Eu big bet on making europe graphene powerhouse – EU Big Bet: Making Europe a Graphene Powerhouse – Graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon, is set to revolutionize countless industries. Its incredible strength, conductivity, and flexibility make it a game-changer, and the European Union is betting big on this material to secure its place as a global leader in technology and innovation.
The EU’s Graphene Flagship initiative is a massive research and development program, investing billions of euros to unlock graphene’s potential and propel Europe to the forefront of this burgeoning field.
This ambitious strategy aims to build a robust ecosystem around graphene, fostering collaboration between research institutions, universities, and companies. The goal is to not only advance graphene research but also to translate scientific breakthroughs into real-world applications, creating new industries and jobs.
Europe’s commitment to graphene is not just about technological dominance; it’s about shaping a future where this revolutionary material can address global challenges and improve lives.
The Rise of Graphene
Graphene, a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb lattice, has emerged as a revolutionary material with unparalleled properties. Its exceptional strength, conductivity, and flexibility have captivated scientists and engineers, promising a paradigm shift across numerous industries.
The Unique Properties of Graphene
Graphene’s remarkable properties stem from its unique atomic structure. Its two-dimensional nature and strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms create a material that is exceptionally strong, lightweight, and flexible.
- Strength:Graphene is the strongest material ever discovered, with a tensile strength 200 times greater than steel. This exceptional strength makes it ideal for applications requiring high durability and resistance to wear and tear.
- Conductivity:Graphene is an excellent conductor of electricity and heat, surpassing even copper in conductivity. Its ability to carry high currents without significant resistance makes it a promising material for electronics and energy storage applications.
- Flexibility:Graphene’s thin and flexible nature allows it to be easily integrated into various materials and devices. This flexibility opens up possibilities for applications in flexible electronics, wearable technology, and advanced sensors.
Potential Applications of Graphene
The exceptional properties of graphene have sparked immense interest in its potential applications across diverse industries, including:
- Electronics:Graphene’s high conductivity and flexibility make it a promising material for next-generation electronics, such as flexible displays, touchscreens, and high-speed transistors. The use of graphene in electronics can lead to faster processing speeds, lower energy consumption, and more durable devices.
In this topic, you find that counterpoint ai far more dangerous than quantum computing is very useful.
- Energy Storage:Graphene’s high surface area and excellent conductivity make it an ideal material for electrodes in batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. Graphene-based energy storage devices can offer higher capacity, faster charging times, and longer lifespan compared to traditional technologies.
- Composite Materials:Graphene can be incorporated into composite materials to enhance their strength, stiffness, and conductivity. These graphene-reinforced composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries, leading to lighter, stronger, and more durable structures.
- Biomedical Applications:Graphene’s biocompatibility and high surface area make it a promising material for drug delivery, biosensing, and tissue engineering. Graphene-based devices can enable targeted drug delivery, sensitive disease detection, and improved tissue regeneration.
Examples of Graphene-Based Products
Several graphene-based products have already emerged, demonstrating the material’s real-world potential.
- Graphene-Enhanced Tennis Racquets:Head, a leading sports equipment manufacturer, has introduced tennis racquets incorporating graphene into their frames. The inclusion of graphene enhances the racquet’s stiffness and strength, providing improved power and control for players.
- Graphene-Based Batteries:Companies like Samsung and LG are developing graphene-based batteries for smartphones and electric vehicles. These batteries offer faster charging times, higher capacity, and longer lifespan compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
- Graphene-Reinforced Composites:Boeing has incorporated graphene into its composite materials for aircraft components, resulting in lighter and stronger structures. This reduces fuel consumption and improves aircraft performance.
The Impact of Graphene on the European Economy
The development and adoption of graphene technologies have the potential to create significant economic benefits for Europe.
- Job Creation:The graphene industry is expected to create numerous jobs in research, development, manufacturing, and applications.
- Economic Growth:Graphene-based products and technologies can stimulate innovation and economic growth across various sectors, leading to increased competitiveness and export potential.
- Technological Leadership:Europe has the potential to become a global leader in graphene research and development, attracting investment and talent from around the world.
