European space agency esa budget * – The European Space Agency (ESA) budget is the lifeblood of ambitious space exploration, scientific discovery, and technological advancement. It’s not just about rockets and satellites; it’s about pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and understanding.
This budget, a complex tapestry woven from political priorities, scientific ambitions, and technological breakthroughs, determines the scope of ESA’s projects and the impact they have on our world. It’s a fascinating story of how resources are allocated, priorities are set, and dreams are pursued in the vast expanse of space.
ESA Budget Overview: European Space Agency Esa Budget *
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a leading international organization dedicated to space exploration and research. Its budget reflects its ambitious goals and its commitment to pushing the boundaries of human knowledge. Understanding the ESA’s budget is crucial to grasp its capabilities, its priorities, and its impact on the global space sector.
ESA Budget Size and Sources
The ESA’s budget is substantial and reflects the importance of space exploration to its member states. The agency’s budget is determined by its member states, each contributing based on their gross national product (GNP). This means that countries with larger economies contribute more to the ESA’s overall budget.
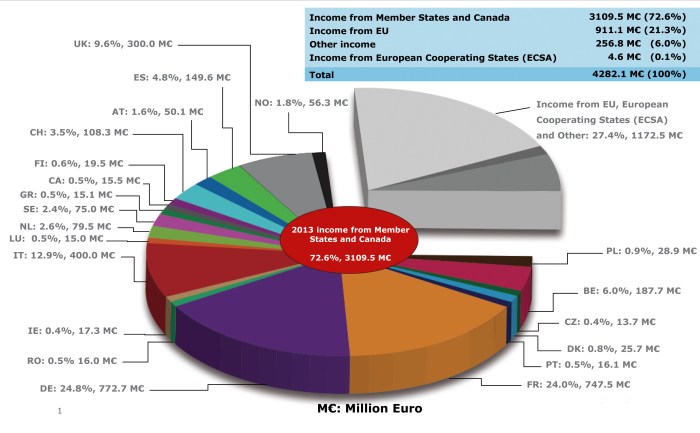
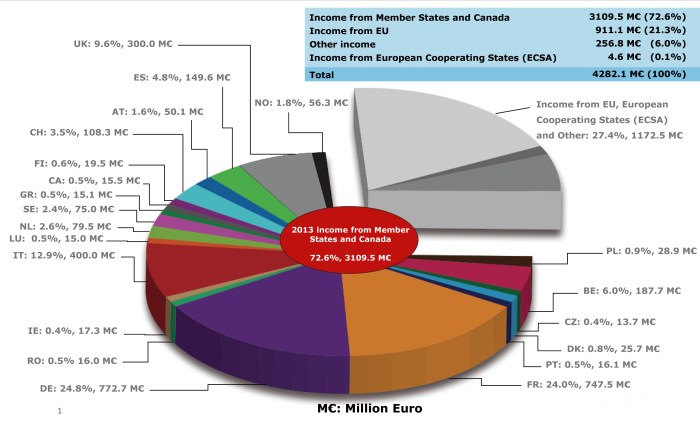
For 2023, the ESA’s budget is set at €7.04 billion. This represents a significant increase from previous years, demonstrating the member states’ continued commitment to space exploration and research. The majority of the ESA’s funding comes from its member states’ contributions, with a smaller portion coming from other sources, such as commercial contracts and international partnerships.
ESA Budget Historical Evolution
The ESA’s budget has undergone significant changes over its history, reflecting the evolving priorities of its member states and the changing landscape of space exploration.
- The ESA was established in 1975, and its initial budget was relatively modest. However, the budget has steadily increased over the decades, reflecting the growing importance of space exploration and the increasing complexity of space missions.
- The budget saw significant growth in the 1990s and 2000s, driven by major projects like the International Space Station (ISS) and the development of the Ariane 5 launch vehicle.
- The budget has continued to grow in recent years, driven by ambitious projects like the James Webb Space Telescope, the ExoMars mission, and the development of new launch vehicles like the Ariane 6.
Factors Influencing ESA Budget Allocation, European space agency esa budget *
The ESA’s budget allocation is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including political priorities, scientific advancements, and technological developments.
- Political Priorities: Member states’ political priorities play a significant role in shaping the ESA’s budget. For example, a member state’s focus on climate change research may lead to increased funding for Earth observation missions.
- Scientific Advancements: Breakthroughs in science and technology often drive the ESA’s budget allocation. For example, the discovery of exoplanets has led to increased funding for missions dedicated to studying these distant worlds.
