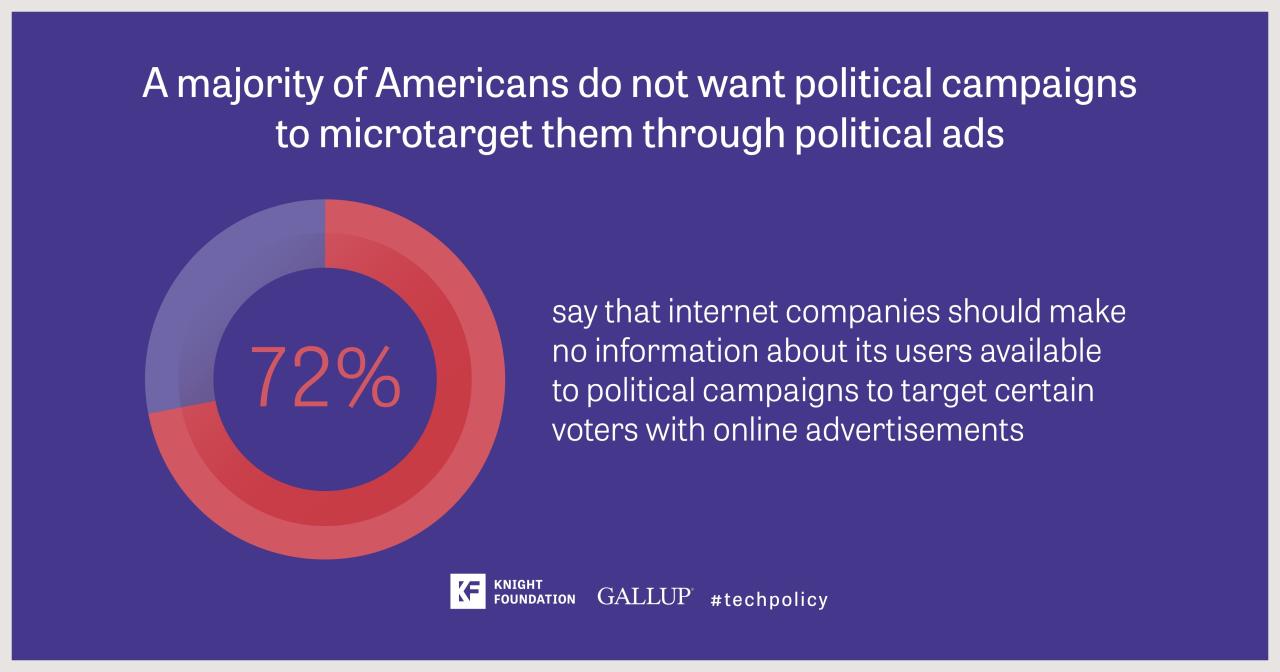
Is momentum shifting toward a ban on behavioral advertising? This question has become increasingly relevant as concerns about privacy and data security escalate. Behavioral advertising, once seen as a revolutionary tool for targeted marketing, is now facing growing scrutiny from regulators, privacy advocates, and the public alike.
The rise of behavioral advertising has been fueled by the explosion of data available online. From cookies to tracking pixels, advertisers have developed sophisticated methods to collect and analyze user data, creating detailed profiles that predict individual preferences and behaviors.
This information is then used to tailor advertisements, making them more relevant and effective. However, this personalized approach comes at a cost: the erosion of privacy and the potential for misuse of personal data.
The Rise of Behavioral Advertising: Is Momentum Shifting Toward A Ban On Behavioral Advertising
The evolution of behavioral advertising has been a fascinating journey, marked by advancements in technology and a growing understanding of consumer behavior. From its humble beginnings as a simple way to target ads based on demographics, it has transformed into a sophisticated system that uses vast amounts of data to personalize the advertising experience.
Techniques Employed in Behavioral Advertising
Behavioral advertising relies on various techniques to gather and analyze user data. These techniques include:
- Cookies:Cookies are small text files stored on a user’s computer by websites they visit. They contain information about the user’s browsing history, preferences, and other online activities. This data is used to tailor ads based on the user’s interests and past behavior.
