Open letter eu ai act regulation stifle innovation artificial intelligence – Open Letter: Does EU AI Act Stifle Innovation? sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
The EU’s AI Act, a landmark piece of legislation aiming to regulate the development and deployment of artificial intelligence, has sparked a lively debate. While proponents see it as a crucial step towards responsible AI, critics argue that its stringent regulations could stifle innovation and hinder the growth of the AI sector.
This open letter, penned by leading AI researchers and entrepreneurs, highlights these concerns and urges policymakers to reconsider certain aspects of the Act.
The EU AI Act
The EU AI Act, formally known as the Artificial Intelligence Act, represents a landmark regulatory effort by the European Union to establish a comprehensive framework for the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems. This Act aims to address the potential risks associated with AI while fostering innovation and promoting ethical and responsible AI development.
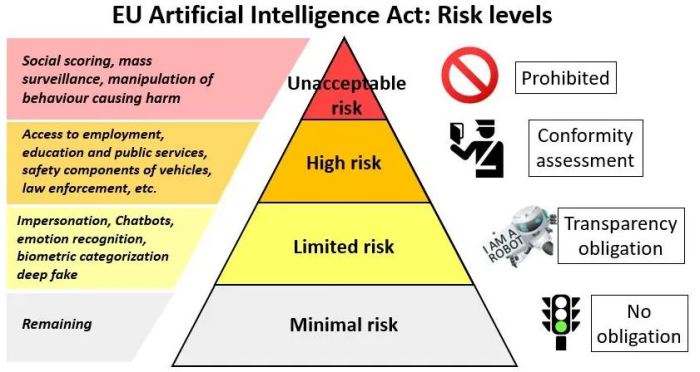
Risk Categories for AI Systems
The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems into four risk categories, each with varying levels of regulation and requirements. This risk-based approach recognizes the diverse nature of AI applications and aims to tailor regulations accordingly.
- Unacceptable Risk AI Systems: These systems are considered to pose a clear and unacceptable risk to fundamental rights and safety. They are prohibited under the Act. Examples include AI systems used for social scoring, real-time facial recognition in public spaces, and AI-powered weapons that operate autonomously.
- High-Risk AI Systems: These systems are subject to the most stringent regulatory requirements, including conformity assessments, risk management measures, and transparency obligations. Examples include AI systems used in critical infrastructure, healthcare, education, and law enforcement.
- Limited-Risk AI Systems: These systems are subject to less stringent requirements but must still comply with basic transparency and safety standards. Examples include AI systems used in chatbots, spam filters, and recommendation algorithms.
- Minimal-Risk AI Systems: These systems are considered to pose minimal risks and are largely exempt from regulatory oversight. Examples include AI systems used in video games, entertainment applications, and personal assistants.
Regulatory Framework for High-Risk AI Systems
The EU AI Act proposes a comprehensive regulatory framework for high-risk AI systems, encompassing various stages of the AI lifecycle. This framework aims to ensure that high-risk AI systems are developed, deployed, and used responsibly, minimizing potential risks to individuals and society.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Developers of high-risk AI systems are required to conduct thorough risk assessments, identifying potential harms and implementing appropriate mitigation measures. This includes addressing bias, discrimination, and privacy concerns.
- Transparency and Explainability: High-risk AI systems must be designed and deployed with transparency in mind, enabling users to understand how the system works and the rationale behind its decisions. This includes providing clear information about the system’s purpose, limitations, and potential risks.
- Human Oversight and Control: The Act emphasizes the importance of human oversight and control over high-risk AI systems. This means ensuring that humans retain the ability to intervene, monitor, and override AI decisions when necessary. This safeguards against unintended consequences and promotes ethical decision-making.
- Data Governance and Quality: High-risk AI systems rely on large datasets, which must be accurate, reliable, and representative. The Act emphasizes the importance of data governance, ensuring that data used to train AI systems is collected and used responsibly and ethically.
- Conformity Assessment and Certification: The Act introduces a system of conformity assessment and certification for high-risk AI systems. This involves independent assessments to verify that systems comply with regulatory requirements, ensuring their safety, reliability, and ethical development.
Concerns Regarding Innovation Stifling

The EU AI Act, while aiming to regulate the development and deployment of AI responsibly, has drawn criticism from some quarters, who argue that its stringent requirements could stifle innovation in the field. These concerns stem from the potential impact of the Act on various aspects of AI development and deployment, including bureaucratic hurdles, excessive regulation, and the potential to hinder the growth of AI startups and small businesses.
