Oxygen generating battery rock discovery life on earth – Oxygen-generating battery rock discovery life on earth – it sounds like science fiction, but this incredible discovery has scientists rethinking the very origins of life on our planet. Imagine a time before plants, before the air we breathe, when Earth’s atmosphere was a toxic cocktail of gases.
Now, picture rocks that, like tiny batteries, were silently producing oxygen, paving the way for the evolution of life as we know it. This is the fascinating story we’re about to unravel, exploring how these ancient rocks may have sparked the flame of life on Earth.
Scientists have unearthed these remarkable rocks, rich in minerals capable of generating oxygen, in geological formations that date back billions of years. These discoveries offer a glimpse into a time when life was just beginning to emerge, and they challenge our understanding of how oxygen first appeared in Earth’s atmosphere.
The implications are profound, potentially reshaping our understanding of life’s origins and the potential for life on other planets.
The Significance of Oxygen in Earth’s History
Oxygen, a seemingly ubiquitous element in our modern world, played a pivotal role in shaping the evolution of life on Earth. Its emergence and gradual increase in the atmosphere transformed the planet, paving the way for the development of complex life forms.
The Rise of Oxygen and Its Impact on Life
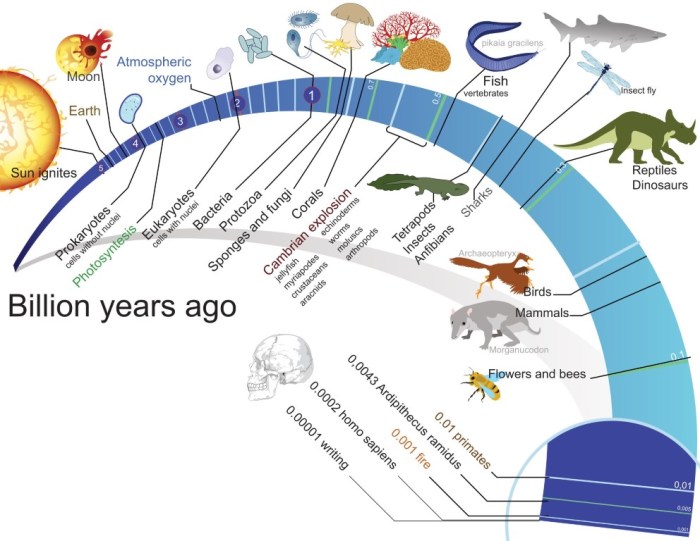
The rise of oxygen in Earth’s atmosphere, a process known as the Great Oxidation Event, began approximately 2.4 billion years ago. This dramatic shift was primarily driven by the evolution of photosynthetic cyanobacteria, which harnessed sunlight to produce energy and release oxygen as a byproduct.
This oxygen, initially toxic to most life forms, gradually accumulated in the atmosphere, creating a new selective pressure that led to the emergence of oxygen-tolerant and, eventually, oxygen-dependent organisms.
Early Life Forms in Oxygen-Poor Environments
Before the rise of oxygen, Earth’s atmosphere was dominated by methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. Early life forms, predominantly single-celled organisms, thrived in these oxygen-poor environments. These anaerobic organisms utilized alternative energy sources like sulfur, iron, or hydrogen sulfide, which they could readily access.
The Transition from Anaerobic to Aerobic Respiration
The increasing availability of oxygen presented a challenge for early life forms. Some organisms adapted to tolerate oxygen, while others developed mechanisms to detoxify it. This transition from anaerobic to aerobic respiration was a significant evolutionary leap. Aerobic respiration, which utilizes oxygen to break down glucose and produce energy, is far more efficient than anaerobic respiration, allowing for the development of larger, more complex organisms.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring eu pushes further domestic production green tech.
The Discovery of Oxygen-Generating Rocks: Oxygen Generating Battery Rock Discovery Life On Earth
The discovery of rocks capable of generating oxygen has revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s early atmosphere and the origins of life. These ancient rocks, found in various geological formations around the world, provide compelling evidence of a time when our planet was a very different place.These rocks, known as banded iron formations (BIFs), are a testament to the early stages of Earth’s history, a time when the atmosphere was devoid of oxygen.
The process of oxygen generation within these rocks, while distinct from modern photosynthesis, played a crucial role in shaping the planet’s environment and paving the way for the evolution of complex life.
The Formation of Banded Iron Formations
Banded iron formations are sedimentary rocks composed of alternating layers of iron oxide (primarily hematite and magnetite) and silica (chert). These layers are often thin and finely laminated, giving the rocks a distinctive banded appearance. BIFs are found in a variety of geological settings, including ancient ocean basins, continental margins, and even some volcanic environments.The formation of BIFs is a complex process that involves the interaction of several geological and chemical factors.