- Tracking Pixels:Tracking pixels are tiny images embedded in websites and emails. When a user views a page or opens an email containing a tracking pixel, it sends information about the user’s activity to the advertiser. This data is then used to track the user’s behavior across multiple websites and platforms.
- User Profiling:User profiling is the process of creating detailed profiles of individual users based on their online behavior. This information is gathered from cookies, tracking pixels, and other sources. User profiles can include details about the user’s demographics, interests, browsing history, and purchase history.
Benefits of Behavioral Advertising for Businesses
Behavioral advertising offers several benefits for businesses, including:
- Increased Ad Relevance:By targeting ads based on user behavior, businesses can deliver more relevant and engaging ads to their target audience. This leads to higher click-through rates and conversions.
- Improved ROI:Behavioral advertising helps businesses optimize their ad spending by targeting the most likely customers. This results in a higher return on investment (ROI) compared to traditional advertising methods.
- Enhanced Customer Experience:By delivering personalized ads based on user preferences, businesses can provide a more relevant and enjoyable experience for their customers. This can lead to increased brand loyalty and customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Behavioral Advertising for Consumers
While concerns about privacy have arisen, behavioral advertising can also benefit consumers:
- Personalized Recommendations:By analyzing user data, businesses can provide personalized recommendations for products and services that are more likely to be of interest to the consumer. This can help consumers discover new products and services they might not have found otherwise.
For descriptions on additional topics like critical review eus ethics guidelines for trustworthy ai, please visit the available critical review eus ethics guidelines for trustworthy ai.
- Improved Shopping Experience:Behavioral advertising can make the online shopping experience more efficient and enjoyable. For example, by remembering past purchases, websites can provide personalized product suggestions and streamline the checkout process.
- Access to Exclusive Offers:Businesses can use behavioral advertising to offer exclusive discounts and promotions to targeted groups of consumers. This can help consumers save money and access deals that are relevant to their interests.
Concerns Regarding Privacy and Data Security
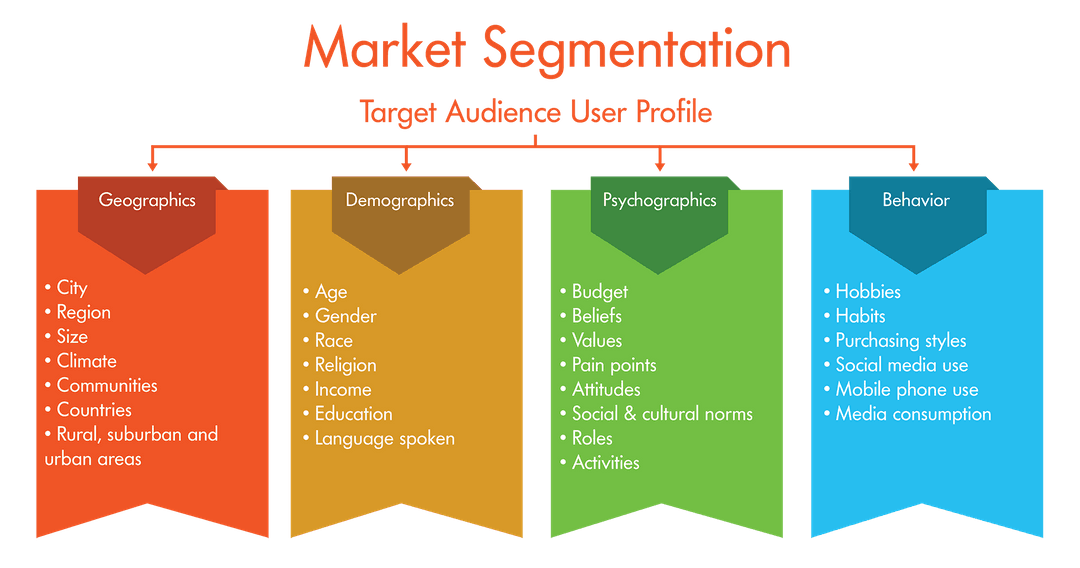
The rise of behavioral advertising has sparked significant concerns about privacy and data security. Collecting and using personal data to target ads raises ethical and legal questions, prompting discussions about the balance between personalized experiences and individual rights.
