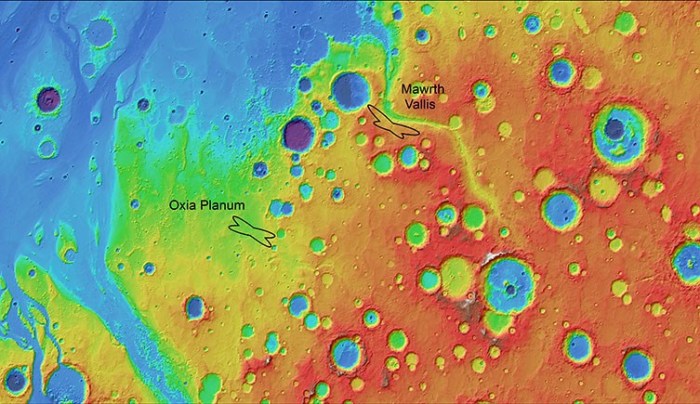
European space agency first water map mars reveals potential landing spots – ESA’s First Water Map of Mars Reveals Potential Landing Spots: Imagine a map of Mars, not just showing its dusty surface, but revealing hidden reservoirs of water. That’s exactly what the European Space Agency (ESA) has accomplished, creating the first-ever comprehensive water map of the Red Planet.
This groundbreaking achievement is not just a scientific triumph; it’s a game-changer for future Martian exploration, potentially paving the way for human missions and unlocking secrets about the planet’s past and potential for life.
The map, compiled from data gathered by ESA’s Mars Express orbiter, reveals a treasure trove of information about Mars’s water history. By analyzing the distribution and abundance of water ice, frozen water, and hydrated minerals, scientists can now piece together a more complete picture of how water has shaped the Martian landscape over billions of years.
This understanding is crucial for identifying potential landing sites for future missions, ensuring that astronauts have access to vital resources like water and understanding the geological processes that have shaped the planet.
The First Water Map of Mars: A New Era of Martian Exploration
The European Space Agency (ESA) has released the first comprehensive water map of Mars, a groundbreaking achievement that will revolutionize our understanding of the Red Planet and its potential for past and present life. This map, meticulously compiled using data from the ESA’s Mars Express orbiter, provides an unprecedented glimpse into the distribution of water ice and hydrated minerals across the Martian surface.
Its significance lies in its ability to shed light on the history of water on Mars, a crucial factor in determining the planet’s habitability.This water map is not just a scientific marvel; it is also a critical tool for future Martian exploration.
It provides invaluable insights into the distribution of water resources, which are essential for sustaining human missions and conducting scientific research. The map highlights potential landing sites for future missions, including areas where water ice could be readily accessible for use as a resource.
The Significance of the Water Map
The ESA’s water map is a landmark achievement in our quest to understand Mars. It provides a comprehensive overview of the distribution of water ice and hydrated minerals across the Martian surface, revealing a complex and dynamic history of water on the planet.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out 5 tips to get the most out of your workation now.
- The map reveals that water ice is present in significant quantities at high latitudes and in polar regions, suggesting that Mars may have once been a much warmer and wetter planet.
- The map also identifies numerous locations where hydrated minerals are found, indicating that water may have interacted with the Martian surface in the past, possibly creating conditions conducive to life.
- This information is invaluable for understanding the evolution of the Martian climate and the potential for past and present life on the planet.
The Importance of the Water Map for Future Exploration
The ESA’s water map is a critical resource for future Martian exploration. It provides valuable insights into the distribution of water resources, which are essential for sustaining human missions and conducting scientific research.
- The map highlights potential landing sites for future missions, including areas where water ice could be readily accessible for use as a resource.
- For example, the map reveals that water ice is present in significant quantities at high latitudes and in polar regions, suggesting that these areas could be ideal for establishing future outposts or research stations.
- The map also identifies locations where hydrated minerals are found, which could be used for extracting water or other resources.
