Generative AI business customer issues are taking center stage as businesses grapple with the transformative potential and complexities of this cutting-edge technology. While generative AI holds the promise of revolutionizing industries, it also presents a unique set of challenges for businesses and their customers.
From data privacy concerns to the potential for job displacement, navigating this new landscape requires a thoughtful and strategic approach.
This blog post explores the key issues surrounding generative AI implementation, focusing on the perspectives of both businesses and their customers. We’ll delve into the practical considerations, ethical implications, and future trends shaping this rapidly evolving field.
Understanding Generative AI in Business: Generative Ai Business Customer Issues
Generative AI is rapidly transforming businesses across various industries. Unlike traditional AI, which focuses on analyzing data and making predictions, Generative AI focuses on creating new content, ideas, and solutions. This capability opens up exciting possibilities for businesses looking to enhance creativity, efficiency, and customer experience.
Applications of Generative AI in Business
Generative AI is finding applications in various business sectors, including:
- Marketing and Advertising: Generative AI can be used to create compelling marketing copy, generate unique ad campaigns, and personalize customer experiences. For instance, AI-powered tools can analyze customer data and create personalized product recommendations, leading to increased sales and customer engagement.
- Content Creation: Generative AI can be used to create high-quality content, including articles, blog posts, social media updates, and even scripts for videos. This can help businesses save time and resources while producing engaging and informative content for their audiences.
- Product Development: Generative AI can be used to design new products, optimize existing ones, and even create prototypes. This can help businesses accelerate their product development cycles and bring innovative products to market faster.
- Customer Service: Generative AI can be used to create chatbots that can answer customer queries, provide support, and resolve issues efficiently. This can help businesses improve customer satisfaction and reduce operational costs.
Benefits of Implementing Generative AI
Implementing Generative AI can provide businesses with several benefits, including:
- Increased Efficiency: Generative AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. For example, AI-powered tools can automatically generate reports, translate documents, and create presentations, saving significant time and effort.
- Enhanced Creativity: Generative AI can help businesses explore new ideas and create innovative solutions. By analyzing data and identifying patterns, AI can suggest new product designs, marketing campaigns, and business strategies.
- Improved Customer Experience: Generative AI can personalize customer interactions, providing tailored recommendations and support. This can lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced Costs: Generative AI can help businesses optimize operations and reduce costs. For example, AI-powered tools can automate tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce the need for manual labor.
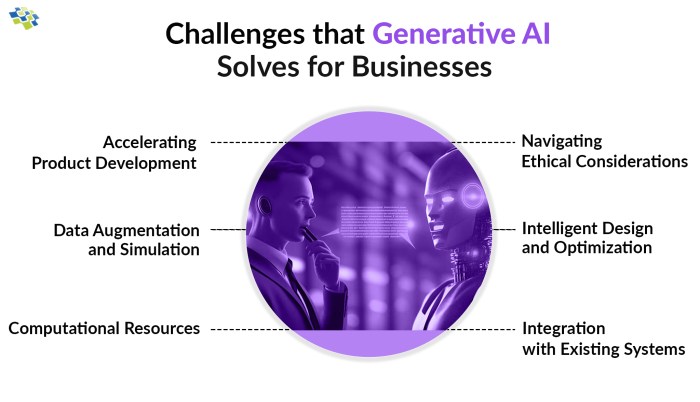
Customer Issues with Generative AI Implementation
While the potential of generative AI is undeniable, businesses are facing a range of challenges when integrating this technology. Navigating these hurdles is crucial for successful implementation and realizing the promised benefits.
Data Quality and Availability
Generative AI models are trained on massive datasets, and the quality and availability of this data are critical. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate outputs and biased results, hindering the model’s effectiveness.
- Data Bias:Models trained on biased data can perpetuate existing societal prejudices, leading to discriminatory outputs. For example, a text generation model trained on a dataset of historical news articles might produce text that reinforces gender stereotypes.
- Data Incompleteness:Insufficient or incomplete data can result in inaccurate predictions and limit the model’s ability to generalize to new situations. For instance, a financial forecasting model trained on data from a limited time period might not accurately predict future market trends.
- Data Privacy:Businesses must ensure they comply with data privacy regulations when collecting and using data for AI training. Failure to do so can result in legal consequences and reputational damage.
Model Explainability and Transparency
One of the significant challenges with generative AI is understanding how the model arrives at its outputs. This lack of transparency can make it difficult to trust the model’s decisions and identify potential biases.
- Black Box Problem:Generative AI models, particularly deep learning models, often operate as black boxes, making it difficult to understand the logic behind their outputs. This lack of explainability can be problematic in applications where transparency is crucial, such as healthcare or finance.
