Critical infrastructure radio hacked backdoor tetra – a chilling phrase that highlights a growing threat to our modern world. Imagine a scenario where power grids, transportation systems, and emergency communication networks are vulnerable to malicious actors, potentially crippling entire cities and nations.
This is the reality we face as critical infrastructure radio systems, particularly those relying on the TETRA standard, become increasingly susceptible to backdoor exploits.
TETRA, a widely adopted digital radio standard, is designed to offer secure communication for emergency services, public safety, and critical infrastructure. However, despite its robust security features, the potential for backdoors – hidden pathways allowing unauthorized access – introduces a significant vulnerability.
Hackers could exploit these backdoors to gain control over critical radio systems, potentially disrupting operations, stealing sensitive data, and even causing physical harm. This article delves into the complexities of this issue, exploring the vulnerabilities of TETRA systems, the consequences of a successful backdoor exploit, and the crucial steps we must take to secure our critical infrastructure.
Introduction to Critical Infrastructure Radio Systems
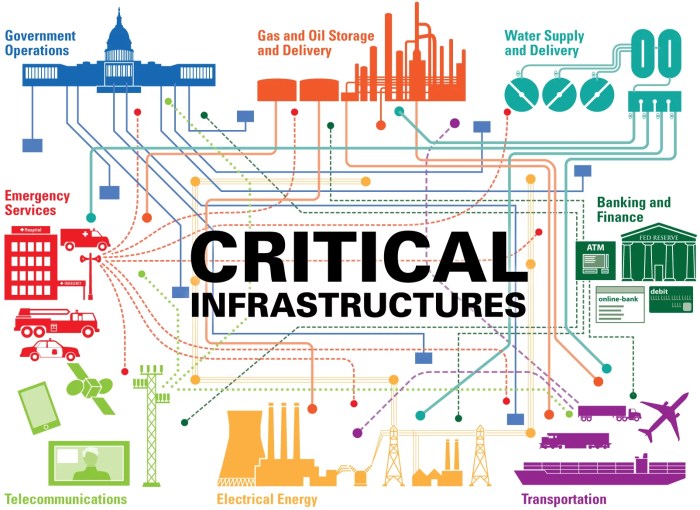
Radio communication systems play a vital role in the smooth operation and safety of critical infrastructure sectors, ensuring uninterrupted service and timely response in emergency situations. These sectors, including power grids, water treatment plants, transportation systems, and emergency services, heavily rely on reliable radio communication to maintain their operations and respond effectively to unforeseen events.
Vulnerabilities in Radio Systems
Radio systems, despite their critical role, are not immune to vulnerabilities that can compromise their security and reliability. These vulnerabilities can arise from various sources, including physical tampering, unauthorized access, and signal interference. In the context of TETRA technology, specifically designed for critical communications, vulnerabilities can arise from weaknesses in the encryption algorithms, software bugs, or improper configuration.
TETRA Technology and its Vulnerabilities
TETRA (Terrestrial Trunked Radio) is a digital radio communication standard widely adopted for critical infrastructure and public safety applications. While TETRA offers enhanced security features compared to analog systems, it is not entirely impervious to vulnerabilities. TETRA systems, like any other technology, can be susceptible to various vulnerabilities, including:
- Weak Encryption Algorithms:Older versions of TETRA encryption algorithms might be vulnerable to brute-force attacks or known cryptanalytic techniques, potentially allowing unauthorized access to sensitive communications.
- Software Bugs:Software vulnerabilities in TETRA base stations, handsets, or network management systems could be exploited to gain unauthorized access, disrupt communication, or even manipulate data transmission.
- Improper Configuration:Misconfigured TETRA systems, such as weak passwords or inadequate access controls, can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Signal Jamming:Intentional interference with TETRA signals can disrupt communication and cause operational disruptions, particularly in critical situations.
These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of robust security measures and continuous vigilance to mitigate potential risks and ensure the reliable operation of TETRA systems in critical infrastructure sectors.
The TETRA Standard and its Security Features: Critical Infrastructure Radio Hacked Backdoor Tetra
The TETRA (Terrestrial Trunked Radio) standard is a digital radio communication system widely used in critical infrastructure sectors like public safety, transportation, and utilities. Designed to be highly secure, TETRA incorporates various security features to protect communications from unauthorized access and interference.The TETRA standard emphasizes robust encryption and authentication protocols to ensure secure communication between users.