Impact on AI Development and Deployment
Critics argue that the EU AI Act’s focus on risk assessment and mitigation could lead to overly cautious development practices, hindering the exploration of novel AI technologies and applications. For instance, the Act’s classification of AI systems into different risk categories, with higher-risk systems subject to more stringent requirements, could discourage experimentation with emerging technologies that fall under the higher-risk category.
This could potentially slow down the pace of AI innovation, particularly in sectors like healthcare and autonomous vehicles, where the development of cutting-edge AI solutions is crucial for advancing societal progress.
Bureaucratic Hurdles and Excessive Regulation
The Act’s extensive documentation requirements, compliance procedures, and oversight mechanisms could impose a significant administrative burden on AI developers, particularly smaller companies with limited resources. Critics argue that these bureaucratic hurdles could create a disincentive for innovation, as developers might be deterred by the complexity and cost of complying with the Act’s regulations.
Obtain access to wikipedia influencing judicial decisions could manipulate judges mit to private resources that are additional.
This could lead to a situation where larger companies with more resources are better positioned to navigate the regulatory landscape, potentially creating an uneven playing field and hindering the growth of smaller AI startups.
Impact on AI Startups and Small Businesses
The EU AI Act’s regulatory framework could pose a significant challenge for AI startups and small businesses, which often operate with limited resources and rely on agility and rapid innovation. The Act’s requirements for risk assessments, data governance, and transparency could impose substantial financial and operational burdens on these companies, potentially hindering their ability to compete with larger, more established players.
This could stifle the growth of the AI ecosystem, as smaller companies play a crucial role in fostering innovation and driving the development of new AI solutions.
Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
The EU AI Act represents a significant step towards regulating artificial intelligence (AI) and ensuring its responsible development and deployment. The Act aims to strike a delicate balance between fostering innovation and addressing the potential risks associated with AI. This approach reflects the EU’s commitment to harnessing the benefits of AI while safeguarding individual rights and societal values.
Rationale for AI Regulation
The EU’s approach to AI regulation is rooted in the understanding that AI technologies are rapidly evolving and have the potential to profoundly impact various aspects of life. The rationale behind the EU AI Act can be summarized as follows:
- Promoting Trust and Confidence:Clear regulations are crucial for building trust in AI systems and encouraging their adoption by businesses and individuals.
- Addressing Ethical Concerns:AI systems can raise ethical concerns related to bias, discrimination, privacy, and transparency. Regulation helps ensure that AI development and deployment adhere to ethical principles.
- Mitigating Potential Risks:AI technologies can pose risks to individuals and society, such as job displacement, misuse for malicious purposes, and unintended consequences. Regulation aims to mitigate these risks through risk-based approaches and appropriate safeguards.
Addressing Ethical Concerns and Mitigating Risks
The EU AI Act recognizes the need to address ethical concerns and mitigate potential risks associated with AI. The Act proposes a risk-based approach, categorizing AI systems into different risk levels and applying appropriate regulatory measures accordingly.
- Unacceptable Risk:AI systems deemed to pose unacceptable risks, such as those used for social scoring or real-time facial recognition in public spaces, are prohibited.
- High Risk:High-risk AI systems, such as those used in critical infrastructure, healthcare, and law enforcement, are subject to stringent requirements for transparency, accountability, and human oversight.
- Limited Risk:AI systems with limited risk, such as spam filters or chatbots, are subject to less stringent regulations.
Examples of AI Applications Requiring Regulation
The EU AI Act identifies specific AI applications where regulation is deemed necessary to protect individuals and society. These include:
- Biometric Identification Systems:AI-powered facial recognition systems raise concerns about privacy, surveillance, and potential misuse. The Act proposes strict regulations for the use of such systems, limiting their deployment and requiring consent.
- AI-Based Recruitment and Loan Approval Systems:These systems can perpetuate bias and discrimination if not developed and deployed responsibly. The Act requires developers to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability in these systems.
- Autonomous Vehicles:The development and deployment of self-driving cars raise safety concerns and require robust regulations to ensure the safety of passengers and pedestrians.
Comparison with Other Regulatory Approaches
The EU AI Act is one of the most comprehensive and ambitious regulatory frameworks for AI globally. While other regions are also developing AI regulations, the EU’s approach stands out for its focus on risk-based categorization, ethical considerations, and the protection of fundamental rights.