- Trust and Confidence:Businesses need to be able to trust the outputs of their generative AI models. Lack of transparency can erode trust and hinder adoption, especially in sensitive industries.
Integration and Scalability, Generative ai business customer issues
Integrating generative AI into existing business processes can be complex and require significant technical expertise. Scaling the implementation to meet evolving business needs can also pose challenges.
- Technical Expertise:Implementing and maintaining generative AI systems requires specialized technical skills, which may be scarce within organizations. This can lead to delays and increased costs.
- Legacy Systems:Integrating generative AI with legacy systems can be challenging due to compatibility issues and data format differences. This can hinder the adoption of AI and limit its potential benefits.
- Scalability:Scaling generative AI solutions to meet growing business needs can be costly and complex. This requires careful planning and resource allocation.
Cost and Return on Investment (ROI)
Generative AI can be expensive to implement and maintain, and businesses need to carefully consider the potential ROI before investing.
- Infrastructure Costs:Training and deploying generative AI models require significant computational resources, which can lead to high infrastructure costs.
- Data Preparation Costs:Preparing data for AI training can be a time-consuming and expensive process, requiring expertise in data cleaning, transformation, and labeling.
- Maintenance and Support Costs:Generative AI models require ongoing maintenance and support to ensure their accuracy and effectiveness. This can add significant costs over time.
Data Management and Privacy Concerns
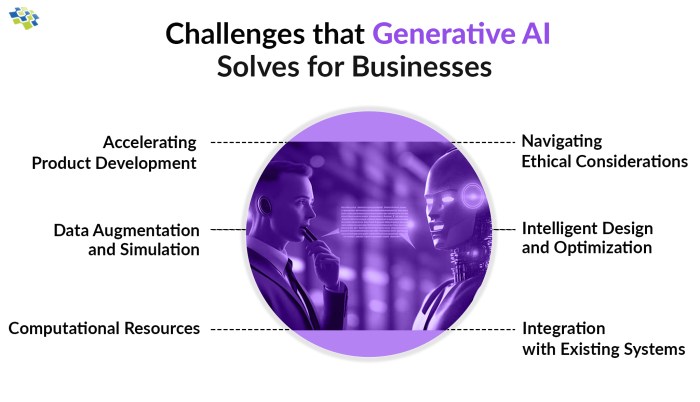
Generative AI models are trained on vast datasets, and the quality and diversity of this data significantly impact the quality and accuracy of their outputs. Data management and privacy concerns are paramount when implementing generative AI in a business setting.
Data Quality and its Impact on Generative AI Outputs
The quality of the data used to train a generative AI model directly affects the quality of its outputs. If the training data is biased, incomplete, or inaccurate, the model will likely produce outputs that reflect these flaws. For example, a chatbot trained on a dataset with limited diversity may generate responses that are biased or insensitive.
- Bias: Biased data can lead to biased outputs. For example, if a language model is trained on a dataset with predominantly male authors, it may generate text that reinforces gender stereotypes.
- Accuracy: Inaccurate data can lead to inaccurate outputs.
For example, a model trained on financial data with errors may generate incorrect predictions.
- Completeness: Incomplete data can limit the model’s ability to generate comprehensive and accurate outputs. For example, a model trained on a dataset of customer reviews that only includes positive feedback may not accurately reflect the overall customer sentiment.
Ethical Implications of Using Customer Data for Generative AI Training
Using customer data to train generative AI models raises significant ethical concerns. Customers may have privacy concerns about how their data is being used, and there is a risk that sensitive information could be leaked or misused. Transparency and consent are crucial in addressing these concerns.
- Transparency: Companies should be transparent about how they are using customer data to train generative AI models. This includes providing clear and concise information about the types of data being collected, how it is being used, and what safeguards are in place to protect it.
- Consent: Companies should obtain explicit consent from customers before using their data to train generative AI models. This consent should be informed, meaning customers should understand the potential risks and benefits of having their data used in this way.
- Data Minimization: Companies should only collect and use the minimum amount of data necessary to train their generative AI models. This helps to minimize the risk of data breaches and protect customer privacy.
Framework for Ensuring Data Privacy and Security in Generative AI Projects
A comprehensive framework is essential for ensuring data privacy and security in generative AI projects. This framework should include measures to protect data throughout its lifecycle, from collection to disposal.
- Data Security: Companies should implement robust data security measures to protect customer data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This includes using encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
- Data Anonymization: Companies should anonymize customer data whenever possible to protect their privacy.
This involves removing or modifying identifying information, such as names, addresses, and phone numbers.
