New eu battery regulations spell trouble for manufacturers tech giants – EU Battery Rules: Trouble for Tech and Manufacturers sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with personal blog style and brimming with originality from the outset. The European Union has unveiled strict new regulations aimed at transforming the battery industry, and these rules are poised to have a significant impact on manufacturers and tech giants alike.
From design and production to recycling and disposal, these regulations are set to redefine the entire battery lifecycle.
These regulations aim to address concerns surrounding battery production, environmental impact, and the need for a more sustainable approach to managing these crucial components. The EU is setting the bar high, demanding that manufacturers take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their batteries, from sourcing materials to ensuring proper recycling.
These regulations are a bold step towards a greener future for the battery industry, but they also pose a significant challenge for manufacturers and tech giants who will need to adapt their processes and practices to meet these new requirements.
The EU Battery Regulation: New Eu Battery Regulations Spell Trouble For Manufacturers Tech Giants
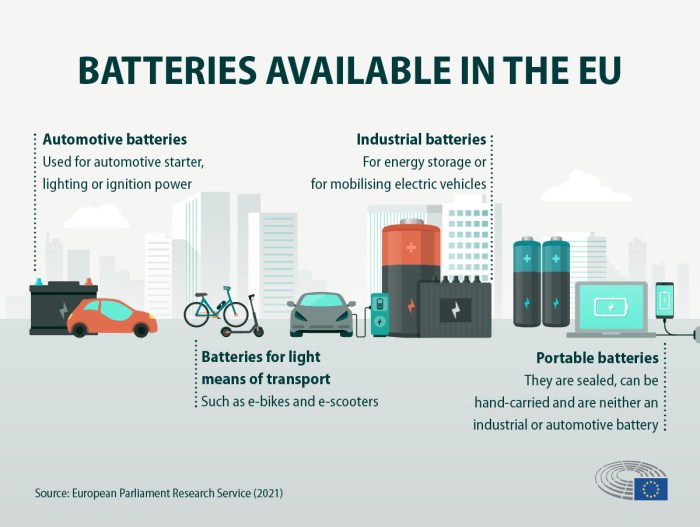
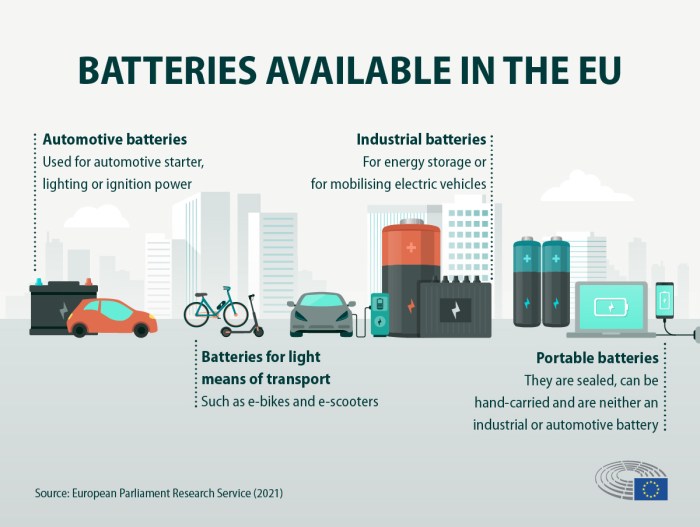
The EU Battery Regulation, officially known as Regulation (EU) 2020/852, is a landmark piece of legislation aimed at transforming the battery industry in Europe. It sets out a comprehensive framework for the entire battery lifecycle, from the sourcing of raw materials to the recycling of end-of-life batteries.
The regulation’s purpose is to ensure that batteries are sustainable, safe, and environmentally friendly, while also boosting Europe’s competitiveness in the rapidly growing battery market.The EU Battery Regulation establishes a wide range of requirements for batteries and battery manufacturers, encompassing various aspects of the battery lifecycle.
These requirements cover the design, composition, performance, and recycling of batteries. The regulation also introduces a “battery passport” system, which will provide detailed information about the battery’s origin, composition, and recycling potential.
The Regulation’s Impact on the Battery Lifecycle
The EU Battery Regulation has a significant impact on the entire battery lifecycle. It aims to promote sustainable battery production and consumption, while also ensuring the safe and environmentally sound management of end-of-life batteries.The regulation promotes the use of recycled materials in battery production.
