Intervention in Tech Mergers and Acquisitions
The debate over government intervention in tech mergers and acquisitions centers around the potential benefits and drawbacks of such intervention.
Arguments for Government Intervention
- Reduced Competition:Acquisitions by tech giants can lead to reduced competition in the market. This can result in higher prices for consumers, lower quality products and services, and less innovation.
- Stifled Innovation:Acquisitions can stifle innovation by eliminating potential competitors. Smaller companies with innovative ideas may be acquired and then shut down or their innovations may be integrated into the acquiring company’s products and services, giving the tech giant an unfair advantage.
- Increased Market Power:Acquisitions can give tech giants increased market power, allowing them to dictate terms to suppliers and customers. This can lead to a loss of consumer choice and reduced bargaining power.
Arguments Against Government Intervention
- Innovation and Efficiency:Proponents of mergers argue that they can lead to innovation and efficiency by combining resources and expertise. They claim that acquisitions can help companies scale up their operations and bring new products and services to market more quickly.
- Global Competition:They also argue that antitrust intervention could hinder U.S. companies from competing effectively in the global marketplace. They contend that allowing U.S. companies to acquire foreign competitors can help them stay ahead in the global tech race.
- Job Creation:Mergers can create jobs and stimulate economic growth. Proponents argue that blocking mergers could harm the economy by hindering job creation and investment.
The Impact on Innovation: Plans To Stop Tech Giants Buying Smaller Rivals Threaten Future Innovations
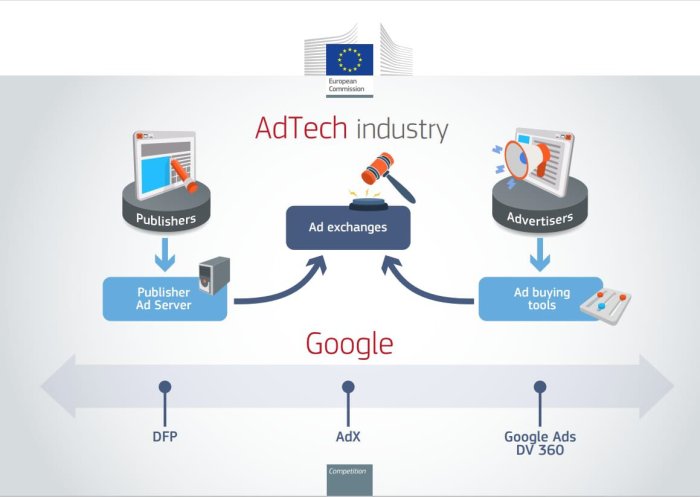
The proposed regulations aimed at curbing tech giants’ acquisitions of smaller rivals raise concerns about their potential impact on innovation. While the intention is to foster competition and prevent monopolies, some argue that these regulations could stifle the very innovation they seek to protect.This section explores the potential effects of these regulations on the development of new technologies and startups, examines how smaller companies have historically contributed to innovation in the tech sector, and discusses the potential for increased competition and diversification within the tech industry if regulations are implemented.
The Potential Impact on Startups and New Technologies
The proposed regulations could significantly impact startups and the development of new technologies. The acquisition of smaller companies by larger tech giants often provides startups with access to resources, expertise, and distribution networks, enabling them to scale and reach a wider audience.
Restricting these acquisitions could limit startups’ growth potential and discourage venture capitalists from investing in them, as the exit strategy through acquisition becomes less viable. This could lead to a decrease in funding for early-stage companies, hindering the development of innovative technologies and potentially slowing down the pace of innovation.
Examples of Smaller Companies Contributing to Innovation
Smaller companies have historically played a crucial role in driving innovation in the tech sector. For instance,
- Instagramwas acquired by Facebook in 2012. This acquisition allowed Instagram to leverage Facebook’s resources and reach a global audience, but it also limited its ability to compete directly with its parent company.
- WhatsAppwas acquired by Facebook in 2014. This acquisition gave WhatsApp access to Facebook’s infrastructure and user base, enabling it to expand its reach. However, it also raised concerns about data privacy and competition.
- Androidwas initially developed by a small company called Android Inc.and was later acquired by Google in 2005. This acquisition allowed Android to become the dominant mobile operating system, but it also raised concerns about Google’s dominance in the mobile market.
These examples illustrate how smaller companies have contributed significantly to innovation in the tech sector, often through their acquisition by larger companies. Restricting these acquisitions could potentially stifle innovation by limiting the growth potential of startups and reducing the incentive for venture capitalists to invest in them.
Increased Competition and Diversification
The proposed regulations aim to increase competition and diversification within the tech industry. By preventing tech giants from acquiring smaller companies, the regulations could encourage the emergence of new players and foster a more competitive market. This increased competition could lead to greater innovation and consumer choice, as companies are forced to compete on price, features, and quality.
For example, the antitrust lawsuit filed against Google by the US Department of Justice in 2020 alleges that Google has engaged in anti-competitive practices to maintain its dominance in the digital advertising market. If successful, this lawsuit could lead to increased competition in the digital advertising market, potentially benefiting consumers and fostering innovation.
The Role of Government Regulation
The debate over tech giants and their dominance has sparked intense discussions about the role of government regulation. While some argue for minimal intervention, others advocate for stricter measures to ensure fair competition and protect consumers. This section delves into the various regulatory approaches governments could implement, the challenges they face, and the diverse strategies employed by different countries.
Types of Government Regulations, Plans to stop tech giants buying smaller rivals threaten future innovations
Government regulation plays a crucial role in addressing antitrust concerns in the tech industry. Various regulatory approaches can be employed, each with its unique strengths and limitations.
