Booking com joins tech giants gatekeeper eu competition rules dma – Booking.com joins tech giants gatekeeper eu competition rules dma, a significant move that shakes up the online travel industry. The European Union’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) targets companies with dominant market positions, like Booking.com, Google, and Amazon, and aims to level the playing field for smaller businesses and consumers.
This new legislation could have a profound impact on how Booking.com operates and interacts with its users.
The DMA Artikels specific rules for these “gatekeeper” companies, including restrictions on self-preferencing, data access, and interoperability. The act aims to prevent these companies from using their dominance to stifle competition and limit consumer choice. While Booking.com has been a major player in the online travel industry for years, the DMA presents a new set of challenges and opportunities for the company.
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) and its Impact on Tech Giants
The Digital Markets Act (DMA), adopted by the European Union in 2022, is a landmark piece of legislation aimed at regulating the power of tech giants and promoting fair competition in the digital marketplace. The DMA targets companies with a “gatekeeper” status, meaning they have a significant market share and influence over online services.The DMA seeks to create a more level playing field for businesses and consumers by addressing anti-competitive practices, such as self-preferencing, data access restrictions, and unfair terms of service.
Provisions Relevant to Booking.com and Online Travel Platforms
The DMA contains several provisions that are directly relevant to online travel platforms like Booking.com. These provisions aim to ensure that gatekeeper platforms like Booking.com operate in a fair and transparent manner, preventing them from using their dominant position to disadvantage competitors or consumers.Here are some of the key provisions:
- Interoperability:The DMA mandates that gatekeeper platforms allow interoperability between their services and those of competitors. This means that Booking.com would have to allow other travel platforms to integrate with its booking system, enabling users to compare prices and services across different platforms.
This could increase competition and offer consumers more choices.
- Non-discrimination:The DMA prohibits gatekeeper platforms from discriminating against competing services. Booking.com would be required to treat all travel providers equally, regardless of whether they are competitors or not. This could prevent Booking.com from favoring its own hotel listings or offering preferential treatment to certain partners.
- Data Access:The DMA gives businesses access to data they need to compete effectively. This means that competitors of Booking.com could potentially access data on booking trends, pricing, and user behavior, enabling them to better tailor their offerings and compete on a more equal footing.
- Transparency:The DMA requires gatekeeper platforms to be transparent about their algorithms and data usage. This could help users understand how Booking.com’s search results are generated and how their personal data is being used.
Impact on Booking.com’s Business Practices
The DMA could have a significant impact on Booking.com’s business practices, forcing the company to adapt its operations to comply with the new regulations. For example, Booking.com may need to:
- Revise its algorithms:To ensure non-discrimination, Booking.com may need to adjust its algorithms to prevent self-preferencing and ensure that all travel providers are presented fairly in search results.
- Open up its platform to competitors:Booking.com may have to allow other travel platforms to integrate with its booking system, enabling users to compare prices and services across different platforms. This could lead to increased competition and potentially lower prices for consumers.
- Provide greater transparency to users:Booking.com may need to provide more information about how its algorithms work and how user data is used, potentially affecting its marketing and data collection practices.
- Change its terms of service:Booking.com may need to revise its terms of service to comply with the DMA’s requirements for fairness and transparency.
Booking.com’s Business Model and its Potential Conflicts with the DMA
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) aims to regulate the power of large online platforms and ensure a fairer digital landscape. Booking.com, a leading online travel booking platform, could be significantly impacted by the DMA due to its unique business model and potential “gatekeeping” practices.
Booking.com’s Business Model and Revenue Generation
Booking.com operates as an online travel agent (OTA), connecting travelers with accommodation providers like hotels, apartments, and guesthouses. The platform facilitates bookings by offering a comprehensive search engine, detailed property information, and secure payment processing. Booking.com generates revenue primarily through commissions charged to accommodation providers for each booking made through its platform.
These commissions are typically a percentage of the total booking price.
Booking.com’s Potential Conflicts with the DMA
Booking.com’s business model, particularly its dominant market position in the online travel industry, raises concerns regarding potential conflicts with the DMA. The DMA targets gatekeeping practices, which can be defined as behaviors that restrict competition and limit consumer choice.
Booking.com’s practices, such as its commission structure, data collection, and use of algorithms, could be interpreted as gatekeeping practices under the DMA.
Browse the implementation of health tracking wearable oura ring review in real-world situations to understand its applications.
Booking.com’s Commission Structure and its Potential Impact on Competition
Booking.com’s commission structure, which often ranges from 15% to 25% of the booking price, has been criticized for potentially stifling competition among accommodation providers. These high commissions can significantly impact the profitability of smaller hotels and independent guesthouses, potentially making it challenging for them to compete with larger hotel chains that can absorb the higher costs.
Booking.com’s Data Collection and Use of Algorithms
Booking.com collects vast amounts of data on user preferences, booking behavior, and accommodation provider performance. This data is used to personalize user experiences, optimize search results, and recommend accommodations. While this data collection and use of algorithms can benefit consumers by providing tailored travel recommendations, it raises concerns about potential data-based market manipulation.