These security mechanisms aim to prevent eavesdropping, message tampering, and unauthorized access to the network.
TETRA’s Encryption and Authentication Protocols
TETRA employs a combination of encryption and authentication protocols to safeguard communication.
- Encryption:TETRA utilizes the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm with a 128-bit key to encrypt voice and data transmissions. AES is a widely recognized and secure encryption algorithm, offering strong protection against unauthorized decryption.
- Authentication:TETRA uses a challenge-response authentication mechanism to verify the identity of users and devices. During authentication, the network challenges a user or device with a random code. The user or device must respond with a correct answer derived from a shared secret key, confirming their authenticity.
These security features significantly enhance the confidentiality and integrity of TETRA communications, making it a robust and reliable system for critical infrastructure operations.
Potential Vulnerabilities in TETRA
Despite its robust security features, TETRA is not immune to potential vulnerabilities.
- Key Compromise:If the encryption key is compromised, an attacker could potentially decrypt all communications using that key. This vulnerability highlights the importance of strong key management practices to prevent unauthorized access to encryption keys.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks:An attacker could potentially intercept communications between a user and the network, impersonating either party. This could allow the attacker to eavesdrop on communications, modify messages, or even gain access to sensitive information.
- Weaknesses in Authentication:While the challenge-response mechanism is effective, it can be susceptible to attacks if the shared secret keys are not properly managed or if the authentication process is not implemented correctly.
TETRA’s security features are designed to protect against common threats, but it is essential to address potential vulnerabilities through ongoing security audits, updates, and best practices.
The Threat of Hacked Backdoors in TETRA Systems
The TETRA standard, while robust, is not immune to the threat of backdoors. These hidden pathways, intentionally built into systems, can allow unauthorized access, compromising the security of critical infrastructure communications. Understanding the implications of backdoors in TETRA systems is crucial for safeguarding their integrity and resilience.
Methods of Introducing Backdoors
Backdoors can be introduced into TETRA systems through various methods, each posing a significant risk to security.
- Software Vulnerabilities:Exploiting vulnerabilities in the software used in TETRA systems, such as operating systems or communication protocols, can allow attackers to gain access and introduce backdoors.
- Hardware Tampering:Physical access to TETRA equipment, such as base stations or handsets, can enable attackers to modify hardware components, implanting backdoors that bypass security measures.
- Supply Chain Attacks:Compromising the supply chain of TETRA components, including hardware and software, can allow attackers to introduce backdoors during the manufacturing or distribution process.
- Insider Threats:Individuals with legitimate access to TETRA systems, such as network administrators or developers, could introduce backdoors intentionally or unintentionally, potentially for malicious purposes or to facilitate espionage.
Consequences of a Successful Backdoor Exploit, Critical infrastructure radio hacked backdoor tetra
A successful backdoor exploit in a TETRA system can have severe consequences, disrupting critical operations and compromising sensitive information.
- Data Breaches:Backdoors can allow attackers to intercept and steal sensitive data transmitted over TETRA networks, including operational data, location information, and confidential communications.
- Disruption of Operations:Attackers can use backdoors to manipulate TETRA systems, disrupting communications and causing operational failures. For example, they could disable emergency response systems or interfere with critical infrastructure control systems.
- Loss of Trust and Reputation:A backdoor compromise can erode public trust in the security of critical infrastructure communications, impacting the reputation of organizations and the reliability of their systems.
- Espionage and Sabotage:Backdoors can facilitate espionage by allowing attackers to monitor and gather intelligence from TETRA networks. Additionally, they can be used to conduct sabotage, disrupting critical operations and causing significant damage.
Impact of Radio System Compromise on Critical Infrastructure
The compromise of a critical infrastructure radio system can have devastating consequences, potentially leading to widespread disruption and chaos. These systems are essential for the smooth operation of various services, including power generation and distribution, transportation, and emergency response. A successful attack could cripple these services, causing significant economic and societal impacts.
Disruption of Essential Services
A compromised radio system could disrupt essential services in several ways:* Power Grids:Communication between power plants, substations, and control centers relies heavily on radio systems. A disruption in this communication could lead to power outages, affecting homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
Transportation
Radio systems are vital for air traffic control, train operations, and maritime navigation. A successful attack could lead to delays, cancellations, and accidents, impacting transportation networks and causing widespread disruption.
