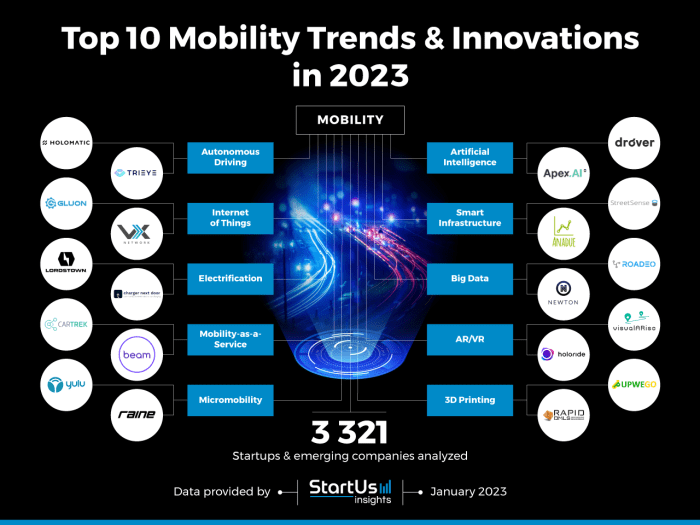
Key trends global mobility * – Key trends in global mobility are shaping our world in profound ways, driving changes in how we live, work, and travel. From the rise of remote work and digital nomadism to the evolving landscape of travel and tourism, global mobility is transforming societies and economies at an unprecedented pace.
This dynamic shift is fueled by a confluence of factors, including technological advancements, changing demographics, and a growing desire for experiences beyond borders. As we navigate this new era of mobility, understanding these trends is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments alike.
The Rise of Remote Work and Digital Nomadism: Key Trends Global Mobility *
The global mobility landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation, fueled by the rise of remote work and digital nomadism. This shift is reshaping how people live, work, and travel, leading to new opportunities and challenges.
Impact of Remote Work on Global Mobility Patterns
Remote work has fundamentally altered global mobility patterns, allowing individuals to work from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility has resulted in increased migration, particularly to destinations offering a desirable lifestyle, lower cost of living, and a more relaxed work environment.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting ai startup launches fastest data processing engine market today.
Remote work is also fostering the growth of “remote-first” companies, which are geographically dispersed and rely on technology to connect and collaborate. This trend is leading to a more diverse and international workforce, blurring traditional geographical boundaries.
Factors Driving the Growth of Digital Nomadism
Digital nomadism is a lifestyle choice where individuals travel the world while working remotely. The growth of digital nomadism is driven by several factors:
- Advancements in Technology:The proliferation of high-speed internet access and mobile devices has made it easier than ever to work remotely.
- Changing Work Culture:Many companies are embracing flexible work arrangements, allowing employees to work from anywhere.
- Desire for Travel and Adventure:Digital nomads are drawn to the opportunity to experience new cultures and explore different parts of the world.
- Cost of Living Considerations:Some destinations offer a lower cost of living compared to traditional work hubs, allowing digital nomads to stretch their budgets further.
Countries Attracting Digital Nomads
Several countries have embraced the digital nomad movement and implemented programs to attract remote workers. These countries often offer:
- Visas specifically designed for digital nomads:These visas allow individuals to stay for extended periods and work remotely.
- High-speed internet infrastructure:Reliable internet access is crucial for digital nomads.
- Co-working spaces and communities:These spaces provide a professional environment for remote workers and foster a sense of community.
- Affordable living costs:Lower living expenses make it easier for digital nomads to manage their finances.
Some notable examples include:
- Portugal:The “Digital Nomad Visa” allows individuals to stay for up to a year and work remotely.
- Costa Rica:The “Remote Worker Visa” offers a one-year visa for individuals working remotely.
- Thailand:The “Smart Visa” is designed for highly skilled professionals, including digital nomads.