The EU’s Graphene Strategy
The European Union’s Graphene Flagship initiative represents a bold vision for Europe to become a global leader in graphene research and development. This ambitious program aims to translate cutting-edge scientific discoveries into real-world applications, fostering economic growth and societal progress.
Key Objectives of the Graphene Flagship, Eu big bet on making europe graphene powerhouse
The Graphene Flagship’s primary goal is to accelerate the development and deployment of graphene and related two-dimensional (2D) materials across various sectors. This involves a multi-pronged approach:
- Fundamental Research:The initiative supports fundamental research to further explore the properties and potential of graphene and 2D materials, leading to new scientific breakthroughs and discoveries.
- Technology Development:The Flagship focuses on developing new technologies based on graphene and 2D materials, encompassing applications in electronics, energy, healthcare, composites, and more.
- Industrial Collaboration:The program emphasizes collaboration between research institutions, industry, and startups to ensure that research findings translate into practical and commercially viable applications.
- Innovation Ecosystem:The Flagship aims to create a vibrant innovation ecosystem by supporting the development of new companies and fostering entrepreneurship in the field of graphene and 2D materials.
The Role of Research and Innovation
Research and innovation are the cornerstones of the EU’s graphene strategy. The Flagship recognizes the critical role of scientific advancements in driving technological progress and achieving the goal of becoming a global graphene powerhouse.
- Scientific Excellence:The Flagship fosters scientific excellence by bringing together leading researchers from across Europe to collaborate on cutting-edge projects. This collaborative approach allows for the pooling of expertise and resources, accelerating scientific discovery and pushing the boundaries of knowledge.
- Technological Breakthroughs:The Flagship supports research that leads to technological breakthroughs, focusing on developing novel applications and solutions based on graphene and 2D materials. This includes exploring the potential of these materials in areas like flexible electronics, energy storage, advanced composites, and biomedicine.
- Commercialization:The Flagship prioritizes the translation of research findings into commercially viable products and technologies. This involves close collaboration with industry partners to bridge the gap between scientific discovery and market applications.
EU Funding and Resources
The EU has committed significant funding and resources to support graphene research and development. The Graphene Flagship itself has received €1 billion in funding over a decade, demonstrating the EU’s commitment to this strategic area.
- Flagship Funding:The Graphene Flagship receives €1 billion in funding over a decade, showcasing the EU’s dedication to this strategic initiative.
- Horizon Europe:The EU’s research and innovation framework program, Horizon Europe, provides further funding opportunities for graphene-related projects. This program supports collaborative research, innovation, and technology development across a range of fields.
- National Funding:Member states also contribute to graphene research through national funding programs and initiatives. These national efforts complement the EU’s overarching strategy and create a robust network of research and innovation across Europe.
Key Players in the European Graphene Ecosystem
The European Union (EU) has emerged as a global leader in graphene research and development, with a robust ecosystem of research institutions, universities, and companies actively contributing to the field. This vibrant ecosystem fosters collaboration, innovation, and the translation of scientific breakthroughs into practical applications.
Leading Research Institutions and Universities
Europe boasts a strong network of research institutions and universities that are at the forefront of graphene research. These institutions are home to world-renowned scientists and engineers who are pushing the boundaries of graphene science and technology.
- Graphene Flagship: Launched in 2013, the Graphene Flagship is a €1 billion, 10-year research initiative funded by the European Union. It involves over 170 academic and industrial partners from across Europe, working collaboratively to advance graphene research and development. The Flagship has significantly contributed to the advancement of graphene science and technology, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of research and innovation.
- Manchester University: The University of Manchester, UK, holds a special place in the history of graphene, as it is where the material was first isolated in 2004 by Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov, who later received the Nobel Prize in Physics for their groundbreaking work.
The university continues to be a leading center for graphene research, with strong research groups focusing on various aspects of graphene science and technology.
- Chalmers University of Technology: Located in Gothenburg, Sweden, Chalmers University of Technology is another prominent research institution in the European graphene landscape. It has a strong research group focusing on graphene-based electronics and sensors, with a particular emphasis on flexible and transparent electronics.
- Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Madrid (ICMM): This institute in Spain has a long history of excellence in materials science, with a strong focus on graphene and other two-dimensional materials. The ICMM has made significant contributions to the development of graphene-based composites and energy storage devices.