Emergency Response
Remember to click europe lightning hunter first images of severe storms to understand more comprehensive aspects of the europe lightning hunter first images of severe storms topic.
Emergency services rely on radio systems for communication and coordination during emergencies. A compromised system could hinder their ability to respond effectively, potentially leading to increased casualties and damage.
Communication Networks
Radio systems play a crucial role in communication networks, providing connectivity for various services, including mobile phone networks, internet access, and broadcasting. A disruption in radio communication could lead to widespread communication outages, impacting businesses, individuals, and emergency services.
Economic and Societal Impacts
The economic and societal impacts of a large-scale radio system compromise could be significant:* Economic Losses:The disruption of essential services could lead to substantial economic losses, including lost productivity, business closures, and increased insurance claims.
Public Safety Risks
A compromised radio system could hinder emergency response efforts, increasing the risk of casualties and damage during emergencies.
Social Disruptions
Widespread communication outages and disruptions to essential services could lead to social unrest and panic.
National Security Concerns
A compromised radio system could pose a significant threat to national security, potentially enabling hostile actors to disrupt critical infrastructure and communication networks.
Mitigation Strategies and Best Practices
The vulnerability of critical infrastructure to cyberattacks through compromised TETRA systems demands robust mitigation strategies and best practices to ensure resilience and security. By implementing a comprehensive approach encompassing encryption, access control, regular security audits, and ongoing monitoring, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of exploitation and maintain the integrity of their communication networks.
Encryption Protocols
Encryption plays a pivotal role in safeguarding TETRA communications by transforming data into an unreadable format, rendering it incomprehensible to unauthorized parties. Implementing strong encryption protocols, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a robust key length, is crucial for protecting sensitive information transmitted over TETRA networks.
“AES with a key length of 256 bits is considered highly secure and is widely recommended for sensitive communications.”
Access Control
Access control mechanisms are essential for restricting unauthorized access to TETRA systems. Implementing multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and regular password rotation can effectively limit access to authorized personnel, reducing the risk of unauthorized modifications or data breaches.
“Multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a one-time code generated by a mobile device.”
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are critical for identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities within TETRA systems. These audits should involve a comprehensive assessment of the system’s configuration, software, and network infrastructure to identify potential weaknesses and implement corrective measures.
“Security audits should be conducted by qualified security professionals with expertise in TETRA systems and cyber security best practices.”
Ongoing Monitoring and Threat Intelligence
Continuous monitoring and threat intelligence are essential for detecting and responding to potential attacks. Implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems, monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity, and staying informed about emerging threats can help organizations proactively address security risks.
“Threat intelligence can provide valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures used by attackers, enabling organizations to anticipate and counter potential threats.”
Future Trends and Research Directions
The realm of critical infrastructure radio communications is continuously evolving, driven by technological advancements and the ever-present need for enhanced security. Emerging technologies and trends are shaping the future landscape, while the impact of next-generation technologies, like 5G, on radio system security demands careful consideration.
Research efforts are actively exploring ways to build more robust and secure communication systems, ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure in the face of evolving threats.
The Impact of 5G and Other Next-Generation Technologies on Radio System Security
The advent of 5G and other next-generation technologies is poised to significantly impact critical infrastructure radio communications. These technologies promise enhanced speed, capacity, and latency, but they also introduce new security challenges. The increased complexity and interconnectedness of 5G networks present opportunities for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities.
- Increased Attack Surface:5G networks involve a larger number of devices and connections, creating a wider attack surface for malicious actors.
- Network Slicing:The ability to create virtualized network slices within 5G networks introduces the risk of slice isolation failures, potentially impacting critical infrastructure communication.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN):While SDN offers flexibility and programmability, it also creates new vulnerabilities if not implemented securely.
Research efforts are focusing on developing security solutions to address these challenges.
- Network Segmentation:Isolating critical infrastructure networks from the broader 5G ecosystem to limit the impact of potential breaches.
- Enhanced Authentication and Authorization:Implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to critical infrastructure networks.
- Security by Design:Incorporating security considerations into the design and deployment of 5G networks to mitigate vulnerabilities from the outset.