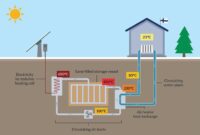
Europe high tech scramble for better energy storage – Europe’s high-tech scramble for better energy storage is a race against time, driven by a growing need for reliable and sustainable energy sources. As the continent transitions towards a greener future, the demand for energy storage solutions has skyrocketed. This scramble is fueled by a multitude of factors, including the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, the growing concerns about energy security, and the ambitious goals set by the European Union to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels.
This quest for better energy storage involves a diverse range of technologies, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. From advanced battery technologies to pumped hydro storage and compressed air energy storage, the innovation landscape is teeming with exciting developments.
The European Union is actively promoting the development and deployment of these technologies through various policies and financial incentives, creating a fertile ground for innovation and investment.
The Energy Storage Landscape in Europe
Europe is at the forefront of the global transition to renewable energy sources. However, the intermittent nature of solar and wind power poses a significant challenge. Energy storage plays a crucial role in bridging this gap by providing flexibility and reliability to the grid, ensuring a smooth transition to a clean energy future.
The Role of Energy Storage in Achieving Europe’s Renewable Energy Targets
Energy storage is essential for achieving Europe’s ambitious renewable energy targets. It helps address the intermittency of renewable energy sources by storing excess energy generated during periods of high production and releasing it when demand exceeds supply. This ensures grid stability and reliability, minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Drivers of the High-Tech Scramble

Europe’s energy storage market is experiencing a rapid transformation, driven by a confluence of factors that are propelling the development of innovative solutions. The scramble for better energy storage is not just a technological race but a strategic imperative for the continent’s energy future.
The Growing Demand for Renewable Energy
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power, is a key driver of the demand for energy storage. Renewable energy sources are inherently intermittent, meaning their output fluctuates depending on weather conditions. Energy storage systems are crucial for bridging the gap between energy supply and demand, ensuring a reliable and stable power grid.
- Intermittency of Renewable Energy:Solar and wind power generation are subject to fluctuations due to weather conditions. Energy storage systems can buffer these fluctuations, ensuring a consistent power supply even when renewable energy sources are not producing at their peak capacity.
- Grid Stability and Reliability:Energy storage systems can help stabilize the grid by providing fast-response reserves that can be deployed in case of sudden changes in demand or supply. This improves the overall reliability of the power grid and reduces the risk of blackouts.
Find out further about the benefits of saudi arabia unveils designs for the line vision a 170km long 200m wide city that can provide significant benefits.
- Integration of Renewable Energy:As the share of renewable energy sources in the grid increases, energy storage becomes essential for managing the intermittency and ensuring seamless integration of these sources into the existing energy system.
Geopolitical Tensions and Energy Security
Geopolitical tensions and the desire for energy independence are also driving the demand for energy storage. Europe’s reliance on fossil fuel imports from Russia has highlighted the vulnerabilities of its energy system. Energy storage solutions can help reduce dependence on imported fuels and enhance energy security.
- Energy Independence:Energy storage can enable countries to store energy generated domestically, reducing their reliance on imports and enhancing energy independence. This is particularly relevant for countries seeking to diversify their energy sources and reduce their vulnerability to geopolitical risks.
- Resilience and Disaster Preparedness:Energy storage systems can provide backup power during emergencies and natural disasters, ensuring critical infrastructure remains operational and minimizing disruption to essential services.
- Decentralized Energy Systems:Energy storage can facilitate the development of decentralized energy systems, where energy is generated and consumed locally, reducing reliance on centralized power grids and improving resilience to disruptions.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the development and deployment of energy storage solutions. Governments across Europe are implementing a range of measures to encourage investment in energy storage, including financial incentives, regulatory frameworks, and research and development programs.
- Financial Incentives:Governments are offering subsidies, tax breaks, and other financial incentives to encourage the adoption of energy storage technologies. These incentives help reduce the upfront costs of installing energy storage systems, making them more attractive to businesses and consumers.
- Regulatory Frameworks:Governments are establishing regulatory frameworks that create a level playing field for energy storage and ensure its integration into the existing energy system. These frameworks include standards for interconnection, safety, and performance of energy storage systems.
- Research and Development:Governments are investing in research and development programs to advance the development of innovative and cost-effective energy storage technologies. This includes funding for research projects, pilot deployments, and demonstration projects.
Key Players and Innovations: Europe High Tech Scramble For Better Energy Storage
The European energy storage landscape is a dynamic ecosystem, with a diverse range of companies and research institutions pushing the boundaries of innovation. These entities are actively developing and deploying a wide array of energy storage technologies, contributing to the continent’s ambitious goal of achieving energy independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Leading Players and Their Areas of Expertise
The European energy storage sector boasts a diverse array of players, each with its unique strengths and areas of expertise. These companies and research institutions are actively driving the development and deployment of innovative energy storage solutions.
