Can ai design better streets for pedestrians dalle 2 – SKIPPED
Pedestrian-Centric Design Principles: Can Ai Design Better Streets For Pedestrians Dalle 2
The concept of pedestrian-centric street design is a shift in urban planning that prioritizes the needs and safety of pedestrians over motorized vehicles. This approach aims to create streets that are more enjoyable, accessible, and inviting for walking, cycling, and public transportation.
Key Principles of Pedestrian-Centric Street Design
Pedestrian-centric street design is guided by a set of principles that ensure a safe, accessible, and comfortable experience for pedestrians.
- Safety: The primary concern in pedestrian-centric design is the safety of pedestrians. This involves reducing vehicle speeds, separating pedestrian and vehicular traffic, and providing clear visibility for both drivers and pedestrians.
- Accessibility: Streets should be accessible to everyone, regardless of age, ability, or mobility.
This includes providing ramps, curb cuts, and crosswalks that are compliant with accessibility standards.
- Comfort: Pedestrian-centric streets prioritize comfort by providing shade, seating, and landscaping. This encourages people to spend more time walking and enjoying the public space.
Examples of Successful Pedestrian-Centric Streets
There are many examples of successful pedestrian-centric streets around the world that demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach.
- The High Line in New York City: This elevated park built on a former railway line is a prime example of a pedestrian-centric space. The High Line is designed to prioritize pedestrians and provide stunning views of the city, making it a popular destination for locals and tourists alike.
- The Rambla in Barcelona: This pedestrian-only street is a vibrant hub of activity, lined with shops, restaurants, and street performers. The Rambla is a popular destination for locals and tourists alike, showcasing the benefits of prioritizing pedestrian access.
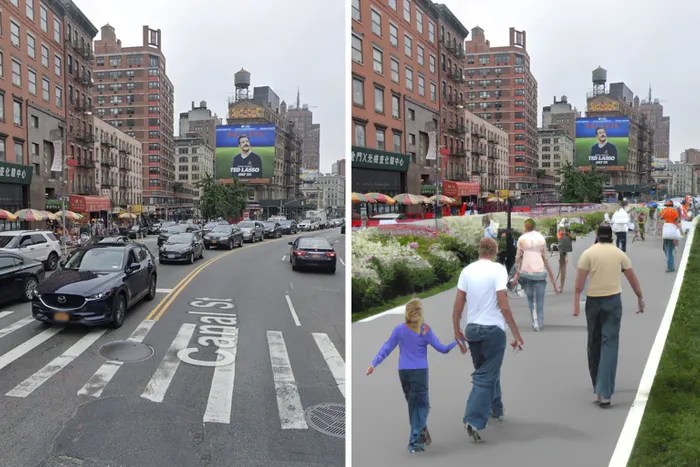
- The Canal Street in Amsterdam: This street is a great example of a successful pedestrian-centric street that prioritizes cycling and walking over motorized vehicles.
The Canal Street is a popular destination for locals and tourists alike, showcasing the benefits of prioritizing pedestrian access.
Comparison with Traditional Street Design
Traditional street design often prioritizes vehicular traffic over pedestrian needs. This can lead to streets that are dangerous, uncomfortable, and inaccessible for pedestrians.
- Speed: Traditional streets are designed for high-speed traffic, which can pose a serious risk to pedestrians.
- Width: Traditional streets are often wide, making it difficult for pedestrians to cross safely.
- Lack of Amenities: Traditional streets often lack amenities like shade, seating, and landscaping, making them less inviting for pedestrians.
AI’s Role in Street Design
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into street design presents a transformative opportunity to create more pedestrian-friendly and efficient urban environments. By leveraging the power of AI, we can analyze vast amounts of data to understand pedestrian behavior, traffic patterns, and environmental factors, leading to data-driven design decisions.
Benefits of AI in Pedestrian-Friendly Street Planning
The application of AI in street design offers numerous advantages, leading to safer, more accessible, and more enjoyable pedestrian experiences.
- Enhanced Pedestrian Safety:AI can analyze accident data and identify high-risk areas, allowing for the implementation of targeted safety measures such as improved lighting, crosswalk visibility, and traffic calming devices. For example, in a study conducted by the University of California, Berkeley, AI algorithms were used to analyze pedestrian accident data in San Francisco.
The results revealed high-risk areas, leading to the implementation of traffic calming measures and increased pedestrian safety.