- Estonia:The “e-Residency” program allows individuals to start and run a business online from anywhere in the world.
Challenges and Opportunities of Remote Work and Digital Nomadism
While remote work and digital nomadism offer numerous advantages, they also present unique challenges:
- Work-life balance:The blurred lines between work and personal life can be challenging for some individuals.
- Loneliness and isolation:Working remotely can lead to feelings of loneliness and isolation, particularly when traveling alone.
- Security and safety:Digital nomads need to be aware of security risks, both online and offline.
- Cultural differences:Adapting to different cultures and languages can be challenging.
Despite these challenges, remote work and digital nomadism offer significant opportunities:
- Increased flexibility and autonomy:Individuals have greater control over their work schedules and locations.
- Exposure to new cultures and experiences:Traveling the world provides opportunities to broaden horizons and gain new perspectives.
- Career advancement:Remote work can open doors to new job opportunities and career growth.
- Improved work-life balance:For some, the flexibility of remote work allows for a better balance between work and personal life.
The Changing Landscape of Travel and Tourism
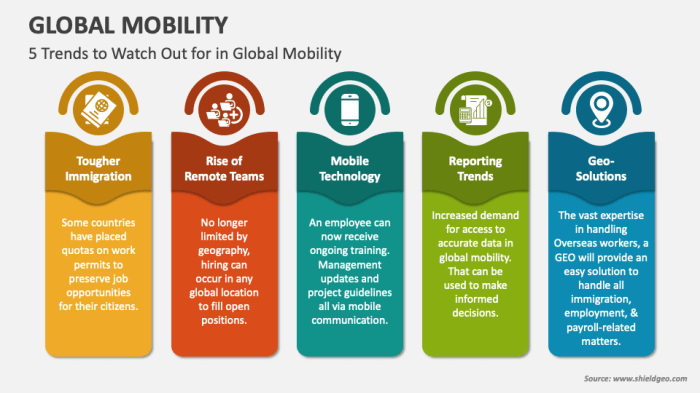
The global travel and tourism industry has undergone a significant transformation in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Travelers are now prioritizing health and safety, seeking authentic experiences, and embracing sustainability. This shift has led to a new era of travel, characterized by evolving preferences, technological advancements, and a growing focus on responsible tourism.
The Evolving Preferences of Travelers, Key trends global mobility *
The pandemic has fundamentally altered the way people travel. Travelers are now placing a higher premium on health and safety, seeking destinations with robust hygiene protocols and flexible cancellation policies. Additionally, there’s a growing preference for outdoor experiences, with travelers seeking to explore nature and immerse themselves in local cultures.
- Focus on Health and Safety:Travelers are increasingly prioritizing destinations with strong health and safety protocols, including vaccination requirements, mask mandates, and social distancing measures. They are also seeking accommodations with enhanced cleaning procedures and contactless check-in options.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:The pandemic has made travelers more adaptable, with a preference for flexible booking options and travel itineraries that can be easily adjusted. This includes seeking destinations with easy access to healthcare facilities and insurance coverage.
- Authentic Experiences:Travelers are now seeking more immersive and authentic experiences, often opting for off-the-beaten-path destinations and engaging with local communities. This trend has led to a surge in popularity for niche travel experiences and adventure tourism.
Sustainable Tourism and Responsible Travel
Sustainable tourism is gaining momentum as travelers become more aware of the environmental and social impacts of their travel choices. Travelers are increasingly seeking out eco-friendly accommodations, supporting local businesses, and minimizing their carbon footprint.
- Eco-Friendly Accommodations:Travelers are opting for hotels and resorts that implement sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy sources, reducing water consumption, and minimizing waste. This includes choosing accommodations certified by organizations like LEED or Green Globe.
- Support for Local Communities:Travelers are actively seeking out opportunities to support local communities by staying in locally owned accommodations, participating in cultural tours led by local guides, and purchasing souvenirs from local artisans.