- Data Governance: Companies should establish clear data governance policies and procedures to ensure that customer data is used ethically and responsibly. This includes defining roles and responsibilities for data management, implementing data retention policies, and establishing mechanisms for handling data breaches.
- Privacy Impact Assessments: Companies should conduct privacy impact assessments (PIAs) to identify and mitigate potential privacy risks associated with their generative AI projects. These assessments should consider the purpose of the project, the types of data being used, and the potential impact on customer privacy.
Generative AI and Human Interaction
Generative AI is poised to revolutionize how businesses interact with their customers, impacting everything from customer service to personalized marketing. This technology has the potential to significantly enhance customer experiences while simultaneously raising questions about the role of human interaction in the future of business.
The Impact of Generative AI on Customer Service and Support
Generative AI can significantly improve customer service and support by automating various tasks, streamlining processes, and providing personalized assistance.
- Automated Customer Support:Generative AI-powered chatbots can provide 24/7 customer support, handling common queries, resolving simple issues, and providing information efficiently. These chatbots can learn from interactions and adapt to new situations, improving their accuracy and responsiveness over time. Examples include virtual assistants like Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa, which are increasingly used for customer support purposes.
Discover how can ai make better art than humans seth dobrin has transformed methods in this topic.
- Personalized Support:Generative AI can analyze customer data and preferences to personalize interactions, providing tailored solutions and recommendations. This can include suggesting relevant products, providing customized support, and anticipating customer needs. For example, a customer service chatbot can recommend products based on a customer’s previous purchases or browsing history, leading to a more personalized experience.
- Increased Efficiency:By automating routine tasks, Generative AI frees up human customer service agents to focus on more complex issues and provide specialized support. This can lead to faster response times, reduced wait times, and increased customer satisfaction. For example, a Generative AI-powered chatbot can handle basic inquiries, allowing human agents to focus on resolving complex issues or providing personalized support.
Enhancing Customer Experiences with Generative AI
Generative AI can create a more engaging and personalized customer experience by providing tailored content, interactive experiences, and personalized recommendations.
- Personalized Content:Generative AI can create customized content, such as product descriptions, marketing materials, and educational content, based on individual customer preferences. This personalized approach can make content more relevant and engaging, leading to higher conversion rates and increased customer satisfaction.
For example, a clothing retailer could use Generative AI to create personalized product recommendations based on a customer’s style preferences and past purchases.
- Interactive Experiences:Generative AI can power interactive experiences, such as virtual try-on tools, product configurators, and personalized quizzes. These interactive elements can make the customer journey more engaging and enjoyable, leading to increased brand loyalty and positive customer sentiment. For example, a furniture retailer could use Generative AI to create a virtual try-on tool that allows customers to see how different furniture pieces would look in their homes.
- Personalized Recommendations:Generative AI can analyze customer data and preferences to provide personalized recommendations for products, services, and content. These recommendations can be tailored to individual customers, leading to higher conversion rates and increased customer satisfaction. For example, a streaming service could use Generative AI to recommend movies and TV shows based on a customer’s viewing history and preferences.
The Potential for Generative AI to Replace Human Roles
While Generative AI can significantly enhance customer experiences and streamline operations, it’s important to consider the potential impact on human roles. While Generative AI is unlikely to completely replace human customer service agents, it is expected to automate many routine tasks, leading to a shift in the nature of customer-facing roles.
- Automation of Routine Tasks:Generative AI can automate tasks such as answering basic questions, providing information, and resolving simple issues. This will free up human agents to focus on more complex issues and provide personalized support. However, this automation may lead to job displacement for some customer service roles.
- Shifting Skills:As Generative AI takes over routine tasks, human customer service agents will need to develop new skills, such as problem-solving, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence. These skills will be essential for handling complex customer issues and providing personalized support.
- Focus on Human Interaction:While Generative AI can automate many tasks, it’s important to remember that human interaction is still essential for building trust and rapport with customers. Human agents will be needed to handle complex issues, provide emotional support, and build long-term relationships with customers.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Generative AI holds immense potential for businesses across various industries, but its adoption often faces technical and organizational hurdles. Successfully integrating Generative AI requires a strategic approach that addresses these challenges and leverages the technology’s capabilities to achieve tangible business outcomes.
Technical Hurdles and Strategies
Technical barriers are common during Generative AI implementation. These can include data preparation, model selection, and integration with existing systems. Strategies to overcome these hurdles involve:
- Data Preparation:Generative AI models require high-quality, well-structured data for optimal performance. This involves data cleaning, labeling, and formatting to ensure consistency and accuracy. Techniques like data augmentation can expand limited datasets.
