Eu tech policy predictions * – EU Tech Policy Predictions: Shaping the Digital Future takes center stage, as the European Union navigates the complex and rapidly evolving landscape of technology. From the rise of artificial intelligence to the implications of blockchain, the EU faces a pivotal moment in defining its digital destiny.
The bloc’s approach to regulating technology will have profound implications for its economy, society, and global influence. This post delves into the key trends and challenges shaping EU tech policy, offering insights into its future trajectory.
The EU’s tech policy landscape is marked by a commitment to fostering innovation while safeguarding fundamental values like privacy, security, and fairness. The bloc has taken a proactive approach to regulating technology, enacting landmark legislation like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Digital Markets Act (DMA).
These regulations aim to create a level playing field for businesses, protect consumer rights, and ensure the responsible development and deployment of emerging technologies.
EU Tech Policy Landscape: Eu Tech Policy Predictions *
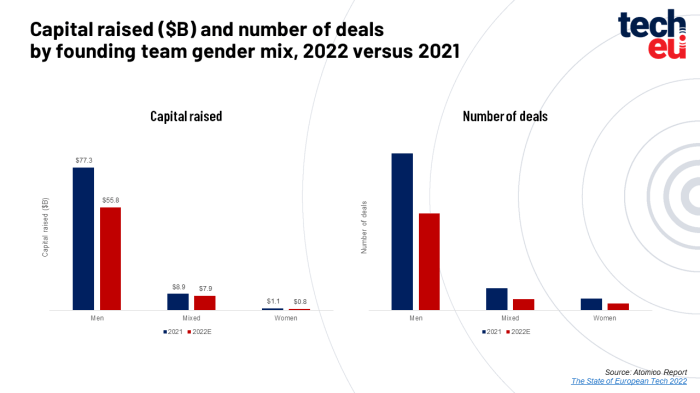
The European Union (EU) is at the forefront of global efforts to regulate technology, driven by a complex mix of concerns about privacy, competition, and the potential impact of technology on society. The EU’s approach to tech policy is characterized by a proactive stance, with a focus on establishing robust regulations and fostering innovation within a framework of ethical considerations.
Key Regulations and Initiatives
The EU’s tech policy landscape is marked by a series of landmark regulations and initiatives that aim to shape the digital economy and address the challenges posed by technology.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation, which came into effect in 2018, has become a global standard for data privacy, granting individuals more control over their personal data and imposing stringent obligations on companies that collect and process it. It has significantly impacted how companies handle data, particularly in areas like targeted advertising and data analytics.
- Digital Markets Act (DMA): This act, which came into effect in 2023, targets “gatekeeper” platforms, including major online marketplaces, search engines, and social media companies. It aims to prevent anti-competitive practices and ensure a level playing field for smaller businesses. The DMA mandates specific obligations for gatekeepers, such as interoperability requirements and restrictions on self-preferencing.
- Digital Services Act (DSA): This act, also enacted in 2023, focuses on regulating online content and platforms. It aims to combat illegal content, such as hate speech and disinformation, and to protect users from harmful content. The DSA introduces transparency requirements for online platforms, including obligations to disclose algorithms and take down illegal content promptly.
- Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act): This proposed legislation aims to regulate the development and deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) systems. It seeks to promote ethical and trustworthy AI, while also addressing potential risks associated with AI, such as bias, discrimination, and job displacement. The AI Act is still under negotiation, but it is expected to have a significant impact on the development and use of AI in the EU.
Motivations Behind EU Tech Policy
The EU’s approach to regulating technology is driven by several key motivations:
- Protecting Fundamental Rights: The EU prioritizes the protection of fundamental rights, including privacy, freedom of expression, and non-discrimination. Tech regulations are designed to ensure that technology is used in a way that respects these rights.
- Promoting Fair Competition: The EU aims to create a level playing field for businesses in the digital economy, preventing dominant platforms from abusing their market power and hindering innovation.
- Addressing Societal Challenges: The EU recognizes the potential of technology to address societal challenges, such as climate change, healthcare, and education. However, it also acknowledges the risks associated with technology, such as misinformation, social polarization, and job displacement. Tech regulations aim to mitigate these risks and ensure that technology is used for the benefit of society.
- Building a European Digital Sovereignty: The EU seeks to strengthen its position in the global digital economy by developing its own digital infrastructure and fostering innovation within its borders.
