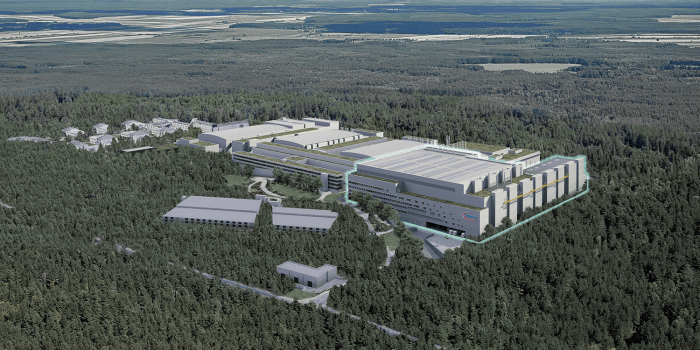
German chip plant breaks ground semiconductor industry infineon: Infineon Technologies, a leading semiconductor manufacturer, has made a bold move to invest in the future of the German economy. The company has broken ground on a new chip plant in Dresden, signaling a significant expansion that will bolster the country’s semiconductor industry and position it as a key player in the global tech landscape.
This investment, estimated to be in the billions of euros, reflects Infineon’s confidence in the potential of the German semiconductor market and its commitment to supporting the country’s economic growth.
The new plant will not only create thousands of jobs but also attract further investment in the sector, boosting the overall competitiveness of the German economy. The move comes at a crucial time as the global semiconductor industry faces challenges related to supply chain disruptions and geopolitical tensions.
Infineon’s expansion is a testament to the company’s strategic vision and its commitment to innovation, and it could serve as a catalyst for further growth in the German semiconductor industry.
Infineon’s Chip Plant Expansion

Infineon Technologies’ decision to build a new chip plant in Germany is a significant move for the company and the European semiconductor industry. This investment marks a major step towards strengthening Europe’s position in the global chip market and reducing its reliance on Asian manufacturers.
The Significance of Infineon’s Decision
Infineon’s decision to invest in a new chip plant in Germany reflects the growing importance of semiconductors in the global economy. The demand for chips is expected to continue to rise in the coming years, driven by the growth of industries such as automotive, data centers, and consumer electronics.
Building a new plant in Germany allows Infineon to secure its supply chain, reduce its dependence on Asia, and tap into the skilled workforce and research capabilities available in Europe.
Infineon’s Investment and its Impact on the German Economy, German chip plant breaks ground semiconductor industry infineon
The investment in the new chip plant is expected to be significant, with Infineon committing billions of euros to the project. This investment will create thousands of jobs in Germany, both during the construction phase and once the plant is operational.
It will also stimulate the German economy by creating demand for construction materials, equipment, and services. Moreover, the plant will attract other businesses to the region, creating a cluster of semiconductor-related companies.
Comparison with Other Recent Investments in the Semiconductor Industry
Infineon’s investment is part of a broader trend of companies investing in new semiconductor production facilities. Other companies, such as Intel, TSMC, and Samsung, have also announced plans to build new plants in various regions, including the United States, Europe, and Asia.
These investments are driven by several factors, including the growing demand for chips, the need to reduce geopolitical risks, and government incentives.However, Infineon’s investment differs from other recent investments in several key ways. Firstly, Infineon is focusing on automotive semiconductors, a market segment that is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years.
Secondly, the company is building its plant in Germany, a country with a strong tradition of manufacturing and engineering. This location gives Infineon access to a highly skilled workforce and a well-developed supply chain. Finally, Infineon’s investment is supported by the German government, which is committed to strengthening the country’s semiconductor industry.
The German Semiconductor Industry Landscape

Germany has long been a powerhouse in the global semiconductor industry, boasting a rich history of innovation and technological prowess. The country’s expertise in manufacturing, engineering, and research has propelled its semiconductor companies to become leaders in various segments.