- Responsible Travel Practices:Travelers are becoming more mindful of their environmental impact, choosing to travel responsibly by reducing their carbon footprint through eco-friendly transportation options, minimizing waste, and supporting conservation efforts.
Technology’s Impact on Travel Experiences
Technology has revolutionized the travel industry, providing travelers with access to a wealth of information, booking tools, and personalized travel experiences. Mobile apps, online travel agencies (OTAs), and virtual reality (VR) are transforming the way travelers plan, book, and experience their journeys.
- Mobile Apps and Online Travel Agencies:Travelers are increasingly relying on mobile apps and OTAs to research destinations, compare prices, book flights and accommodations, and access real-time travel information. These platforms offer convenience, personalized recommendations, and access to exclusive deals.
- Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality:VR and AR technologies are emerging as powerful tools for enhancing travel experiences. VR allows travelers to virtually explore destinations before booking, while AR can provide real-time information and interactive experiences during their travels.
- Personalized Travel Experiences:Technology enables personalized travel experiences, with AI-powered recommendations, customized itineraries, and tailored travel content based on individual preferences and interests.
The Rise of Niche Travel Experiences and Adventure Tourism
Travelers are increasingly seeking out unique and adventurous experiences that cater to their specific interests and passions. This has led to a surge in popularity for niche travel experiences, such as culinary tours, wildlife safaris, and adventure activities.
- Culinary Tours:Food tourism is gaining popularity, with travelers seeking out immersive culinary experiences that allow them to taste local cuisine, learn about food traditions, and interact with local chefs and food producers.
- Wildlife Safaris:Wildlife tourism offers travelers the opportunity to observe and interact with animals in their natural habitats. This includes destinations like national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and eco-lodges.
- Adventure Tourism:Adventure tourism provides travelers with adrenaline-pumping experiences, such as hiking, trekking, rock climbing, whitewater rafting, and skydiving.
Immigration and Global Talent Mobility

The world is becoming increasingly interconnected, and the movement of people across borders is a key driver of this globalization. This movement of people, especially skilled workers, is known as global talent mobility, and it is reshaping the global economy and society.
Factors Influencing Global Talent Migration
The decision to migrate for work is complex and influenced by a multitude of factors, both personal and professional. Here are some key factors that contribute to global talent migration:
- Economic Opportunities:The pursuit of better job prospects, higher salaries, and greater career advancement opportunities is a primary motivator for many migrants. This is particularly true in countries with robust economies and high demand for skilled labor.
- Education and Skills:Individuals with specialized skills and advanced degrees are often highly sought after in global talent markets. The desire to access better educational institutions and enhance their skillsets can also drive migration.
- Quality of Life:Factors like safety, healthcare, education systems, and cultural amenities play a significant role in attracting talent. Individuals often prioritize a high quality of life for themselves and their families.
- Political and Social Stability:Countries with stable political systems, a strong rule of law, and a tolerant and inclusive society are more likely to attract and retain skilled workers.
- Family Ties and Networks:Existing family connections and social networks in a destination country can significantly influence migration decisions. These networks provide support, guidance, and access to opportunities.
The Role of Government Policies and Visa Programs
Governments play a crucial role in shaping global talent mobility through their immigration policies and visa programs. These policies can either facilitate or restrict the movement of skilled workers. Here’s how:
- Attracting Skilled Workers:Many countries implement specific visa programs designed to attract highly skilled workers, such as fast-track visa processing, specialized work permits, and pathways to permanent residency. These programs often target professionals in high-demand sectors like technology, healthcare, and engineering.
- Facilitating International Student Mobility:Governments also play a vital role in attracting international students, who often become skilled workers after completing their studies. This includes providing scholarships, streamlined visa processes, and post-study work options.
- Addressing Labor Shortages:In countries facing labor shortages, immigration policies can help fill critical skills gaps. This can involve targeted recruitment programs and flexible visa options for specific occupations.