- United States:The US approach to AI regulation is more fragmented, with different agencies focusing on specific aspects of AI. There is no overarching federal AI law, but there are regulations in place for specific AI applications, such as autonomous vehicles.
- China:China has implemented a series of AI regulations aimed at promoting the development and deployment of AI while ensuring its responsible use. These regulations focus on areas such as data privacy, algorithmic transparency, and the ethical use of AI.
- Canada:Canada’s approach to AI regulation emphasizes ethical guidelines and voluntary principles. The government has published a framework for responsible AI development and use, encouraging organizations to adopt these principles.
Impact on Artificial Intelligence Development: Open Letter Eu Ai Act Regulation Stifle Innovation Artificial Intelligence
The EU AI Act, with its aim to regulate the development and deployment of AI systems, has the potential to significantly influence the future of AI development. The Act’s impact on AI research, innovation, and industry adoption will be multifaceted, with both potential benefits and challenges.
Impact on Specific AI Research Areas
The EU AI Act could have a profound impact on specific AI research areas. The Act’s focus on high-risk AI systems might incentivize researchers to explore and develop alternative approaches that minimize risk and comply with regulatory requirements. For example, research on explainable AI (XAI) and robust AI, which focus on making AI systems more transparent and reliable, could be accelerated.
Conversely, the Act’s restrictions on certain AI technologies, such as facial recognition, could potentially hinder research in these areas.
Implications for AI Development in Various Sectors
The Act’s implications for AI development will vary across different sectors. For instance, in healthcare, the Act’s requirements for transparency and accountability could lead to the development of AI systems that are more readily accepted by patients and healthcare professionals.
In the automotive industry, the Act’s focus on safety could drive innovation in autonomous driving technologies. However, the Act’s regulations could also pose challenges for certain sectors, such as finance, where AI systems are used for complex risk assessment and decision-making.
Influence on the Design and Implementation of AI Systems
The EU AI Act could significantly influence the design and implementation of AI systems. Developers will need to consider the Act’s requirements for risk assessment, transparency, and human oversight during the development process. This could lead to the development of AI systems that are more ethical, robust, and accountable.
For example, AI systems might be designed with features that allow users to understand the reasoning behind the system’s decisions or to intervene in the decision-making process.
Open Letter: A Call for Dialogue

The open letter, signed by prominent figures in the AI community, expresses deep concerns about the potential stifling impact of the EU AI Act on innovation. It argues that the proposed regulations, while well-intentioned, could inadvertently hinder the development and deployment of beneficial AI technologies.
Key Arguments and Concerns, Open letter eu ai act regulation stifle innovation artificial intelligence
The open letter highlights several key arguments and concerns regarding the EU AI Act. The authors argue that the Act’s broad definitions and risk-based approach could lead to overregulation and stifle innovation. They specifically express concerns about the following:
- Overly Broad Definitions:The letter criticizes the Act’s broad definitions of “high-risk AI systems,” arguing that they encompass a wide range of AI applications, potentially leading to unnecessary regulation of less risky systems.
- Risk-Based Approach:The authors express concern that the Act’s risk-based approach could be overly burdensome for developers, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), hindering their ability to innovate and compete.
- Impact on Research and Development:The letter highlights the potential impact of the Act on fundamental research and development, arguing that overly stringent regulations could discourage experimentation and exploration of new AI technologies.
- Stifling of Competition:The authors warn that the Act’s regulatory framework could create a competitive disadvantage for European AI companies compared to their counterparts in other regions with less stringent regulations.
Recommendations for Addressing Concerns
The open letter proposes several recommendations to address these concerns and promote a more balanced approach to AI regulation. These recommendations include:
- Refine Definitions:The authors call for a more precise definition of “high-risk AI systems” to avoid overregulation of less risky applications.
- Proportionate Regulation:The letter recommends a more proportionate approach to regulation, tailored to the specific risks posed by different AI systems.
- Promote Innovation:The authors emphasize the need for regulations that foster innovation and encourage the development of beneficial AI technologies.
- Focus on Ethical Guidelines:The letter suggests a greater emphasis on ethical guidelines and best practices for AI development rather than overly prescriptive regulations.
Influence on the Ongoing Debate
The open letter has sparked significant debate and discussion within the AI community and beyond. It has contributed to a broader conversation about the need to balance innovation and responsibility in the development and deployment of AI. The letter’s arguments have been cited by various stakeholders, including policymakers, industry leaders, and researchers, as they navigate the complex landscape of AI regulation.





