Nhs artificial pancreas diabetes patients – NHS Artificial Pancreas: Hope for Diabetes Patients – Imagine a world where managing diabetes is no longer a constant struggle. That’s the promise of the artificial pancreas, a groundbreaking technology that’s revolutionizing diabetes care. This revolutionary device automatically monitors blood sugar levels and delivers insulin, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas.
The NHS is actively involved in research and development, making this life-changing technology accessible to more people.
This blog post will delve into the exciting world of the NHS artificial pancreas, exploring its workings, benefits, and the impact it’s having on the lives of diabetes patients. We’ll also discuss the challenges and future directions of this transformative technology.
Introduction to the NHS Artificial Pancreas: Nhs Artificial Pancreas Diabetes Patients
Living with diabetes can be challenging, requiring constant monitoring and adjustments to manage blood sugar levels. The artificial pancreas, a revolutionary technology, offers a potential game-changer for people with diabetes. This blog post delves into the NHS’s involvement in artificial pancreas research and development, exploring its potential benefits and how it could transform diabetes management.
The Artificial Pancreas: A Technological Marvel
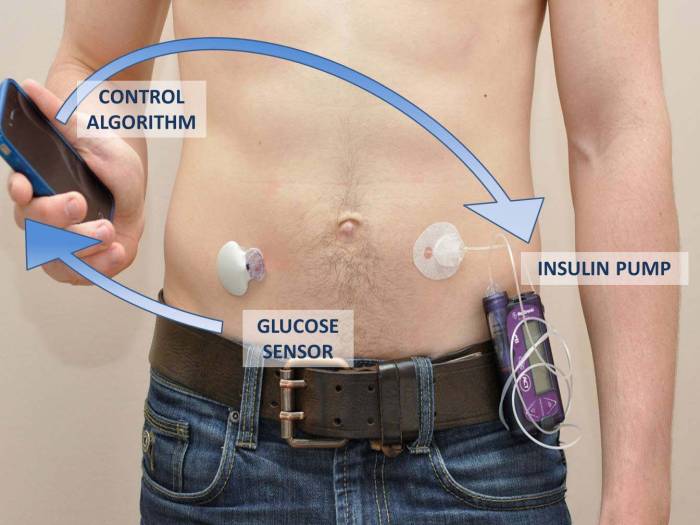
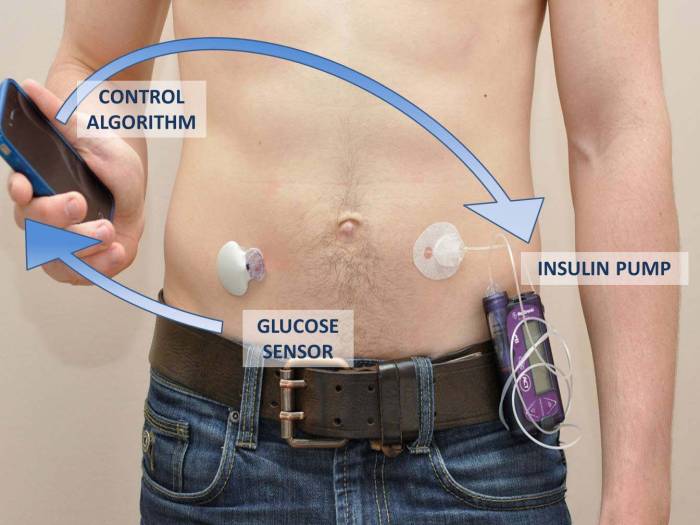
The artificial pancreas is a closed-loop system that automatically regulates blood sugar levels, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas. It typically comprises three components: a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), an insulin pump, and an algorithm. The CGM continuously monitors blood sugar levels, sending this data to the algorithm.
The algorithm analyzes the information and calculates the appropriate insulin dose, which is then delivered by the insulin pump. This closed-loop system operates in real-time, providing a more consistent and accurate blood sugar control compared to traditional methods.
Benefits of the Artificial Pancreas for Diabetes Patients
The artificial pancreas holds immense potential for improving the quality of life for diabetes patients. It offers several benefits, including:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control:By continuously monitoring and adjusting insulin delivery, the artificial pancreas can significantly reduce blood sugar fluctuations, minimizing the risk of dangerous highs and lows.
- Reduced Hypoglycemia Risk:The artificial pancreas’s ability to predict and prevent low blood sugar levels is a significant advantage, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia, a potentially life-threatening condition.
- Increased Freedom and Flexibility:The artificial pancreas allows individuals to manage their diabetes with greater freedom and flexibility. It reduces the need for frequent finger pricking and manual insulin injections, allowing for a more spontaneous lifestyle.
- Improved Quality of Life:By reducing the burden of diabetes management, the artificial pancreas can improve overall well-being, reducing stress and anxiety associated with the condition.
