Germany Intel chip plant funding is a game-changer, not just for Germany but for Europe’s entire tech landscape. This strategic investment marks a significant shift in the global semiconductor industry, with the potential to reshape the technological playing field.
As the world grapples with chip shortages and geopolitical tensions, Germany’s move to attract a major player like Intel underscores the importance of domestic chip production.
The decision to invest in a state-of-the-art chip manufacturing facility in Germany signifies a bold commitment to technological independence and innovation. The investment is expected to create thousands of jobs, attract skilled talent, and propel Germany to the forefront of advanced chip technology.
This move is not just about manufacturing; it’s about building a future-proof economy powered by cutting-edge technology.
Germany’s Chip Plant Funding Landscape
Germany’s investment in chip manufacturing is experiencing a significant resurgence, driven by a growing awareness of the strategic importance of semiconductors in the modern economy. The government is actively pursuing initiatives to bolster domestic chip production, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign suppliers and strengthen its technological competitiveness.
Government Chip Funding Initiatives
The German government is actively pursuing a multi-pronged approach to chip funding, encompassing a range of initiatives aimed at attracting investment and supporting the development of a robust domestic semiconductor ecosystem.
- The “National Semiconductor Strategy”, launched in 2021, Artikels a comprehensive plan to promote the development and production of microchips in Germany. This strategy includes provisions for financial support, research and development funding, and regulatory streamlining to create a favorable environment for chip manufacturers.
- The “Microelectronics Initiative”, a joint effort between the federal government and the state of Saxony, has allocated €2 billion to support the construction of a new chip fabrication plant in Dresden. This facility, operated by Infineon Technologies, is expected to create thousands of jobs and strengthen Germany’s position in the global semiconductor industry.
- The “Future Fund”, a €20 billion investment fund established by the German government, is dedicated to supporting innovative technologies, including those related to semiconductors. This fund provides grants, loans, and equity investments to promising startups and established companies in the chip sector.
Motivations Behind Investment
The German government’s chip funding initiatives are driven by a confluence of factors, including:
- National Security:The dependence on foreign suppliers for critical components like semiconductors poses a significant vulnerability for Germany’s economy and national security. Increasing domestic chip production is seen as a vital step towards strengthening supply chain resilience and reducing reliance on external sources.
- Economic Growth:The semiconductor industry is a major driver of innovation and economic growth. By fostering a thriving chip ecosystem, Germany aims to attract investment, create high-skilled jobs, and boost its competitiveness in industries like automotive, manufacturing, and digital technologies.
- Technological Leadership:The development and production of advanced semiconductors is crucial for maintaining Germany’s position as a global leader in technology. Investments in chip manufacturing are seen as a key driver for innovation and the development of cutting-edge technologies.
Role of Private Companies
Private companies play a crucial role in the success of Germany’s chip plant funding landscape. They contribute significantly to the overall investment, providing expertise, infrastructure, and manufacturing capabilities.
- Infineon Technologies:A leading semiconductor manufacturer, Infineon is a key beneficiary of government funding and is actively expanding its chip production capacity in Germany. The company’s commitment to domestic manufacturing is a testament to the growing importance of the German market.
- Bosch:A global technology and engineering company, Bosch is investing heavily in semiconductor research and development. The company is also collaborating with other industry players to build a robust semiconductor ecosystem in Germany.
- Volkswagen:The German automotive giant is a major consumer of semiconductors and is actively engaging with the government and other industry stakeholders to secure reliable access to chips. Volkswagen’s commitment to domestic chip production is a reflection of the automotive industry’s dependence on semiconductors.
Impact of Intel’s Investment in Germany
Intel’s decision to invest in a new chip plant in Germany signifies a major shift in the global semiconductor landscape. This investment will have a significant impact on the German economy, boosting innovation, job creation, and technological advancement. It will also position Germany as a leading player in the global semiconductor industry.
Economic Impact
Intel’s investment in Germany is expected to create a ripple effect across various sectors of the economy. The construction of the chip plant itself will create thousands of jobs, while the operation of the facility will generate even more employment opportunities.
This investment will also attract other technology companies to Germany, creating a hub for innovation and growth.
Job Creation and Technological Advancements
The chip plant is expected to create approximately 1,000 direct jobs and up to 10,000 indirect jobs in related industries. This will have a significant impact on the local economy, boosting employment rates and generating economic activity. The plant will also be a center for research and development, fostering technological advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 5G technology.