Key Players and Strengths
Germany is home to a diverse range of semiconductor companies, each with its own strengths and areas of specialization. Some of the key players include:
- Infineon Technologies: A global leader in power semiconductors, Infineon is known for its expertise in automotive, industrial, and energy applications.
- Bosch: A multinational engineering and technology company, Bosch has a significant presence in the automotive semiconductor market, particularly in areas like sensors and microcontrollers.
- GlobalFoundries: A leading semiconductor foundry, GlobalFoundries operates a major manufacturing facility in Dresden, Germany, contributing to the country’s production capabilities.
- Siemens: A global technology powerhouse, Siemens is active in the semiconductor industry through its involvement in automation, design, and manufacturing equipment.
- NXP Semiconductors: A Dutch company with a strong presence in Germany, NXP specializes in automotive, industrial, and communication semiconductors.
These companies have established a strong foundation for the German semiconductor industry, characterized by:
- World-class manufacturing capabilities: Germany possesses advanced manufacturing infrastructure and skilled workforce, enabling efficient and high-quality semiconductor production.
- Strong research and development: German companies invest heavily in R&D, driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of semiconductor technology.
- Focus on specialized markets: German semiconductor companies often target niche markets, leveraging their expertise in specific applications and technologies.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its strengths, the German semiconductor industry faces challenges and opportunities that shape its future trajectory:
- Talent Acquisition: The industry is facing a shortage of skilled engineers and technicians, particularly in specialized areas like semiconductor design and manufacturing. This is a global issue, but it is particularly acute in Germany due to its aging workforce and limited university programs focused on semiconductor engineering.
Obtain access to eu reopens door to uk rejoining horizon with payments pledge for missing years to private resources that are additional.
- Research and Development: While Germany excels in R&D, maintaining its competitive edge requires continuous investment and collaboration with universities and research institutions. The industry needs to foster a culture of innovation and support the development of cutting-edge technologies.
- Government Support: Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the industry’s future. Germany needs to provide incentives for semiconductor companies to invest in domestic production, attract talent, and support research and development. The government can also facilitate collaboration between industry and academia to foster innovation and talent development.
The Impact of Infineon’s Expansion
Infineon’s expansion is a significant development for the German semiconductor ecosystem. It signals a commitment to domestic production and strengthens the country’s position in the global semiconductor landscape. The expansion is expected to have a positive impact on the industry in several ways:
- Increased Production Capacity: The expansion will create new manufacturing capacity, boosting Germany’s overall semiconductor output and reducing its reliance on imports.
- Job Creation: The expansion will create new jobs in various areas, including engineering, manufacturing, and research, contributing to economic growth and talent development.
- Supply Chain Resilience: By increasing domestic production, Infineon’s expansion will contribute to a more resilient semiconductor supply chain, reducing dependence on other countries and mitigating risks associated with global disruptions.
- Technological Advancements: The expansion will likely drive investments in research and development, fostering innovation and advancements in semiconductor technology.
Global Semiconductor Industry Trends
The global semiconductor industry is a dynamic and complex ecosystem, characterized by rapid technological advancements, evolving market dynamics, and increasing geopolitical influences. This section delves into key trends and drivers shaping the industry landscape, examining the role of geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions, and analyzing the implications for Infineon’s expansion and long-term competitiveness.
Key Trends and Drivers of Growth
The semiconductor industry is experiencing a period of robust growth, driven by several key factors:
- Increasing Demand for Connected Devices:The proliferation of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and other connected devices fuels demand for semiconductors, particularly for memory chips, processors, and wireless communication components.
- Growth in Data Centers and Cloud Computing:The increasing adoption of cloud computing services and the expansion of data centers drive demand for high-performance computing chips, storage solutions, and networking components.
- Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):The development of AI and ML applications requires powerful processors, specialized chips, and advanced memory technologies, driving growth in the semiconductor industry.
- Automotive Semiconductor Demand:The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous driving technologies significantly increases the demand for automotive semiconductors, including power management chips, sensors, and microcontrollers.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Expansion:The interconnectedness of devices and the growth of the IoT ecosystem create demand for a wide range of semiconductors, including sensors, microcontrollers, and wireless communication components.
