NATO Backs Dutch Underwater Robots: This isn’t a scene from a sci-fi movie, it’s the reality of modern warfare. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is investing in Dutch underwater robots, a move that signals the increasing reliance on technology in the modern battlefield.
These robots are not just toys, they are cutting-edge tools designed to navigate the depths and perform tasks that are too dangerous or impossible for human divers.
These robots are capable of a wide range of missions, including mine detection, surveillance, and reconnaissance. Their ability to operate autonomously in hostile environments makes them invaluable assets in the fight against terrorism, piracy, and other threats. This support from NATO highlights the strategic importance of underwater robotics in modern warfare, and it’s likely to have a significant impact on Dutch defense capabilities and maritime security.
NATO’s Support for Dutch Underwater Robots
NATO’s support for the development and deployment of Dutch underwater robots is a significant strategic initiative that underscores the alliance’s commitment to maintaining maritime security and technological advancement. This collaborative effort aims to enhance the capabilities of NATO members in countering emerging threats in the underwater domain.
Types of Underwater Robots Supported
NATO’s support encompasses a range of underwater robots, each designed to fulfill specific operational roles. These robots can be broadly categorized into two main types:
- Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs): These robots operate independently, navigating and executing missions without direct human control. AUVs are equipped with advanced sensors and navigation systems, allowing them to perform tasks such as seabed mapping, underwater surveillance, and data collection.
- Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs): ROVs are tethered to a surface vessel, enabling operators to control their movements and actions in real-time. These robots are often equipped with powerful cameras, manipulator arms, and specialized tools, making them suitable for tasks such as underwater inspection, maintenance, and even intervention operations.
Get the entire information you require about chip designer arm files for public listing that could revive flat ipo market on this page.
Capabilities of Dutch Underwater Robots
Dutch underwater robots are known for their advanced capabilities, contributing significantly to NATO’s maritime security efforts. Some key capabilities include:
- High-resolution sonar imaging: Dutch robots are equipped with state-of-the-art sonar systems capable of generating detailed images of the seabed, enabling the detection of underwater objects, potential threats, and submerged infrastructure.
- Advanced navigation and autonomy: Dutch robots leverage sophisticated navigation systems and artificial intelligence algorithms, allowing them to operate autonomously for extended periods, navigate complex underwater environments, and perform complex tasks.
- Data collection and analysis: Dutch robots are capable of collecting vast amounts of data from the underwater environment, including acoustic, optical, and chemical data. This data is analyzed to provide valuable insights into marine ecosystems, identify potential threats, and support scientific research.
Strategic Significance of NATO Support
NATO’s support for Dutch underwater robots holds significant strategic implications for the alliance’s overall defense posture:
- Enhanced maritime security: Underwater robots contribute to maintaining maritime security by detecting and deterring threats, such as illegal activities, underwater sabotage, and potential hostile operations.
- Technological advantage: By supporting the development and deployment of advanced underwater robots, NATO strengthens its technological edge in the maritime domain, ensuring its ability to counter evolving threats.
- Interoperability and collaboration: This initiative promotes interoperability among NATO members, facilitating information sharing and joint operations involving underwater robots.
The Role of Underwater Robots in Modern Warfare
The realm of modern warfare has seen a dramatic shift, with underwater robots emerging as powerful tools that are revolutionizing naval operations. These autonomous machines, equipped with advanced sensors and capabilities, are proving their worth in various military applications, offering significant advantages over traditional methods.
Capabilities of Underwater Robots Compared to Human Divers
The capabilities of underwater robots are distinct from those of human divers, each possessing unique strengths and limitations.
- Endurance:Underwater robots can operate for extended periods, even in harsh environments, without experiencing fatigue or decompression sickness, unlike human divers who are limited by their physiological constraints.
- Depth:Underwater robots can reach depths far beyond the capabilities of human divers, allowing for exploration and operation in previously inaccessible areas.
- Precision:Underwater robots are capable of executing complex tasks with precision, such as manipulating objects or deploying explosives, which may be challenging for human divers.
- Payload:Underwater robots can carry heavier payloads than human divers, enabling them to transport equipment or weapons for specific missions.
- Data Collection:Underwater robots are equipped with advanced sensors that can collect detailed data, including sonar images, video footage, and environmental readings, providing valuable intelligence for strategic decision-making.
- Human Expertise:Human divers possess the ability to make nuanced decisions and adapt to unexpected situations, which may be challenging for robots.
- Problem-Solving:Human divers can troubleshoot complex problems in real-time, while robots require pre-programmed solutions or human intervention.
- Situational Awareness:Human divers have a broader understanding of the underwater environment and can react to unforeseen circumstances more effectively than robots.
Key Applications of Underwater Robots in Warfare
Underwater robots are proving their value in various military applications, particularly in:
- Mine Detection:Underwater robots are increasingly used for detecting and neutralizing mines, minimizing the risk to human divers and enhancing maritime security.
- Surveillance and Reconnaissance:Underwater robots can conduct covert surveillance operations, gathering intelligence on enemy activities, infrastructure, or potential threats. Their stealthy nature and advanced sensors make them ideal for reconnaissance missions.