The iron-rich layers likely formed from the precipitation of dissolved iron from seawater. This iron was likely dissolved by hydrothermal vents or other sources of dissolved iron. The silica layers, on the other hand, are thought to have originated from the deposition of silica from volcanic eruptions or the weathering of rocks.
The Minerals Responsible for Oxygen Generation
The key to oxygen generation in BIFs lies in the presence of iron-containing minerals, specifically iron oxides like hematite (Fe 2O 3) and magnetite (Fe 3O 4). These minerals are formed through a process called oxidation, where iron atoms lose electrons and combine with oxygen atoms.In the case of BIFs, the oxidation of iron was likely driven by the interaction of dissolved iron with oxygen produced by early forms of life.
These early life forms, possibly similar to modern cyanobacteria, released oxygen as a byproduct of their metabolic processes. The oxygen then reacted with the dissolved iron, causing it to precipitate out of the water and form iron oxide layers.
The Age and Location of Banded Iron Formations
Banded iron formations are found in geological formations dating back to the Archean eon, a period that spans from about 4.0 billion to 2.5 billion years ago. The most significant deposits of BIFs are found in the Precambrian Shield, a vast area of ancient rocks that covers much of Canada, Greenland, Australia, and South Africa.The presence of BIFs in these ancient rocks suggests that oxygen production was already occurring on Earth during the Archean eon.
This is significant because it provides evidence for the early evolution of life and the emergence of oxygen-producing organisms.
Comparing Oxygen Generation in BIFs with Modern Photosynthesis
While both BIFs and modern photosynthesis involve the production of oxygen, the processes are fundamentally different. In BIFs, oxygen generation was a passive process driven by the interaction of dissolved iron with oxygen released by early life forms. In contrast, modern photosynthesis is an active process where plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.Modern photosynthesis is a much more efficient process of oxygen production than the process that occurred in BIFs.
However, the oxygen produced by early life forms in BIFs played a crucial role in the early evolution of Earth’s atmosphere and the emergence of complex life.
The Implications of Oxygen-Generating Rocks for Life on Earth
The discovery of oxygen-generating rocks has profound implications for our understanding of the early Earth and the emergence of life. These rocks provide tangible evidence of a process that played a crucial role in shaping our planet’s atmosphere and making it habitable.
The Impact on the Early Atmosphere
The presence of oxygen-generating rocks suggests that Earth’s early atmosphere was not entirely devoid of oxygen, as previously thought. This has significant implications for the evolution of life. Early life forms were likely anaerobic, meaning they did not require oxygen to survive.
However, as oxygen levels gradually increased, it paved the way for the development of aerobic organisms, which utilize oxygen for energy production.
The Contribution to the Emergence of Life
While oxygen is essential for most life on Earth today, it was initially toxic to early life forms. The gradual increase in oxygen levels, driven by oxygen-generating rocks, likely led to a period of intense selective pressure. This pressure favored the evolution of organisms that could tolerate and even utilize oxygen, ultimately leading to the diversity of life we see today.
Oxygen-Generating Processes on Other Planets
The discovery of oxygen-generating rocks on Earth raises the intriguing possibility that similar processes might be occurring on other planets. If we find evidence of oxygen-generating rocks on Mars or other celestial bodies, it would significantly increase the likelihood of finding life, or at least the potential for life, beyond Earth.
Implications for the Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The search for extraterrestrial life often focuses on the presence of liquid water. However, the discovery of oxygen-generating rocks suggests that we should also consider the potential for oxygen production as a key indicator of habitability. This expands the scope of our search for life beyond Earth and motivates the development of new techniques for detecting oxygen in the atmospheres of exoplanets.
The Role of Batteries in Oxygen Generation

While the Earth’s early atmosphere was devoid of oxygen, the discovery of oxygen-generating rocks has provided invaluable insights into the evolution of our planet. These rocks, containing iron oxides, are evidence of the ancient process of photosynthesis, which released oxygen as a byproduct.
The ability to generate oxygen, particularly in environments where it is scarce, has become a critical factor in space exploration. Batteries, through electrochemical reactions, offer a promising solution for producing oxygen on demand.
Oxygen Generation Using Batteries
Electrochemical reactions within batteries can be harnessed to generate oxygen. This process typically involves the electrolysis of water, where an electric current is passed through water, splitting it into its constituent elements: hydrogen and oxygen.
The electrolysis of water can be represented by the following equation:
H2O(l) → 2H 2(g) + O 2(g)
A Hypothetical Scenario for Oxygen Generation in Space
Imagine a future space mission to Mars. Astronauts require a reliable source of oxygen for breathing and life support systems. Oxygen-generating batteries could be a game-changer in this scenario. These batteries would utilize Martian water ice, a readily available resource, to produce oxygen on-site.