- University of Cambridge: The University of Cambridge, UK, is a leading center for graphene research, with strong research groups focusing on graphene-based electronics, photonics, and composites. The university also plays a key role in translating graphene research into practical applications.
Leading Companies
Alongside research institutions, Europe is home to a growing number of companies that are commercializing graphene technologies. These companies are developing innovative products and applications based on graphene, contributing to the growth of the global graphene market.
- Graphenea: Founded in 2010, Graphenea is a Spanish company that specializes in the production and commercialization of high-quality graphene materials. The company offers a range of graphene products for various applications, including electronics, composites, and energy storage.
- Avanzare: Based in Italy, Avanzare is a leading manufacturer of graphene-based inks and coatings. The company’s graphene inks are used in various applications, including printed electronics, transparent conductive films, and anti-corrosion coatings.
- Haydale Graphene Industries: Located in the UK, Haydale Graphene Industries is a leading producer of functionalized graphene materials. The company’s graphene products are used in various applications, including composites, energy storage, and sensors.
- Applied Graphene Materials (AGM): Based in the UK, AGM is a leading producer of graphene nanoplatelets. The company’s graphene nanoplatelets are used in various applications, including composites, coatings, and inks.
- Versarien: This UK-based company specializes in the development and commercialization of graphene-enhanced materials. Versarien’s graphene products are used in various applications, including composites, coatings, and energy storage.
Strengths of the European Graphene Ecosystem
The European graphene ecosystem boasts several strengths that have positioned it as a global leader in the field:
- Strong Research Base: Europe has a strong research base in graphene, with a large number of research institutions and universities dedicated to graphene research and development. This strong research base has been instrumental in generating a wealth of knowledge and expertise in the field.
- Government Support: The European Union has provided significant funding for graphene research and development through initiatives such as the Graphene Flagship. This government support has been crucial in driving innovation and accelerating the commercialization of graphene technologies.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: The European graphene ecosystem is characterized by strong collaboration and partnerships between research institutions, universities, and companies. This collaborative approach has fostered innovation and accelerated the translation of scientific breakthroughs into practical applications.
- Focus on Applications: The European graphene ecosystem has a strong focus on developing practical applications for graphene. This focus has led to the development of a wide range of graphene-based products and technologies with potential for various industries.
Weaknesses of the European Graphene Ecosystem
While the European graphene ecosystem has many strengths, it also faces certain challenges:
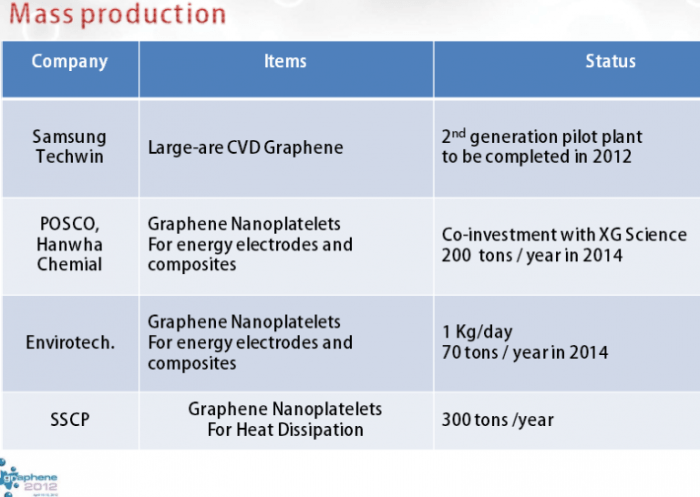
- Scale-Up Challenges: One of the major challenges facing the European graphene ecosystem is scaling up production of graphene materials. While Europe has a strong research base and a growing number of companies developing graphene technologies, the production of graphene materials at a commercial scale remains a challenge.
- Competition from Asia: Asia, particularly China, has emerged as a major player in the graphene market, with significant investments in graphene production and research. The increasing competition from Asia poses a challenge to European companies seeking to commercialize graphene technologies.
- Funding Challenges: While the EU has provided significant funding for graphene research and development, securing funding for commercialization and scale-up remains a challenge for many European companies.
