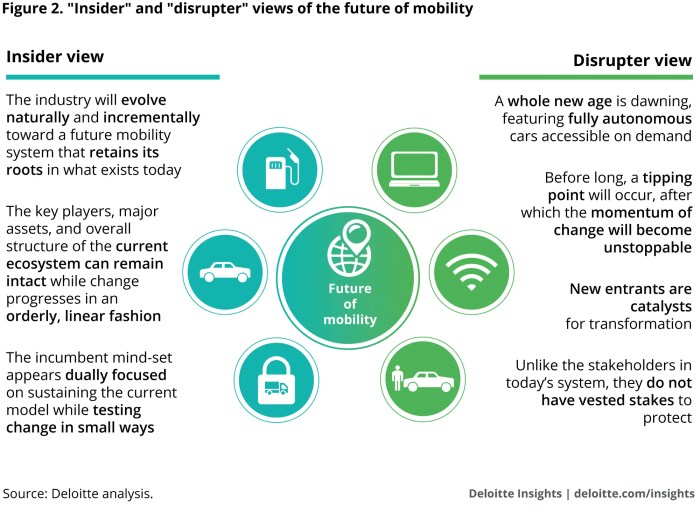
How mobility will change in * – How mobility will change in our world is a question that’s sparking conversations across industries. The future of transportation is being redefined by a convergence of technological advancements, shifting societal priorities, and a growing demand for sustainable solutions. From self-driving cars to electric scooters, we’re witnessing a revolution in how we move, work, and live.
This evolution isn’t just about the vehicles themselves, but about the entire ecosystem of mobility. It’s about reimagining urban spaces, optimizing commutes, and creating a more efficient and accessible world for everyone. As we delve deeper into these trends, we’ll explore how mobility will shape our cities, our workplaces, and our global outlook.
The Future of Personal Mobility: How Mobility Will Change In *
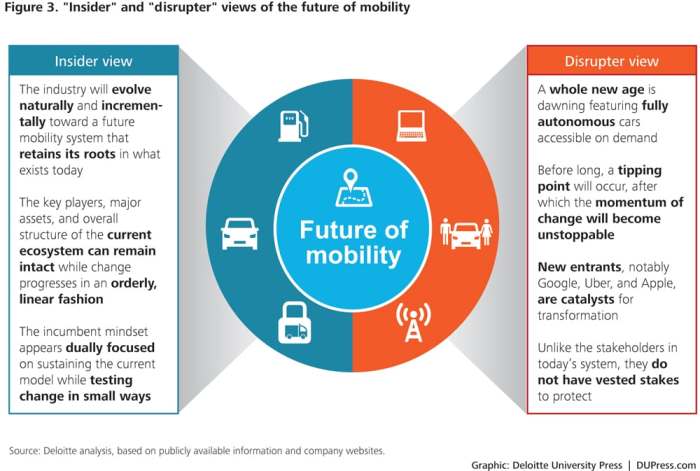
The way we move around is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements and a growing awareness of environmental concerns. From self-driving cars to electric bikes, the future of personal mobility promises a more efficient, sustainable, and convenient experience.
The Impact of Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, or self-driving cars, are poised to revolutionize individual transportation. By eliminating human error, these vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce accidents, improve traffic flow, and increase accessibility for people with disabilities. For example, in cities like Phoenix, Arizona, and Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, autonomous vehicle trials are underway, demonstrating the real-world potential of this technology.
The Role of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are playing a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions from transportation. With zero tailpipe emissions, EVs contribute to cleaner air quality and combat climate change. The increasing availability of charging infrastructure and the declining cost of battery technology are further accelerating the adoption of EVs.
The Adoption of Micro-Mobility Solutions
Micro-mobility solutions, such as e-scooters and e-bikes, are gaining popularity in urban areas, offering a convenient and sustainable alternative to traditional transportation. These vehicles are compact, affordable, and environmentally friendly, making them ideal for short-distance commutes. For instance, cities like Paris and Amsterdam have successfully integrated e-scooters and e-bikes into their transportation systems, encouraging sustainable urban mobility.
Advancements in Ride-Sharing Services
Ride-sharing services, such as Uber and Lyft, are transforming urban transportation by providing flexible and on-demand mobility options. Advancements in technology, including ride-hailing apps and real-time data analysis, are enhancing the efficiency and accessibility of these services.