ESA’s Water Map of Mars
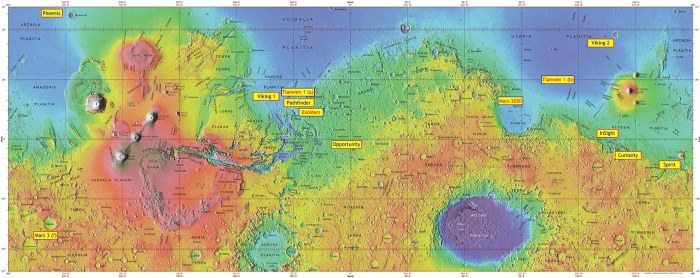
The European Space Agency (ESA) has created the first comprehensive water map of Mars, revealing a treasure trove of information about the Red Planet’s past and present. This map, derived from data collected by the Mars Express spacecraft, offers unprecedented insights into the distribution and abundance of water on Mars, shaping our understanding of its potential for past and present life.
Methods Used to Create the Water Map
The water map was created using data from the Mars Express spacecraft’s MARSIS (Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionosphere Sounding) instrument. MARSIS emits radar pulses that penetrate the Martian surface, allowing scientists to study the subsurface structure and composition.
By analyzing the radar signals, researchers can identify regions containing water ice, liquid water, and other materials.
Key Findings from the Water Map
The water map reveals a complex and diverse distribution of water on Mars. It shows that water ice is abundant in the Martian polar regions, particularly in the northern plains. This ice is thought to be a significant reservoir of water on Mars, potentially holding more water than all the Earth’s oceans combined.
The map also reveals the presence of water ice in the mid-latitudes and even in some equatorial regions, suggesting that water may be more widespread on Mars than previously thought.
Implications for Martian History and Habitability
The water map provides crucial insights into Martian history and its potential for habitability. The abundance of water ice suggests that Mars may have once been a much warmer and wetter planet, potentially supporting liquid water on its surface. This raises the possibility that life may have existed on Mars in the past, and perhaps even persists in some form today.
The presence of water ice also offers a valuable resource for future human exploration, potentially providing a source of drinking water and fuel for rockets.
Potential Landing Sites
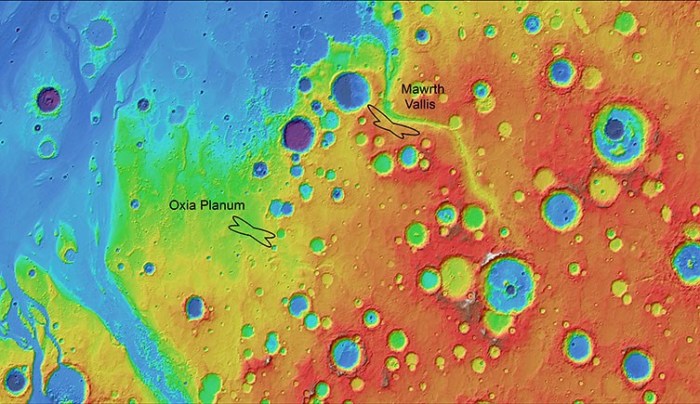
The water map of Mars, compiled by the European Space Agency (ESA), has revealed a wealth of information about the distribution of water ice on the Martian surface. This data is invaluable for future missions, as it helps identify potential landing sites that could offer access to resources, support scientific investigations, and potentially even facilitate the establishment of a human outpost.
Identifying Promising Landing Sites
The water map has identified several promising landing sites, each with its own unique advantages and disadvantages. The selection of these sites is based on factors such as the presence of water ice, geological stability, and the availability of resources.
Landing Sites Based on Water Ice Presence
- Valles Marineris: This massive canyon system is thought to contain significant amounts of water ice, both on the surface and below ground. It is a prime location for studying the history of water on Mars and potentially accessing this resource.
- North Polar Cap: The Martian north polar cap is a vast expanse of water ice and frozen carbon dioxide. This site offers a unique opportunity to study the evolution of the Martian climate and investigate the potential for accessing water ice.
- Mid-latitude regions: The water map has revealed the presence of water ice in mid-latitude regions, particularly in areas that are shadowed from the sun. These locations could provide access to water ice for future missions and offer opportunities for studying the Martian climate.
Landing Sites Based on Geological Stability
- Elysium Planitia: This vast plain is known for its geological stability, making it a suitable landing site for future missions. The presence of water ice in the subsurface makes it even more attractive.