Check what professionals state about 6 ways eu startups can cut spending during the recession and its benefits for the industry.
Implications for Germany’s Position in the Global Semiconductor Industry
Intel’s investment in Germany strengthens the country’s position in the global semiconductor industry. This investment will enhance Germany’s technological capabilities, making it a more attractive destination for technology companies and research institutions. It will also contribute to the country’s efforts to become a leader in the development and production of advanced semiconductors.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Chip Plant: Germany Intel Chip Plant Funding
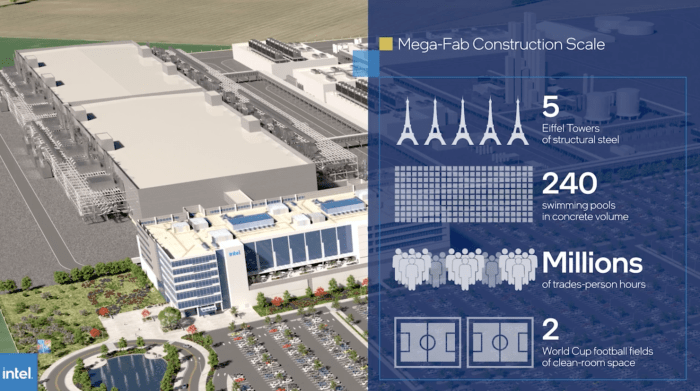
Intel’s decision to build a new chip plant in Germany represents a significant investment in European technology and manufacturing. However, the project also faces a number of challenges and opportunities.
Challenges Associated with Building and Operating a Chip Plant
Building and operating a chip plant is a complex undertaking that requires significant capital investment, advanced technology, and a highly skilled workforce. In Germany, these challenges are amplified by factors such as:
- High Labor Costs:Germany has a high cost of living and a strong labor union presence, which can lead to higher labor costs compared to other chip manufacturing locations. This can impact the plant’s overall cost structure and profitability.
- Regulatory Complexity:Germany has a complex regulatory environment, with strict environmental regulations and safety standards. Navigating these regulations can be time-consuming and expensive, potentially delaying the plant’s construction and operation.
- Energy Costs:Germany has a high reliance on renewable energy sources, which can lead to fluctuating energy prices. This can impact the plant’s operating costs, especially if it requires a large amount of energy for its manufacturing processes.
- Infrastructure Challenges:Germany’s infrastructure, while generally well-developed, may need upgrades to support the demands of a large-scale chip plant. This could include improvements to transportation networks, power grids, and water supply systems.
Potential Supply Chain Disruptions and Logistical Hurdles
The global chip shortage has highlighted the vulnerabilities of supply chains, particularly for critical components like semiconductors. Building a new chip plant in Germany can help address these vulnerabilities, but it also faces its own challenges in terms of supply chain and logistics:
- Global Dependencies:Even with a new chip plant in Germany, the supply chain for semiconductor manufacturing remains heavily reliant on global suppliers. Disruptions in these global supply chains, due to factors such as natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics, can still impact the plant’s operations.
- Transportation and Logistics:The efficient movement of materials and finished products is crucial for chip manufacturing. Germany’s reliance on rail and road transportation can lead to logistical challenges, especially in the context of potential disruptions to transportation networks.
- Access to Critical Materials:Semiconductor manufacturing requires access to a range of critical materials, some of which are sourced from countries with potential geopolitical risks. Securing a stable supply of these materials will be essential for the plant’s long-term success.
Competitive Landscape for Chip Manufacturing in Europe
Intel’s investment in Germany is part of a broader trend of chip manufacturing returning to Europe. However, the region faces competition from established players in Asia and the United States:
- Asian Dominance:Asia, particularly Taiwan and South Korea, dominates the global chip manufacturing landscape. These countries have established ecosystems of chip manufacturers, suppliers, and research institutions, giving them a significant competitive advantage.
- US Investment:The United States is also investing heavily in domestic chip manufacturing, aiming to reduce its reliance on foreign suppliers. This competition could impact the availability of skilled workers and capital for European chip plants.
- EU Chip Act:The European Union has launched the “EU Chip Act” to support the development of a more resilient semiconductor industry in Europe. This initiative aims to provide financial incentives, research funding, and other measures to boost chip manufacturing in the region.