- Model Selection:Choosing the right Generative AI model is crucial. Factors to consider include the specific business problem, data availability, and computational resources. Pre-trained models can be fine-tuned for specific tasks, while custom models offer greater flexibility.
- Integration with Existing Systems:Integrating Generative AI with existing infrastructure and workflows is essential for seamless operation. API integration and data pipelines can facilitate data flow and model deployment.
Organizational Challenges and Solutions
Beyond technical hurdles, organizational challenges can hinder Generative AI adoption. These include resistance to change, lack of expertise, and data privacy concerns. Strategies to overcome these challenges include:
- Change Management:Effective communication and training programs are vital to address employee concerns and promote understanding of Generative AI. Highlighting the benefits and demonstrating real-world applications can build buy-in.
- Expertise Development:Investing in training programs and hiring experts can bridge the skills gap. Partnering with technology providers can offer access to specialized knowledge and support.
- Data Privacy and Security:Addressing data privacy and security concerns is crucial. Implementing robust data governance policies, ensuring compliance with regulations, and adopting responsible AI practices are essential.
Successful Business Cases
Several companies have successfully implemented Generative AI, demonstrating its transformative potential:
- Content Creation:Content marketing agencies leverage Generative AI to generate high-quality content, such as blog posts, social media updates, and product descriptions. This enhances content creation efficiency and improves audience engagement.
- Customer Service:Chatbots powered by Generative AI can provide 24/7 customer support, answering frequently asked questions and resolving issues. This improves customer satisfaction and reduces operational costs.
- Drug Discovery:Pharmaceutical companies use Generative AI to accelerate drug discovery by identifying promising drug candidates and optimizing their design. This reduces time and costs associated with traditional drug development processes.
Step-by-Step Guide for Adoption
Businesses looking to adopt Generative AI solutions can follow a structured approach:
- Identify Business Needs:Determine the specific business problems that Generative AI can address. Consider areas like content creation, customer service, or product development.
- Data Assessment:Evaluate the availability, quality, and suitability of data for Generative AI training. Identify data gaps and develop strategies for data acquisition or augmentation.
- Model Selection:Choose a Generative AI model that aligns with the business needs and data characteristics. Consider pre-trained models or custom model development.
- Pilot Implementation:Start with a pilot project to test the Generative AI solution in a controlled environment. This allows for evaluation and refinement before full-scale deployment.
- Integration and Deployment:Integrate the Generative AI solution with existing systems and workflows. Ensure seamless data flow and user access.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:Continuously monitor the performance of the Generative AI solution and adjust it as needed. Track key metrics and evaluate the impact on business outcomes.
Future Trends in Generative AI for Businesses
Generative AI is rapidly evolving, and its impact on businesses is only beginning to be felt. As the technology continues to develop, we can expect to see even more innovative applications that will transform the way businesses operate.
Emerging Trends in Generative AI
The rapid evolution of generative AI is driven by several emerging trends.
- Increased Model Complexity:Generative AI models are becoming increasingly complex, with larger datasets and more powerful algorithms. This allows them to generate more realistic and nuanced outputs, expanding their potential applications in various industries.
- Multimodal Generative AI:The ability to generate content across multiple modalities, such as text, images, audio, and video, is becoming increasingly common. This opens up new possibilities for businesses to create immersive and engaging experiences for their customers.
- Democratization of Generative AI:Generative AI tools are becoming more accessible to businesses of all sizes, thanks to cloud-based platforms and pre-trained models. This allows businesses to experiment with generative AI and leverage its capabilities without significant upfront investment.
- Ethical Considerations:As generative AI becomes more powerful, ethical considerations are becoming increasingly important. Businesses need to address concerns around bias, fairness, and the potential for misuse of generative AI technologies.
Potential Impact on Business Processes
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize various business processes, creating new opportunities and efficiencies.
- Content Creation:Generative AI can automate content creation tasks, such as writing marketing copy, generating social media posts, and creating product descriptions. This frees up human resources to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Customer Service:Generative AI-powered chatbots can provide personalized and efficient customer support, answering questions, resolving issues, and providing recommendations.
- Product Development:Generative AI can assist in product design, prototyping, and testing, accelerating the development process and reducing costs.
- Marketing and Sales:Generative AI can personalize marketing campaigns, generate targeted advertising, and automate lead generation processes, improving marketing ROI.
- Operations:Generative AI can optimize supply chains, predict demand, and automate repetitive tasks, improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Timeline of Key Milestones
The development and adoption of generative AI is progressing rapidly, with several key milestones marking its evolution.