- Battery Technologies: Companies like Northvolt (Sweden), FREYR Battery (Norway), and Britishvolt (UK) are focusing on developing large-scale battery production facilities, while others like EIT InnoEnergy (EU) and Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Germany) are actively researching and developing next-generation battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries.
- Pumped Hydro Storage: Companies like Andritz Hydro (Austria), Voith Hydro (Germany), and GE Renewable Energy (France) are leading the development and construction of pumped hydro storage projects, leveraging their expertise in hydropower technology.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage: Companies like Hydrostor (Canada) and Energy Vault (Switzerland) are developing and deploying compressed air energy storage (CAES) solutions, which utilize existing underground caverns to store energy.
- Thermal Energy Storage: Companies like E.ON (Germany), Engie (France), and Ørsted (Denmark) are exploring and deploying thermal energy storage technologies, including seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) and ice storage systems.
- Flow Batteries: Companies like Redflow (Australia) and PriMe (Germany) are developing and deploying flow batteries, which are particularly well-suited for large-scale grid applications.
Latest Innovations and Breakthroughs
The European energy storage landscape is characterized by rapid innovation, with breakthroughs occurring across various technologies.
- Battery Technologies: The development of solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries, is a major area of focus for researchers and companies. Researchers at the Helmholtz Institute Ulm (Germany) have made significant progress in developing solid-state electrolytes, a crucial component for these batteries.
- Pumped Hydro Storage: Innovations in pumped hydro storage include the development of reversible pump turbines, which can operate as both pumps and turbines, increasing efficiency and reducing costs. Companies like Andritz Hydro (Austria) are leading the development of these technologies.
- Compressed Air Energy Storage: The development of hybrid CAES systems, which combine compressed air storage with thermal energy storage, is a significant innovation. These systems can improve efficiency and reduce costs by capturing and storing waste heat. Companies like Hydrostor (Canada) are pioneering this technology.
- Thermal Energy Storage: The development of innovative materials and systems for thermal energy storage is a key area of focus. Researchers at the Technical University of Denmark (DTU) are developing new materials for STES systems, while E.ON (Germany) is exploring the use of ice storage systems for cooling buildings.
- Flow Batteries: The development of flow batteries with higher energy density and longer lifespans is a key area of focus. Companies like Redflow (Australia) are developing vanadium redox flow batteries, which offer long lifespans and high energy capacity.
Key Players, Expertise, and Innovations, Europe high tech scramble for better energy storage
| Company/Institution | Area of Expertise | Latest Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Northvolt (Sweden) | Battery Production | Large-scale battery production facility in northern Sweden |
| FREYR Battery (Norway) | Battery Production | Developing a battery production facility in Norway, focused on sustainable battery production |
| Britishvolt (UK) | Battery Production | Building a battery gigafactory in the UK, aiming to become a leading battery producer in Europe |
| EIT InnoEnergy (EU) | Battery Research and Development | Supporting research and development of next-generation battery technologies, including solid-state batteries |
| Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (Germany) | Battery Research and Development | Developing innovative battery technologies, such as lithium-sulfur batteries |
| Andritz Hydro (Austria) | Pumped Hydro Storage | Developing reversible pump turbines for increased efficiency in pumped hydro storage |
| Voith Hydro (Germany) | Pumped Hydro Storage | Providing engineering and construction services for pumped hydro storage projects |
| GE Renewable Energy (France) | Pumped Hydro Storage | Developing and deploying pumped hydro storage solutions, leveraging its expertise in hydropower technology |
| Hydrostor (Canada) | Compressed Air Energy Storage | Developing and deploying hybrid CAES systems, combining compressed air storage with thermal energy storage |
| Energy Vault (Switzerland) | Compressed Air Energy Storage | Developing and deploying gravity-based energy storage solutions, using large concrete blocks to store energy |
| E.ON (Germany) | Thermal Energy Storage | Exploring the use of ice storage systems for cooling buildings |
| Engie (France) | Thermal Energy Storage | Developing and deploying seasonal thermal energy storage (STES) systems |
| Ørsted (Denmark) | Thermal Energy Storage | Investing in thermal energy storage technologies, including STES and ice storage systems |
| Redflow (Australia) | Flow Batteries | Developing vanadium redox flow batteries with long lifespans and high energy capacity |
| PriMe (Germany) | Flow Batteries | Developing and deploying flow batteries for grid-scale energy storage applications |
Economic and Social Impacts
The high-tech scramble for energy storage in Europe is not just a technological race but also a significant economic and social endeavor. It promises to reshape the continent’s energy landscape, impacting job creation, investment, and overall well-being.
Economic Implications
The pursuit of advanced energy storage technologies is generating a wave of economic activity in Europe. This includes:
- Job Creation:The development, manufacturing, and deployment of energy storage systems are creating new jobs in various sectors, including engineering, manufacturing, construction, and operations. For example, the European Battery Alliance, a consortium of industry and research institutions, aims to create 1.4 million jobs by 2025.
