Dummy guide to infecting apple mac with malware – Dummy Guide to Infecting Apple Macs with Malware: While Macs are known for their robust security, they’re not immune to malware attacks. This guide delves into the vulnerabilities of macOS, explores common malware infection methods, and provides a comprehensive overview of how malicious actors target Apple users.
We’ll examine various types of Mac malware, their impact, and the telltale signs of infection. Additionally, we’ll equip you with practical tips to safeguard your Mac and remove any existing threats.
From understanding the security measures built into macOS to identifying common vulnerabilities and user behavior patterns that increase risk, this guide will empower you to protect your Mac from malware. We’ll discuss how social engineering, malicious websites, and email attachments can be used to spread malware, and provide real-world examples of specific Mac malware families and their characteristics.
Understanding Apple Mac Security
Apple Macs are known for their user-friendly interface and sleek design, but they are not immune to malware attacks. While macOS has robust security features, understanding these features and common vulnerabilities is crucial to safeguarding your Mac. This section will delve into the security measures built into macOS, explore common vulnerabilities, and examine the impact of user behavior on Mac security.
macOS Security Features
macOS comes equipped with several built-in security features that aim to protect your Mac from malicious threats. These features include:
- Gatekeeper:This feature restricts the installation of applications from unknown developers, preventing the execution of potentially harmful software. It verifies the digital signature of applications before allowing them to run on your Mac. This ensures that the software you install comes from a trusted source.
- XProtect:This malware detection and prevention system is integrated into macOS and continuously scans your Mac for known malware signatures. It updates its malware database regularly, ensuring it can identify and neutralize new threats.
- FileVault:This feature encrypts your entire hard drive, protecting your data from unauthorized access. If someone steals your Mac, they won’t be able to access your files without the correct password.
- System Integrity Protection (SIP):Also known as “Rootless,” SIP restricts unauthorized modifications to critical system files, making it harder for malware to gain control of your Mac. This feature protects core system components from tampering, making your Mac more resilient against attacks.
Common macOS Vulnerabilities
While macOS has robust security features, it’s important to acknowledge that no system is perfect. Some common vulnerabilities in macOS include:
- Phishing Attacks:These attacks often involve deceptive emails or websites that trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details. Users may click on malicious links or download infected files, unknowingly compromising their Mac’s security.
- Social Engineering:This technique relies on manipulating users into performing actions that compromise their security. Attackers may impersonate trusted individuals or organizations to gain access to sensitive information or trick users into installing malware.
- Outdated Software:Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities discovered in previous versions. Keeping your software up-to-date is essential to protect your Mac from known exploits.
- Unsecured Wi-Fi Networks:Connecting to public or unsecured Wi-Fi networks can expose your Mac to eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks, where attackers intercept data transmitted between your Mac and other devices.
- Third-Party Software:While the App Store offers a curated selection of applications, downloading software from untrusted sources can increase the risk of installing malware. Always be cautious about the software you install and ensure it comes from a reputable source.
User Behavior and Mac Security
User behavior plays a crucial role in maintaining Mac security. Here are some key factors that influence your Mac’s security:
- Password Strength:Using strong, unique passwords for different accounts significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. A strong password is at least 12 characters long, includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols, and is not easily guessable.
- Software Updates:Regularly updating your macOS and applications is essential to stay protected against known vulnerabilities. Software updates often include security patches that address newly discovered exploits.
- Email and Website Security:Be cautious about clicking on links in emails or visiting websites from unknown sources. Verify the authenticity of emails and websites before providing any sensitive information.
- File Downloads:Only download files from trusted sources. Avoid downloading files from suspicious websites or attachments from unknown senders. Before opening a downloaded file, scan it with antivirus software to ensure it’s safe.
- Antivirus Software:While macOS has built-in security features, using reputable antivirus software can provide an additional layer of protection against malware. Antivirus software scans your Mac for malicious files and can block suspicious websites and downloads.