Ethical and Legal Concerns Surrounding Data Collection and Use
The collection and use of personal data in behavioral advertising raise a range of ethical and legal concerns. These concerns revolve around the potential for:
- Unfair Discrimination: Behavioral advertising algorithms may inadvertently perpetuate biases based on demographics, interests, or online behavior, leading to unfair treatment in advertising opportunities.
- Invasion of Privacy: The constant tracking and profiling of individuals’ online activities can create a sense of intrusion and erode their privacy, particularly when data is collected without explicit consent.
- Lack of Transparency: The complex algorithms used in behavioral advertising often lack transparency, making it difficult for individuals to understand how their data is being used and what implications it might have.
- Data Security Risks: Storing and processing large amounts of personal data create vulnerabilities to data breaches and security threats, potentially exposing sensitive information to unauthorized access.
Examples of Data Breaches and Privacy Violations, Is momentum shifting toward a ban on behavioral advertising
Numerous examples of data breaches and privacy violations associated with behavioral advertising have emerged over the years. These incidents highlight the real-world consequences of data misuse and the need for stronger privacy protections.
- Cambridge Analytica Scandal: In 2018, the Cambridge Analytica scandal exposed how personal data collected from Facebook users was used to target political advertising during the 2016 US presidential election. This incident raised concerns about the potential for manipulation and misuse of personal data in political campaigns.
- Google’s Tracking Practices: Google has been criticized for its extensive data collection practices, including tracking user browsing history and location data. This data is used to target ads and personalize search results, raising concerns about privacy and the potential for surveillance.
- Data Breaches at Major Ad Tech Companies: Several ad tech companies have experienced data breaches, leading to the exposure of sensitive user information, including browsing history, location data, and even financial details. These incidents underscore the need for robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access.
Comparison of Privacy Regulations Across Countries and Regions
Different countries and regions have implemented varying levels of privacy regulations to address the concerns surrounding behavioral advertising. Here’s a comparison of some key regulations:
| Region | Key Regulations | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| European Union (EU) | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Data protection, user consent, data portability, right to be forgotten. |
| California, USA | California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) | Data access, deletion, and opt-out rights for consumers. |
| Brazil | General Data Protection Law (LGPD) | Comprehensive data protection, including consent requirements and data breach notification. |
Growing Public Opposition and Regulatory Scrutiny
The meteoric rise of behavioral advertising has been accompanied by growing public concern and a surge in regulatory scrutiny. Consumers have become increasingly aware of the data collection practices behind personalized ads, leading to a wave of opposition and calls for stricter regulation.
This section explores the timeline of events, the impact of lawsuits and investigations, and the actions taken by key regulatory bodies to address these concerns.
A Timeline of Public Awareness and Opposition
Public awareness and opposition to behavioral advertising have been steadily growing over the years, fueled by several key events and initiatives. Here’s a timeline highlighting some of the most significant milestones:
- Early 2000s:The emergence of online advertising and the rise of data-driven marketing practices sparked initial concerns about privacy and data security. While the industry was still nascent, privacy advocates and researchers began raising alarms about the potential for misuse of personal data.
- 2010s:The proliferation of smartphones and social media platforms further intensified data collection practices, leading to a surge in public awareness about the extent of tracking and profiling. High-profile data breaches, such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal in 2018, brought the issue of data privacy to the forefront of public discourse.
- 2018:The implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union marked a watershed moment in data privacy regulations. GDPR imposed stricter rules on data collection, processing, and storage, empowering individuals with greater control over their personal data.
This legislation served as a catalyst for similar privacy laws and regulations worldwide.
- 2020s:The rise of privacy-focused browsers and ad-blocking technologies, coupled with growing public distrust in tech giants, has further accelerated the movement towards greater data privacy and control. Many consumers are actively seeking ways to limit the tracking and profiling of their online activities.
Impact of Lawsuits and Regulatory Investigations
High-profile lawsuits and regulatory investigations have played a crucial role in shaping the landscape of behavioral advertising. These legal challenges have forced the industry to confront its data practices and adopt more transparent and accountable approaches.
