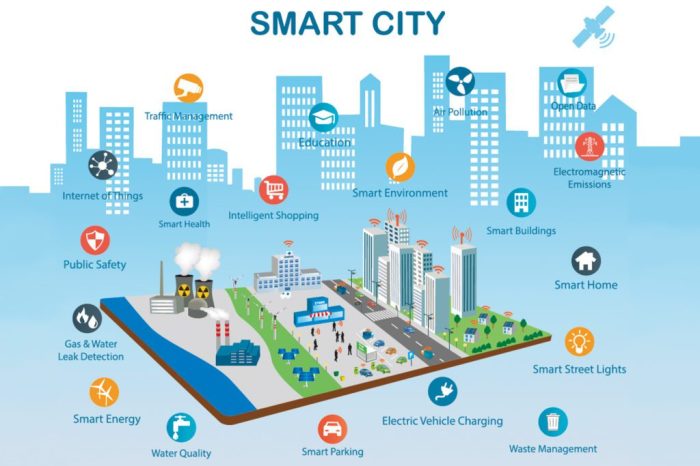
New tech trends smart cities of tomorrow are more than just a buzzword – they’re the blueprint for a future where technology seamlessly integrates with urban life, transforming the way we live, work, and interact with our environment. Imagine a city where traffic flows smoothly, energy is efficiently managed, and public services are personalized to meet individual needs.
This vision, once a futuristic dream, is rapidly becoming a reality as cities around the world embrace innovative technologies to address pressing challenges and create more sustainable, resilient, and equitable urban environments.
This exciting evolution is driven by a convergence of factors, including rapid urbanization, growing environmental concerns, and the ever-increasing power of data and artificial intelligence. From self-driving cars and smart grids to interconnected sensors and data-driven decision-making, these technologies are reshaping urban landscapes and offering unprecedented opportunities to improve the quality of life for millions of citizens.
The Rise of Smart Cities: New Tech Trends Smart Cities Of Tomorrow
The concept of smart cities is rapidly gaining momentum, transforming urban landscapes into interconnected ecosystems that leverage technology to enhance quality of life, improve efficiency, and address pressing challenges.
Driving Forces Behind Smart City Development
The development of smart cities is driven by a confluence of factors, including population growth, urbanization, technological advancements, and a growing need for sustainable solutions.
- Rapid Urbanization:As populations continue to migrate to urban centers, cities are facing increasing pressure on resources, infrastructure, and services. Smart city initiatives aim to manage these challenges by optimizing resource allocation and enhancing urban planning.
- Technological Advancements:The proliferation of sensors, internet of things (IoT) devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics has created a fertile ground for smart city applications. These technologies enable real-time data collection, analysis, and insights that can inform decision-making and optimize urban operations.
- Sustainability Concerns:Climate change, resource depletion, and environmental degradation are pressing concerns that smart cities are addressing through initiatives that promote energy efficiency, reduce waste, and improve air quality. Smart technologies can help monitor environmental conditions, optimize resource consumption, and promote sustainable practices.
- Citizen Engagement and Participation:Smart city initiatives aim to empower citizens by providing them with access to information, services, and platforms for participation. By leveraging technology, cities can foster transparency, improve communication, and create more responsive and inclusive urban environments.
Examples of Leading Smart Cities
Several cities around the world are leading the way in smart city initiatives, showcasing innovative approaches to urban challenges.
- Singapore:Known for its forward-thinking approach, Singapore has implemented a comprehensive smart city strategy, leveraging technology to enhance its transportation system, improve public safety, and promote sustainability. The city-state has invested heavily in sensors, data analytics, and smart infrastructure to create a more efficient and livable urban environment.
- Barcelona, Spain:Barcelona has embraced a citizen-centric approach to smart city development, focusing on improving the quality of life for residents. The city has implemented initiatives such as smart street lighting, public Wi-Fi networks, and a platform for citizen engagement to enhance public services and create a more connected community.
- Amsterdam, Netherlands:Amsterdam has adopted a holistic approach to smart city development, integrating technology across various sectors. The city has implemented smart traffic management systems, smart waste collection, and a digital platform for citizen services to optimize urban operations and enhance sustainability.
- Seoul, South Korea:Seoul has emerged as a global leader in smart city technology, focusing on leveraging technology to improve mobility, safety, and environmental sustainability. The city has implemented initiatives such as smart parking systems, real-time traffic monitoring, and a network of smart sensors to create a more efficient and resilient urban environment.
Challenges and Opportunities of Smart City Development, New tech trends smart cities of tomorrow
While smart cities hold immense potential, their development also presents challenges and opportunities that need to be addressed.
- Data Privacy and Security:The collection and use of vast amounts of data in smart cities raise concerns about data privacy and security. Robust cybersecurity measures and transparent data governance frameworks are crucial to protect citizen data and ensure responsible data usage.
- Digital Divide and Accessibility:The benefits of smart city initiatives may not be accessible to all citizens, particularly those who lack access to technology or digital literacy. Cities need to address the digital divide and ensure that smart city solutions are inclusive and equitable.