The NHS’s Role in Artificial Pancreas Research and Development
The NHS has been actively involved in artificial pancreas research and development, playing a vital role in its advancement. The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) has funded numerous clinical trials evaluating the safety and effectiveness of artificial pancreas systems.
- Clinical Trials:The NHS has conducted several large-scale clinical trials involving artificial pancreas systems, gathering valuable data on their efficacy and safety in real-world settings.
- Collaboration with Industry:The NHS has collaborated with leading medical technology companies to develop and refine artificial pancreas systems, ensuring their compatibility with existing healthcare infrastructure.
- Patient Engagement:The NHS prioritizes patient engagement in artificial pancreas research, involving patients in the design and evaluation of these systems, ensuring they meet the needs and preferences of users.
How the Artificial Pancreas Works
The artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop insulin delivery system, is a revolutionary technology that automates insulin delivery for people with type 1 diabetes. It’s designed to mimic the function of a healthy pancreas, constantly monitoring blood glucose levels and delivering the appropriate amount of insulin to keep them within a target range.
Components of the Artificial Pancreas System
The artificial pancreas system comprises several key components that work together seamlessly:
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM):This device continuously measures blood glucose levels through a small sensor inserted under the skin. The CGM transmits data wirelessly to the insulin pump.
- Insulin Pump:This device delivers insulin through a small tube inserted under the skin. The pump is programmed to deliver insulin based on the blood glucose readings received from the CGM.
- Control Algorithm:This software program processes the blood glucose data from the CGM and calculates the amount of insulin needed to maintain target blood glucose levels. The algorithm is designed to adjust insulin delivery in real-time, anticipating fluctuations in blood glucose.
How the System Monitors Blood Glucose Levels and Delivers Insulin
The artificial pancreas system operates on a continuous feedback loop. Here’s how it works:
- Blood Glucose Monitoring:The CGM continuously monitors blood glucose levels and transmits the data to the insulin pump.
- Insulin Calculation:The control algorithm analyzes the blood glucose data and calculates the appropriate amount of insulin needed to maintain target levels. The algorithm takes into account factors such as meal times, physical activity, and individual patient characteristics.
- Insulin Delivery:The insulin pump receives instructions from the algorithm and delivers the calculated amount of insulin through a small tube inserted under the skin.
- Feedback Loop:The system continuously monitors blood glucose levels, adjusts insulin delivery based on the data, and repeats the cycle to maintain blood glucose within the target range.
Technology Behind the Artificial Pancreas
The development of the artificial pancreas has been driven by significant advancements in several key areas:
- Miniaturization and Wireless Technology:The components of the artificial pancreas system, particularly the CGM and insulin pump, have become smaller and more portable, making them more user-friendly and discreet.
- Advanced Control Algorithms:The control algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated, incorporating machine learning and artificial intelligence to predict blood glucose fluctuations and optimize insulin delivery.
- Improved Sensor Technology:Continuous glucose monitors have become more accurate and reliable, providing real-time data that enables more precise insulin delivery.
- User-Friendly Interfaces:The artificial pancreas systems are designed with intuitive interfaces that allow users to easily monitor their blood glucose levels, adjust settings, and manage their diabetes.
Eligibility and Access to the Artificial Pancreas
The artificial pancreas, a groundbreaking technology for managing type 1 diabetes, is gradually becoming available within the NHS. However, access to this life-changing device is not yet widespread and is subject to specific eligibility criteria. Understanding these criteria and the current availability of the artificial pancreas within the NHS is crucial for patients seeking this treatment option.
Eligibility Criteria for the Artificial Pancreas
Eligibility for the artificial pancreas within the NHS is determined by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, diabetes specialists, and nurses. The specific criteria may vary slightly depending on the local NHS trust, but generally include:
- A confirmed diagnosis of type 1 diabetes.
- Adequate glycemic control, despite optimal medication and lifestyle management.
- The ability to self-manage diabetes effectively, including regular blood glucose monitoring and insulin administration.
- The absence of any significant medical conditions that could interfere with the use of the artificial pancreas.
- The patient’s willingness and ability to participate in the ongoing monitoring and follow-up required for artificial pancreas therapy.
Availability of the Artificial Pancreas within the NHS
The artificial pancreas is currently available at a limited number of NHS hospitals and clinics. The rollout of this technology is ongoing, with more sites expected to offer it in the coming years.
Accessing the Artificial Pancreas
Patients who believe they may be eligible for the artificial pancreas should discuss their options with their diabetes healthcare team. The process for accessing the artificial pancreas typically involves:
- A referral from a GP or diabetes specialist to a specialist diabetes center.
- A comprehensive assessment by a multidisciplinary team, including a review of medical history, current diabetes management, and suitability for artificial pancreas therapy.
- If deemed eligible, the patient will be enrolled in a program that provides training and support for using the artificial pancreas.
- Ongoing monitoring and follow-up with the diabetes team to ensure optimal device function and patient well-being.