Challenges and Opportunities
The EU faces a number of challenges in shaping its tech policy, including:
- Balancing Innovation and Regulation: Striking a balance between promoting innovation and regulating technology is a complex task. The EU aims to foster a dynamic digital economy while ensuring that technology is used responsibly.
- Global Coordination: Technology operates on a global scale, making it difficult to regulate effectively within national borders. The EU seeks to coordinate with other countries and international organizations to address global challenges related to technology.
- Enforcement and Implementation: Enforcing tech regulations and ensuring their effective implementation can be challenging, particularly given the rapid pace of technological change. The EU is investing in resources and developing mechanisms to ensure effective enforcement.
- Public Trust and Acceptance: Public trust in technology is essential for its successful development and adoption. The EU aims to engage with citizens and stakeholders to ensure that tech policy is informed by public values and concerns.
Opportunities for EU Tech Policy
The EU’s tech policy presents a number of opportunities:
- Global Leadership: The EU has the potential to become a global leader in shaping the future of technology, setting standards for data privacy, competition, and ethical AI.
- Boosting Innovation: By fostering a regulatory environment that is both robust and supportive of innovation, the EU can encourage the development of new technologies and businesses within its borders.
- Addressing Societal Challenges: Technology can be a powerful tool for addressing societal challenges, such as climate change, healthcare, and education. The EU’s tech policy can help to ensure that technology is used to achieve these goals.
Emerging Trends and Technologies

The EU is facing a rapidly evolving technological landscape, characterized by the emergence of transformative technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and quantum computing. These technologies hold immense potential for economic growth, societal progress, and global competitiveness. However, they also present significant challenges in terms of ethical considerations, social implications, and regulatory frameworks.
This section delves into the impact of these emerging technologies on EU tech policy, exploring their potential benefits and risks, and examining how the EU is preparing to address their multifaceted implications.
Discover the crucial elements that make is momentum shifting toward a ban on behavioral advertising the top choice.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence
AI is poised to revolutionize numerous industries, from healthcare and manufacturing to finance and transportation. The EU recognizes the transformative potential of AI and its ability to drive economic growth, improve public services, and enhance citizens’ lives. However, AI also presents significant challenges, particularly in terms of ethical considerations, privacy, and job displacement.
The EU is taking a proactive approach to AI, aiming to foster innovation while ensuring ethical and responsible development.
- The EU’s AI Strategy: The EU’s AI Strategy, adopted in 2020, Artikels a comprehensive framework for promoting responsible AI development and deployment. It emphasizes the importance of ethical guidelines, data governance, and robust regulatory frameworks. The strategy aims to create a favorable environment for AI innovation while addressing potential risks.
- The AI Act: The EU is currently developing a comprehensive AI Act, which will establish a regulatory framework for AI systems based on risk levels. The Act proposes a tiered approach, with higher-risk AI systems subject to stricter requirements, including conformity assessments, risk management measures, and transparency obligations.
The Act aims to ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed in a safe, ethical, and transparent manner.
- Investment in AI Research and Development: The EU is investing heavily in AI research and development, supporting initiatives such as the European High-Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC) and the Horizon Europe program. These investments aim to strengthen the EU’s technological leadership in AI and foster a vibrant ecosystem of AI innovation.
The Impact of Blockchain, Eu tech policy predictions *
Blockchain technology offers a decentralized and secure platform for recording and verifying transactions, with potential applications in various sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and healthcare. The EU recognizes the potential of blockchain to enhance transparency, efficiency, and security across different industries.
However, blockchain technology also presents challenges related to data privacy, regulatory clarity, and cybersecurity.
- The EU’s Blockchain Strategy: The EU has adopted a Blockchain Strategy to promote the adoption and development of blockchain technology within the EU. The strategy focuses on supporting innovation, fostering collaboration, and promoting regulatory clarity. It aims to create a conducive environment for the development and deployment of blockchain solutions.
- Regulation of Cryptocurrencies: The EU is actively working to regulate cryptocurrencies, aiming to balance innovation with consumer protection and financial stability. The Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) Regulation, currently under negotiation, aims to establish a comprehensive framework for the regulation of cryptocurrencies and crypto-asset service providers.
- Promoting Blockchain Adoption: The EU is encouraging the adoption of blockchain technology in various sectors through initiatives such as the Blockchain Observatory and Forum, which provides a platform for collaboration and knowledge sharing. The EU is also supporting pilot projects and research activities to explore the practical applications of blockchain technology.
