Analysis europe quantum sector poised massive growth – Analysis: Europe’s Quantum Sector Poised for Massive Growth – The European quantum landscape is buzzing with activity, and for good reason. Quantum computing, a field that harnesses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations, is on the cusp of revolutionizing industries from healthcare to finance.
Europe, with its robust research institutions and government initiatives, is strategically positioned to be a global leader in this burgeoning field.
This analysis delves into the key drivers of growth in the European quantum sector, highlighting the technological advancements, potential applications, and the role of investments in shaping the future of this transformative technology. We’ll explore the landscape of key players, including companies, research institutions, and startups, and examine how their contributions are fueling innovation and progress.
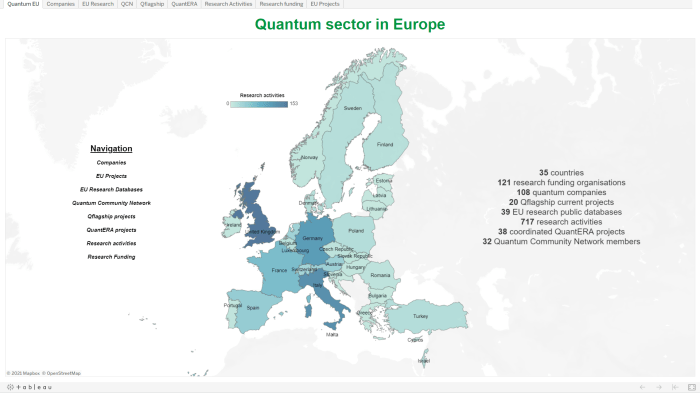
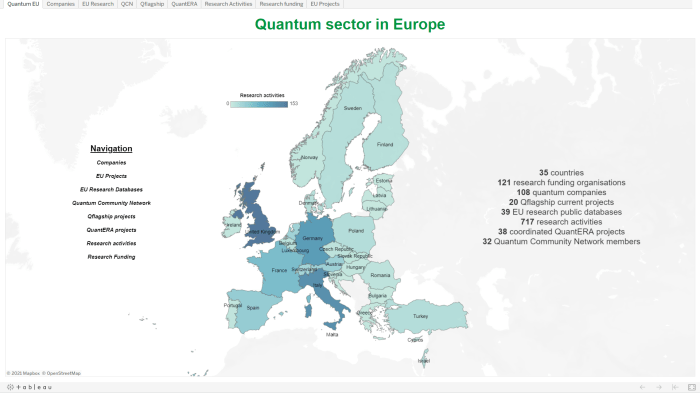
The European Quantum Landscape

Europe is rapidly emerging as a global leader in the quantum technology race. The region boasts a rich history of scientific innovation, a thriving ecosystem of research institutions and startups, and a growing number of public and private investments dedicated to developing and deploying quantum technologies.
Key Players and Research Institutions
The European quantum landscape is characterized by a diverse array of key players, including leading research institutions, technology companies, and startups.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of cant remember good day work quit that is effective.
- Research Institutions:Prominent research institutions such as the University of Oxford, the University of Copenhagen, the Technical University of Munich, and the University of Delft play a crucial role in driving fundamental research and developing new quantum technologies. These institutions house world-renowned physicists and engineers who are at the forefront of quantum computing, quantum communication, and quantum sensing.
- Technology Companies:Companies like Airbus, Thales, and Bosch are actively exploring the potential of quantum technologies to revolutionize their respective industries. Airbus, for instance, is researching quantum computing applications for optimizing aircraft design and operations, while Thales is developing quantum-secure communication systems for critical infrastructure.
- Startups:Europe is witnessing a surge in the number of quantum startups. Companies like IQM, Pasqal, and Quandela are developing innovative quantum computing platforms and solutions, targeting various applications ranging from drug discovery to materials science.
Major Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the significant progress made, the European quantum sector faces several challenges and opportunities that will shape its future trajectory.
- Talent Acquisition and Development:The quantum field requires a highly skilled workforce with specialized expertise in quantum physics, computer science, and engineering. Europe needs to invest in training and education programs to cultivate a pipeline of quantum talent.
- Funding and Investment:Securing adequate funding for research, development, and commercialization of quantum technologies is crucial for Europe’s competitiveness. Governments and private investors need to collaborate to bridge the funding gap and support the growth of the quantum ecosystem.
- Collaboration and Standardization:Fostering collaboration between research institutions, companies, and policymakers is essential to accelerate innovation and ensure the development of interoperable quantum technologies. Establishing industry standards and guidelines will also be vital for the widespread adoption of quantum technologies.
- Ethical and Societal Considerations:The development and deployment of quantum technologies raise ethical and societal concerns that need to be addressed proactively. These include issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and the potential impact on employment.
Quantum Strategies and Investments Across Europe
Different European countries have adopted distinct strategies and investment levels in quantum technologies, reflecting their national priorities and research strengths.
