China still asml biggest market falling sales drop profit – China Still ASML’s Biggest Market: Falling Sales Drop Profit. This headline might seem paradoxical, but it reflects the complex reality of the global semiconductor industry. ASML, the Dutch company that makes the world’s most advanced lithography machines, is facing a significant drop in sales and profit.
This downturn can be attributed to several factors, including the ongoing trade tensions between the US and China, and the slowing global economy. However, despite these challenges, China remains ASML’s largest market, underscoring the critical role it plays in the future of semiconductor technology.
ASML’s technology is crucial for producing the advanced chips that power our smartphones, computers, and cars. The company’s machines are so sophisticated that they are considered a strategic asset by many governments. China, in particular, has made significant investments in developing its own semiconductor industry.
However, China’s ambitions to achieve self-sufficiency in chip production face significant hurdles, including the reliance on ASML’s technology. The US has imposed restrictions on ASML’s ability to sell its most advanced machines to China, citing national security concerns. This has created a complex geopolitical landscape that is impacting the entire semiconductor supply chain.
ASML’s Dominance in the Semiconductor Market
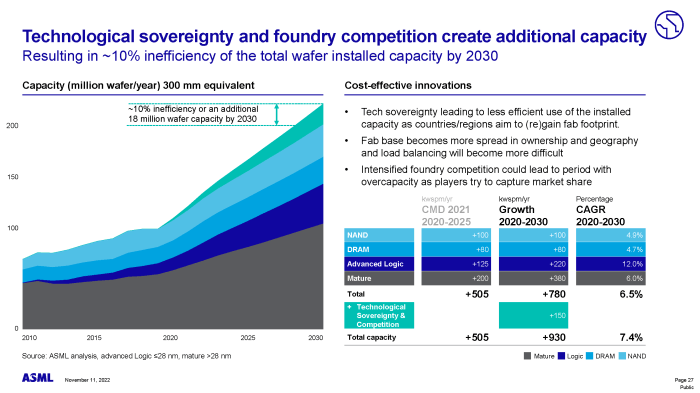
ASML, a Dutch company, holds a dominant position in the semiconductor industry due to its unique and sophisticated technology. Their extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines are essential for manufacturing the most advanced chips, driving innovation in computing, mobile devices, and other technology sectors.
Further details about riddled with debt swedens embracer sells star wars game maker for 500m is accessible to provide you additional insights.
ASML’s Technology Significance
ASML’s EUV lithography machines are crucial for the production of leading-edge semiconductors, allowing chipmakers to create smaller, more powerful, and energy-efficient chips. The EUV technology utilizes a short-wavelength ultraviolet light to etch intricate patterns onto silicon wafers, enabling the creation of chips with smaller transistors and higher densities.
This advancement is critical for driving Moore’s Law, which states that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years.
ASML’s Market Share and Competitive Landscape
ASML holds a near-monopoly in the EUV lithography market, with a market share exceeding 90%. This dominance stems from the complexity and technological expertise required to develop and manufacture these sophisticated machines. The company’s closest competitors include Nikon and Canon, but they primarily focus on older, less advanced lithography technologies.
Impact of ASML’s Technology on Global Chip Production
ASML’s technology has a profound impact on global chip production. The availability of EUV machines has enabled chipmakers to push the boundaries of semiconductor technology, leading to advancements in artificial intelligence, high-performance computing, and mobile devices.
China’s Role in the Semiconductor Industry: China Still Asml Biggest Market Falling Sales Drop Profit
China’s ambitions in the semiconductor industry are vast, driven by a desire to become a global leader in technology and reduce its dependence on foreign suppliers. The country has poured billions of dollars into research, development, and manufacturing, aiming to achieve self-sufficiency in chip production.
However, this journey faces significant challenges.
Challenges in Achieving Self-Sufficiency
China’s path to semiconductor self-sufficiency is fraught with obstacles. While the country has made strides in manufacturing less advanced chips, it still lags behind in developing cutting-edge technologies.