Comparison with Other Global Players
Europe is a leading player in the global graphene landscape, alongside other regions such as Asia and North America. While Europe has a strong research base and a growing number of companies developing graphene technologies, it faces challenges in scaling up production and competing with Asian players, particularly China, which has made significant investments in graphene production and research.
- Asia: Asia, particularly China, has emerged as a major player in the graphene market, with significant investments in graphene production and research. China has a strong focus on developing large-scale graphene production facilities, which has given it a significant advantage in terms of cost and scale.
- North America: North America is another major player in the global graphene landscape, with a strong research base and a growing number of companies developing graphene technologies. The United States has a particular focus on developing graphene-based electronics and sensors.
Challenges and Opportunities for European Graphene Development

While the EU’s ambition to become a graphene powerhouse is ambitious and exciting, it faces significant challenges and opportunities that will shape its success. The technical challenges associated with scaling up graphene production, the vast market potential across diverse sectors, and the ethical and regulatory considerations surrounding graphene use all play a crucial role in the journey ahead.
Technical Challenges of Scaling Up Graphene Production
Scaling up graphene production to meet the growing demand poses significant technical challenges. The current methods for producing high-quality graphene are often expensive and inefficient, limiting large-scale applications.
- Yield and Quality Control:Achieving consistent high-quality graphene with high yield remains a major challenge. Existing methods, such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and mechanical exfoliation, often result in low yields or variations in graphene properties.
- Cost-Effective Production:The cost of graphene production is a significant barrier to its widespread adoption. Developing cost-effective and scalable production methods is crucial for making graphene accessible to a wider range of applications.
- Uniformity and Consistency:Ensuring the uniformity and consistency of graphene properties across large-scale production is essential for reliable performance in various applications.
The Future of Graphene in Europe: Eu Big Bet On Making Europe Graphene Powerhouse
The EU’s graphene strategy, with its ambitious goals and dedicated funding, has set the stage for a transformative future in graphene technology. This forward-looking approach is poised to propel Europe to the forefront of this revolutionary material, ushering in a new era of innovation and economic prosperity.
Economic and Societal Impact
The long-term impact of the EU’s graphene strategy extends beyond the realm of scientific breakthroughs. It aims to create a thriving graphene ecosystem that will stimulate economic growth, foster job creation, and improve the quality of life for European citizens.
- Boosting European Competitiveness:The strategy aims to establish Europe as a global leader in graphene production and applications, enhancing its competitiveness in key industries like electronics, energy, and healthcare.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth:The development and commercialization of graphene technologies will create new jobs in research, manufacturing, and related sectors, contributing to economic growth and prosperity.
- Improving Quality of Life:Graphene-based innovations have the potential to revolutionize healthcare, energy, and transportation, leading to improved quality of life for European citizens. For example, graphene-based sensors can be used to develop early detection systems for diseases, while graphene-enhanced batteries can power electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
Potential Breakthroughs and Innovations
The coming years are expected to witness a surge in groundbreaking innovations driven by graphene technology. These advancements will not only redefine existing industries but also create entirely new markets.
- Flexible Electronics:Graphene’s exceptional electrical conductivity and flexibility make it ideal for developing flexible and transparent displays, wearable electronics, and even implantable medical devices.
- High-Performance Computing:Graphene’s unique properties can be harnessed to create faster and more efficient transistors and other components for next-generation computers and data centers.
- Energy Storage:Graphene-based batteries and supercapacitors promise to revolutionize energy storage, enabling longer-lasting and more efficient devices, from smartphones to electric vehicles.
- Advanced Materials:Graphene can be incorporated into various materials to enhance their strength, conductivity, and other properties, leading to the development of lighter, stronger, and more durable structures and products.
Collaborations and Partnerships
To fully realize the potential of graphene, collaboration and partnerships between European and global players are crucial. These collaborations will foster knowledge sharing, accelerate innovation, and create a truly global graphene ecosystem.
- Industry-Academia Partnerships:Strong collaborations between research institutions and industry players are essential to bridge the gap between fundamental research and commercial applications.
- International Research Networks:Establishing international research networks and collaborations will facilitate knowledge exchange and accelerate progress in graphene research and development.
- Joint Ventures and Investments:Joint ventures and investments between European and global companies will drive the commercialization of graphene technologies and create new markets.