- Infrastructure Investment and Technological Integration:Implementing smart city initiatives requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and skilled personnel. Cities need to develop sustainable funding models and collaborate with private sector partners to bridge the funding gap and ensure successful technological integration.
- Public Acceptance and Engagement:Public acceptance and engagement are crucial for the success of smart city initiatives. Cities need to effectively communicate the benefits of smart city technologies, address concerns, and empower citizens to participate in the development and implementation of these solutions.
Investigate the pros of accepting vinyl industry mess british company tech fix elasticstage in your business strategies.
Emerging Technologies Shaping Smart Cities
Smart cities are not just a futuristic vision; they are rapidly becoming a reality, driven by the convergence of various emerging technologies. These technologies are transforming urban environments, improving the quality of life for citizens, and making cities more sustainable and efficient.
Transportation
Transportation is a key area where smart technologies are making a significant impact. By integrating advanced technologies, cities can optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve public transportation.
- Autonomous Vehicles:Self-driving cars and buses are revolutionizing urban transportation. They have the potential to improve safety, reduce traffic congestion, and increase accessibility for people with disabilities. Cities like Singapore and Dubai are already piloting autonomous vehicle programs.
- Intelligent Traffic Management Systems:These systems use sensors, cameras, and data analytics to monitor traffic flow in real-time, optimize traffic signal timing, and provide real-time information to drivers. This helps to reduce congestion and improve travel times.
- Smart Parking:Smart parking systems use sensors and mobile apps to help drivers find available parking spaces quickly, reducing the time spent circling for parking. Cities like San Francisco and London are implementing smart parking solutions.
- Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS):MaaS platforms integrate various transportation options, such as buses, trains, taxis, and ride-sharing services, into a single platform. This allows users to plan their journeys seamlessly, regardless of the mode of transportation.
Energy
Smart cities are leveraging technology to improve energy efficiency and sustainability. By integrating smart grids, renewable energy sources, and energy management systems, cities can reduce their carbon footprint and create more resilient energy systems.
- Smart Grids:Smart grids use advanced technologies to monitor and control energy flow in real-time. They can optimize energy distribution, reduce energy losses, and integrate renewable energy sources more effectively.
- Renewable Energy Integration:Smart cities are increasingly adopting renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. By integrating these sources into the grid, cities can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and lower their carbon emissions.
- Energy Management Systems:Building management systems use sensors and data analytics to monitor energy consumption and identify areas for improvement. This can help reduce energy waste and lower energy costs.
- Demand Response:Demand response programs allow utilities to incentivize consumers to reduce their energy consumption during peak hours. This helps to reduce strain on the grid and avoid blackouts.
Infrastructure
Smart cities are using technology to improve the efficiency and resilience of their infrastructure, including water management, waste management, and public safety.
- Smart Water Management:Smart water management systems use sensors and data analytics to monitor water usage, detect leaks, and optimize water distribution. This helps to reduce water waste and ensure water security.
- Smart Waste Management:Smart waste management systems use sensors to monitor waste levels in bins and optimize waste collection routes. This reduces waste collection costs and improves sanitation.
- Smart Lighting:Smart lighting systems use sensors to adjust street lighting based on real-time conditions, reducing energy consumption and improving public safety.
- Public Safety:Smart cities are using technology to improve public safety, including surveillance cameras, facial recognition software, and emergency response systems.
Smart City Infrastructure
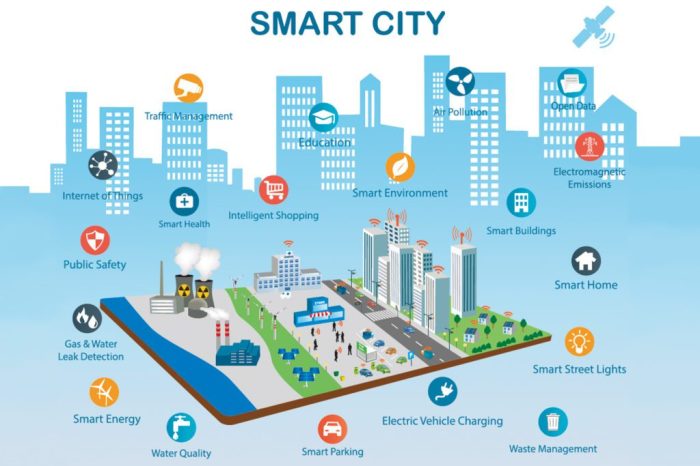
A smart city’s infrastructure is its backbone, connecting various systems and services to create a cohesive and efficient urban environment. It encompasses physical, digital, and social elements that work together to enhance the quality of life for residents.
Components of Smart City Infrastructure
The components of smart city infrastructure are interconnected and interdependent, forming a complex ecosystem.
- Sensors and Data Collection:These are the eyes and ears of the smart city, gathering real-time data on various aspects of urban life, including traffic flow, air quality, and energy consumption. Examples include traffic sensors, air quality monitors, and smart meters.
- Communication Networks:These networks act as the nervous system, transmitting data collected by sensors to processing centers and enabling communication between different systems. Examples include fiber optic cables, wireless networks, and 5G infrastructure.