- Technology Gap:China’s domestic chipmakers struggle to match the technological prowess of companies like TSMC and Samsung, particularly in areas like lithography, which is crucial for producing advanced chips.
- Talent Shortage:The industry faces a shortage of skilled engineers and researchers, hindering its ability to innovate and develop its own technology.
- Supply Chain Dependence:Despite investments in domestic production, China remains heavily reliant on foreign suppliers for critical components and materials.
- US Export Controls:US restrictions on exports of advanced chipmaking equipment, particularly from ASML, have significantly impacted China’s ability to acquire the tools needed for producing leading-edge chips.
ASML’s Technology and its Impact
ASML’s extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines are crucial for producing the most advanced chips. The Netherlands-based company holds a near-monopoly in this technology, making it a key player in the global semiconductor landscape.
- Limited Access:US export controls restrict ASML from selling its most advanced EUV machines to China, limiting the country’s ability to manufacture cutting-edge chips.
- Impact on Innovation:The lack of access to advanced lithography technology hinders China’s ability to develop its own chipmaking capabilities, potentially slowing down its progress in the semiconductor industry.
- Alternative Solutions:China is exploring alternative solutions, such as investing in domestic lithography equipment development and seeking partnerships with other countries to overcome technology limitations.
Falling Sales and Profit at ASML
ASML, the world’s leading supplier of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines, has reported a decline in sales and profit in recent quarters. This trend is a significant development in the semiconductor industry, particularly considering ASML’s dominant position and the crucial role EUV technology plays in advanced chip manufacturing.
Factors Contributing to the Decline
The decline in ASML’s sales and profit can be attributed to several factors.
- Weakening Global Demand:The global economic slowdown has impacted demand for semiconductors, particularly in the consumer electronics and automotive sectors. This has led to a reduction in orders for EUV machines, as chipmakers adjust their production plans to align with lower demand.
- Inventory Adjustments:Semiconductor manufacturers have been working to reduce their inventory levels, which has also contributed to lower demand for new equipment. This is a natural response to the slowdown in demand and is expected to continue for some time.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China have created uncertainty in the semiconductor industry. These tensions have made it more difficult for ASML to sell its EUV machines to Chinese chipmakers, as the U.S. government has imposed restrictions on the export of advanced technology to China.
Impact of Global Economic Conditions
The global economic slowdown has had a significant impact on ASML’s business. The decline in demand for semiconductors has led to a reduction in orders for EUV machines, and the company has had to adjust its production plans accordingly.
“The global economic slowdown has impacted demand for semiconductors, particularly in the consumer electronics and automotive sectors. This has led to a reduction in orders for EUV machines, as chipmakers adjust their production plans to align with lower demand.”
ASML CEO Peter Wennink
Potential Implications for ASML’s Future
The decline in ASML’s sales and profit raises concerns about the company’s future prospects. However, it is important to note that ASML remains the dominant player in the EUV lithography market, and the long-term demand for advanced chip manufacturing technology is expected to remain strong.
- Market Recovery:ASML is confident that the semiconductor market will eventually recover, and the company is well-positioned to benefit from this recovery. The company has a strong backlog of orders and is investing heavily in research and development to maintain its technological leadership.
- New Applications:The demand for EUV technology is expected to grow in the coming years as it is used in new applications, such as artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and 5G networks.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty:Geopolitical tensions remain a significant risk to ASML’s business. The company is working with governments to ensure that its technology is not used for military purposes and that it is not subject to export restrictions.
The Future of ASML and China
The current situation between ASML and China is complex, with both short-term challenges and long-term implications. The question is whether ASML can regain its market share in China and what impact its technology will have on China’s semiconductor industry.
The Potential for ASML to Regain Market Share in China
ASML’s ability to regain its market share in China depends on a complex interplay of factors, including political considerations, technological advancements, and market demand. While China’s semiconductor industry is experiencing rapid growth, the government’s focus on self-reliance may limit ASML’s access to the market.