- Antitrust Laws:These laws aim to prevent monopolies and promote competition. Governments can use these laws to break up large tech companies, prevent mergers that would stifle competition, and impose fines for anti-competitive practices. Examples include the Sherman Antitrust Act in the United States and the Competition Act in Canada.
- Data Privacy Regulations:These regulations focus on protecting user data and ensuring transparency in data collection and usage. Examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
- Content Moderation Regulations:Governments can regulate the content that tech platforms allow on their services. This can involve requiring platforms to remove harmful content like hate speech, misinformation, and illegal materials. Examples include the European Union’s Digital Services Act (DSA) and the United States’ Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act.
- Interoperability Regulations:These regulations aim to ensure that different platforms can communicate and exchange data seamlessly. This could prevent tech giants from locking users into their ecosystems and promote competition. An example is the European Union’s proposed Interoperability Act, which aims to force tech giants to open up their platforms to competition.
Challenges of Regulating the Tech Industry
Regulating the tech industry presents unique challenges due to its rapid evolution, global reach, and complex business models.
- Keeping up with Technological Advancements:The tech industry is constantly evolving, making it difficult for regulators to keep up with new technologies and business models. This can lead to regulations becoming outdated or ineffective.
- Global Reach:Tech companies operate globally, making it challenging for governments to regulate them effectively. Different countries have varying regulatory frameworks, which can create complexities for enforcement.
- Innovation and Competition:Striking a balance between regulation and fostering innovation is crucial. Overly stringent regulations could stifle innovation and discourage competition.
- Defining Anti-Competitive Practices:Identifying and defining anti-competitive practices in the tech industry can be complex. Traditional antitrust laws may not adequately address the unique characteristics of digital markets.
- Potential Pitfalls:Overly aggressive regulation could lead to unintended consequences, such as stifling innovation, reducing consumer choice, or creating barriers to entry for new companies.
Comparative Approaches to Tech Monopolies
Different countries have adopted diverse approaches to addressing tech monopolies.
- United States:The United States has historically favored a more hands-off approach to antitrust regulation. However, recent years have seen increased scrutiny of tech giants, with investigations into anti-competitive practices and calls for stronger regulations.
- European Union:The European Union has taken a more proactive approach to regulating tech companies. The GDPR, DSA, and Interoperability Act are examples of its efforts to protect consumers, promote competition, and ensure fair market practices.
- China:China has implemented strict regulations on tech companies, including antitrust investigations and data privacy laws. The government has also promoted the development of domestic tech giants to compete with international players.
The Future of Tech Acquisitions
The proposed regulations aimed at curbing tech giants’ acquisition sprees have the potential to significantly alter the landscape of mergers and acquisitions in the tech sector. These regulations, if implemented, will likely introduce new hurdles for tech giants seeking to acquire smaller rivals, potentially impacting the pace and nature of innovation in the industry.
The Potential Impact of Increased Antitrust Scrutiny
The increased scrutiny from antitrust regulators could have several significant impacts on future tech acquisitions.
- Increased Regulatory Hurdles:Tech giants may face more stringent regulatory reviews and approvals for any proposed acquisitions. This could involve extended timelines, additional paperwork, and more demanding conditions for approval, making acquisitions more complex and time-consuming.
- Reduced Acquisition Activity:The increased risk of regulatory rejection or delays could discourage tech giants from pursuing certain acquisitions, potentially leading to a decrease in overall acquisition activity in the tech sector.
- Shift in Acquisition Strategies:Tech giants might adjust their acquisition strategies to focus on smaller, less impactful acquisitions that are less likely to attract significant regulatory attention. This could result in a shift towards acquisitions that are more focused on specific technologies or talent acquisition rather than acquiring entire companies.
- Increased Litigation:Tech giants might face increased litigation from competitors or regulatory bodies challenging acquisitions. This could lead to protracted legal battles, further delaying acquisitions and increasing the financial and reputational costs associated with them.
A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a major tech giant, like Google, attempts to acquire a promising AI startup specializing in natural language processing. Under the current regulatory climate, such an acquisition might face minimal scrutiny. However, under increased antitrust scrutiny, this acquisition would likely face significant challenges.
- Antitrust Review:The acquisition would likely trigger a thorough antitrust review by regulatory bodies, examining the potential impact on competition in the AI and search markets. This review would involve analyzing the market share of both companies, the potential for the acquisition to create a dominant player in the AI market, and the potential for the acquisition to stifle innovation in the field.
- Public Scrutiny:The acquisition would also attract public scrutiny, with concerns raised about the potential for Google to leverage the AI startup’s technology to enhance its dominance in search and advertising. This public pressure could further complicate the acquisition process.
- Potential Rejection:Given the potential antitrust concerns and public pressure, the acquisition could be rejected by regulatory bodies. This would prevent Google from acquiring the AI startup and potentially limit its ability to compete in the rapidly evolving AI market.
Strategies for Tech Giants
In light of these potential challenges, tech giants are likely to adopt various strategies to navigate the evolving regulatory landscape.
- Focus on Organic Growth:Tech giants might prioritize organic growth through internal research and development, rather than relying on acquisitions to expand their product offerings and market reach.
- Strategic Partnerships:Tech giants might opt for strategic partnerships with smaller companies instead of outright acquisitions. This would allow them to access valuable technologies and talent without triggering antitrust scrutiny.
- Early Stage Investments:Tech giants might focus on investing in early-stage startups, providing them with funding and mentorship without seeking full control of the company. This would allow them to stay connected to promising innovations without triggering regulatory concerns.
- Compliance and Lobbying:Tech giants are likely to invest heavily in compliance efforts, ensuring their acquisition strategies align with evolving regulations. They will also engage in lobbying efforts to influence regulatory frameworks and ensure a more favorable environment for future acquisitions.