- Data Processing and Analytics:This is the brain of the smart city, analyzing data collected by sensors and extracting valuable insights to optimize city operations. Advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence play a crucial role in this process.
- Smart Applications and Services:These are the applications that leverage data and insights to provide residents with improved services and experiences. Examples include intelligent traffic management systems, smart parking solutions, and personalized city information platforms.
- Smart Infrastructure:This refers to the physical infrastructure that is equipped with sensors, actuators, and communication capabilities to enhance its efficiency and responsiveness. Examples include smart street lighting, smart buildings, and intelligent water management systems.
Role of Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are crucial for optimizing city operations and improving the efficiency of smart city infrastructure.
- Predictive Maintenance:AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors and predict potential failures in infrastructure components, enabling timely maintenance and reducing downtime. This is particularly relevant for critical infrastructure like power grids, water systems, and transportation networks.
- Traffic Management:AI-powered traffic management systems can analyze real-time traffic data to optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and improve travel times. These systems can also provide real-time information to drivers, helping them avoid traffic jams and plan their routes efficiently.
- Resource Optimization:AI can analyze data on energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation to identify patterns and optimize resource allocation. This can lead to significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
- Public Safety:AI-powered surveillance systems can analyze video feeds from cameras to detect suspicious activity, identify potential threats, and alert security personnel. These systems can also help in crime prevention and response.
Improving Public Safety, Transportation, and Resource Management
Smart city infrastructure can significantly improve public safety, transportation, and resource management.
- Public Safety:Smart lighting systems can deter crime by providing better visibility in public spaces. AI-powered surveillance systems can help identify potential threats and respond quickly to emergencies.
- Transportation:Intelligent traffic management systems can reduce congestion, improve traffic flow, and optimize public transportation routes. Smart parking solutions can help drivers find available parking spaces quickly and efficiently.
- Resource Management:Smart water management systems can monitor water consumption and detect leaks, reducing water waste and improving efficiency. Smart energy grids can optimize energy distribution and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
The Future of Smart Cities
The future of smart cities is an exciting landscape filled with potential advancements that promise to transform urban living. From the integration of cutting-edge technologies to the emergence of new urban planning paradigms, smart cities are poised to become more sustainable, efficient, and livable.
Timeline of Potential Advancements
The evolution of smart city technologies is a continuous process, with innovations emerging at an accelerated pace. A timeline can provide a glimpse into potential advancements and their expected impact on urban environments:
- 2025-2030:Widespread adoption of 5G networks will enable faster data transfer and connectivity, paving the way for real-time data analysis and seamless communication between devices and infrastructure. This will facilitate the development of advanced applications such as autonomous vehicles, smart grids, and immersive virtual reality experiences.
- 2030-2035:Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a crucial role in optimizing city operations. AI-powered systems will analyze data from various sources, including sensors, traffic cameras, and social media, to predict traffic patterns, manage energy consumption, and improve public safety.
- 2035-2040:The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) will connect billions of devices, creating a vast network of interconnected systems. Smart homes, buildings, and infrastructure will communicate with each other, enabling automated processes and enhanced efficiency.
- 2040-2045:The integration of blockchain technology will create secure and transparent systems for managing data and transactions. This will improve the efficiency of city services, enhance citizen engagement, and foster trust in government institutions.
Key Trends Shaping Urban Development
Several key trends are shaping the future of urban development, driving the transformation of cities into smart and sustainable environments:
- Data-Driven Decision Making:Smart cities are leveraging data analytics to gain insights into urban processes, optimize resource allocation, and improve service delivery. This data-driven approach enables city planners and policymakers to make informed decisions based on real-time information.
- Sustainable Urbanism:Sustainability is a core principle of smart city development. Cities are adopting green building practices, promoting renewable energy sources, and implementing smart transportation systems to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Citizen Engagement and Participation:Smart cities are fostering greater citizen engagement by providing platforms for feedback, collaboration, and co-creation. This participatory approach empowers residents to contribute to the development and improvement of their communities.
- Vertical Urbanism:As urban populations grow, cities are increasingly turning to vertical urbanism, which involves building upwards to maximize land use. This trend is driven by the need to accommodate increasing populations while preserving green spaces and minimizing urban sprawl.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While smart cities offer numerous benefits, they also raise ethical considerations and challenges that need to be addressed:
- Data Privacy and Security:The collection and use of vast amounts of personal data in smart cities raise concerns about privacy and security. It is crucial to establish robust data protection measures and ensure transparency in data collection and usage.
- Digital Divide:The benefits of smart city technologies may not be equally accessible to all residents. Ensuring equitable access to technology and digital literacy programs is essential to bridge the digital divide and prevent social exclusion.
- Job Displacement:Automation and AI-powered systems may lead to job displacement in certain sectors. It is important to develop strategies for retraining and upskilling workers to adapt to the changing job market.
- Algorithmic Bias:Algorithms used in smart city systems can perpetuate existing biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. It is crucial to develop algorithms that are fair, transparent, and accountable.