A Hypothetical Future City
Imagine a future city where autonomous vehicles seamlessly navigate the streets, electric buses provide clean and efficient public transportation, and micro-mobility options are readily available for short-distance trips. This integrated mobility system would prioritize sustainability, efficiency, and accessibility, creating a more livable and enjoyable urban environment.
Mobility in the Workplace
The way we work is changing, and with it, the way we commute. The rise of remote work and flexible work arrangements is transforming the landscape of workplace mobility, creating both challenges and opportunities. This shift is leading to a re-evaluation of traditional commuting patterns and the emergence of new mobility solutions tailored to the needs of the modern workforce.
In this topic, you find that germany blocking china sales of chip companies is like putting plaster on decapitation is very useful.
The Impact of Remote Work on Commuting Patterns
The increasing popularity of remote work has significantly altered commuting patterns. A study by Global Workplace Analytics found that 35.4% of the U.S. workforce worked from home at least one day per week in 2021. This trend has led to a decline in daily commutes for many employees, reducing traffic congestion and carbon emissions.
However, it has also created new challenges, such as the need for reliable internet access and dedicated workspaces at home.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) for Work Commutes
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms offer a comprehensive and integrated approach to work commutes. MaaS platforms combine various transportation options, including public transit, ride-hailing, bike sharing, and carpooling, into a single, user-friendly interface. These platforms provide real-time information on service availability, pricing, and estimated travel times, enabling employees to plan their commutes efficiently and seamlessly.
For example, a MaaS platform could help an employee find the fastest route to work, combining a bike share ride with a public bus to avoid traffic congestion.
The Influence of Flexible Work Arrangements on Public Transportation Demand
Flexible work arrangements, such as hybrid work models and compressed workweeks, have a significant impact on the demand for public transportation. These arrangements often reduce the need for daily commutes, leading to a decrease in peak-hour demand for public transit.
However, flexible work arrangements can also increase the demand for public transportation during non-peak hours, as employees may choose to travel at different times to avoid rush hour congestion. Public transportation agencies need to adapt to these changing demand patterns by offering flexible schedules and fares to accommodate the needs of a more diverse workforce.
The Role of Technology in Optimizing Employee Travel
Technology plays a crucial role in optimizing employee travel and reducing commuting costs. Companies are increasingly using mobile apps and online platforms to manage employee travel expenses, track mileage, and book transportation services. These tools can help employees find the most cost-effective travel options, reduce wasted time, and improve overall commuting efficiency.
For example, a company could use a travel expense management app to track employee mileage and reimburse them for fuel costs, reducing the need for employees to use their personal vehicles for work-related travel.
Benefits and Challenges of Different Mobility Solutions for Work Commutes
| Mobility Solution | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Cost-effective, environmentally friendly, reduces traffic congestion | Limited routes and schedules, potential for delays, lack of privacy |
| Ride-hailing | Convenience, flexibility, on-demand availability | Costly, potential for traffic congestion, limited parking availability |
| Bike Sharing | Environmentally friendly, promotes physical activity, affordable | Weather-dependent, limited range, safety concerns |
| Carpooling | Cost-effective, reduces traffic congestion, promotes social interaction | Finding compatible carpool partners, scheduling challenges, safety concerns |
| Telecommuting | Flexibility, reduced commuting time and costs, improved work-life balance | Potential for isolation, need for reliable internet access, distractions at home |
Mobility and Urban Development
The relationship between urban planning and transportation infrastructure is crucial for creating sustainable and livable cities. Efficient mobility systems are not just about moving people from point A to point B; they play a vital role in shaping urban environments, influencing economic growth, and impacting the quality of life for residents.
The Interplay of Urban Planning and Sustainable Transportation
Sustainable transportation infrastructure is essential for fostering sustainable urban development. This involves prioritizing public transportation, walking, cycling, and other sustainable modes of transport over private vehicles. Effective urban planning integrates these elements, creating walkable and bikeable neighborhoods, promoting efficient public transit systems, and discouraging car dependence.
This approach not only reduces congestion and pollution but also creates healthier, more vibrant, and more equitable cities.
