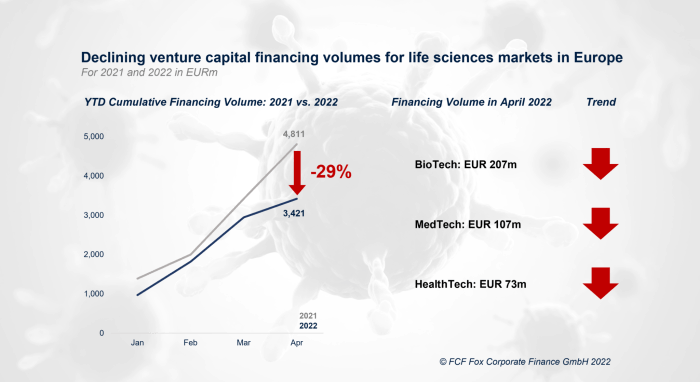
European VC deals continue to sink economic downturn, painting a stark picture of the current investment landscape. The once vibrant startup ecosystem is facing headwinds from rising inflation, interest rates, and global economic uncertainty. This cocktail of challenges is making it increasingly difficult for startups to secure funding, impacting their growth and ability to hire.
Investors are adapting to this new reality, shifting their focus towards later-stage companies with proven track records and stronger financial fundamentals. Investment criteria are becoming more stringent, and timelines are extending as investors seek greater certainty in their investments.
The impact of this VC slowdown is being felt across various sectors, with fintech, healthcare, and cleantech experiencing a noticeable decline in deal activity.
Impact on Startups and Investors
The European startup ecosystem is facing a challenging period as venture capital (VC) funding dries up amidst an economic downturn. This slowdown has far-reaching implications for both startups and investors, affecting their ability to raise capital, scale their businesses, and navigate the current market landscape.
Investigate the pros of accepting a glimpse into ais future in architecture inflatable skyscrapers in your business strategies.
Challenges for Startups, European vc deals continue to sink economic downturn
The reduced availability of VC funding presents a significant challenge for European startups. Fundraising has become more difficult, with investors being more selective and demanding higher returns. This has forced startups to adjust their strategies, often leading to extended fundraising rounds and a need to demonstrate stronger traction and profitability.
- Fundraising Challenges:The current market conditions have made it harder for startups to secure funding, with investors focusing on later-stage companies with proven track records. This has resulted in longer fundraising rounds and a need for startups to demonstrate greater traction and profitability.
- Growth and Expansion:With limited access to capital, startups face constraints in scaling their operations, hiring new talent, and expanding into new markets. This can hinder their ability to compete with larger, well-established players.
- Hiring Challenges:The economic downturn has also led to a more competitive hiring landscape, with companies facing difficulties attracting and retaining top talent. Startups may struggle to offer competitive salaries and benefits, further impacting their growth trajectory.
Investor Strategies
Investors are adapting to the changing market conditions by adopting a more cautious approach to investments. This involves focusing on later-stage companies with proven business models and strong financial performance, adjusting investment criteria to favor companies with higher growth potential and profitability, and extending investment timelines to provide greater support during challenging market conditions.
- Focus on Later-Stage Companies:Investors are shifting their attention to later-stage companies that have already demonstrated strong traction and profitability. This strategy aims to mitigate risk and ensure a higher probability of successful exits.
- Adjusted Investment Criteria:Investors are now placing greater emphasis on factors such as revenue growth, profitability, and unit economics. Startups with strong unit economics and a clear path to profitability are more likely to attract investment.
- Extended Investment Timelines:Investors are extending their investment timelines to provide greater support for startups during challenging market conditions. This allows startups to navigate the downturn and build a more sustainable business.
Industry-Specific Trends: European Vc Deals Continue To Sink Economic Downturn
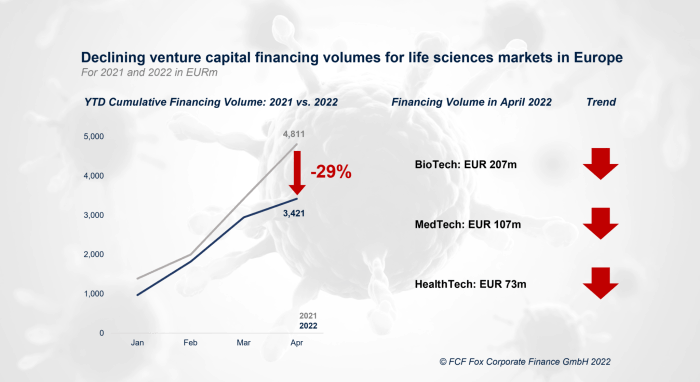
Despite the economic downturn, the European startup ecosystem continues to demonstrate resilience, with specific sectors showing notable growth and attracting significant investment. These trends are driven by evolving market demands, technological advancements, and a growing focus on sustainability and social impact.
Fintech
The fintech sector remains a hotbed of innovation, with investors recognizing the potential for disruptive technologies to transform financial services. The increasing adoption of digital banking, payments, and investment platforms, coupled with the rise of open banking and regulatory changes, has fueled growth in this area.