Booking.com’s algorithms could potentially prioritize listings from preferred partners or manipulate search results to favor certain accommodation providers, limiting consumer choice and hindering competition.
Comparison with Other Tech Giants, Booking com joins tech giants gatekeeper eu competition rules dma
Booking.com’s business model shares similarities with other tech giants like Google and Amazon, which have also been scrutinized for their gatekeeping practices. Google, with its dominant search engine, has been accused of favoring its own products and services in search results, while Amazon has been criticized for its preferential treatment of its own brands and its use of data to disadvantage competitors.
Like these tech giants, Booking.com’s position in the online travel industry raises concerns about potential market manipulation and the need for regulations to ensure a fair and competitive environment.
The Potential Consequences of the DMA for Booking.com
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is poised to significantly impact the operations of online platforms like Booking.com. The act, designed to promote competition and protect consumers, could bring about a range of consequences for Booking.com, affecting its business practices, user experience, and the broader online travel industry.
Potential Fines and Restrictions
The DMA empowers regulators to impose substantial fines on companies that violate its provisions. For Booking.com, non-compliance could result in fines up to 10% of its global annual turnover. These fines could be triggered by various actions, such as:
- Self-preferencing: Booking.com might face penalties if it favors its own accommodations over those of competitors on its platform.
- Restricting interoperability: If Booking.com prevents users from seamlessly integrating its services with other platforms, it could be subject to fines.
- Excessive data collection: The DMA limits the data that platforms can collect from users without their explicit consent. Booking.com’s data collection practices might need to be adjusted to comply with these regulations.
Furthermore, the DMA could impose restrictions on Booking.com’s business practices, such as:
- Prohibiting the use of opaque pricing: Booking.com might be required to display all fees and charges upfront, eliminating hidden costs.
- Restricting the use of unfair contracts: The DMA aims to ensure fair and transparent contracts between platforms and businesses. Booking.com’s contracts with accommodation providers might need to be revised to comply with these requirements.
Impact on Booking.com’s Users
The DMA’s impact on Booking.com could extend to its users, both consumers and accommodation providers:
- Increased choice and transparency for consumers: By promoting competition and restricting unfair practices, the DMA could empower consumers with more choices and greater transparency in their booking process. This could lead to better deals and more informed decisions.
- Potential benefits for accommodation providers: The DMA could level the playing field for smaller accommodation providers by restricting Booking.com’s dominance. This could translate into better terms and conditions for providers, including potentially lower commission rates.
Impact on the Online Travel Industry
The DMA’s impact on Booking.com could have broader implications for the online travel industry:
- Increased competition and innovation: By promoting competition, the DMA could encourage new entrants and innovation in the online travel market. This could lead to more diverse offerings and potentially lower prices for consumers.
- Shifts in market power: The DMA’s regulations could shift the balance of power within the online travel industry, potentially empowering smaller players and reducing the dominance of large platforms like Booking.com.
The Role of Competition in the Online Travel Industry: Booking Com Joins Tech Giants Gatekeeper Eu Competition Rules Dma
The online travel industry is a fiercely competitive landscape, with numerous players vying for market share. This competitive environment is characterized by constant innovation, evolving consumer preferences, and the pursuit of efficiency. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for understanding the potential impact of the DMA on the industry.
The Current Competitive Landscape
The online travel industry is dominated by a handful of major players, including Booking.com, Expedia Group, Tripadvisor, and Airbnb. These companies have established significant market share through their global reach, extensive inventory, and sophisticated technology platforms. The competitive landscape can be further segmented by the types of services offered.
Online travel agencies (OTAs) like Booking.com and Expedia Group focus on providing a wide range of accommodation options, flights, and other travel services. Metasearch engines like Tripadvisor aggregate information from multiple sources, enabling users to compare prices and options.
Airbnb focuses on short-term rentals, offering a unique alternative to traditional hotels.
The market share of the top online travel platforms is constantly evolving, with new players emerging and existing players adapting their strategies.
The Potential for Increased Competition
The DMA’s aim to promote competition in the digital market could significantly impact the online travel industry. The DMA’s provisions could lead to increased competition in the following ways:* Enhanced Interoperability:The DMA requires large online platforms to allow users to switch between platforms seamlessly.
This could encourage the emergence of new players who can leverage the interoperability of existing platforms to offer competitive services.
Reduced Barriers to Entry
The DMA’s provisions could lower the barriers to entry for new players, allowing them to compete more effectively with established giants. For example, the DMA could make it easier for smaller travel agencies to access booking systems and inventory, giving them a greater opportunity to compete.
Increased Transparency
The DMA requires online platforms to provide users with more information about their services and pricing. This transparency could help users make more informed decisions, potentially leading to greater competition among providers.