Impact on Diabetes Management
The artificial pancreas, also known as a closed-loop system, has the potential to revolutionize diabetes management by automating blood glucose control. This technology works by continuously monitoring blood sugar levels and delivering insulin doses automatically, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas.
Learn about more about the process of ai analysis sertraline antidepressant prescriptions in the field.
Improved Blood Glucose Control
The artificial pancreas can significantly improve blood glucose control by reducing the frequency and severity of both high and low blood sugar levels. This is achieved through its ability to automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time blood sugar readings.
Studies have shown that individuals using an artificial pancreas experience fewer episodes of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), leading to better overall glycemic control.
Reduced Risk of Complications
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is crucial for preventing long-term complications associated with diabetes. The artificial pancreas can play a vital role in reducing the risk of these complications by minimizing the time spent with high or low blood sugar levels.
Some of the complications that can be reduced with improved blood glucose control include:
- Diabetic retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to vision loss.
- Diabetic nephropathy: Damage to the kidneys, which can lead to kidney failure.
- Diabetic neuropathy: Nerve damage, which can cause pain, numbness, and tingling.
- Cardiovascular disease: Heart disease and stroke, which are major causes of death among people with diabetes.
- Amputations: Loss of limbs due to poor blood flow and infection.
Enhanced Quality of Life
The artificial pancreas can significantly improve the quality of life for people with diabetes by reducing the burden of managing their condition. This technology allows individuals to experience greater freedom and flexibility in their daily routines, reducing the constant worry and stress associated with diabetes management.
Reduced Need for Frequent Blood Sugar Checks
With an artificial pancreas, individuals can reduce the number of blood sugar checks they need to perform each day. This is because the system continuously monitors blood sugar levels and automatically adjusts insulin delivery, eliminating the need for frequent manual checks.
This frees up time and reduces the inconvenience of having to prick their fingers multiple times a day.
Improved Sleep Quality
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is a common concern for people with diabetes, particularly at night. The artificial pancreas can help improve sleep quality by minimizing the risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia. This allows individuals to sleep soundly without worrying about waking up with low blood sugar levels.
Increased Flexibility in Diet and Exercise, Nhs artificial pancreas diabetes patients
The artificial pancreas can provide individuals with greater flexibility in their diet and exercise routines. This is because the system automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on changes in blood sugar levels, reducing the need for strict dietary restrictions and exercise schedules.
Challenges and Future Directions
While the artificial pancreas holds immense promise for improving diabetes management, several challenges remain before it becomes widely accessible and fully optimized.
Challenges in Widespread Adoption
The widespread adoption of the artificial pancreas is hindered by several factors.
- Cost and Insurance Coverage:The current cost of artificial pancreas systems can be a significant barrier for many individuals. Insurance coverage for these devices varies widely, and the approval process can be lengthy and complex.
- Technical Complexity and Maintenance:Artificial pancreas systems require careful calibration and maintenance, which can be challenging for some users. Regular sensor replacements and software updates are also necessary, adding to the overall cost and complexity.
- Safety and Reliability:While the technology has advanced significantly, safety and reliability remain concerns. The possibility of malfunctions or inaccurate readings can lead to dangerous fluctuations in blood glucose levels.
- User Acceptance and Training:Some individuals may be hesitant to use a device that requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Adequate training and support are essential for ensuring user acceptance and proper device utilization.
Patient Experiences and Perspectives
The artificial pancreas has revolutionized diabetes management for many individuals, offering them a newfound sense of freedom and control over their condition. Real-life experiences of patients using this technology provide valuable insights into its impact on their lives and the challenges they face.
Impact on Daily Life
The artificial pancreas has significantly improved the quality of life for many diabetes patients. It has allowed them to regain a sense of normalcy, reducing the constant worry and stress associated with managing their blood sugar levels. This technology has enabled individuals to engage in activities they previously avoided due to the constraints of diabetes management, such as traveling, attending social events, and enjoying spontaneous meals.
Testimonials and Stories
“Before the artificial pancreas, I was constantly checking my blood sugar and adjusting my insulin doses. It was a huge burden, and I was always worried about having a hypo or hyper. Now, I can live my life without constantly thinking about my diabetes. It’s given me back my freedom.”
Sarah, Type 1 diabetes patient
“The artificial pancreas has been a game-changer for me. I used to be so tired all the time due to the constant fluctuations in my blood sugar. Now, I have more energy and feel much healthier overall.”
John, Type 1 diabetes patient
Challenges Faced by Patients
While the artificial pancreas offers significant benefits, it also presents some challenges for patients. One common concern is the potential for technical issues, such as device malfunctions or software glitches. These issues can be frustrating and require prompt attention. Another challenge is the need for ongoing monitoring and maintenance, including regular sensor changes and device calibration.
Benefits Experienced by Patients
The artificial pancreas has provided patients with several benefits, including:
- Improved blood sugar control
- Reduced risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia
- Increased freedom and flexibility in daily life
- Reduced anxiety and stress associated with diabetes management
- Enhanced quality of life