- Target Acquisition:Underwater robots can be deployed to identify and track targets, providing crucial information for precision strikes and minimizing collateral damage.
- Underwater Infrastructure Inspection:Underwater robots can be used to inspect and maintain critical underwater infrastructure, such as pipelines, cables, and maritime structures, ensuring their operational integrity and safety.
Ethical Implications of Underwater Robots in Warfare
The use of underwater robots in warfare raises important ethical concerns, including:
- Autonomous Decision-Making:The increasing autonomy of underwater robots raises concerns about the potential for unintended consequences or miscalculations, especially in situations involving human life.
- Lack of Accountability:Determining accountability for actions taken by autonomous underwater robots can be challenging, raising questions about responsibility and legal liability.
- Potential for Misuse:The advanced capabilities of underwater robots could be exploited for malicious purposes, such as sabotage or espionage, raising concerns about national security and international stability.
- Environmental Impact:The deployment of underwater robots may have unintended environmental consequences, such as disturbing marine life or polluting the ocean.
Technological Advancements in Underwater Robotics: Nato Backs Dutch Underwater Robots
The field of underwater robotics is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in sensor capabilities, autonomy, and endurance. These innovations are transforming the way we explore, monitor, and interact with the underwater world, opening up new possibilities for both military and civilian applications.
Advancements in Underwater Robotics
| Advancement | Description | Impact on Capabilities | Future Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improved Sensor Capabilities | Modern underwater robots are equipped with sophisticated sensors, including sonar, cameras, and laser scanners, which provide high-resolution data for mapping, object identification, and environmental monitoring.
For example, multibeam sonar systems are capable of generating detailed bathymetric maps of the seafloor, while synthetic aperture sonar (SAS) can penetrate sediment layers to detect buried objects. Advanced cameras with high-definition imaging and low-light capabilities allow for visual inspection of underwater structures and the identification of marine life. |
Enhanced situational awareness, improved target identification, and more accurate data collection for scientific research and environmental monitoring. | Development of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) capable of conducting detailed seabed surveys for oil and gas exploration, mapping marine ecosystems, and detecting underwater hazards. |
| Increased Autonomy | Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have enabled the development of autonomous underwater robots that can navigate and perform tasks without human intervention.
These robots can plan their own routes, avoid obstacles, and adapt to changing environmental conditions. For example, AUVs are being used for tasks such as underwater inspection of pipelines, surveillance of maritime borders, and data collection for oceanographic research. |
Extended mission durations, reduced human risk in hazardous environments, and increased efficiency in data collection and analysis. | Deployment of swarms of autonomous robots for collaborative tasks, such as underwater search and rescue operations, environmental monitoring, and infrastructure inspection. |
| Enhanced Endurance | Improvements in battery technology and energy management systems have significantly increased the operational time of underwater robots.
For example, some AUVs can now operate for several days or even weeks on a single charge, enabling them to undertake long-duration missions and cover vast distances. |
Increased mission range and duration, allowing for more extensive exploration and data collection. | Development of hybrid-powered AUVs that can utilize multiple energy sources, such as solar power and fuel cells, for extended operation in remote areas. |
The Impact of NATO’s Support on Dutch Defense Capabilities
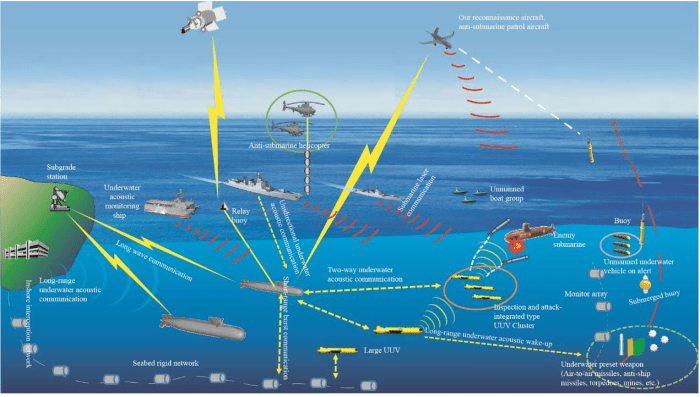
NATO’s support for Dutch underwater robots is a significant boost to the Netherlands’ defense capabilities, particularly in the realm of maritime security and defense. This support is not just about providing advanced technology; it’s about fostering collaboration, sharing expertise, and strengthening the Netherlands’ role within NATO’s collective defense framework.
Impact on Dutch Maritime Security and Defense
The strategic implications of NATO’s support for Dutch underwater robots are far-reaching. These robots enhance the Netherlands’ ability to monitor and protect its vast maritime territory, including vital shipping lanes and critical infrastructure. They provide a significant advantage in detecting and deterring threats, such as illegal activities, potential attacks, and environmental damage.
Impact on Dutch Role Within NATO
The Netherlands’ enhanced capabilities, thanks to NATO’s support, contribute significantly to collective security efforts. These robots allow the Netherlands to actively participate in NATO operations, share intelligence, and contribute to the overall maritime security of the alliance. This strengthens the Netherlands’ standing within NATO and demonstrates its commitment to collective defense.