Market Share Comparison
The following table provides a hypothetical comparison of market share among top online travel platforms before and after the implementation of the DMA. These figures are estimations and are subject to change based on the specific implementation of the DMA and the market’s response.| Platform | Market Share Before DMA | Market Share After DMA ||—|—|—|| Booking.com | 25% | 20% || Expedia Group | 15% | 12% || Airbnb | 10% | 15% || Other Players | 50% | 53% |The table suggests that the DMA could lead to a shift in market share, with smaller players potentially gaining ground.
However, it’s important to note that the actual impact of the DMA on market share will depend on various factors, including the effectiveness of the regulations, the response of established players, and the emergence of new competitors.
Future Implications of the DMA for Booking.com and the Online Travel Industry
The Digital Markets Act (DMA) is poised to reshape the online travel industry, potentially creating a more competitive and consumer-friendly landscape. Its impact on Booking.com and other major online travel platforms will be significant, leading to changes in their business models, operations, and market dominance.
The DMA’s Potential Impact on Booking.com’s Business Model
The DMA’s gatekeeper designation for Booking.com will force the company to adapt its business practices to comply with the new regulations. These regulations will likely lead to significant changes in Booking.com’s business model, including:
- Increased Interoperability:The DMA mandates that gatekeepers like Booking.com must allow users to switch between different platforms easily. This means Booking.com will have to allow users to access and manage their data on other platforms, promoting competition and giving users more control over their travel arrangements.
- Transparency and Fairness in Pricing:The DMA requires gatekeepers to provide transparent and comparable pricing information to users. This will likely force Booking.com to disclose all fees and charges associated with bookings, including hidden fees, and present them in a clear and easily understandable format.
- Restrictions on Self-Preferencing:The DMA prohibits gatekeepers from favoring their own products or services over those of competitors. This means Booking.com will have to ensure that it does not prioritize its own hotel listings over those of competitors on its platform, creating a more level playing field for smaller hotels and accommodation providers.
The DMA’s Potential Influence on the Future Development of the Online Travel Industry
The DMA’s impact on Booking.com and other online travel platforms will have a ripple effect across the industry, leading to several potential changes:
- Emergence of New Players:The DMA’s emphasis on interoperability and fairness could create opportunities for smaller online travel platforms and niche travel providers to compete more effectively with established giants like Booking.com. This could lead to a more fragmented market with a greater diversity of offerings.
- Increased Consumer Choice and Empowerment:The DMA’s focus on user rights and data control will empower consumers to make more informed travel decisions. This could lead to increased competition on price, quality, and customer service, as online travel platforms strive to attract and retain customers.
- Shifting Power Dynamics:The DMA’s regulations could lead to a shift in power dynamics within the online travel industry. Smaller hotels and accommodation providers may gain more bargaining power, as they will be able to leverage the DMA’s provisions to access a wider audience and negotiate more favorable terms with online travel platforms.
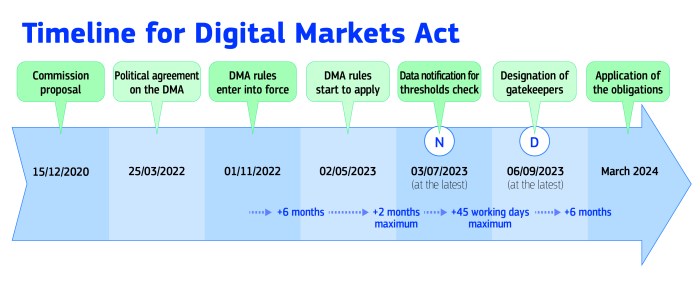
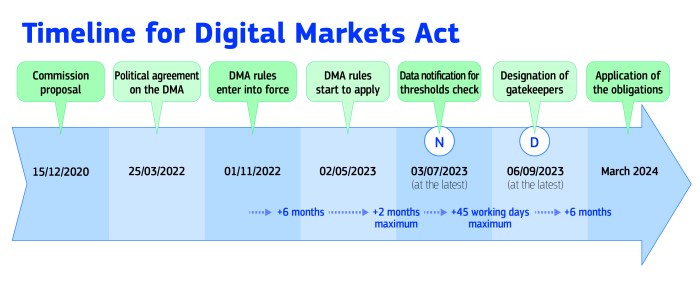
Potential Timeline of Events Related to the DMA’s Implementation and Impact on the Online Travel Industry
The DMA’s implementation and its impact on the online travel industry will likely unfold over several years, with various milestones and key events:
- 2023:The DMA is expected to come into full effect, with gatekeepers like Booking.com required to comply with its provisions. This will likely trigger initial changes in Booking.com’s business practices and user experience.
- 2024-2025:The DMA’s impact on competition and innovation within the online travel industry will become more evident. New players may emerge, and existing platforms may adapt their strategies to comply with the regulations.
- 2026-2027:The DMA’s long-term impact on the online travel industry will become clearer. The industry may see a more fragmented market with greater consumer choice and potentially a more balanced power dynamic between online travel platforms and accommodation providers.