Manufacturers are required to use a certain percentage of recycled materials in their batteries, with the target percentage increasing over time. This requirement encourages the development of robust recycling infrastructure and incentivizes the circular economy for batteries.
Requirements for Battery Design and Composition
The EU Battery Regulation sets out specific requirements for the design and composition of batteries. These requirements are aimed at improving battery performance, safety, and sustainability.One key requirement is the use of specific materials in battery production. The regulation restricts the use of certain hazardous substances, such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, in batteries.
It also encourages the use of environmentally friendly materials, such as lithium iron phosphate (LFP) for electric vehicle batteries.
Requirements for Battery Performance
The EU Battery Regulation also sets out requirements for the performance of batteries. These requirements are designed to ensure that batteries meet certain standards of performance, durability, and safety.One example of a performance requirement is the minimum capacity and lifespan of batteries.
The regulation specifies that batteries must meet certain performance criteria, such as the number of charge cycles and the retention of capacity over time. This ensures that batteries are reliable and can perform adequately throughout their lifespan.
The Battery Passport
The EU Battery Regulation introduces a “battery passport” system. This system will provide detailed information about the battery’s origin, composition, and recycling potential.The battery passport will contain information about the battery’s manufacturing process, the materials used, and the battery’s performance characteristics.
This information will be crucial for facilitating the recycling of batteries and ensuring that they are properly managed at the end of their life.
Challenges for Manufacturers
The new EU Battery Regulation presents a significant challenge for battery manufacturers, requiring them to adapt their production processes, design practices, and supply chains to meet the stringent requirements. These regulations aim to ensure the sustainability and safety of batteries throughout their lifecycle, from production to recycling.
However, this transition comes with substantial costs and complexities that manufacturers must navigate.
Impact on Production Costs
The new regulations will increase production costs for manufacturers in several ways. First, the requirement to use recycled materials in battery production will necessitate the development of new sourcing and processing technologies, which can be expensive. Second, the regulations mandate the use of specific materials, such as cobalt, which are subject to price volatility and potential supply chain disruptions.
Finally, the regulations require manufacturers to invest in new testing and certification processes to ensure compliance, adding to the overall cost of production.
Impact on Design Processes
The EU Battery Regulation requires manufacturers to design batteries that are easily recyclable and have a long lifespan. This will necessitate changes in design processes, including the use of modular components, the selection of easily separable materials, and the optimization of battery chemistry for longevity.
Check what professionals state about now you can try the one person vtol jetracer and its benefits for the industry.
These changes will require significant investment in research and development and may impact existing product designs, potentially leading to longer development cycles and delays in product launches.
Impact on Supply Chains
The regulations have implications for the entire battery supply chain, requiring manufacturers to ensure the ethical and sustainable sourcing of materials. This will involve establishing robust traceability systems, verifying the origin of materials, and collaborating with suppliers to implement sustainable practices.
Additionally, manufacturers will need to adapt their supply chains to incorporate the collection and recycling of end-of-life batteries, potentially requiring investments in new infrastructure and partnerships with recycling companies.
Challenges for Different Types of Battery Manufacturers
The challenges posed by the new regulations will vary depending on the type of battery manufacturer. For example, manufacturers of lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used in electric vehicles and consumer electronics, will face significant challenges in sourcing materials and adapting their production processes to comply with the new regulations.
Manufacturers of lead-acid batteries, traditionally used in cars and stationary applications, will need to invest in new technologies to improve their recycling capabilities. Manufacturers of emerging battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, will need to demonstrate compliance with the regulations early in their development process.
Impact on Tech Giants
The EU Battery Regulation’s impact on tech giants like Apple, Samsung, and Google will be significant, forcing them to adapt their product development, manufacturing, and sales strategies to comply with the new rules. These regulations will not only influence the design and composition of batteries but also impact the entire lifecycle of these products, from sourcing materials to recycling.
Implications for Product Development
The EU Battery Regulation will necessitate changes in product design and development for tech giants. The regulation requires manufacturers to use a minimum percentage of recycled materials in their batteries, which could influence the choice of materials and battery chemistry.