- Germany:Germany has established a comprehensive quantum strategy, investing heavily in research and development through initiatives like the “Quantum Flagship” and the “National Quantum Technologies Roadmap.”
- France:France has a strong focus on quantum computing and cryptography, with initiatives like the “National Quantum Technology Plan” and the “Quantum National Research Agency.”
- United Kingdom:The UK has a thriving quantum ecosystem, with a focus on quantum computing, sensing, and communication. Initiatives like the “National Quantum Technologies Programme” and the “Quantum Technologies Hubs” have played a significant role in driving innovation.
- Netherlands:The Netherlands is a leader in quantum computing, with institutions like QuTech and Delft University of Technology contributing to the development of cutting-edge quantum technologies.
Drivers of Growth in the European Quantum Sector

The European quantum sector is poised for rapid growth, fueled by a confluence of technological advancements, burgeoning applications, and supportive government policies. This dynamic environment is fostering innovation and attracting significant investment, propelling the region towards a quantum-powered future.
Technological Advancements
The European quantum sector is witnessing remarkable advancements in various areas, including:
- Superconducting Qubits:These qubits, based on superconducting circuits, are highly coherent and have achieved impressive performance metrics. European researchers have made significant strides in developing and scaling up these qubits, paving the way for larger and more complex quantum computers.
- Trapped Ions:This technology uses lasers to manipulate individual ions, offering high-fidelity operations and long coherence times.
European research groups are leading the way in developing ion-trap quantum computers, focusing on applications in quantum simulation and precision measurement.
- Photonic Quantum Technologies:Photonic qubits, encoded in the properties of light, offer advantages in terms of scalability and potential for long-distance communication.
European researchers are exploring diverse photonic quantum technologies, including quantum key distribution and quantum computing.
These technological breakthroughs are driving the development of more powerful and versatile quantum computers, enabling the exploration of previously intractable problems and unlocking new possibilities across diverse industries.
Applications Across Industries
The potential applications of quantum technologies extend across a wide range of industries, with the potential to revolutionize various sectors.
- Healthcare:Quantum computing can accelerate drug discovery and development, enabling researchers to simulate complex molecular interactions and identify potential drug candidates more efficiently. Quantum sensors can also revolutionize medical imaging, providing more precise and detailed information about the human body.
- Finance:Quantum algorithms can enhance risk management, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection. They can also accelerate financial modeling and analysis, enabling more informed decision-making in complex financial markets.
- Materials Science:Quantum simulations can help researchers design and discover new materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity, strength, or catalytic activity.
This could lead to breakthroughs in energy storage, solar energy, and other critical areas.
The transformative potential of quantum technologies across these industries is driving significant investment and research efforts in Europe, as stakeholders recognize the immense opportunities for economic growth and societal benefit.
Government Policies and Regulations
European governments are playing a crucial role in shaping the development and adoption of quantum technologies by implementing targeted policies and regulations.
- Funding Programs:European governments are allocating substantial resources to support quantum research and development through dedicated funding programs. The European Union’s Quantum Flagship initiative, for example, is investing over €1 billion in quantum technologies over a decade.
- Research Collaboration:Governments are fostering collaboration among researchers and industry players through joint research initiatives, networking events, and technology transfer programs.
This collaborative approach is accelerating innovation and promoting the development of a vibrant quantum ecosystem in Europe.
- Standards and Regulations:Governments are working to establish standards and regulations for quantum technologies, ensuring interoperability and promoting responsible development. This framework is crucial for building trust and confidence in the emerging quantum industry.
These policies are creating a favorable environment for quantum innovation in Europe, attracting talent, fostering investment, and paving the way for widespread adoption of quantum technologies.
Key Players and Investments in the European Quantum Sector
The European quantum sector is home to a vibrant ecosystem of companies, research institutions, and startups pushing the boundaries of quantum technology. This section delves into the key players driving innovation and the investment landscape fueling the sector’s growth.
Major Players in the European Quantum Sector
The European quantum landscape is diverse, encompassing companies, research institutions, and startups specializing in various quantum technologies. Here’s a glimpse into some of the key players shaping the sector:
| Company/Institution | Focus Area | Funding Sources | Notable Achievements |
|---|---|---|---|
| QuTech (Netherlands) | Quantum computing, quantum communication, quantum sensing | Public funding (Dutch government, EU), private investment | Developed the world’s first quantum computer based on spin qubits, established a quantum internet testbed |
| Atos (France) | Quantum computing, cybersecurity, high-performance computing | Private investment, public funding | Launched a quantum computing platform, Atos Quantum Learning Machine, partnered with various research institutions |
| IQM Quantum Computers (Finland) | Superconducting quantum computers | Private investment, EU grants | Built Europe’s first commercial superconducting quantum computer, established partnerships with industry players |
| Oxford Quantum Circuits (UK) | Superconducting quantum computers | Private investment, public funding | Developed a 16-qubit superconducting quantum processor, established partnerships with industry players |
| Pasqal (France) | Neutral-atom quantum computers | Private investment, public funding | Developed a quantum computer based on neutral atoms, secured funding from major investors |
| Multiverse Computing (Spain) | Quantum software, algorithms, and applications | Private investment, public funding | Developed quantum algorithms for various industries, established partnerships with research institutions |
| Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Solid State Physics (Germany) | Quantum computing, quantum communication, quantum sensing | Public funding | Led research and development in quantum technologies, established partnerships with industry players |
| University of Innsbruck (Austria) | Trapped-ion quantum computers | Public funding | Developed a trapped-ion quantum computer, established a leading research group in quantum technologies |
Venture Capital and Public Funding
Venture capital and public funding play crucial roles in driving innovation and growth in the European quantum sector. Venture capitalists provide critical funding for startups developing new technologies, while public funding supports research institutions and helps bridge the gap between research and commercialization.