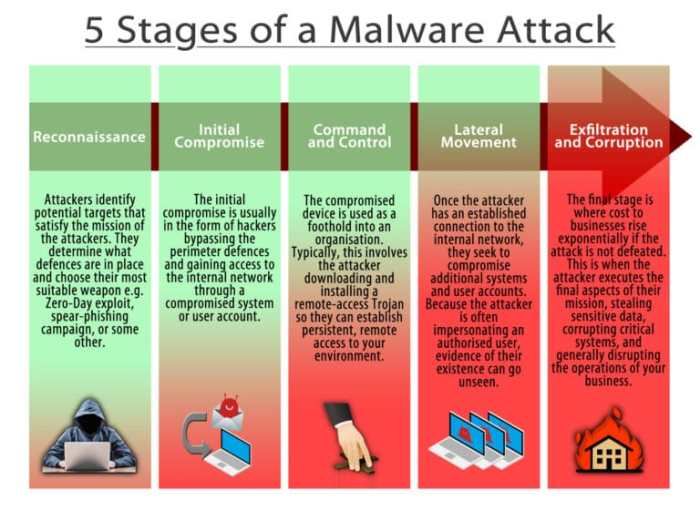
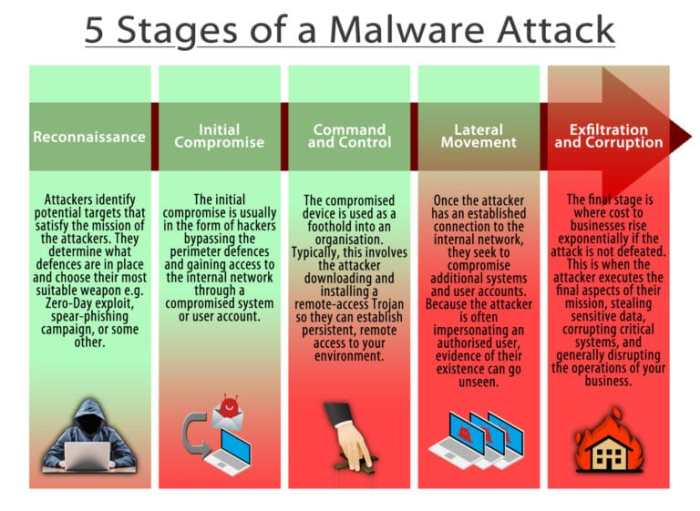
Malware Infection Methods
While Apple Macs are known for their robust security, they are not immune to malware. Attackers are constantly devising new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to your system. Understanding how malware infects Macs is crucial for protecting your data and privacy.
Common Malware Infection Methods
Malware can spread through various methods, targeting vulnerabilities in the Mac operating system or user behavior.
- Exploiting Software Vulnerabilities:Malware can exploit security holes in software applications, including operating system updates, web browsers, and other programs. Attackers can use these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to your Mac and install malicious code.
- Phishing Attacks:Phishing attacks involve tricking users into clicking malicious links or opening infected attachments in emails or messages. These links often lead to fake websites that resemble legitimate ones, designed to steal your personal information or install malware on your device.
- Drive-by Downloads:Drive-by downloads occur when malware is automatically installed on your Mac without your explicit consent. This can happen when visiting compromised websites or clicking on malicious advertisements.
- Malicious Software Bundles:Some free software downloads may include bundled malware that is installed alongside the desired application. Users often overlook these bundled programs during the installation process, inadvertently exposing their Macs to threats.
- Social Engineering:Attackers often use social engineering techniques to manipulate users into giving up sensitive information or granting access to their devices. This can involve convincing users to click on malicious links, download infected files, or provide personal data through fake websites or emails.
Social Engineering in Malware Distribution, Dummy guide to infecting apple mac with malware
Social engineering plays a significant role in malware distribution. Attackers leverage human psychology to manipulate users into taking actions that compromise their security. They may use various tactics, including:
- Urgency and Scarcity:Attackers create a sense of urgency or scarcity, encouraging users to act quickly without thinking critically about the risks involved. For example, a message might claim that your account is about to be suspended unless you click a link to verify your identity.
- Authority and Trust:Attackers may impersonate legitimate organizations or individuals to gain the trust of users. For example, a fake email might appear to be from Apple, warning you about a security threat and prompting you to download a malicious update.
- Fear and Intimidation:Attackers may use fear or intimidation tactics to manipulate users into giving up information or granting access to their devices. For example, a message might claim that your computer has been infected with a virus and demand immediate payment to remove it.
