Ai powered deep medicine could transform healthcare in the nhs – AI-Powered Deep Medicine: Transforming NHS Healthcare sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Imagine a future where personalized medicine is the norm, where AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to predict and prevent diseases, and where treatment plans are tailored to individual needs.
This is the promise of AI-powered deep medicine, a transformative force poised to revolutionize healthcare within the NHS.
The potential applications of AI in deep medicine are vast and diverse. From diagnosing diseases with greater accuracy to developing personalized treatment plans, AI algorithms are already making significant strides in improving patient care. By analyzing medical images, genetic data, and patient records, AI can identify patterns and insights that may be missed by human doctors.
This data-driven approach can lead to earlier disease detection, more effective treatments, and ultimately, better patient outcomes.
The Promise of AI-Powered Deep Medicine
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into healthcare, specifically in the realm of deep medicine, holds immense promise for revolutionizing patient care within the National Health Service (NHS). Deep medicine, fueled by AI, leverages sophisticated algorithms and machine learning to analyze vast amounts of data, providing deeper insights into individual patients’ health conditions and enabling more personalized and effective treatments.
AI Applications in Deep Medicine
AI-powered deep medicine is poised to transform various aspects of healthcare delivery. These applications could significantly impact patient care by enhancing diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease prevention.
- Early Disease Detection and Diagnosis:AI algorithms can analyze medical images, such as X-rays, mammograms, and CT scans, with remarkable accuracy, enabling early detection of diseases like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. This early detection can lead to more effective treatment options and improved patient outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Planning:AI can analyze patient data, including medical history, genetic information, and lifestyle factors, to predict individual responses to different treatments. This allows for the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs, maximizing treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- Drug Discovery and Development:AI can accelerate the process of drug discovery by analyzing vast datasets of chemical compounds and identifying potential drug candidates. This can lead to the development of new and more effective treatments for a wide range of diseases.
- Precision Medicine:AI can be used to identify patients who are most likely to benefit from specific treatments based on their genetic makeup and other factors. This allows for more targeted and effective interventions, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Improving Diagnosis, Treatment Planning, and Disease Prevention
AI-powered deep medicine can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease prevention.
- Diagnosis:AI algorithms can analyze medical images, lab results, and patient data to identify patterns and anomalies that may be missed by human clinicians. This can lead to faster and more accurate diagnoses, enabling timely interventions and improving patient outcomes.
- Treatment Planning:AI can analyze patient data to predict the effectiveness of different treatment options and personalize treatment plans to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects. This can lead to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
- Disease Prevention:AI can be used to identify individuals at high risk of developing certain diseases based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and other data. This allows for early interventions and lifestyle modifications to prevent or delay the onset of disease.
Key Applications of AI in Deep Medicine
The potential of AI in deep medicine is vast, with applications across various aspects of healthcare. These applications leverage AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions, ultimately leading to improved patient care.
AI-Powered Diagnosis and Prognosis
AI algorithms can analyze medical images, patient records, and genetic data to identify potential diseases and predict their progression. This can lead to earlier detection, more accurate diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans.
- Application:Image Analysis for Disease Detection
- Description:AI algorithms can analyze medical images like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs to detect abnormalities that may be missed by human eyes. For example, AI can assist in identifying tumors, detecting early signs of pneumonia, and analyzing retinal images for diabetic retinopathy.
- Benefits:Improved accuracy and speed of diagnosis, early detection of diseases, and potentially reduced misdiagnosis rates.
- Challenges:Ensuring data quality and privacy, addressing ethical concerns related to bias in algorithms, and ensuring proper interpretation of AI results by healthcare professionals.
AI-Driven Drug Discovery and Development
AI can accelerate drug discovery and development by analyzing vast datasets of molecular structures, identifying potential drug candidates, and optimizing their properties.
- Application:Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery
- Description:AI algorithms can analyze massive databases of chemical compounds to identify potential drug candidates that could interact with specific target proteins involved in diseases. This virtual screening process significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional drug discovery methods.
You also can investigate more thoroughly about the digital markets act will change how you use apps to enhance your awareness in the field of the digital markets act will change how you use apps.
- Benefits:Faster and more efficient drug discovery, potentially leading to new treatments for currently untreatable diseases.
- Challenges:Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AI predictions, validating drug candidates through clinical trials, and addressing ethical concerns related to drug development.
AI-Assisted Treatment Planning and Optimization
AI can analyze patient data to personalize treatment plans, optimize drug dosages, and predict treatment outcomes. This can lead to more effective and tailored care.