- Technological Developments: Technological advancements can also influence the ESA’s budget. For example, the development of reusable launch vehicles has the potential to significantly reduce the cost of space access, potentially leading to increased funding for space missions.
Budget Allocation and Prioritization
The European Space Agency (ESA) allocates its budget across a wide range of programs and activities, reflecting its multifaceted mission to advance space exploration, scientific research, and technological innovation. This budget allocation is guided by strategic priorities, aiming to maximize the impact of ESA’s endeavors on global scientific understanding, technological progress, and societal benefits.
Distribution of Budget Across Programs
The ESA budget is distributed across various programs, each addressing a specific area of focus. These programs represent the agency’s strategic priorities and reflect its commitment to different aspects of space exploration and utilization.
- Human and Robotic Exploration: This program encompasses missions to the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies, including the development of technologies for human spaceflight and robotic exploration. This area receives a significant portion of the budget, reflecting the ambitious goals of ESA’s exploration programs.
- Earth Observation: This program focuses on monitoring Earth’s environment, climate, and natural resources using satellites and other space-based technologies. The program plays a crucial role in understanding and mitigating climate change, managing natural disasters, and supporting sustainable development.
- Space Science: This program encompasses missions to study the universe, including the Sun, planets, stars, and galaxies. This area includes research into fundamental physics, cosmology, and astrobiology, contributing to our understanding of the cosmos.
- Navigation: This program focuses on developing and maintaining satellite navigation systems, such as Galileo, which provides accurate positioning, timing, and navigation services globally. This program is essential for various applications, including transportation, communication, and emergency response.
- Telecommunications: This program focuses on developing and deploying space-based telecommunication systems, enabling high-speed data transmission and communication services in remote areas and disaster zones.
- Technology Development: This program invests in developing new technologies for space exploration, scientific research, and applications on Earth. This area includes advancements in areas such as propulsion systems, materials science, and artificial intelligence.
Budgetary Challenges and Constraints
The European Space Agency (ESA) operates in a complex and dynamic environment, facing various challenges and constraints in managing its budget. These challenges stem from factors such as economic downturns, political uncertainties, and competing priorities, which can significantly impact the ESA’s financial resources and, consequently, its ability to execute its ambitious space exploration programs.
Impact of Economic Downturns
Economic downturns can significantly impact the ESA’s budget, as member states may reduce their contributions to the agency in response to domestic economic pressures. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, several ESA member states faced budget cuts, leading to a reduction in the agency’s overall funding.
This reduction in funding can lead to delays or cancellations of planned missions and projects, hindering the ESA’s ability to achieve its scientific and technological goals.
Political Uncertainties
Political uncertainties, such as changes in government policies or international relations, can also create challenges for the ESA’s budget. These uncertainties can affect the stability of funding commitments from member states and make it difficult for the ESA to plan for the long term.
For instance, the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union has raised concerns about the future of the ESA’s budget, as the UK was a significant contributor to the agency.
Competing Priorities
The ESA’s budget faces competition from other national and international priorities, such as defense, healthcare, and education. This competition for resources can make it challenging for the ESA to secure sufficient funding to support its ambitious space exploration programs. To address this challenge, the ESA must effectively communicate the value of its programs to policymakers and the public, highlighting their scientific, technological, and economic benefits.
Browse the multiple elements of europols operation spector leads massive dark web drug bust to gain a more broad understanding.
Potential Implications of Budgetary Challenges
The budgetary challenges faced by the ESA have potential implications for its future programs and activities. These implications include:
- Delays or cancellations of missions:Budget cuts may force the ESA to delay or cancel planned missions, impacting the agency’s scientific and technological progress.
- Reduced scope of missions:To stay within budget constraints, the ESA may have to reduce the scope of its missions, limiting their scientific and technological returns.
- Focus on less ambitious projects:The ESA may prioritize less ambitious projects that require lower funding, potentially hindering its ability to achieve its long-term goals.
- Increased reliance on partnerships:The ESA may need to increase its reliance on partnerships with other space agencies or private companies to share costs and resources.
Budgetary Transparency and Accountability
The European Space Agency (ESA) operates with a high degree of transparency and accountability in its budget management. This commitment ensures public trust and confidence in the agency’s financial practices.