- Promoting Economic Growth:Attracting skilled workers can contribute to economic growth by fostering innovation, entrepreneurship, and competitiveness. This can lead to job creation, increased productivity, and higher tax revenues.
Challenges and Opportunities Associated with International Student Mobility
International student mobility presents both challenges and opportunities for individuals and countries.
- Challenges:
- Financial Costs:International students often face significant financial burdens, including tuition fees, living expenses, and travel costs.
- Cultural Adjustment:Adapting to a new culture, language, and educational system can be challenging for international students.
- Access to Employment:Finding employment after graduation can be difficult for international students, especially in countries with strict work permit regulations.
- Integration into Society:International students may face challenges integrating into the host society, particularly in terms of social connections and cultural understanding.
- Opportunities:
- Access to World-Class Education:International students gain access to high-quality education and research opportunities at leading universities worldwide.
- Global Networking:Studying abroad provides opportunities to build international networks, which can be beneficial for future careers and personal growth.
- Cultural Enrichment:International students experience diverse cultures, broaden their perspectives, and develop intercultural skills.
- Career Advancement:An international education can enhance career prospects and open doors to global employment opportunities.
The Impact of Immigration on Different Countries and Regions
The impact of immigration on different countries and regions varies greatly depending on factors like economic development, demographic trends, and existing immigration policies. Here are some key considerations:
- Economic Impact:Immigration can contribute to economic growth by filling labor shortages, increasing productivity, and fostering innovation. However, it can also lead to competition for jobs and resources, particularly in countries with high unemployment rates.
- Demographic Impact:Immigration can influence population growth and age distribution, impacting social services, housing, and infrastructure needs.
- Social Impact:Immigration can lead to cultural diversity and enrichment but also create challenges related to social cohesion, integration, and language barriers.
- Political Impact:Immigration can be a sensitive political issue, with varying public opinions and government policies. It can also influence political discourse and electoral outcomes.
Technological Advancements and Mobility Solutions
The convergence of technology and transportation is revolutionizing how we move around the world. From autonomous vehicles to smart cities, the landscape of global mobility is being reshaped by innovation, offering new possibilities for efficiency, sustainability, and accessibility.
Autonomous Vehicles and Their Impact on Mobility
Autonomous vehicles, powered by artificial intelligence and advanced sensors, are poised to transform transportation systems. These self-driving cars, buses, and trucks have the potential to significantly impact global mobility in several ways.
- Increased Safety:Autonomous vehicles are programmed to follow traffic rules and react quickly to changing conditions, potentially reducing human error-related accidents. Studies have shown that autonomous vehicles could significantly decrease traffic fatalities.
- Improved Efficiency:Autonomous vehicles can operate continuously without breaks, optimizing routes and reducing congestion. They can also communicate with each other, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced travel times.
- Enhanced Accessibility:Autonomous vehicles can provide transportation options for people with disabilities or those who cannot drive, promoting greater mobility and independence.
- Reduced Emissions:Autonomous vehicles can be integrated with electric powertrains, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation sector.
The Role of Smart Cities and Infrastructure
Smart cities, characterized by interconnected infrastructure and data-driven decision-making, are crucial for facilitating seamless travel. By leveraging technology, smart cities can optimize mobility solutions and create a more efficient and sustainable transportation ecosystem.
- Real-time Traffic Management:Smart cities can use sensors and data analytics to monitor traffic flow, identify bottlenecks, and adjust traffic signals in real time. This helps reduce congestion and improve travel times.
- Integrated Public Transportation:Smart cities can integrate different modes of public transportation, such as buses, trains, and ride-sharing services, providing seamless connections for travelers.
- Sustainable Mobility:Smart cities can encourage the use of sustainable transportation options, such as electric vehicles and bicycles, through infrastructure development and incentives.