Additionally, the regulations emphasize the need for longer battery life and improved performance, pushing tech giants to invest in research and development to achieve these goals.
- Increased Research and Development:Tech giants will need to invest heavily in R&D to develop batteries that meet the new sustainability and performance requirements. This could involve exploring new battery chemistries, like solid-state batteries, and optimizing existing ones.
- Material Sourcing and Recycling:Companies will need to ensure they have access to sustainable and ethically sourced materials, including recycled materials, to meet the new regulations. This will require collaboration with suppliers and investments in recycling infrastructure.
- Product Design Modifications:The regulations could lead to changes in product design, particularly for devices with batteries. This might involve optimizing battery size and placement to maximize battery life and minimize environmental impact.
Implications for Manufacturing
The EU Battery Regulation will also affect the manufacturing processes of tech giants. The regulation requires manufacturers to ensure that batteries can be easily disassembled and recycled, which will necessitate changes in manufacturing practices. Additionally, the regulation’s emphasis on transparency and traceability will require companies to implement robust tracking systems for their batteries.
- Modular Design:Tech giants may need to adopt modular designs for their products, allowing for easier disassembly and recycling. This could lead to more complex manufacturing processes and potentially higher production costs.
- Traceability and Transparency:Companies will need to implement systems to track the origin of materials and the entire lifecycle of their batteries. This will require investments in technology and data management systems.
- Manufacturing Infrastructure:The new regulations could require tech giants to adapt their existing manufacturing facilities or invest in new ones to comply with the new standards for battery recycling and disposal.
Implications for Sales and Marketing Strategies
The EU Battery Regulation will also have implications for sales and marketing strategies of tech giants. The regulation requires manufacturers to provide consumers with clear information about the battery’s performance, lifespan, and recyclability. This will require companies to adapt their marketing materials and communicate the environmental benefits of their products.
- Transparency and Labeling:Companies will need to provide detailed information about their batteries, including their environmental impact, lifespan, and recycling capabilities, on product packaging and online platforms. This will require new labeling and information systems.
- Marketing Focus on Sustainability:Tech giants will need to emphasize the sustainability aspects of their products in their marketing campaigns. This could involve highlighting the use of recycled materials, battery lifespan, and recycling programs.
- Consumer Education:Companies may need to invest in consumer education programs to inform consumers about the new battery regulations and the importance of responsible battery disposal.
Impact on Key Tech Products, New eu battery regulations spell trouble for manufacturers tech giants
The EU Battery Regulation will have a significant impact on key tech products, particularly those with integrated batteries, such as smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. The table below summarizes the potential impact on these products:
| Product | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Smartphones |
|
| Laptops |
|
| Electric Vehicles |
|
Environmental Implications
The EU Battery Regulation is not just about technological advancements; it’s also about safeguarding our planet. The regulations aim to reduce the environmental impact of battery production, use, and disposal, promoting a more sustainable future for this crucial technology.
Impact on Battery Recycling and Waste Management Practices
The regulations mandate that manufacturers collect and recycle a significant percentage of the batteries they place on the market. This requirement pushes for improved battery recycling infrastructure and incentivizes the development of more efficient recycling processes.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR):The EU Battery Regulation strengthens the principle of EPR, making manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including end-of-life management. This encourages manufacturers to design batteries with recyclability in mind, minimizing waste and maximizing resource recovery.
- Recycling Targets:The regulation sets specific recycling targets for different battery types, pushing for higher recovery rates of critical materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These targets drive innovation in recycling technologies, leading to more efficient and environmentally friendly processes.
- Waste Management Practices:The regulations promote the development of efficient battery collection and sorting systems, ensuring proper handling and disposal of used batteries. This helps prevent hazardous materials from contaminating the environment and ensures responsible waste management practices.
Innovative Technologies for Sustainable Battery Production and Disposal
The EU Battery Regulation encourages innovation in battery production and disposal, paving the way for more sustainable practices.
- Closed-Loop Recycling:The regulation promotes the development of closed-loop recycling systems, where valuable materials are recovered and reused in new battery production. This reduces reliance on virgin materials and minimizes environmental impact.