Mechanisms and Processes for Transparency and Accountability
Transparency and accountability are fundamental principles guiding the ESA’s budget management. Several mechanisms and processes are in place to ensure these principles are upheld:
- Publicly Available Budget Documents:The ESA publishes its budget documents, including the annual budget, financial statements, and audit reports, on its website. This allows stakeholders, including the public, to access and scrutinize the agency’s financial activities.
- Detailed Budget Breakdown:The ESA provides a detailed breakdown of its budget, outlining how funds are allocated to different programs and activities. This allows for a clear understanding of how the agency prioritizes its spending.
- Regular Reporting:The ESA submits regular reports to its member states, outlining its financial performance, progress on projects, and any challenges faced. These reports are reviewed by member state representatives, who can ask questions and provide feedback.
Role of Independent Audits and Oversight Bodies
Independent audits and oversight bodies play a crucial role in ensuring the ESA’s financial activities are conducted ethically and efficiently.
- External Audits:The ESA’s financial statements are subject to independent audits by external auditors. These auditors are appointed by the ESA Council and have the authority to review the agency’s financial records and procedures. Their reports are publicly available and provide an objective assessment of the ESA’s financial health.
- Internal Audit Service:The ESA has an internal audit service that conducts independent audits of the agency’s internal controls and processes. This service reports directly to the ESA Director General and provides recommendations for improvement.
- ESA Council:The ESA Council, which is composed of representatives from all member states, has oversight responsibility for the agency’s budget and financial activities. The Council approves the ESA’s budget and monitors its implementation.
Impact of Public Scrutiny and Media Attention
Public scrutiny and media attention can have a significant impact on the ESA’s budgetary decisions.
- Public Opinion:Public opinion can influence the ESA’s priorities and funding decisions. For example, if there is strong public support for a particular space exploration mission, it is more likely to receive funding.
- Media Coverage:Media coverage of the ESA’s activities can shape public perception and influence budgetary decisions. Positive media coverage can generate public support for the agency’s programs, while negative coverage can lead to scrutiny and calls for budget cuts.
- Transparency and Accountability:Public scrutiny and media attention can encourage the ESA to be more transparent and accountable in its financial management. This can lead to improvements in the agency’s processes and procedures.
Future Budgetary Outlook
The ESA’s budget for the coming years will be influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including technological advancements, scientific discoveries, and global challenges. While the exact trajectory remains uncertain, understanding these factors can provide insights into potential trends and developments that could shape the ESA’s financial priorities.
Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping the ESA’s future budget. Advancements in areas such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 3D printing have the potential to revolutionize space exploration and research.
- For example, AI-powered systems could enhance mission control, data analysis, and autonomous spacecraft operations, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Similarly, quantum computing could enable breakthroughs in astrophysics and cosmology by simulating complex phenomena that are currently beyond the capabilities of classical computers.
These technological advancements could lead to increased investment in research and development, potentially driving budget growth. However, the ESA will need to carefully assess the potential benefits and costs of adopting these new technologies to ensure that investments are strategically aligned with its long-term goals.
Influence of Scientific Discoveries
Scientific discoveries can significantly influence the ESA’s budget by creating new avenues for exploration and research. Recent discoveries, such as the detection of gravitational waves and the potential for life on other planets, have generated tremendous excitement and interest in space exploration.
- These discoveries could lead to the development of new missions and projects, potentially requiring significant budget increases.
- The ESA will need to prioritize these new endeavors while maintaining its existing commitments to ongoing projects and research activities.
Balancing the need for new initiatives with the existing obligations will be a key challenge for the ESA in the years to come.
Global Challenges and Budgetary Priorities
Global challenges, such as climate change, resource scarcity, and the threat of space debris, are increasingly influencing the ESA’s budgetary priorities. These challenges demand innovative solutions and require international cooperation.
- For example, the ESA is actively involved in developing Earth observation systems to monitor climate change and its impacts.
- The agency is also working on technologies to mitigate the risks posed by space debris, such as active debris removal and collision avoidance systems.
These initiatives require significant financial investments, highlighting the growing importance of addressing global challenges through space-based solutions.
Potential for Growth, Stagnation, or Reduction
The ESA’s budget could experience growth, stagnation, or even reduction depending on various factors.
- Continued technological advancements and scientific discoveries could drive budget growth as new opportunities for exploration and research emerge.
- However, budgetary constraints and competing priorities could limit the ESA’s ability to fully capitalize on these opportunities.
- Furthermore, economic downturns or political instability could lead to a reduction in funding, impacting the agency’s ability to pursue its ambitious goals.
The ESA’s future budget will be shaped by a delicate balance between these competing forces.