- Data-Driven Decision Making:Smart cities can collect data on transportation patterns and preferences, enabling better planning and resource allocation for future mobility needs.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Platforms
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms are emerging as a comprehensive approach to transportation, integrating various modes of travel into a single, user-friendly platform. These platforms offer a range of benefits for travelers, including:
- Convenience:MaaS platforms provide a single point of access for booking and paying for all modes of transportation, from public transit to ride-sharing and bike rentals.
- Personalized Travel Planning:MaaS platforms can analyze user preferences and travel patterns to provide personalized route suggestions and optimize travel times.
- Reduced Costs:MaaS platforms can offer bundled travel packages and subscriptions, potentially reducing overall transportation costs.
- Sustainable Travel:MaaS platforms can encourage the use of public transportation and other sustainable modes of travel, contributing to a greener transportation sector.
The Future of Transportation and Its Impact on Global Mobility Patterns
The future of transportation is likely to be characterized by further advancements in technology, leading to significant changes in global mobility patterns.
- Increased Urbanization:As cities continue to grow, the demand for efficient and sustainable transportation solutions will increase. Autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and MaaS platforms are expected to play a key role in addressing these challenges.
- Shift to Shared Mobility:Shared mobility services, such as ride-sharing and bike-sharing, are gaining popularity. This trend is expected to continue, reducing car ownership and promoting more sustainable transportation options.
- Global Connectivity:Advancements in air travel, high-speed rail, and other long-distance transportation modes are likely to improve global connectivity, facilitating faster and more efficient travel between cities and countries.
- Increased Personalization:Future transportation systems are expected to be more personalized, with tailored travel options based on individual preferences and needs. This will empower travelers to choose the most convenient and sustainable modes of transportation.
The Impact of Global Mobility on Societies and Economies
Global mobility, encompassing migration, travel, and the movement of people across borders, has profound implications for societies and economies worldwide. The interconnectedness fostered by increased mobility presents both opportunities and challenges, influencing economic growth, cultural exchange, and social cohesion.
Economic Benefits and Challenges of Global Mobility
The economic benefits of global mobility are undeniable. Migration, for instance, contributes to labor force growth, particularly in developed economies facing aging populations. Skilled migrants often bring valuable expertise and innovation, boosting productivity and competitiveness. The tourism sector, fueled by international travel, generates significant revenue and employment opportunities, particularly in developing countries.
However, challenges arise with uncontrolled migration, potentially leading to strain on social services, housing, and infrastructure. Additionally, the brain drain phenomenon, where highly skilled individuals leave their home countries for better opportunities abroad, can hinder economic development in origin countries.
Cultural Exchange and Diversity Fostered by Global Mobility
Global mobility fosters cultural exchange and diversity, enriching societies with new perspectives, traditions, and experiences. Travel and migration expose individuals to different cultures, promoting understanding and tolerance. This cultural exchange can lead to innovation in art, cuisine, and other aspects of life, creating a more vibrant and diverse society.
However, challenges arise when cultural differences are not adequately addressed, potentially leading to misunderstandings, discrimination, and social tensions.
The Impact of Mobility on Social Cohesion and Integration
Global mobility can impact social cohesion and integration. The influx of migrants can challenge existing social structures and lead to tensions over resources, identity, and social values. However, effective integration policies, promoting language learning, intercultural dialogue, and access to social services, can help mitigate these challenges and foster a sense of belonging for newcomers.
Successful integration can contribute to a more diverse and resilient society, with a broader range of perspectives and experiences.
Opportunities for Collaboration and Partnerships in Promoting Responsible Mobility
Promoting responsible mobility requires collaborative efforts between governments, international organizations, businesses, and civil society. This involves developing policies that address the challenges of migration, promoting responsible tourism practices, and fostering cross-border cooperation on issues such as labor mobility and skills development.
Partnerships between governments and the private sector can help develop infrastructure and support services for migrants and travelers, ensuring a more sustainable and inclusive approach to global mobility.