- Amazonis Planitia: This plain is another geologically stable location with potential for water ice. Its relatively flat terrain and proximity to other interesting features make it a promising landing site.
Landing Sites Based on Resource Availability
- Gale Crater: This crater, explored by the Curiosity rover, has been found to contain evidence of past water activity, including a lake bed. The presence of water ice in the subsurface makes it a prime location for studying the potential for habitability.
- Jezero Crater: This crater is another promising site for studying past water activity and the potential for habitability. It is thought to have once been a lake and may contain evidence of ancient life.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Landing Sites, European space agency first water map mars reveals potential landing spots
Each potential landing site presents its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
- Access to water ice: This is a crucial resource for future missions, as it can be used for drinking, producing rocket fuel, and growing crops.
- Geological stability: This is essential for landing and operating spacecraft safely.
- Scientific value: These sites offer opportunities to study the history of water on Mars, the potential for habitability, and the Martian climate.
Disadvantages
- Harsh environment: Mars is a cold, dry, and radiation-exposed environment. Landing sites must be carefully chosen to minimize risks to spacecraft and crew.
- Limited resources: The availability of resources such as water ice and other materials may be limited in some locations.
- Technological challenges: Landing and operating spacecraft in these locations may present significant technological challenges.
Future Missions and Research
The newly released water map of Mars will revolutionize future Martian exploration missions. It provides invaluable data for selecting ideal landing sites, understanding the distribution of water ice, and planning scientific investigations.
Potential Landing Sites
The water map identifies potential landing sites for future missions, offering a comprehensive understanding of the distribution of water ice and its potential for scientific exploration. These sites can be selected based on the presence of water ice, its accessibility, and the potential for scientific investigations.
- Polar Regions:The polar regions of Mars are known to contain significant amounts of water ice, both at the surface and beneath the ground. These regions are ideal for studying the history of water on Mars and its potential for supporting life.
- Mid-Latitude Regions:Mid-latitude regions on Mars also show evidence of water ice, particularly in the form of permafrost. These regions are of interest for understanding the evolution of Martian climate and the potential for past or present life.
- Equatorial Regions:While the equatorial regions of Mars are generally considered dry, the water map reveals localized areas with potential water ice deposits. These areas could be valuable for studying the distribution of water on Mars and its relationship to the planet’s climate.
Scientific Research Objectives
The water map provides valuable insights for future missions to Mars, enabling scientists to conduct a wide range of scientific investigations.
- Water Ice Characterization:Future missions can use the water map to investigate the composition, purity, and accessibility of water ice. This information will be crucial for understanding the potential for using water ice as a resource for future human missions.
- Past Habitability:The water map will help scientists identify locations where liquid water may have existed in the past, offering insights into the potential for past life on Mars.
- Climate Evolution:By studying the distribution of water ice, scientists can learn more about the history of Martian climate and its potential for future habitability.
- Resource Utilization:The water map will be essential for planning future missions that aim to utilize water ice as a resource for drinking water, rocket fuel, or oxygen production.
Potential for Scientific Discoveries
The water map of Mars opens up exciting possibilities for future scientific discoveries related to water on Mars.
- Evidence of Past Life:The water map may reveal new locations where liquid water once flowed, increasing the chances of finding evidence of past life on Mars.
- Understanding Martian Climate:By studying the distribution of water ice, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the history of Martian climate and its potential for future habitability.
- Potential for Life Today:The water map may reveal hidden pockets of liquid water beneath the surface, potentially providing a habitat for microbial life.
- New Resources for Human Missions:The water map could lead to the discovery of new sources of water ice that could be used to support future human missions to Mars.
Impact on Our Understanding of Mars: European Space Agency First Water Map Mars Reveals Potential Landing Spots
This water map is a game-changer for our understanding of Mars. It’s like having a detailed roadmap of where water has been, where it might still be, and how it’s shaped the Martian landscape. It’s a crucial piece of the puzzle that helps us unravel the mysteries of Mars’s past and present.
Implications for the Search for Life
The presence of water is essential for life as we know it. This map provides crucial insights into where water existed on Mars, and where it might still be hidden beneath the surface. This information is vital for the search for past or present life on Mars.