The Impact of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize scientific research, drug discovery, and materials science. It offers significantly faster processing speeds and capabilities that exceed those of traditional computers. The EU recognizes the immense potential of quantum computing for economic growth and scientific advancement.
However, quantum computing also raises concerns about cybersecurity, data privacy, and the potential for job displacement.
- The EU’s Quantum Strategy: The EU has adopted a Quantum Strategy to foster research, development, and innovation in quantum technologies. The strategy aims to position the EU as a global leader in quantum computing and related fields. It includes investments in research and development, infrastructure, and talent development.
- Addressing Cybersecurity Concerns: The EU is addressing cybersecurity concerns related to quantum computing by investing in research on quantum-resistant cryptography and developing standards for secure quantum communication. The EU is also working to raise awareness about the potential threats posed by quantum computing and the need for proactive measures.
- Promoting Ethical Considerations: The EU is promoting ethical considerations in quantum computing, recognizing the potential social and economic impacts of this technology. The EU is encouraging discussions and collaborations on responsible development and deployment of quantum technologies, ensuring that they are used for the benefit of society.
Key Policy Areas
The EU’s approach to regulating the tech sector is characterized by a focus on protecting fundamental rights, fostering innovation, and ensuring a level playing field for businesses. This approach is reflected in a series of key policy areas, including data privacy, cybersecurity, and competition.
Data Privacy
The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a landmark piece of legislation that sets a high bar for data protection and gives individuals more control over their personal data. The GDPR has had a significant impact on businesses around the world, prompting them to adopt more robust data protection practices.
For example, many companies have implemented new policies and procedures for obtaining consent from individuals before collecting their data. The GDPR’s impact on European businesses and consumers is multifaceted. On the one hand, it has empowered consumers by giving them more control over their personal data and increasing their awareness of data protection issues.
On the other hand, it has placed a significant administrative burden on businesses, particularly smaller companies that may lack the resources to comply with the regulation’s requirements.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is another area where the EU is taking a proactive approach. The EU’s Network and Information Security (NIS) Directive aims to improve cybersecurity across the EU by establishing a framework for cooperation between member states and by requiring critical infrastructure operators to implement cybersecurity measures.
The NIS Directive has been praised for its emphasis on risk management and for its focus on collaboration between public and private actors. The NIS Directive has already had a positive impact on cybersecurity in the EU. For example, it has led to the development of national cybersecurity strategies in many member states and has encouraged companies to invest in cybersecurity technologies.
However, there are still challenges to be addressed, such as the need to ensure that the directive is implemented consistently across all member states.
Competition
The EU’s competition policy is designed to ensure a level playing field for businesses and to prevent anti-competitive practices. The EU’s competition authorities have been active in regulating the tech sector, investigating and taking action against companies that have engaged in anti-competitive behavior.
For example, the EU has fined Google billions of euros for antitrust violations related to its search engine and its Android operating system. The EU’s competition policy has had a significant impact on the tech sector, leading to greater competition and innovation.
For example, the EU’s antitrust investigations into Google have forced the company to make changes to its business practices, which has benefited consumers and competitors. However, the EU’s competition policy is not without its critics, who argue that it can stifle innovation and make it more difficult for European companies to compete on a global scale.
Fostering Innovation
The EU is also working to foster innovation and growth in the tech sector. The EU’s Horizon Europe program, for example, provides funding for research and innovation projects across a wide range of fields, including artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and biotechnology.
The EU is also working to create a more favorable environment for tech startups. For example, the EU’s Startup Europe initiative provides support to startups through funding, mentorship, and networking opportunities. The EU’s efforts to foster innovation are helping to create a more dynamic and competitive tech sector in Europe.
EU’s Global Role in Tech Policy
The European Union (EU) is a major player in the global tech landscape, with a significant impact on the development and regulation of technology. Its tech policy approach, driven by a focus on protecting fundamental rights, fostering innovation, and promoting a level playing field, has become a model for other regions.
This section explores how the EU’s tech policy interacts with those of other key players, its role in shaping global tech governance, and its potential impact on international relations and trade.
Comparison with Other Major Players
The EU’s tech policy approach differs significantly from those of other major players, particularly the United States (US) and China.
- The US tech policy is often characterized by a more laissez-faire approach, emphasizing free markets and minimal government intervention. The US government typically favors industry self-regulation and prioritizes fostering innovation and economic growth.
- China’s tech policy is driven by a strong government role in shaping the tech landscape. It prioritizes national security, data sovereignty, and technological self-reliance. The Chinese government actively promotes domestic tech companies and invests heavily in research and development.