- Investment Opportunities:The energy storage sector is attracting significant investment, with both public and private entities pouring resources into research, development, and commercialization. This includes venture capital, government grants, and corporate investments. The European Union has pledged €10 billion for battery research and innovation under its Horizon Europe program.
- Economic Growth:The widespread adoption of energy storage is expected to stimulate economic growth in Europe. This will be driven by increased energy efficiency, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and the creation of new industries and businesses related to energy storage.
Social Benefits
The development and deployment of energy storage technologies offer numerous social benefits, including:
- Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels:Energy storage can help reduce Europe’s reliance on fossil fuels by enabling the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which are intermittent. This will contribute to achieving climate change goals and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved Energy Security:Energy storage can enhance energy security by providing a buffer against supply disruptions and price volatility. This is particularly important in Europe, which relies heavily on imported energy.
- Increased Energy Access:Energy storage can improve energy access in remote and underserved areas, where grid connections are limited. This can empower communities and support economic development.
Challenges and Opportunities
The large-scale deployment of energy storage technologies presents both challenges and opportunities:
- Cost Reduction:One of the key challenges is reducing the cost of energy storage technologies to make them more competitive with traditional energy sources. Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving efficiency and reducing production costs.
- Infrastructure Development:The integration of energy storage systems requires significant investment in infrastructure, including grid upgrades and smart grid technologies. This requires collaboration between governments, utilities, and industry.
- Public Acceptance:Public acceptance is crucial for the successful deployment of energy storage technologies. Addressing concerns about safety, environmental impact, and potential land use conflicts is essential.
Potential Economic and Social Impacts of Energy Storage Development in Europe
| Impact | Economic | Social |
|---|---|---|
| Job Creation | Increased employment opportunities in manufacturing, engineering, construction, and operation of energy storage systems. | Improved employment prospects and economic well-being for individuals and communities. |
| Investment Opportunities | Attracts significant investment in research, development, and commercialization of energy storage technologies. | Supports innovation and technological advancements in the energy sector. |
| Economic Growth | Stimulates economic growth through increased energy efficiency, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and creation of new industries. | Contributes to a more sustainable and resilient economy. |
| Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels | Promotes the development of renewable energy sources and reduces dependence on fossil fuels. | Reduces greenhouse gas emissions and contributes to climate change mitigation. |
| Improved Energy Security | Enhances energy security by providing a buffer against supply disruptions and price volatility. | Increases energy independence and reduces vulnerability to external shocks. |
| Increased Energy Access | Expands access to energy in remote and underserved areas. | Empowers communities and supports economic development in disadvantaged regions. |
Future Outlook and Trends

The European energy storage landscape is poised for significant growth, driven by ambitious clean energy targets and the increasing need for grid flexibility. Emerging technologies, market trends, and policy initiatives will shape the future of energy storage in Europe, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming the energy storage industry, enabling more efficient and intelligent operation of storage systems. AI algorithms can optimize charging and discharging schedules, predict energy demand, and enhance grid stability by analyzing real-time data from various sources.
- AI-powered energy management systems can optimize the use of energy storage assets, ensuring that they are charged and discharged at the most beneficial times, maximizing their efficiency and reducing costs.
- ML algorithms can predict energy demand patterns, allowing storage systems to be pre-charged or discharged in anticipation of peak demand, minimizing grid stress and enhancing reliability.
- AI-driven predictive maintenance can analyze sensor data from storage systems to identify potential issues and schedule maintenance before they lead to failures, extending the lifespan of storage assets.
Key Challenges and Opportunities
The successful development and deployment of energy storage technologies in Europe face a number of challenges and opportunities:
- Cost Reduction:While energy storage costs have been declining, they still remain a significant barrier to widespread adoption. Continued research and development efforts are needed to reduce costs and make storage more affordable for a wider range of applications.
- Integration with the Grid:Integrating large-scale energy storage systems into existing grids requires robust infrastructure and advanced control systems. This involves developing standardized protocols and communication systems to ensure seamless integration and interoperability.
- Regulation and Policy:Clear and supportive regulatory frameworks are essential to encourage investment in energy storage and create a level playing field for different technologies. Policies that incentivize the use of storage and address potential risks are crucial for driving adoption.
- Public Acceptance:Building public trust and understanding of energy storage technologies is essential for their successful deployment. Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives can help address concerns and highlight the benefits of storage.
Timeline of Energy Storage Adoption
The adoption of energy storage technologies in Europe is expected to accelerate over the coming years, driven by policy targets, technological advancements, and falling costs:
- 2025-2030:Widespread deployment of battery energy storage systems for residential and commercial applications, alongside increased use of pumped hydro storage for larger-scale grid services.
- 2030-2040:Emergence of new storage technologies, such as flow batteries and hydrogen storage, alongside increased integration of storage into renewable energy systems.
- 2040-2050:Mature energy storage market with a diverse range of technologies providing grid flexibility and resilience, supporting the transition to a fully decarbonized energy system.