Geopolitical Factors and Supply Chain Disruptions
Geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions are increasingly impacting the semiconductor industry:
- Trade Tensions:Trade disputes and sanctions between countries can disrupt supply chains, leading to price increases and production delays.
- Regionalization and Reshoring:Governments are increasingly promoting semiconductor manufacturing within their own countries to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers and enhance national security.
- Supply Chain Resilience:Companies are focusing on building more resilient supply chains, diversifying their sourcing, and increasing their own production capabilities.
- Government Support and Incentives:Governments are providing financial support and incentives to encourage semiconductor manufacturing within their territories, aiming to attract investment and create jobs.
Implications for Infineon’s Expansion and Competitiveness
The trends discussed above have significant implications for Infineon’s expansion and long-term competitiveness:
- Strategic Location:Infineon’s expansion in Germany aligns with the global trend of regionalization and reshoring, positioning the company to benefit from government support and incentives.
- Focus on Key Growth Markets:Infineon’s focus on automotive semiconductors, industrial applications, and power management aligns with the growing demand in these sectors, ensuring its continued relevance and competitiveness.
- Innovation and Technology Leadership:Infineon’s commitment to research and development and its focus on advanced technologies will be crucial for maintaining its leadership position in the evolving semiconductor landscape.
- Supply Chain Resilience:Infineon’s efforts to diversify its supply chain and strengthen its manufacturing capabilities will be essential for navigating geopolitical uncertainties and ensuring its long-term sustainability.
Technological Innovations and Future Directions: German Chip Plant Breaks Ground Semiconductor Industry Infineon
The semiconductor industry is constantly evolving, driven by relentless advancements in materials science, chip design, and manufacturing processes. These innovations are shaping the future of electronics, from smartphones and cars to artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things. For Infineon, staying at the forefront of these advancements is crucial to maintaining its competitive edge in the global semiconductor market.
Advanced Node Technologies
The pursuit of smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient chips has led to the development of advanced node technologies. These technologies involve shrinking the size of transistors on a chip, allowing for greater integration and performance. Infineon is actively involved in the development and adoption of these advanced nodes, such as 10nm and 7nm, which are crucial for high-performance applications in areas like automotive, industrial, and data centers.
For instance, Infineon’s latest automotive microcontrollers utilize 10nm technology to deliver enhanced performance and efficiency for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS).
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are revolutionizing the semiconductor industry, enabling chip designers to optimize chip design and manufacturing processes. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and trends that can be used to improve chip performance, reduce manufacturing defects, and accelerate development cycles.
Infineon is leveraging AI and ML to enhance its chip design capabilities, improve yield in its manufacturing facilities, and develop new chip architectures that are optimized for AI workloads.
Heterogeneous Integration
The increasing complexity of electronic systems has led to the development of heterogeneous integration technologies, which involve combining different types of chips and components on a single substrate. This approach allows for greater functionality and performance, while reducing the size and power consumption of electronic devices.
Infineon is exploring heterogeneous integration to develop advanced chips for applications like automotive, industrial, and communication infrastructure. For example, Infineon is combining its power management and analog expertise with advanced digital processors to create highly integrated chips for automotive applications, enabling advanced functionalities like autonomous driving and connected vehicles.
Advanced Packaging Technologies
Advanced packaging technologies are crucial for improving chip performance and reducing costs. These technologies involve using new materials and processes to connect chips and components in more efficient ways, enabling higher bandwidth, lower power consumption, and increased functionality. Infineon is investing in advanced packaging technologies like 2.5D and 3D packaging, which are essential for developing high-performance chips for applications like data centers, artificial intelligence, and high-performance computing.
For example, Infineon’s latest high-performance computing chips utilize 2.5D packaging to achieve high bandwidth and low latency, enabling faster data processing and analysis.