- Facebook Privacy Lawsuits:In 2018, Facebook faced numerous lawsuits alleging violations of user privacy and data misuse, stemming from the Cambridge Analytica scandal. These legal battles have resulted in significant financial settlements and forced Facebook to implement stricter privacy controls.
- Google Antitrust Investigations:Antitrust investigations by various regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Department of Justice and the European Commission, have focused on Google’s dominance in online advertising and its data collection practices. These investigations have raised concerns about potential anti-competitive behavior and the potential for Google to leverage its vast data trove to stifle competition.
- Privacy Shield Invalidation:In 2020, the European Court of Justice invalidated the Privacy Shield framework, which had previously allowed U.S. companies to transfer personal data from the EU to the United States. This ruling has significantly impacted the transatlantic data flow and highlighted the importance of robust data protection mechanisms.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Actions
Numerous regulatory bodies around the world are actively working to address concerns about behavioral advertising and data privacy. These organizations are implementing policies, issuing guidelines, and conducting investigations to ensure that data collection and processing practices are ethical, transparent, and compliant with privacy regulations.
- The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR):GDPR is a landmark piece of legislation that grants individuals greater control over their personal data and imposes strict requirements on companies that collect and process personal information. GDPR has significantly impacted the global data privacy landscape, serving as a model for other jurisdictions.
- The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA):CCPA is a California state law that grants consumers the right to know what personal information is being collected about them, the right to delete that information, and the right to opt out of the sale of their personal data.
CCPA has been influential in shaping data privacy regulations in other U.S. states.
- The U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC):The FTC has a long history of enforcing consumer protection laws, including those related to privacy and data security. The FTC has issued numerous guidance documents and enforcement actions targeting companies that engage in deceptive or unfair data collection practices.
Alternative Advertising Models
The growing concerns over privacy and data security have spurred the development of alternative advertising models that prioritize user consent and data protection. These models aim to deliver targeted advertising while respecting user privacy and offering greater transparency in data usage.
Contextual Advertising
Contextual advertising leverages the content of a webpage or app to display relevant ads. It relies on s and topics present in the content to match ads that align with the user’s interests.
- For example, if a user is reading an article about travel, contextual advertising might display ads for airlines, hotels, or travel agencies.
- This approach avoids tracking user behavior across multiple websites and relies on the context of the current page.
Privacy-Focused Advertising
Privacy-focused advertising models prioritize user control and transparency. They emphasize user consent and data minimization, offering users greater control over their data and how it is used for advertising purposes.
- One example is differential privacy, which adds noise to data sets to protect individual user information while still enabling statistical analysis for advertising purposes.
- Another approach is federated learning, where user data is processed locally on their devices and only aggregated summaries are shared with advertisers, preserving individual user privacy.
Comparison of Advertising Models
The following table compares and contrasts the features and benefits of different advertising models:
| Feature | Behavioral Advertising | Contextual Advertising | Privacy-Focused Advertising |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Extensive tracking of user behavior across multiple websites and apps | Limited data collection based on the current webpage or app content | Minimal data collection with user consent and data minimization techniques |
| Targeting | Highly targeted based on user profiles and browsing history | Targeted based on the content of the current page or app | Targeted based on user preferences and interests with limited data usage |
| Privacy | Raises significant privacy concerns due to extensive data tracking | Relatively privacy-friendly as it avoids cross-site tracking | Prioritizes user privacy with data minimization and consent mechanisms |
| Transparency | Lack of transparency in data collection and usage practices | More transparent as it relies on the visible content of the page | High transparency with clear explanations of data collection and usage |
| Examples | Google AdSense, Facebook Ads | Google AdSense (contextual targeting option), Amazon Advertising | Apple’s App Tracking Transparency framework, DuckDuckGo’s privacy-focused search engine |
Examples of Companies Implementing Alternative Advertising Models
Several companies are successfully implementing alternative advertising models, demonstrating the growing shift towards privacy-focused advertising.
- DuckDuckGoprioritizes user privacy in its search engine and advertising platform. It avoids tracking user behavior and offers contextual advertising based on search queries.
- Braveis a privacy-focused web browser that blocks intrusive ads and offers a unique advertising platform that rewards users for viewing ads.