Smart Cities and Their Impact on Mobility
Smart cities leverage technology to enhance urban living, and mobility is a key area of focus. These cities utilize data analytics, sensor networks, and intelligent transportation systems to optimize traffic flow, improve public transportation efficiency, and offer personalized mobility solutions.
For example, real-time traffic information, dynamic route optimization, and smart parking systems help reduce congestion and travel times. Additionally, ride-hailing services, electric vehicle charging infrastructure, and autonomous vehicle technologies are being integrated into smart city frameworks, transforming how people move around urban areas.
Integrating Public and Private Mobility Options
Integrating public transportation with private mobility options is a crucial aspect of creating a seamless and efficient urban transportation system. This involves providing convenient connections between public transit hubs and private vehicle access points, promoting seamless transfers between different modes of transport, and encouraging the use of multimodal travel.
For example, integrating bike-sharing programs with bus and rail networks, providing dedicated lanes for electric scooters, and offering last-mile solutions for commuters can create a more connected and accessible urban mobility ecosystem.
Examples of Cities Implementing Innovative Mobility Solutions
Many cities around the world are implementing innovative mobility solutions to address urban challenges and enhance the quality of life for their residents. Here are a few examples:
- Copenhagen, Denmark:Copenhagen is renowned for its cycling infrastructure, with dedicated bike lanes, bike paths, and a bike-friendly culture. This has significantly reduced car dependence and created a healthier and more sustainable city.
- Singapore:Singapore has implemented a comprehensive public transportation system, including an extensive metro network, buses, and taxis, making it one of the most efficient and accessible cities in the world. They also use intelligent traffic management systems to optimize traffic flow.
- Amsterdam, Netherlands:Amsterdam has embraced sustainable mobility, with a focus on cycling, walking, and public transportation. They have implemented innovative initiatives such as electric car-sharing programs, bike-sharing systems, and pedestrian-friendly streets.
Impact of Different Mobility Solutions on Urban Congestion and Pollution
| Mobility Solution | Impact on Congestion | Impact on Pollution ||—|—|—|| Public Transportation| Reduces congestion by carrying more passengers per vehicle. | Reduces pollution by decreasing the number of individual cars on the road. || Cycling| Reduces congestion by taking up less space than cars.
| Zero-emission mode of transport. || Walking| Reduces congestion and pollution by eliminating the need for vehicles. | || Ride-hailing Services| Can increase congestion during peak hours. | Contributes to pollution depending on the type of vehicles used. || Electric Vehicles| Can reduce congestion by using dedicated lanes in some cities.
| Reduces air pollution but may contribute to noise pollution. || Autonomous Vehicles| Potential to reduce congestion by optimizing traffic flow. | Can reduce pollution depending on the power source. |
Global Mobility Trends
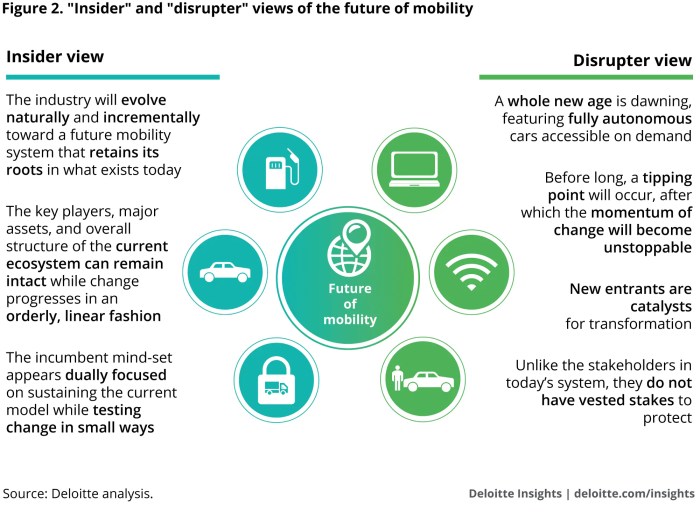
The global mobility landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements, urbanization, and evolving societal needs. This evolution presents both opportunities and challenges, with stark contrasts emerging between developed and developing countries. Understanding these trends is crucial for shaping a more sustainable and equitable future of mobility.