Examples of Malicious Websites and Email Attachments
- Malicious Websites:Attackers often create fake websites that mimic legitimate ones, such as online banking sites or social media platforms. These websites may contain malicious scripts or links that can infect your Mac with malware.
- Email Attachments:Email attachments are a common method for distributing malware. Attackers may send emails with attachments disguised as legitimate documents, images, or other files. These attachments can contain malicious code that infects your Mac when opened.
Types of Mac Malware
While Apple’s macOS operating system is generally considered more secure than Windows, it’s not immune to malware attacks. Malware developers are constantly finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities and target Mac users. Understanding the different types of Mac malware is crucial for recognizing and mitigating threats.
This knowledge helps you implement effective security measures and protect your valuable data.
Viruses
Viruses are self-replicating programs that can spread from one computer to another. They often attach themselves to legitimate files and can cause various issues, including data corruption, system crashes, and slow performance. A well-known example of a Mac virus is the “OSX/Filecoder.A” virus, which encrypts files and demands a ransom for their decryption.
This type of virus, known as ransomware, is a significant threat to Mac users.
Signs of Mac Malware Infection: Dummy Guide To Infecting Apple Mac With Malware
Detecting malware on your Mac can be tricky, as it often operates silently in the background. However, there are several signs that could indicate a malware infection. Learning to recognize these symptoms is crucial for protecting your Mac and personal data.
Common Symptoms of Mac Malware Infection
Malware can manifest itself in various ways, impacting your Mac’s performance, behavior, and security. Recognizing these symptoms is essential for identifying potential infections.
- Slow performance:Malware can consume system resources, leading to sluggish performance, slow application loading times, and overall lag. This can be especially noticeable during resource-intensive tasks like video editing or gaming.
- Frequent crashes or freezes:Malware can interfere with your Mac’s operating system, causing unexpected crashes, freezes, or system instability. These issues can disrupt your workflow and require you to restart your Mac.
- Unexpected software installations:If you find unfamiliar software or applications installed on your Mac without your consent, it could be a sign of malware. This can include browser extensions, toolbars, or other unwanted programs.
- Unusual network activity:Malware can connect to external servers or networks without your knowledge, resulting in increased network traffic or unexpected data usage. This can lead to slower internet speeds or higher data bills.
- Increased fan noise:If your Mac’s fan is running unusually loud, it could indicate that malware is consuming significant CPU resources, leading to overheating.
- Unusual pop-ups or ads:Malware can display intrusive pop-ups, advertisements, or other unwanted content, disrupting your browsing experience. These ads may redirect you to malicious websites or try to install additional malware.
- Changes in your browser’s homepage or search engine:Malware can modify your browser settings, changing your homepage or default search engine without your permission. This can redirect you to malicious websites or expose your personal data to hackers.
- Loss of data or files:Malware can delete or corrupt your files, leading to data loss or system instability. This can be especially damaging if you lose important documents, photos, or other critical data.
- Unusual system behavior:Malware can manipulate your Mac’s behavior, leading to unexpected changes in system settings, application behavior, or overall system performance. This can include unauthorized access to your files or the ability to control your Mac remotely.
Differentiating Normal System Behavior from Malware Activity
It’s important to differentiate between normal system behavior and malware activity. Some common system issues can be mistaken for malware, so it’s essential to investigate further before taking any action.
- Slow performance:While malware can cause slow performance, other factors like insufficient RAM, outdated software, or a full hard drive can also contribute. Check your system resources and update your software before suspecting malware.
- Frequent crashes or freezes:Similar to slow performance, crashes or freezes can be caused by hardware issues, driver conflicts, or software bugs. Ensure your drivers are up-to-date and try troubleshooting the specific application or hardware component causing the issue.
- Unexpected software installations:Some software installations may appear unexpected if you forget installing them or if they are bundled with other software. Review your recent downloads and software installations to determine if the unexpected software is legitimate.
- Unusual network activity:If you have recently downloaded or installed new software, it may be responsible for increased network traffic. Monitor your network activity to identify any unusual patterns or spikes in data usage.
- Increased fan noise:While malware can cause overheating, other factors like dust buildup, a faulty fan, or heavy system load can also lead to increased fan noise. Clean your Mac’s vents and check for any hardware issues.
- Unusual pop-ups or ads:While malware can cause intrusive pop-ups, these can also be triggered by legitimate websites or software. Use ad blockers or disable pop-ups in your browser settings to minimize these occurrences.
- Changes in your browser’s homepage or search engine:If you have recently installed new software or visited a suspicious website, it may have modified your browser settings. Reset your browser settings or use a different browser to check if the issue persists.
- Loss of data or files:Data loss can occur due to various reasons, including accidental deletion, hardware failures, or software bugs. Use data recovery software or contact a professional data recovery service to recover lost data.
- Unusual system behavior:If you notice unusual system behavior, try restarting your Mac and checking for any recent software updates or changes in your system settings. If the issue persists, consider performing a clean installation of macOS.
Symptoms and Corresponding Malware Types
Different types of malware can manifest themselves in various ways. Understanding these symptoms can help you identify the specific malware type infecting your Mac.
Find out further about the benefits of how to build brand for startup free that can provide significant benefits.
| Symptom | Malware Type |
|---|---|
| Slow performance, frequent crashes, and unexpected software installations | Adware, Spyware, Trojans |
| Unusual network activity, increased data usage, and unexpected pop-ups or ads | Adware, Spyware, Trojans |
| Changes in browser settings, redirects to malicious websites, and loss of data or files | Trojans, Ransomware, Browser hijackers |
| Unusual system behavior, unauthorized access to files, and remote control of your Mac | Trojans, Remote Access Trojans (RATs) |
Preventing Mac Malware Infection
While Macs are generally considered more secure than Windows PCs, they are not immune to malware. It is crucial to take proactive steps to protect your Mac from malicious attacks.
Securing Your Mac
The best defense against malware is a combination of proactive measures and robust security tools. This section will guide you through essential steps to fortify your Mac’s defenses.
Basic Security Practices
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your macOS, applications, and web browser to patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malware. Apple automatically updates macOS, but you can manually check for updates by going to System Preferences > Software Update.
- Install Security Software: Use reputable antivirus software specifically designed for Mac. These tools scan for malware, detect suspicious activity, and provide real-time protection.
- Enable Firewall: The built-in firewall in macOS helps prevent unauthorized access to your Mac. You can enable it by going to System Preferences > Security & Privacy > Firewall.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ strong and unique passwords for all your online accounts, including your Apple ID. Avoid using common passwords or phrases and consider using a password manager to store and manage your passwords securely.
- Be Cautious with Downloads: Only download software from trusted sources like the Mac App Store or official websites. Be wary of suspicious downloads from unknown websites or email attachments.
- Avoid Clicking Suspicious Links: Be cautious about clicking links in emails, messages, or social media posts, especially if they seem suspicious or unexpected. If you’re unsure, hover over the link to see the actual destination URL.
- Enable FileVault Encryption: FileVault encrypts your entire hard drive, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to access your data. You can enable it by going to System Preferences > Security & Privacy > FileVault.
Recommended Security Software and Tools
- Malwarebytes for Mac: This popular antivirus software offers real-time protection, malware detection, and removal capabilities.
- Intego Mac Internet Security: Intego provides comprehensive protection, including antivirus, anti-phishing, and parental controls.
- Sophos Home Premium: Sophos offers a user-friendly antivirus solution with features like web protection, ransomware protection, and automatic updates.
- Bitdefender Antivirus for Mac: Bitdefender provides real-time protection, malware detection, and a range of security features.
Removing Mac Malware
Malware removal on a Mac can be a complex process that requires careful steps and a combination of methods. It’s essential to understand the different types of malware and how they operate to effectively remove them from your system.
Quarantining and Deleting Infected Files
Quarantining and deleting infected files are crucial steps in the malware removal process. This involves isolating the malicious files from your system to prevent further damage and then permanently removing them.
- Identifying Infected Files:The first step is to identify the infected files. You can use antivirus software, which often provides a list of detected threats and their locations. Alternatively, you can manually search for suspicious files based on their names, file extensions, or locations.
For instance, if you suspect a file named “update.dmg” might be malicious, you should investigate further.