- Optimized Traffic Flow:AI can analyze traffic patterns and predict congestion, enabling the implementation of intelligent traffic management systems that prioritize pedestrian movement and minimize delays. This can be achieved through dynamic traffic light control, optimized lane configurations, and real-time traffic guidance systems.
- Improved Accessibility:AI can analyze accessibility data, such as sidewalk conditions, curb ramps, and public transportation access, to identify areas requiring improvements. This can lead to the creation of more inclusive and accessible streets for people with disabilities, seniors, and families with young children.
- Sustainable Street Design:AI can help optimize street design for sustainability by analyzing environmental factors such as air quality, noise pollution, and solar radiation. This can lead to the implementation of green infrastructure, such as trees and green roofs, to improve air quality and reduce heat island effects.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While AI offers significant potential for improving pedestrian-centric street design, it is crucial to address the associated challenges and ethical considerations.
- Data Privacy and Security:AI-driven street design relies heavily on data collection, raising concerns about data privacy and security. It is essential to ensure that data is collected and used ethically and responsibly, with appropriate safeguards in place to protect individual privacy.
- Bias and Discrimination:AI algorithms can inherit biases present in the data they are trained on, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes in street design. It is crucial to address bias in training data and ensure that AI-driven decisions are fair and equitable for all pedestrians.
- Transparency and Explainability:AI-driven decisions can be complex and difficult to understand, raising concerns about transparency and explainability. It is important to develop mechanisms for explaining AI-driven design choices and ensuring that they are understandable and accountable.
DALL-E 2’s Capabilities for Visualization

DALL-E 2 is a powerful AI system that can generate realistic and imaginative images from text descriptions. This capability opens up exciting possibilities for visualizing pedestrian-friendly streets and exploring different design options. DALL-E 2’s ability to understand and interpret complex prompts allows it to create highly detailed and nuanced visualizations, capturing the essence of pedestrian-centric design principles.
Visualizing Pedestrian-Friendly Streets
DALL-E 2 can generate a wide range of visualizations that showcase pedestrian-friendly streets. It can depict various street layouts, incorporating different design elements such as:
- Wide sidewalks: DALL-E 2 can create visualizations of streets with spacious sidewalks that provide ample room for pedestrians to walk comfortably, stroll, or even gather in small groups.
- Protected bike lanes: DALL-E 2 can generate visualizations of streets with dedicated bike lanes separated from vehicle traffic, enhancing safety and encouraging cycling.
- Crosswalks and pedestrian islands: DALL-E 2 can create visualizations of streets with well-defined crosswalks and pedestrian islands that provide safe and easy passage for pedestrians crossing the street.
- Street furniture and landscaping: DALL-E 2 can visualize streets with benches, trees, and other street furniture that enhance the aesthetics and functionality of the pedestrian environment.
- Traffic calming measures: DALL-E 2 can create visualizations of streets with speed bumps, roundabouts, and other traffic calming measures that prioritize pedestrian safety and reduce vehicle speeds.
Examples of DALL-E 2 Visualizations
- A bustling pedestrian plaza: DALL-E 2 can visualize a vibrant pedestrian plaza with wide, open spaces, outdoor seating, and street performers, creating a lively and inviting atmosphere for pedestrians.
- A tree-lined street with protected bike lanes: DALL-E 2 can visualize a street with a central green strip lined with trees, separated bike lanes, and narrow sidewalks, showcasing a harmonious integration of pedestrian and cyclist needs.
- A narrow, cobblestone street with quaint shops and cafes: DALL-E 2 can visualize a charming pedestrian-only street with historic architecture, cobblestone pavement, and inviting shops and cafes, creating a nostalgic and appealing atmosphere.
Comparison with Real-World Examples, Can ai design better streets for pedestrians dalle 2
DALL-E 2’s visualizations can be compared to real-world examples of pedestrian-friendly streets. For example, DALL-E 2’s visualizations of wide sidewalks with ample space for pedestrians can be compared to the sidewalks in New York City’s Times Square or London’s Oxford Street.
DALL-E 2’s visualizations of tree-lined streets with protected bike lanes can be compared to the streets in Copenhagen, Denmark, which is known for its bike-friendly infrastructure.
DALL-E 2’s ability to generate realistic and imaginative visualizations can help urban planners and designers understand the potential of different design options and make informed decisions about creating more pedestrian-friendly streets.
Expand your understanding about astronomers found sneaky black hole with the sources we offer.