- Applehas introduced the App Tracking Transparency framework, giving users greater control over data sharing and app tracking.
Potential Impacts of a Ban on Behavioral Advertising
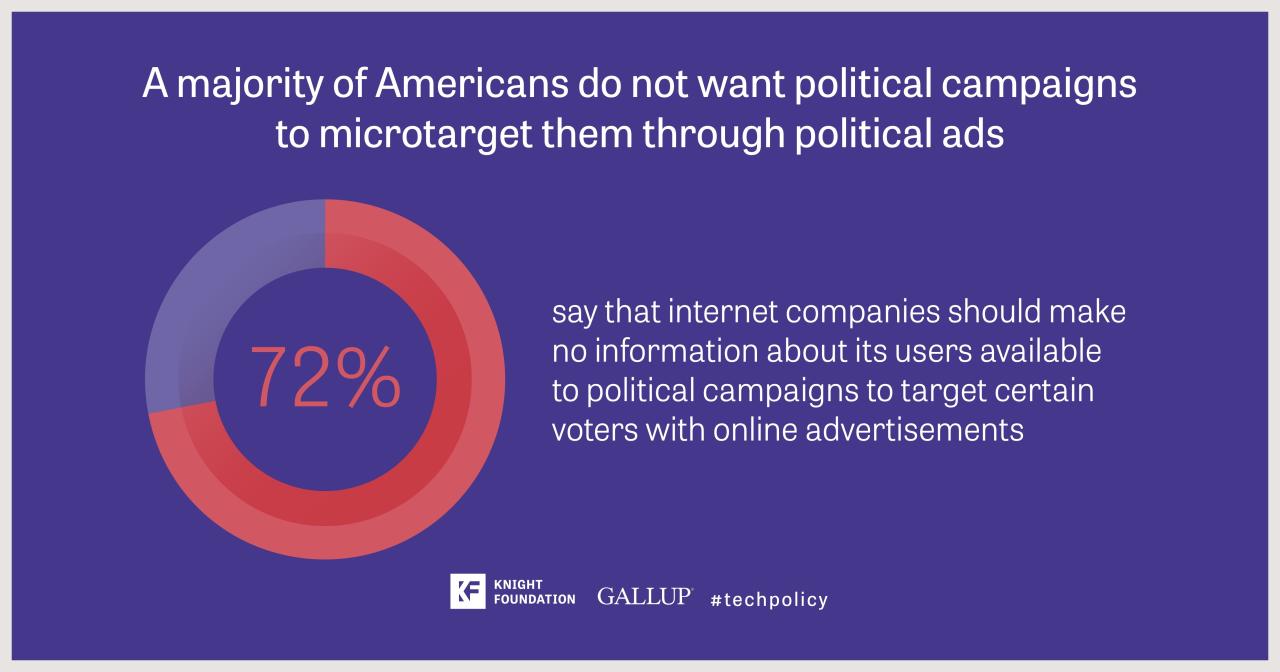
A ban on behavioral advertising would undoubtedly have far-reaching consequences, impacting both businesses and consumers. The shift from targeted advertising to more generalized approaches would necessitate adjustments in business models, consumer experiences, and the overall digital landscape.
Economic Impact
The economic impact of a ban on behavioral advertising would be multifaceted. Businesses heavily reliant on targeted advertising, such as online retailers and social media platforms, could face significant challenges. Their ability to reach specific audiences with tailored messages would be diminished, potentially leading to reduced ad revenue and overall profitability.
On the other hand, consumers could benefit from increased privacy and reduced exposure to unwanted advertisements. However, this might come at the cost of less relevant and personalized content, as businesses might resort to broader targeting strategies.
Implications for the Advertising Industry
A ban on behavioral advertising would fundamentally alter the advertising industry. Traditional advertising models, such as television and print, could experience a resurgence as businesses seek alternative channels to reach their target audiences. Digital marketing strategies would need to evolve, focusing on content marketing, search engine optimization (), and influencer marketing.
This shift could lead to increased competition among content creators and digital marketers, as they vie for attention in a less targeted environment.
Potential Consequences
The potential consequences of a ban on behavioral advertising can be categorized into positive and negative impacts: