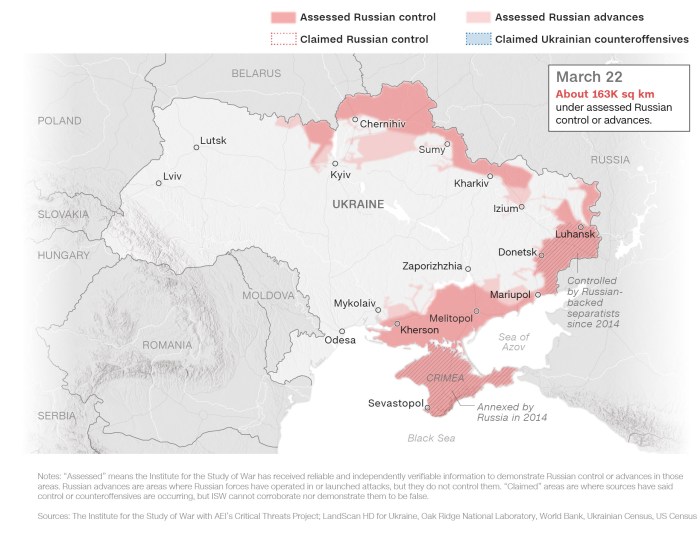
Cybersecurity in Ukraine war one year anniversary russia invasion has become a defining aspect of the conflict, showcasing the evolving landscape of cyber warfare. The war has witnessed a relentless barrage of cyberattacks targeting Ukraine’s critical infrastructure, government institutions, and civilian populations, highlighting the devastating impact of cyberwarfare on modern societies.
As the conflict entered its second year, the cyber landscape has become even more complex, with both sides employing sophisticated tactics and strategies to gain an advantage. This has forced Ukraine to bolster its cyber defenses, relying on international partnerships and innovative strategies to mitigate cyber threats.
The Impact of the War on Ukraine’s Cybersecurity Infrastructure: Cybersecurity In Ukraine War One Year Anniversary Russia Invasion
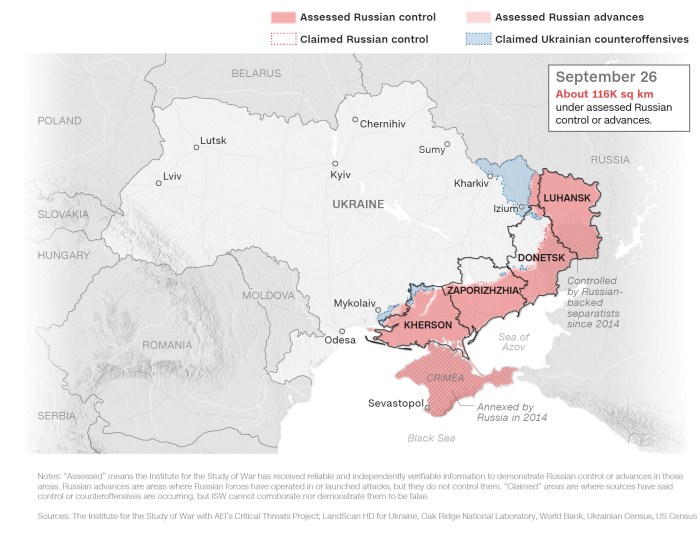
The full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russia on February 24, 2022, marked a significant escalation of the conflict and had a profound impact on Ukraine’s cybersecurity infrastructure. Prior to the invasion, Ukraine had already faced numerous cyberattacks from Russia, but the scale and intensity of these attacks increased dramatically after the invasion.
Ukraine’s Cybersecurity Infrastructure Before the War
Before the war, Ukraine had made significant strides in strengthening its cybersecurity infrastructure. The country had a well-developed cybersecurity strategy, including a national cybersecurity agency, CERT-UA, and a network of cybersecurity professionals. However, Ukraine faced significant challenges, including limited resources and a lack of coordination between government agencies and private sector organizations.
Major Cyberattacks Launched by Russia Against Ukraine
Russia launched a series of coordinated cyberattacks against Ukraine, targeting critical infrastructure, government institutions, and private companies. These attacks included:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: These attacks overwhelmed Ukrainian websites and online services, making them inaccessible to users.
- Malware attacks: Russia deployed malware to disrupt Ukrainian systems and steal sensitive information. Notable examples include NotPetya and Industroyer, which caused significant damage to Ukrainian businesses and critical infrastructure.
- Data breaches: Russian hackers targeted Ukrainian government websites and databases, stealing sensitive information and using it for propaganda purposes.
- Social engineering attacks: Russian hackers used social engineering techniques to trick Ukrainian users into giving them access to their systems or revealing sensitive information.
Challenges Faced by Ukraine in Defending Its Critical Infrastructure
Ukraine faced several challenges in defending its critical infrastructure against Russian cyberattacks:
- Limited resources: Ukraine’s cybersecurity budget was relatively small compared to Russia’s.
- Lack of coordination: Coordination between government agencies and private sector organizations was sometimes lacking, hindering effective cyber defense.
- Constant evolution of cyberattacks: Russia constantly developed new and sophisticated cyberattack techniques, making it difficult for Ukraine to keep up.
- The impact of physical attacks: The physical destruction of infrastructure in Ukraine made it more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Strategies Implemented by Ukraine to Mitigate Cyber Threats
Ukraine implemented a variety of strategies to mitigate cyber threats, including:
- Strengthening cybersecurity infrastructure: Ukraine invested in upgrading its cybersecurity infrastructure, including its national cybersecurity agency and CERT-UA.
- Increasing public awareness: Ukraine launched public awareness campaigns to educate citizens about cyber threats and how to protect themselves.
- International cooperation: Ukraine collaborated with international partners to share information and resources. This included working with NATO, the EU, and other countries to enhance its cyber defense capabilities.
- Proactive defense: Ukraine adopted a proactive defense strategy, actively hunting for and disrupting Russian cyberattacks. This included setting up honeypots to lure attackers and using deception techniques to mislead them.
- Cyber resilience: Ukraine focused on building cyber resilience, ensuring that its critical infrastructure could withstand cyberattacks and quickly recover from them.
Examples of Successful Cyber Defense Measures Employed by Ukraine
Ukraine successfully employed several cyber defense measures to mitigate Russian cyberattacks, including:
- Disrupting Russian cyber operations: Ukraine disrupted several Russian cyber operations, including those targeting critical infrastructure and government websites. This was achieved through a combination of technical and intelligence measures.
- Using deception techniques: Ukraine used deception techniques to mislead Russian attackers, diverting them from their targets and giving Ukrainian defenders more time to respond.
- Building resilience: Ukraine invested in building cyber resilience, ensuring that its critical infrastructure could withstand cyberattacks and quickly recover from them. This included implementing backup systems and data recovery plans.
The Role of International Cybersecurity Cooperation
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has highlighted the critical importance of international cybersecurity cooperation. This collaboration has been crucial in supporting Ukraine’s defense against cyberattacks and mitigating the broader global impact of the conflict.
International Organizations and Government Support
International organizations and governments have played a vital role in bolstering Ukraine’s cyber defenses. The collective effort has involved sharing intelligence, providing technical assistance, and imposing sanctions against malicious actors.
- NATO:The North Atlantic Treaty Organization has provided technical support to Ukraine, including cyber defense training and expertise. NATO’s Cyber Defence Centre of Excellence (CCDCOE) in Estonia has been instrumental in coordinating international cyber assistance efforts.
- EU:The European Union has imposed sanctions on Russian individuals and entities involved in cyberattacks against Ukraine. The EU has also allocated funding to support Ukraine’s cybersecurity infrastructure.
- United States:The US government has provided significant cyber assistance to Ukraine, including intelligence sharing, technical support, and sanctions against Russian cybercriminals.
- United Kingdom:The UK has deployed cyber experts to Ukraine and has provided technical assistance to bolster Ukraine’s cyber defenses.
Effectiveness of International Cooperation
International cooperation has been effective in mitigating cyber threats against Ukraine. The collective response has helped to deter some attacks and disrupt the activities of malicious actors. However, the effectiveness of international cooperation is constantly evolving, and challenges remain.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out why january is the best time to get a new job now.
Challenges of Coordinating Cyber Defense Efforts
Coordinating cyber defense efforts across different countries poses significant challenges. These challenges include:
- Information Sharing:Sharing sensitive intelligence information across borders can be complex and politically sensitive.
- Technical Compatibility:Different countries may have different cybersecurity standards and technologies, which can make it difficult to integrate their defenses.
- Legal Frameworks:Laws and regulations governing cybersecurity vary significantly across countries, which can create legal barriers to cooperation.
Key Examples of International Cyber Assistance
- Intelligence Sharing:Western intelligence agencies have shared critical information with Ukraine about Russian cyber operations, allowing Ukraine to anticipate and counter attacks.
- Technical Assistance:International cybersecurity experts have provided technical assistance to Ukraine, helping to patch vulnerabilities and improve its cyber defenses.
- Cybercrime Investigations:International law enforcement agencies have collaborated to investigate and prosecute Russian cybercriminals involved in attacks against Ukraine.
The Evolution of Cyber Warfare Tactics and Strategies
The first year of the Russia-Ukraine war has witnessed a dramatic evolution in cyber warfare tactics and strategies. The conflict has become a proving ground for new cyber weapons, techniques, and approaches, pushing the boundaries of what was previously considered possible in the digital domain.
This evolution has implications not only for the battlefield but also for the global cybersecurity landscape.
The Changing Nature of Cyber Warfare Tactics, Cybersecurity in ukraine war one year anniversary russia invasion
The use of cyber weapons in the conflict has become increasingly sophisticated and multifaceted. Russia has employed a wide range of tactics, from targeted attacks on critical infrastructure to large-scale disinformation campaigns. Early in the conflict, Russia launched a wave of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks against Ukrainian government websites and critical infrastructure, aiming to disrupt communication and cripple essential services.
These attacks, while initially disruptive, proved to be relatively unsophisticated and easily mitigated by Ukrainian defenders.As the conflict progressed, Russia transitioned to more targeted and destructive attacks. They used malware to infiltrate Ukrainian systems, steal sensitive data, and disrupt operations.
For example, the NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, which targeted Ukrainian businesses and government agencies, caused significant economic damage and disrupted critical services. Russia also employed wiper malware, designed to permanently erase data from infected systems, to cripple Ukrainian government and military networks.
Furthermore, Russia has increasingly relied on cyber espionage, attempting to gather intelligence on Ukrainian military movements, troop deployments, and defense strategies. They have also used cyber tools to monitor and disrupt Ukrainian communication networks, hindering the flow of information and hindering coordination among Ukrainian forces.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Ukraine and Beyond
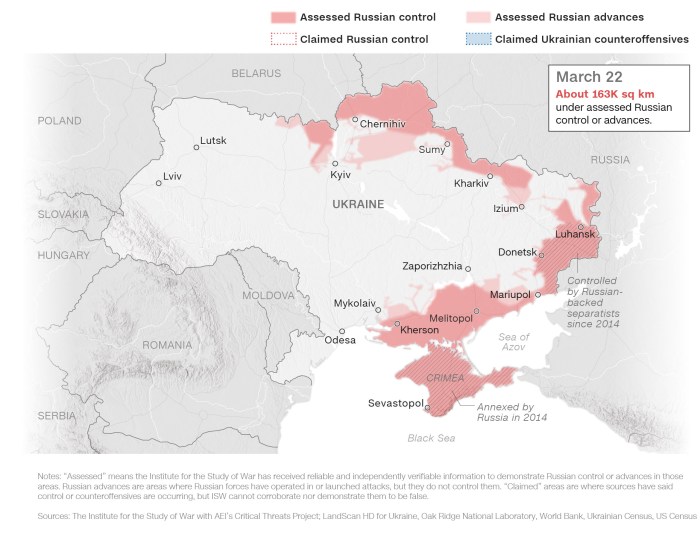
The war in Ukraine has profoundly impacted cybersecurity, revealing vulnerabilities and highlighting the need for robust defenses. The conflict has served as a stark reminder of the evolving nature of cyber warfare and the need for continuous adaptation in the face of new threats.
This section explores the long-term implications of the war on cybersecurity in Ukraine and globally, examines lessons learned, and Artikels a framework for enhancing cybersecurity preparedness and response.
Long-Term Implications for Ukraine’s Cybersecurity
The war has had a significant impact on Ukraine’s cybersecurity infrastructure. The country has faced a relentless barrage of cyberattacks, ranging from denial-of-service attacks to data breaches and malware campaigns. These attacks have targeted critical infrastructure, government agencies, and private businesses.
The war has forced Ukraine to invest heavily in its cybersecurity defenses, adopting new technologies and strategies to counter evolving threats. The long-term implications for Ukraine’s cybersecurity landscape are significant:
- Increased Investment in Cybersecurity:The war has underscored the critical importance of cybersecurity, leading to increased investment in bolstering defenses, upgrading infrastructure, and enhancing personnel training. The government has prioritized cybersecurity as a national security concern, allocating resources to strengthen resilience against future attacks.
- Enhanced Cyber Intelligence and Threat Sharing:Ukraine has learned the value of effective cyber intelligence gathering and sharing threat information with allies. The war has fostered a closer collaboration between government agencies, private companies, and international partners, leading to improved threat detection and response capabilities.
- Focus on Critical Infrastructure Protection:The targeting of critical infrastructure in Ukraine has highlighted the need for robust security measures to protect essential services like energy, transportation, and communication networks. This includes implementing advanced security protocols, hardening systems, and investing in cybersecurity awareness training for personnel.
Lessons Learned for Global Cybersecurity
The war in Ukraine has provided valuable lessons for strengthening cyber defenses globally:
- The Importance of Proactive Defense:The conflict has demonstrated the effectiveness of proactive cybersecurity measures, including threat intelligence, vulnerability assessments, and incident response planning. By anticipating potential threats and implementing preventive measures, organizations can significantly reduce their risk of attack.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing:The war has underscored the critical role of international cooperation in cybersecurity. Sharing threat information, best practices, and resources across borders is crucial for combating global cyber threats. International partnerships can also facilitate joint research and development efforts to enhance cybersecurity capabilities.
- The Need for Resilience and Adaptability:The constant evolution of cyber warfare tactics necessitates a robust and adaptable cybersecurity posture. Organizations must be prepared to respond quickly and effectively to new threats, leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence and automation to enhance their defenses.
Framework for Improving Cybersecurity Preparedness and Response
The war in Ukraine highlights the need for a comprehensive framework to improve cybersecurity preparedness and response. Such a framework should encompass the following key elements:
- National Cybersecurity Strategies:Countries should develop national cybersecurity strategies that Artikel clear goals, priorities, and action plans. These strategies should encompass all aspects of cybersecurity, including critical infrastructure protection, cybercrime prevention, and incident response.
- Investment in Cybersecurity Research and Development:Increased investment in cybersecurity research and development is crucial for developing innovative technologies and solutions to counter emerging threats. This includes funding research into advanced threat detection and response systems, artificial intelligence for cybersecurity, and quantum-resistant cryptography.
- Public-Private Partnerships:Fostering collaboration between government agencies and private sector companies is essential for effective cybersecurity. This can involve sharing threat intelligence, developing joint cybersecurity initiatives, and promoting cybersecurity awareness campaigns.
- Cybersecurity Education and Training:Investing in cybersecurity education and training programs is vital for developing a skilled cybersecurity workforce. This includes supporting cybersecurity education in schools and universities, offering professional development opportunities, and promoting cybersecurity awareness among the general public.
Potential for Future Cyber Conflicts
The war in Ukraine has demonstrated the potential for cyber conflicts to escalate and have a significant impact on international security. The future of cyber warfare is likely to be characterized by:
- Increased Sophistication and Automation:Cyberattacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, leveraging advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning. This trend is likely to continue, leading to more targeted and impactful attacks.
- Blurred Lines Between State and Non-State Actors:The distinction between state-sponsored and non-state actors in cyberspace is becoming increasingly blurred. Private companies and individuals with advanced technical skills are capable of carrying out sophisticated attacks, making it difficult to attribute responsibility and respond effectively.
- The Rise of Cyber Espionage and Sabotage:Cyber espionage and sabotage are likely to become more prevalent, as states and non-state actors seek to gain strategic advantages or disrupt critical infrastructure. This could involve stealing sensitive information, disrupting economic activities, or causing physical damage to critical systems.