Impact on Various Aspects of Dutch Defense
The following table Artikels the impact of NATO’s support for Dutch underwater robots on various aspects of Dutch defense:
| Area of Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Maritime Surveillance and Security | The robots enhance the Netherlands’ ability to monitor and protect its maritime territory, including critical infrastructure and shipping lanes. This capability is crucial for deterring illegal activities, potential attacks, and environmental damage. |
| Underwater Warfare | These robots provide a significant advantage in underwater warfare scenarios, enabling the Netherlands to detect, track, and potentially neutralize threats in the underwater domain. This enhances the Netherlands’ ability to protect its maritime interests and contribute to NATO’s collective defense. |
| Intelligence Gathering and Analysis | The robots can gather real-time data on underwater activities, providing valuable intelligence that can be shared with NATO allies. This improves situational awareness and facilitates better decision-making in maritime security operations. |
| Training and Expertise | NATO’s support also involves training and knowledge sharing, enhancing the Netherlands’ expertise in operating and maintaining underwater robots. This ensures the effective utilization of these technologies and promotes a deeper understanding of their capabilities. |
The Global Landscape of Underwater Robotics
The world of underwater robotics is a dynamic and rapidly evolving field, with a diverse range of actors contributing to its development and application. From government agencies and research institutions to private companies, these stakeholders are driving innovation and shaping the future of underwater exploration, defense, and resource management.
Major Players in the Global Underwater Robotics Industry, Nato backs dutch underwater robots
The global underwater robotics industry is comprised of a diverse array of players, each contributing to the development and deployment of these innovative technologies. This includes government agencies, research institutions, and private companies, each with its own unique focus and priorities.
| Country/Organization | Key Focus | Notable Developments | Potential for Collaboration |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Military applications, scientific research, and commercial development | Development of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) for reconnaissance, surveillance, and mine countermeasures; advanced robotic systems for deep-sea exploration and resource extraction | Strong potential for international collaboration, particularly in areas such as oceanographic research, environmental monitoring, and disaster response |
| China | Rapidly expanding its underwater robotics capabilities, with a focus on military applications and resource exploration | Development of advanced AUVs and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) for naval operations, seabed mapping, and deep-sea mining | Increasingly engaging in international collaborations, particularly in areas such as oceanographic research and marine resource management |
| United Kingdom | Strong focus on research and development, with a particular emphasis on autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) | Development of advanced AUVs for scientific research, environmental monitoring, and offshore energy exploration | Active participant in international collaborations, particularly in areas such as oceanographic research and marine conservation |
| Japan | Longstanding expertise in underwater robotics, with a focus on both scientific and commercial applications | Development of advanced ROVs and AUVs for deep-sea exploration, resource extraction, and underwater construction | Strong potential for international collaboration, particularly in areas such as oceanographic research, disaster response, and underwater infrastructure development |
| France | Significant investments in underwater robotics, with a focus on both military and civilian applications | Development of advanced AUVs and ROVs for naval operations, scientific research, and offshore energy exploration | Active participant in international collaborations, particularly in areas such as oceanographic research, marine conservation, and underwater infrastructure development |
Approaches and Priorities of Different Countries in Developing and Deploying Underwater Robots
Countries around the world are pursuing diverse approaches to the development and deployment of underwater robots, driven by their unique strategic priorities, technological capabilities, and economic interests. These approaches often reflect a nation’s geopolitical landscape, national security concerns, and economic aspirations.
- Military Focus:Countries like the United States, China, and Russia prioritize the development of underwater robots for military applications, including reconnaissance, surveillance, and mine countermeasures. These nations invest heavily in research and development to enhance their underwater capabilities and maintain a strategic advantage.
- Scientific Research:Nations like Japan, the United Kingdom, and France emphasize the role of underwater robots in scientific research, exploring the ocean depths, studying marine life, and monitoring environmental changes. These countries invest in research institutions and collaborations to advance scientific understanding of the oceans.
- Commercial Applications:Countries like Norway, Canada, and Australia focus on the commercial applications of underwater robotics, particularly in sectors such as offshore energy, resource extraction, and underwater infrastructure development. These nations invest in private companies and initiatives to promote the adoption of underwater robots in these industries.
Potential for International Collaboration and Partnerships in the Field of Underwater Robotics
The global nature of the underwater robotics industry presents significant opportunities for international collaboration and partnerships. This collaboration can foster innovation, accelerate technological advancements, and address shared challenges related to ocean exploration, resource management, and environmental protection.
- Joint Research and Development:Collaboration between countries can enable the sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise, leading to more efficient and effective development of underwater robotics technologies. This can involve joint research projects, technology transfer, and the establishment of international research centers.
- International Standards and Regulations:Collaboration is essential for establishing international standards and regulations for the safe and responsible deployment of underwater robots, ensuring the protection of marine ecosystems and the responsible use of ocean resources.
- Data Sharing and Information Exchange:Sharing data and information collected by underwater robots can enhance scientific understanding, improve resource management, and support the development of new applications. International collaborations can facilitate the establishment of data sharing platforms and information exchange networks.