- Political Tensions:The ongoing trade war between the US and China has created a challenging environment for ASML. The US government has imposed restrictions on the export of ASML’s technology to China, making it difficult for the company to operate in the country.
- Technological Advancements:ASML is constantly developing new and more advanced lithography machines. These advancements could potentially allow ASML to regain its market share in China, as the country’s semiconductor industry requires the latest technology to stay competitive.
- Market Demand:The Chinese semiconductor industry is experiencing strong growth, fueled by increasing demand for smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices. This demand could create opportunities for ASML to regain its market share.
The Long-Term Implications of ASML’s Technology on China’s Semiconductor Industry, China still asml biggest market falling sales drop profit
ASML’s technology is crucial for the development of advanced semiconductors, which are essential for a wide range of applications, including smartphones, computers, and artificial intelligence. China’s ambition to become a global leader in the semiconductor industry depends heavily on access to ASML’s technology.
- Innovation and Development:ASML’s technology could enable China to develop more advanced semiconductors, leading to innovation in various industries, including artificial intelligence, 5G, and cloud computing.
- Economic Growth:China’s semiconductor industry is a significant contributor to its economy. The development of advanced semiconductors could boost economic growth and create new jobs.
- National Security:China’s reliance on foreign companies for critical technologies, such as semiconductors, raises concerns about national security. Developing a strong domestic semiconductor industry could reduce this dependence.
The Potential for Alternative Technologies to Challenge ASML’s Dominance
While ASML currently dominates the market for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography machines, several companies are developing alternative technologies that could challenge its dominance.
- Immersion Lithography:This technology uses water to improve the resolution of optical lithography machines. Companies like Nikon and Canon are developing advanced immersion lithography machines that could compete with ASML’s EUV technology for certain applications.
- Direct-Write Lithography:This technology uses lasers to directly write patterns on a semiconductor wafer. Companies like Heidelberg Instruments and Nano-C are developing direct-write lithography systems that could be used for niche applications.
- Electron Beam Lithography:This technology uses a beam of electrons to write patterns on a semiconductor wafer. Companies like Raith and JEOL are developing electron beam lithography systems that are used for research and development purposes.
Impact on Global Semiconductor Supply Chain

ASML’s declining sales have significant implications for the global semiconductor supply chain. The company’s dominance in the lithography equipment market means that any disruption in its operations could have cascading effects on chip production worldwide.
Potential for Disruptions in Chip Production
The ASML-China situation has the potential to disrupt chip production due to the following reasons:* Reduced Chip Production Capacity:ASML’s sales decline could lead to a shortage of advanced lithography equipment, limiting the capacity of chip manufacturers to produce advanced chips. This could result in delays in product launches, increased prices, and a shortage of essential components for various industries.
Impact on Innovation
The availability of advanced lithography equipment is crucial for research and development in the semiconductor industry. ASML’s sales decline could hinder innovation by slowing down the development of new chip designs and technologies. This could have long-term consequences for the competitiveness of the global semiconductor industry.
Geopolitical Tensions
The ASML-China situation is a complex geopolitical issue that could further exacerbate tensions between the two countries. This could lead to unpredictable trade restrictions and export controls, further disrupting the semiconductor supply chain.
Potential Solutions to Address the Challenges
The global semiconductor industry needs to find solutions to address the challenges posed by ASML’s sales decline and the ASML-China situation. These solutions could include:* Diversification of Equipment Suppliers:The industry needs to diversify its reliance on ASML by supporting the development of alternative lithography equipment manufacturers.
This could involve government support, collaborative research initiatives, and investment in emerging technologies.
Increased Domestic Production
Countries are increasingly looking to increase domestic chip production to reduce their reliance on foreign suppliers. This could involve providing incentives to chip manufacturers, investing in research and development, and fostering a skilled workforce.
International Cooperation
Collaboration between countries is crucial to address the challenges in the global semiconductor supply chain. This could involve sharing information, coordinating policies, and promoting open trade.