Mobility in Developed and Developing Countries
The mobility landscape in developed and developing countries differs significantly. Developed countries generally boast robust public transportation systems, extensive road networks, and access to private vehicles. However, they face challenges like traffic congestion, air pollution, and rising costs of car ownership.
Developing countries, on the other hand, often grapple with inadequate infrastructure, limited access to public transportation, and high rates of informal transportation. These challenges are compounded by rapid urbanization and increasing population density. Here is a table comparing the mobility landscape in developed and developing countries:
| Feature | Developed Countries | Developing Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Public Transportation | Well-developed systems with high frequency and reliability | Limited options, often with low frequency and reliability |
| Road Infrastructure | Extensive road networks, with high standards of maintenance | Often inadequate, with poor road conditions and limited access |
| Private Vehicle Ownership | High rates of car ownership, with increasing concerns about congestion and pollution | Limited car ownership, with a greater reliance on public transport, walking, and informal transportation |
| Mobility Costs | High costs associated with car ownership, fuel, and public transport | Lower costs for informal transportation, but higher costs for formal public transport |
| Environmental Impact | Significant contribution to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions | Emerging environmental concerns, but often overshadowed by immediate needs for mobility |
Challenges and Opportunities for Underserved Communities, How mobility will change in *
Improving mobility in underserved communities presents both challenges and opportunities. These communities often lack access to reliable and affordable transportation, hindering their ability to access education, healthcare, and employment opportunities.
Challenges
- Lack of Infrastructure:Inadequate road networks, limited public transport options, and poor infrastructure connectivity create significant barriers to mobility.
- Financial Constraints:High transportation costs, limited access to credit, and low incomes make it difficult for residents to afford reliable transportation.
- Limited Access to Technology:Lack of access to smartphones, internet connectivity, and digital literacy skills hinders the adoption of mobility solutions like ride-hailing services.
- Safety Concerns:Inadequate street lighting, poorly maintained roads, and high crime rates create safety concerns for pedestrians and public transport users.
Opportunities
- Leveraging Technology:Innovative mobility solutions like ride-sharing, micro-mobility, and electric vehicles can be adapted to address specific needs in underserved communities.
- Community Engagement:Collaborative efforts involving community members, local governments, and transportation providers can help develop tailored mobility solutions.
- Public-Private Partnerships:Partnerships between governments and private companies can help attract investment and deploy innovative mobility solutions in underserved areas.
- Policy Interventions:Governments can implement policies that promote affordable and accessible transportation options, including subsidies, tax breaks, and infrastructure investments.
International Collaboration for Sustainable Mobility
International collaboration is essential for advancing sustainable mobility solutions globally. Sharing best practices, knowledge, and technology can accelerate the transition to more efficient, equitable, and environmentally friendly transportation systems.
Key Initiatives
- The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):Goal 11, which focuses on sustainable cities and communities, emphasizes the importance of providing access to safe, affordable, accessible, and sustainable transport systems.
- The Global Green Growth Institute (GGGI):GGGI works with countries to develop and implement green growth strategies, including sustainable transportation policies and infrastructure development.
- The International Transport Forum (ITF):ITF facilitates dialogue and collaboration among governments and stakeholders on transport policy issues, including sustainable mobility solutions.
Revolutionizing Global Transportation: Hyperloop and Flying Cars
Emerging technologies like hyperloop and flying cars have the potential to revolutionize global transportation, offering faster travel times, reduced congestion, and new possibilities for connectivity.
Hyperloop
- High-Speed Ground Transportation:Hyperloop systems use vacuum tubes to propel pods at high speeds, potentially reaching speeds of over 700 miles per hour.
- Reduced Travel Times:Hyperloop could significantly reduce travel times between major cities, making long-distance travel more efficient and affordable.
- Environmental Benefits:Hyperloop systems could operate on renewable energy sources, reducing carbon emissions and air pollution.
Flying Cars
- Urban Air Mobility:Flying cars could offer a new mode of transportation for urban areas, reducing congestion on roads and providing faster commutes.
- Last-Mile Connectivity:Flying cars could connect remote areas to urban centers, improving accessibility and economic opportunities.
- Technological Challenges:The development of flying cars faces significant technological challenges, including safety, regulation, and infrastructure requirements.