The oxygen could then be stored and used for various purposes, including breathing, fuel for rockets, and even growing crops in Martian greenhouses.
Efficiency Comparison of Battery Types for Oxygen Generation
The efficiency of oxygen generation varies depending on the type of battery used. Here is a table comparing the efficiency of different battery types:
| Battery Type | Efficiency (g O2/Ah) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Cells | High | High energy density, but require continuous fuel supply. |
| Metal-Air Batteries | Moderate | Can be recharged, but limited by the availability of the metal. |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | Low | Widely available and efficient, but not specifically designed for oxygen generation. |
Visual Representation of Oxygen Generation from Batteries, Oxygen generating battery rock discovery life on earth
[Image of a battery with a diagram showing the electrochemical reactions involved in water electrolysis, with arrows indicating the flow of electrons and ions.]The image illustrates the process of oxygen generation from a battery. Water molecules are drawn into the battery, where they are split into hydrogen and oxygen ions by the electrical current.
The oxygen ions are then released as oxygen gas.
The Future of Oxygen-Generating Technology

The discovery of oxygen-generating rocks has opened up a world of possibilities for developing innovative technologies that can produce oxygen on demand. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize various fields, from space exploration to healthcare. While the current technology is still in its early stages of development, the future holds exciting prospects for oxygen-generating batteries and systems.
Potential Applications of Oxygen-Generating Batteries
The potential applications of oxygen-generating batteries are vast and diverse. Here are some key areas where these technologies could make a significant impact:
- Space Exploration:Oxygen-generating batteries could provide a reliable and sustainable source of oxygen for astronauts on long-duration space missions. This would eliminate the need to carry large amounts of oxygen, reducing launch weight and improving mission efficiency.
- Medical Applications:Oxygen-generating batteries could be used to create portable oxygen concentrators for patients with respiratory conditions. This would allow individuals to access oxygen therapy more conveniently and affordably.
- Submarine and Underwater Operations:Oxygen-generating batteries could provide a vital source of oxygen for submarines and underwater exploration vehicles. This would enable longer underwater missions and exploration in remote or challenging environments.
- Emergency Response:Oxygen-generating batteries could be deployed in disaster relief situations to provide emergency oxygen supplies to victims. This could be particularly valuable in areas where access to oxygen is limited.
- Sustainable Energy:Oxygen-generating batteries could be integrated with renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to create a closed-loop system for oxygen production. This would reduce reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Challenges and Limitations of Current Oxygen-Generating Technology
Despite the promising potential of oxygen-generating batteries, several challenges and limitations need to be addressed before widespread adoption becomes a reality:
- Efficiency:Current oxygen-generating technologies are not very efficient, requiring a significant amount of energy to produce a small amount of oxygen.
- Durability:Oxygen-generating batteries need to be durable and reliable, capable of withstanding harsh environments and providing long-term operation.
- Cost:The cost of producing oxygen-generating batteries is currently high, making them inaccessible to many potential users.
- Safety:Ensuring the safe operation of oxygen-generating batteries is crucial, particularly in medical and emergency response applications.
Developing More Efficient and Sustainable Oxygen-Generating Systems
Overcoming the challenges and limitations of current oxygen-generating technology will require significant research and development efforts. Some potential avenues for improvement include:
- Improving Battery Efficiency:Research is underway to develop more efficient and powerful oxygen-generating batteries. This includes exploring new materials and optimizing battery design.
- Developing Sustainable Production Methods:Sustainable and environmentally friendly methods for producing oxygen-generating batteries need to be developed. This could involve using recycled materials and reducing the carbon footprint of production.
- Enhancing Durability and Reliability:Researchers are working on developing oxygen-generating batteries that are more durable and reliable, capable of operating in harsh environments for extended periods.
- Reducing Costs:Finding ways to reduce the cost of producing oxygen-generating batteries is essential for making this technology more accessible. This could involve developing more efficient manufacturing processes or exploring alternative materials.
Future Directions for Research and Development
Future research and development in oxygen-generating technology will focus on:
- Developing Advanced Materials:Exploring new materials with improved catalytic properties and oxygen-generating capabilities is crucial for enhancing battery efficiency and performance.
- Optimizing Battery Design:Optimizing battery design to maximize oxygen production, reduce energy consumption, and improve durability is another key area of research.
- Integrating with Renewable Energy Sources:Research is needed to develop integrated systems that combine oxygen-generating batteries with renewable energy sources, creating a sustainable and self-sufficient oxygen production system.
- Developing Smart Oxygen Management Systems:Smart systems that can monitor and control oxygen production and distribution in real-time are essential for ensuring safe and efficient operation.