“Venture capital investment in quantum technologies is rapidly increasing, driven by the potential for disruptive innovation across various sectors.”
McKinsey & Company
Timeline of Investments and Milestones
The European quantum sector has witnessed significant investments and milestones, highlighting its growing momentum. Here’s a timeline showcasing key developments:
- 2016:The European Union launched the Quantum Technologies Flagship program, a €1 billion initiative to support research and innovation in quantum technologies.
- 2018:QuTech secured €130 million in funding from the Dutch government to build a quantum computer.
- 2019:Atos launched its Atos Quantum Learning Machine, a quantum simulation platform.
- 2020:IQM Quantum Computers raised €11.5 million in Series A funding.
- 2021:Oxford Quantum Circuits secured £30 million in Series A funding.
- 2022:Pasqal raised €100 million in Series B funding.
Future Outlook for the European Quantum Sector: Analysis Europe Quantum Sector Poised Massive Growth
The European quantum sector is poised for substantial growth, with the potential to revolutionize various industries and aspects of society. The widespread adoption of quantum technologies will likely have a significant impact on the European economy and society, creating new opportunities and challenges.
Economic Impact and Societal Transformation
The development and application of quantum technologies are expected to have a profound impact on the European economy. The sector is projected to create new industries, generate significant economic activity, and contribute to the overall growth of the European Union.
- Enhanced competitiveness:Quantum technologies are expected to provide European businesses with a competitive edge in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, materials science, and manufacturing. For instance, quantum computing could enable the development of new drugs and materials, while quantum communication could enhance cybersecurity and financial transactions.
- Job creation:The rapid growth of the quantum sector is anticipated to create numerous high-skilled jobs in research, development, engineering, and manufacturing. This will contribute to the overall employment landscape and attract talent to the European Union.
- Improved societal well-being:Quantum technologies have the potential to improve societal well-being by addressing critical challenges in healthcare, energy, and environmental protection. For example, quantum sensors could enable early disease detection, while quantum computing could optimize energy grids and facilitate the development of sustainable solutions.
Challenges and Opportunities, Analysis europe quantum sector poised massive growth
While the future of the European quantum sector holds immense promise, several challenges must be addressed to ensure its successful development and commercialization.
- Research and development investment:Maintaining a high level of investment in quantum research and development is crucial for Europe to remain competitive in the global race. Continued funding for research projects, infrastructure development, and talent acquisition is essential to drive innovation and technological advancements.
- Bridging the gap between research and industry:The successful commercialization of quantum technologies requires a seamless transition from research to industry. Fostering collaboration between academia, research institutions, and businesses is critical to bridge this gap and facilitate the development of practical applications.
- Building a skilled workforce:The rapid growth of the quantum sector necessitates a skilled workforce capable of developing and implementing quantum technologies. Education and training programs at various levels are essential to equip individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in this emerging field.
- Addressing ethical and societal implications:As quantum technologies advance, it is essential to consider their ethical and societal implications. Addressing concerns related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and potential job displacement will be crucial to ensure responsible and equitable development and deployment of these technologies.
Vision for the Future
The European quantum sector has the potential to become a global leader in this rapidly evolving field. To achieve this vision, several key priorities must be addressed.
- Continued investment in research and development:Sustained investment in research and development is essential to maintain Europe’s leading position in quantum technologies. This includes funding for basic research, applied research, and the development of innovative applications.
- Fostering collaboration and innovation:Creating an ecosystem that encourages collaboration between academia, research institutions, and industry is crucial for driving innovation and accelerating the development of quantum technologies.
- Developing a robust regulatory framework:Establishing a clear and comprehensive regulatory framework for quantum technologies will ensure their responsible development and deployment. This will address concerns related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and potential societal impacts.
- Promoting public awareness and engagement:Raising public awareness about quantum technologies and their potential benefits is essential for fostering societal acceptance and support for their development and deployment. Engaging the public in discussions about the ethical and societal implications of these technologies will ensure their responsible use.