- Sustainable Materials:The regulations incentivize the use of sustainable materials in battery production, such as recycled materials, bio-based materials, and materials with lower environmental footprints. This reduces the overall environmental impact of battery production.
- Battery Design for Recyclability:The regulations encourage manufacturers to design batteries with recyclability in mind, making it easier to separate and recover valuable materials at the end of their life. This facilitates efficient recycling and minimizes waste generation.
Consumer Perspectives
The EU’s new battery regulations will have a direct impact on consumers, affecting both the cost and availability of electronic devices. While the regulations aim to promote sustainability and environmental responsibility, it’s crucial to understand how these changes will affect everyday consumers.
Potential Impact on Battery Prices and Product Availability
The new regulations will likely lead to higher battery prices for manufacturers, which could be passed on to consumers. This is because the regulations require manufacturers to use recycled materials in batteries and adhere to stricter performance and safety standards.
The increased costs associated with sourcing recycled materials, conducting additional testing, and meeting new requirements will likely impact the overall cost of battery production. Additionally, the new regulations could potentially lead to limited product availability in the short term. Manufacturers may need to adjust their production processes and supply chains to comply with the new requirements, which could temporarily affect the availability of certain products.
However, in the long term, the regulations are expected to encourage innovation and the development of more sustainable and cost-effective battery technologies.
Increased Consumer Awareness and Demand for Sustainable Battery Products
The EU’s battery regulations are likely to increase consumer awareness of battery sustainability and environmental impact. As consumers become more informed about the environmental consequences of battery production and disposal, they are likely to demand more sustainable battery products. This could drive manufacturers to prioritize the use of recycled materials and invest in more environmentally friendly battery technologies.The regulations will also encourage manufacturers to be more transparent about the environmental footprint of their batteries.
This transparency could lead to increased consumer trust in brands that prioritize sustainability. Consumers may be more willing to pay a premium for products that are produced and disposed of responsibly, as they are becoming increasingly conscious of the environmental impact of their choices.
Pros and Cons of the New Regulations from a Consumer Perspective
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increased availability of sustainable battery products | Potentially higher battery prices |
| Improved battery performance and safety | Potential for limited product availability in the short term |
| Reduced environmental impact of battery production and disposal | Increased complexity in battery recycling and disposal processes |
| Greater transparency and accountability from manufacturers | Potential for increased costs for consumers |
Future Outlook
The EU Battery Regulation’s long-term impact on the battery industry is significant, influencing innovation, production, and sustainability. This regulation’s ripple effect extends beyond the EU, potentially inspiring similar regulations in other countries or regions. It also shapes the future of battery technology and innovation, prompting manufacturers to prioritize sustainable practices and advance battery performance.
Global Regulatory Landscape
The EU Battery Regulation sets a global precedent for battery regulations. It is likely to influence similar regulations in other countries and regions, particularly those focused on environmental sustainability and consumer protection. For example, the United States is currently developing its own battery regulations, drawing inspiration from the EU’s approach.
This global trend towards stricter battery regulations will likely lead to standardized practices and harmonized standards across the world.
Impact on Battery Technology and Innovation
The EU Battery Regulation fosters innovation in battery technology by incentivizing manufacturers to develop more sustainable and efficient batteries. The regulation’s focus on recyclability and resource efficiency will drive manufacturers to explore new materials and production processes. This, in turn, will lead to advancements in battery performance, lifespan, and safety.
The regulation also encourages the development of innovative recycling technologies, enabling the recovery of critical minerals from end-of-life batteries. This circular economy approach is crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for the battery industry.
Examples of Potential Advancements
Solid-state batteries
These batteries offer enhanced safety, energy density, and lifespan compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. The EU Battery Regulation’s focus on sustainability and innovation could accelerate the development and adoption of solid-state batteries, as they are less reliant on scarce materials and offer improved recyclability.
Next-generation lithium-ion batteries
The regulation’s emphasis on resource efficiency could encourage research and development of next-generation lithium-ion batteries that utilize alternative materials and optimize energy density. This would enhance battery performance while reducing reliance on critical minerals.
Recycling technologies
The EU Battery Regulation’s emphasis on recyclability will likely drive innovation in battery recycling technologies. This includes advancements in hydrometallurgical processing, which can efficiently recover valuable metals from end-of-life batteries.