Opportunities for Innovation and Technological Advancements
Despite the challenges, Intel’s chip plant in Germany presents significant opportunities for innovation and technological advancements:
- Research and Development:Germany has a strong tradition of research and development in the semiconductor industry. The plant can leverage this expertise to develop new technologies and processes, potentially leading to breakthroughs in chip design and manufacturing.
- Collaboration and Partnerships:The plant can foster collaboration with universities, research institutions, and other companies in the region, creating a hub for semiconductor innovation. This collaboration can accelerate the development of new technologies and solutions.
- Skilled Workforce:Germany has a highly skilled workforce in engineering and technology. The plant can attract and retain top talent, contributing to the development of a skilled workforce for the European semiconductor industry.
Geopolitical Implications of the Investment
Intel’s investment in Germany is not just a business decision; it carries significant geopolitical implications. This move signifies a shift in the global semiconductor landscape and has the potential to impact international relations, trade dynamics, and technological competition.
Impact on the US-China Trade War and Technological Competition
The investment in Germany is a strategic move by Intel to diversify its manufacturing base and reduce its reliance on China, a key player in the global semiconductor industry. This move comes amidst the ongoing US-China trade war and technological competition, where both countries are vying for dominance in the field of advanced technologies, including semiconductors.
Intel’s investment in Germany is a direct response to this geopolitical landscape, aiming to strengthen its position in the global market and mitigate potential risks associated with reliance on a single manufacturing hub.
The investment in Germany is a strategic move by Intel to diversify its manufacturing base and reduce its reliance on China.
Implications for Germany’s Relationship with the European Union and Other Countries
Intel’s investment in Germany strengthens the country’s position as a key player in the global semiconductor industry. This can enhance Germany’s economic competitiveness and attract further investments in the technology sector. It also strengthens Germany’s relationship with the European Union, as the investment aligns with the EU’s efforts to bolster its own semiconductor production capacity and reduce reliance on external suppliers.
Moreover, the investment can foster stronger ties between Germany and the United States, further solidifying their strategic partnership.
Strategic Importance of Chip Manufacturing in a Global Context, Germany intel chip plant funding
Semiconductors are the backbone of modern technology, powering everything from smartphones and computers to cars and medical devices. The ability to manufacture advanced chips is crucial for national security, economic competitiveness, and technological innovation. Intel’s investment in Germany underscores the strategic importance of chip manufacturing in a global context, as it can influence a country’s technological capabilities, economic growth, and international standing.
The ability to manufacture advanced chips is crucial for national security, economic competitiveness, and technological innovation.
Future Outlook for Chip Manufacturing in Germany

The Intel investment signifies a turning point for Germany’s chip manufacturing landscape. It has the potential to revive the sector and propel it towards a brighter future. The government’s commitment to supporting the industry, coupled with Intel’s technological prowess, creates a fertile ground for growth and innovation.
Growth and Innovation Potential
The Intel investment is expected to stimulate significant growth and innovation in the German chip manufacturing sector. The establishment of a state-of-the-art facility will attract skilled professionals and foster a vibrant ecosystem of research and development. This will lead to advancements in semiconductor technology, design, and manufacturing processes, ultimately boosting Germany’s competitiveness in the global chip market.
Key Factors Shaping the Future
Several key factors will shape the future of chip manufacturing in Germany:
Government Support
The German government has pledged substantial financial support for the Intel project and has Artikeld a comprehensive strategy to bolster the semiconductor industry. This includes tax incentives, research grants, and infrastructure development. Continued government support will be crucial in attracting further investments and fostering a favorable environment for the sector’s growth.
Technological Advancements
The industry is constantly evolving with advancements in semiconductor technology, such as the development of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient chips. Germany’s commitment to research and development will be crucial in keeping pace with these advancements and maintaining its competitiveness.
Talent Acquisition and Development
Attracting and retaining skilled professionals will be critical for the success of the chip manufacturing sector. Germany’s robust education system and focus on STEM fields provide a strong foundation for talent development. However, the country needs to attract international talent and invest in training programs to meet the growing demand for skilled workers.
Global Supply Chain Integration
The chip manufacturing sector is highly globalized, with complex supply chains spanning multiple countries. Germany’s location in the heart of Europe provides a strategic advantage for connecting with global markets and integrating into international supply chains. This will be essential for ensuring the smooth operation and growth of the chip manufacturing industry.