- Embedded Finance:The integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, such as e-commerce, travel, and healthcare, is gaining traction. This allows businesses to offer financial products and services directly to their customers, enhancing user experience and increasing revenue streams. Examples include GoCardless, a payments platform for recurring payments, and Taxfix, a tax-filing app that integrates with banking accounts.
- Alternative Lending:With traditional banks becoming more risk-averse, alternative lending platforms have emerged to provide financing options for businesses and individuals who may not qualify for traditional loans. These platforms leverage data analytics and technology to assess creditworthiness and offer more flexible lending terms.
Notable examples include Stash, a fintech company offering investment and lending products, and Xentral, a platform that provides financing for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Insurtech:The insurance industry is undergoing a digital transformation, with insurtech startups leveraging technology to streamline processes, improve customer experience, and offer innovative insurance products. These companies are using data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology to personalize insurance offerings, automate claims processing, and develop new risk assessment models.
Some notable examples include Lemonade, a digital insurance company known for its AI-powered claims processing, and Alan, a health insurance company that offers transparent pricing and digital services.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector is another area of significant VC activity, driven by the growing demand for personalized medicine, digital health solutions, and technological advancements.
- Telehealth:The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, enabling patients to consult with healthcare professionals remotely. This trend is expected to continue, with startups developing innovative telehealth platforms, wearable devices, and remote monitoring solutions. Examples include Kry, a Swedish telehealth platform offering online consultations with doctors, and Babylon Health, a digital healthcare platform that provides virtual consultations and health management services.
- Digital Therapeutics:These startups develop software-based interventions to prevent, manage, or treat chronic diseases. They leverage data analytics, artificial intelligence, and behavioral science to personalize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. Examples include Omada Health, a digital platform for chronic disease management, and Kaia Health, a mobile app that provides personalized therapy for musculoskeletal conditions.
- Precision Medicine:This approach uses genetic and molecular information to tailor medical treatments to individual patients. Startups are developing innovative diagnostics, personalized therapies, and drug discovery platforms based on this approach. Examples include Genomics England, a UK-based company that is sequencing the genomes of 100,000 patients to advance personalized medicine, and Freenome, a company developing a blood test for early cancer detection.
Cleantech
The cleantech sector is attracting increasing investment as investors seek to capitalize on the growing demand for sustainable solutions.
- Renewable Energy:Startups are developing innovative technologies to improve the efficiency and affordability of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power. These companies are also working on energy storage solutions to address the intermittency of renewable energy generation.
Examples include Sonnen, a German company that provides home energy storage systems, and Enphase Energy, a US-based company that develops microinverters for solar panels.
- Sustainable Materials:With growing concerns about plastic pollution and the environmental impact of traditional materials, startups are developing innovative sustainable alternatives. These include bio-based materials, recycled plastics, and other eco-friendly options. Examples include Bioplastics Europe, a company that develops biodegradable plastics from renewable resources, and Circularise, a platform that tracks the circularity of materials throughout their lifecycle.
- Smart Cities:Startups are developing technologies to improve urban sustainability, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance public transportation. These include smart grids, intelligent traffic management systems, and data-driven urban planning solutions. Examples include Citymapper, a UK-based company that provides real-time public transport information and navigation, and Waze, a community-based traffic and navigation app.
Future Outlook
While the current downturn has dampened European VC activity, it’s crucial to remember that this is a cyclical phenomenon. History has shown that periods of economic contraction are often followed by periods of robust growth, and the European VC landscape is likely to experience a similar rebound.Several factors point to a potential resurgence in European VC activity in the coming years.
Government Support
Government initiatives across Europe are actively promoting innovation and supporting startups. For instance, the European Union’s Horizon Europe program provides significant funding for research and development, fostering the growth of promising tech companies.
Industry Consolidation
The downturn has led to a consolidation of the VC industry, with stronger players emerging. This consolidation can result in more strategic investments and a more efficient allocation of capital, leading to a more robust ecosystem.
Innovation
Despite the economic challenges, European startups continue to innovate at a rapid pace. The continent is a hub for cutting-edge technology in areas like artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and biotechnology. This ongoing innovation will continue to attract investors and drive growth.
Opportunities and Challenges for Startups and Investors
The rebound in European VC activity will present both opportunities and challenges for startups and investors.
Predictions for the European VC Landscape
The following table Artikels key predictions for the European VC landscape in the next 12-24 months:| Aspect | Prediction | Example ||—|—|—|| Deal Volume | A gradual increase in deal volume, with a focus on later-stage investments. | The number of Series B and Series C funding rounds is expected to rise as investors seek out companies with proven traction.
|| Average Deal Size | A slight increase in average deal size as investors prioritize larger, more established companies. | Investors may be more willing to invest larger sums in companies with strong revenue growth and market share. || Investor Sentiment | A cautious optimism, with investors looking for strong fundamentals and clear paths to profitability.
| Investors will likely be more selective in their investments, seeking out companies with a clear value proposition and a strong team. |