- The EU, on the other hand, adopts a more interventionist approach, prioritizing the protection of fundamental rights, such as privacy, data protection, and freedom of expression. This approach has led to the development of comprehensive regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which have had a global impact on data protection laws.
EU’s Role in Shaping Global Tech Governance
The EU has played a crucial role in shaping global tech governance by setting standards and promoting international cooperation.
- The GDPR, for instance, has become a global benchmark for data protection laws, inspiring similar regulations in other countries. It has also significantly impacted the way companies worldwide handle personal data.
- The EU has actively participated in international forums, such as the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and the United Nations (UN), to develop global norms and standards for digital technologies. This engagement has helped to shape the global conversation on issues like artificial intelligence (AI) ethics, cybersecurity, and internet governance.
- The EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) and Digital Services Act (DSA), which aim to regulate large online platforms and address issues like market dominance and content moderation, have also sparked discussions and potential reforms in other jurisdictions.
Impact on International Relations and Trade
EU tech policy has the potential to impact international relations and trade in several ways.
- The EU’s emphasis on data protection and privacy has led to tensions with countries that have different data protection standards. This has raised concerns about potential trade barriers and the flow of data across borders.
- The EU’s regulatory approach to tech giants, such as the DMA and DSA, has also sparked debates about the potential impact on international competition and the role of global tech companies.
- The EU’s tech policy can also influence international relations by promoting cooperation and collaboration on issues like cybersecurity, AI ethics, and digital development. The EU’s commitment to these issues has led to partnerships and initiatives with other countries, fostering global cooperation in the tech domain.
Predictions for the Future
Predicting the future of EU tech policy is a complex task, but by analyzing current trends and considering potential developments, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. The EU’s tech policy landscape is constantly evolving, shaped by technological advancements, societal shifts, and global geopolitical dynamics.
Here, we explore some key predictions for the future of EU tech policy.
The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
The development and deployment of AI technologies will continue to be a central focus of EU tech policy. The EU aims to become a global leader in trustworthy AI, prioritizing ethical considerations, data privacy, and transparency. The impact of AI on the EU’s digital economy and society is multifaceted.
AI-powered applications are expected to transform various industries, boosting productivity and innovation. However, the EU must address potential risks associated with AI, such as job displacement, algorithmic bias, and the misuse of AI for malicious purposes.
Data Governance and Privacy
Data is the lifeblood of the digital economy, and the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has become a global benchmark for data privacy. The EU is expected to further strengthen data governance frameworks, focusing on areas such as data portability, data sharing, and the responsible use of personal data.
These efforts will aim to empower individuals while fostering innovation and competitiveness in the EU’s data economy.
Cybersecurity and Resilience
Cyberattacks and online threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, posing significant risks to critical infrastructure, businesses, and individuals. The EU is strengthening its cybersecurity capabilities to enhance resilience against cyberattacks. This includes investing in cybersecurity research and development, promoting information sharing, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders.
The Digital Single Market
The EU’s Digital Single Market initiative aims to create a seamless digital environment across member states, removing barriers to cross-border e-commerce and digital services. This includes addressing issues such as geo-blocking, online platforms, and copyright enforcement. The EU is expected to continue its efforts to create a truly integrated digital market, fostering competition and innovation.
Sustainable Digital Technologies
The environmental impact of digital technologies is a growing concern. The EU is promoting the development and adoption of sustainable digital technologies, reducing energy consumption and minimizing the carbon footprint of the digital economy. This includes initiatives to encourage the use of energy-efficient devices, promote green data centers, and develop sustainable cloud computing solutions.
The EU’s Global Role in Tech Policy
The EU is increasingly asserting its global role in tech policy, shaping international norms and standards. The EU is working with international partners to address global challenges related to AI, data governance, cybersecurity, and digital trade. The EU’s influence in these areas will be crucial in shaping the future of the global digital landscape.
A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a future where the EU has successfully implemented its tech policy agenda. AI has become a key driver of innovation and economic growth, while ethical considerations are firmly embedded in its development and deployment. Data is flowing freely and securely across borders, fueling a vibrant data economy.
Cybersecurity threats are effectively mitigated, and the EU has become a global leader in digital resilience. The Digital Single Market is fully realized, fostering competition and innovation across member states. The EU has also played a pivotal role in shaping global tech policy, promoting ethical and responsible use of digital technologies.