- Quarantining Infected Files:Once you’ve identified the infected files, you should quarantine them. This involves moving the files to a separate location, such as a dedicated quarantine folder, to prevent them from executing or spreading further. You can do this by dragging the files to a different folder or using a utility like “Trash” on macOS.
- Deleting Infected Files:After quarantining, you can permanently delete the infected files. This involves moving the files to the “Trash” folder and then emptying the “Trash.” Alternatively, you can use a file shredder application to securely erase the files, making them unrecoverable.
Restoring a Mac to a Clean State
Restoring your Mac to a clean state can be an effective way to remove malware, especially if the infection is widespread or you’re unsure about the extent of the damage. This involves resetting your Mac to its factory settings, removing all data and applications.
- Time Machine Backup:Before restoring your Mac, it’s crucial to have a recent backup of your data. This ensures you can recover your files and applications after the restoration process. macOS offers a built-in backup solution called “Time Machine,” which automatically creates backups of your data.
You can also use third-party backup solutions.
- Reinstall macOS:To restore your Mac to a clean state, you need to reinstall macOS. This can be done from the macOS Recovery mode, which is accessible by restarting your Mac and holding down the Command + R keys. In Recovery mode, select “Reinstall macOS” and follow the on-screen instructions.
This will erase your hard drive and install a fresh copy of macOS.
- Restore Data:After reinstalling macOS, you can restore your data from your backup. This can be done using Time Machine or your chosen backup solution. This process will restore your files, applications, and system settings, effectively returning your Mac to its previous state.
Staying Safe from Mac Malware
Now that you understand the threats posed by Mac malware, let’s explore how to stay safe and prevent infection. The key is to practice responsible online behavior, be aware of phishing scams, and stay informed about emerging malware threats.
Maintaining Strong Security Practices
Implementing robust security measures is crucial to protect your Mac from malware. Here are some practical tips:
- Keep Your Software Up-to-Date:Regularly update your operating system, applications, and security software. Updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities exploited by malware.
- Use Strong Passwords:Create unique and complex passwords for all your online accounts. Avoid using the same password across multiple platforms. Use a password manager to help you generate and store strong passwords securely.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):Whenever possible, enable 2FA for your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second authentication factor, usually a code sent to your phone, in addition to your password.
- Be Cautious with Downloads:Only download software from trusted sources like the Mac App Store or official developer websites. Avoid downloading software from unknown or suspicious websites. Be wary of freeware or cracked software, as they often contain malware.
- Install Reputable Antivirus Software:Consider installing a reputable antivirus software specifically designed for Mac. Antivirus software can help detect and remove malware, provide real-time protection, and scan your system for threats.
Recognizing and Avoiding Phishing Scams
Phishing scams are a common method used by cybercriminals to trick users into giving away sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. Be vigilant and learn how to identify and avoid these scams.
- Beware of Suspicious Emails and Links:Don’t click on links or open attachments from unknown senders. Be wary of emails that urge you to take immediate action or that contain grammatical errors or unusual formatting. Hover over links before clicking to check the actual URL.
- Verify the Sender’s Identity:If you receive an email from a seemingly legitimate source, double-check the sender’s address and email signature. Look for inconsistencies or signs that the email may be forged.
- Be Cautious with Social Media Links:Be wary of links shared on social media, especially if they lead to unfamiliar websites or offer too-good-to-be-true deals. Before clicking on a link, consider whether the source is trustworthy and whether the content aligns with your expectations.
- Don’t Provide Personal Information Unnecessarily:Be hesitant about providing personal information, such as your social security number, credit card details, or bank account information, unless you are absolutely sure the website or organization is legitimate.
Staying Informed about Emerging Malware Threats
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new malware strains emerging regularly. It’s essential to stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities to protect yourself.
- Subscribe to Security Newsletters:Sign up for security newsletters from reputable sources, such as cybersecurity companies or technology blogs. These newsletters provide insights into emerging threats, security best practices, and timely updates.
- Follow Security Experts on Social Media:Follow security experts and cybersecurity organizations on social media platforms. They often share insights, news, and warnings about emerging threats.
- Read Security Blogs and Websites:Regularly read security blogs and websites that provide information about malware threats, vulnerabilities, and security tips. These resources can help you stay informed and proactive.