Integrating AI and Visualization

The true power of AI in pedestrian-centric street design lies in its ability to not only analyze data but also visualize the potential outcomes of its analysis. By combining AI’s analytical prowess with DALL-E 2’s artistic capabilities, we can create a powerful tool for designing streets that prioritize pedestrian safety and comfort.
Scenarios for AI and DALL-E 2 Collaboration
The synergy between AI and DALL-E 2 can be harnessed to create compelling visualizations for various pedestrian-centric design scenarios. This table highlights how these technologies can work together to improve streets:
| Scenario | AI Analysis | DALL-E 2 Visualization | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reducing Congestion at Busy Intersections | AI analyzes pedestrian and vehicle traffic patterns to identify bottlenecks and optimize traffic flow. | DALL-E 2 generates images of proposed solutions like wider sidewalks, pedestrian-only zones, or improved crosswalks. | Improved pedestrian flow, reduced congestion, and enhanced safety. |
| Creating Safe and Accessible Routes for People with Disabilities | AI identifies barriers like uneven sidewalks, lack of curb ramps, and inaccessible public transportation. | DALL-E 2 visualizes solutions like ramps, tactile paving, and accessible bus stops. | Increased accessibility and mobility for people with disabilities. |
| Enhancing Street Aesthetics and Pedestrian Comfort | AI analyzes environmental factors like noise levels, air quality, and sunlight exposure. | DALL-E 2 generates images of streets with lush greenery, shade structures, and visually appealing features. | Improved pedestrian experience, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced quality of life. |
In this scenario, AI analyzed pedestrian traffic patterns and identified a dangerous intersection where jaywalking was prevalent. DALL-E 2 then generated multiple visualizations of the intersection, showcasing different solutions like a pedestrian crossing island, a flashing crosswalk signal, and a widened sidewalk. By visualizing these solutions, the city planners could assess their effectiveness and choose the best option to improve pedestrian safety and reduce jaywalking.
Future Implications

The integration of AI and visualization tools into street design holds immense potential to transform urban planning and development. AI-powered insights can inform the creation of pedestrian-friendly streetscapes that prioritize walkability, safety, and livability. This shift towards pedestrian-centric urban design can have a profound impact on cities around the world.
Impact on Urban Planning and Development
The adoption of AI-driven street design can fundamentally alter the way cities are planned and developed. By leveraging AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets, urban planners can gain a deeper understanding of pedestrian behavior, traffic patterns, and environmental factors.
This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, leading to more efficient and effective urban planning strategies.
“AI-driven street design has the potential to reshape urban landscapes, creating more sustainable, equitable, and vibrant cities.”
Creating More Walkable and Livable Cities
AI and visualization tools can play a crucial role in creating more walkable and livable cities. By analyzing pedestrian flow patterns, AI algorithms can identify areas with high pedestrian traffic and areas with potential for improvement. Visualization tools can then be used to create interactive 3D models of proposed street designs, allowing stakeholders to visualize and assess the impact of design changes on pedestrian experience.
This collaborative approach fosters a more inclusive and participatory urban planning process.
“AI-powered visualization tools can help bridge the gap between design concepts and real-world implementation, enabling stakeholders to understand the impact of design decisions on pedestrian experience.”
Potential Future Applications
AI and DALL-E 2 can be applied in various ways to advance pedestrian-centric urban design. Here are some potential future applications:
- Personalized Navigation and Wayfinding:AI can develop personalized navigation apps that guide pedestrians through complex urban environments, considering their individual needs and preferences. This can enhance accessibility and improve the overall pedestrian experience.
- Real-Time Street Optimization:AI can analyze real-time data on traffic flow, pedestrian density, and weather conditions to dynamically optimize street layouts and traffic signals, ensuring smoother pedestrian movement and reduced congestion.
- Predictive Maintenance for Street Infrastructure:AI can monitor the condition of street infrastructure, such as sidewalks and street lighting, and predict potential maintenance needs, preventing safety hazards and ensuring the longevity of urban infrastructure.
- Sustainable Street Design:AI can optimize street designs to minimize environmental impact by considering factors such as solar exposure, wind patterns, and green space integration, contributing to the creation of more sustainable and resilient urban environments.
- Interactive Urban Planning:AI and visualization tools can create interactive platforms that allow citizens to engage in urban planning discussions, providing feedback and shaping the future of their cities. This can lead to more inclusive and citizen-centric urban design solutions.