- Application:Personalized Cancer Treatment Planning
- Description:AI algorithms can analyze a patient’s tumor characteristics, genetic profile, and other factors to predict the best treatment options, including radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or surgery. This personalized approach can improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects.
- Benefits:Improved treatment effectiveness, reduced side effects, and potentially longer survival rates for cancer patients.
- Challenges:Ensuring the ethical use of AI in treatment planning, addressing concerns about data privacy, and ensuring the transparency and explainability of AI algorithms.
AI-Enabled Patient Monitoring and Management
AI can analyze patient data from wearable devices, sensors, and electronic health records to identify potential health risks, predict disease progression, and provide timely interventions.
- Application:Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Diseases
- Description:AI algorithms can analyze data from wearable devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, to monitor patients with chronic diseases like diabetes, heart failure, and asthma. This data can provide early warning signs of health deterioration and allow for timely interventions.
- Benefits:Improved patient outcomes, reduced hospital readmissions, and potentially lower healthcare costs.
- Challenges:Ensuring data privacy and security, addressing ethical concerns related to data collection and usage, and integrating AI-powered monitoring systems with existing healthcare infrastructure.
Benefits for Patients and the NHS
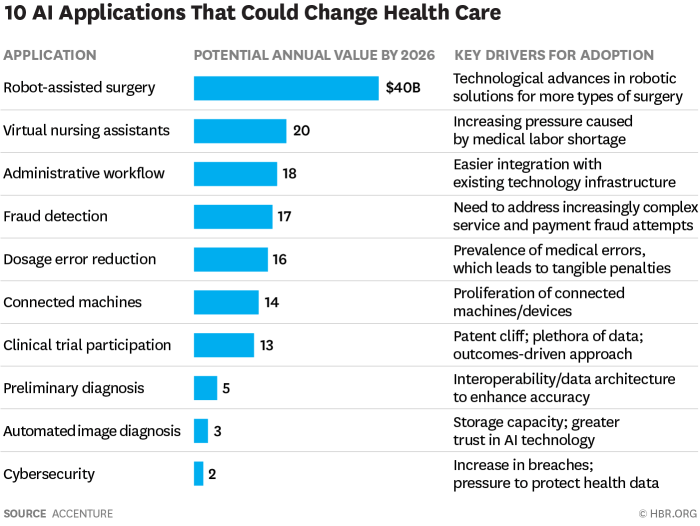
The potential of AI-powered deep medicine to revolutionize healthcare is undeniable, with profound implications for both patients and the NHS. This transformative technology holds the promise of improving diagnosis, treatment, and overall healthcare outcomes.
Improved Accuracy of Diagnoses
AI algorithms, trained on vast datasets of medical records and images, can analyze patient data with unparalleled precision, leading to more accurate diagnoses. This increased accuracy is particularly valuable in complex cases where human interpretation might be limited. For example, AI can assist radiologists in identifying subtle abnormalities in medical images, leading to earlier detection and more effective treatment.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI can tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, medical history, and lifestyle. This personalized approach can improve treatment effectiveness and reduce the risk of adverse side effects. For instance, AI can identify patients who are most likely to respond to specific medications, enabling doctors to prescribe the most effective treatments for each individual.
Early Disease Detection
AI algorithms can analyze patient data to identify early signs of disease, even before symptoms manifest. This proactive approach can lead to earlier intervention, improving treatment outcomes and potentially preventing the progression of serious conditions. For example, AI can analyze retinal scans to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy, allowing for timely treatment and reducing the risk of vision loss.
Reduced Waiting Times
By automating routine tasks and streamlining administrative processes, AI can help reduce waiting times for patients. For example, AI-powered chatbots can handle patient inquiries, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on more complex tasks. Additionally, AI can help optimize appointment scheduling, ensuring that patients are seen in a timely manner.
Enhanced Efficiency and Resource Allocation
AI can help the NHS optimize resource allocation by identifying areas where resources are being underutilized or overutilized. For example, AI can analyze data on patient admissions and discharges to predict future demand for hospital beds, allowing for more efficient resource allocation.
Improved Patient Satisfaction
By providing personalized care and reducing waiting times, AI-powered deep medicine can lead to improved patient satisfaction. Patients are more likely to feel confident in their care when they know that their treatment plan is tailored to their individual needs and that they are receiving timely and efficient care.
Lower Healthcare Costs
AI can help reduce healthcare costs by improving efficiency, preventing unnecessary treatments, and detecting diseases early. For example, AI can identify patients who are at risk of developing chronic conditions, allowing for early intervention and potentially preventing the need for more expensive treatments later.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the potential of AI-powered deep medicine in the NHS is vast, its implementation faces significant challenges, particularly regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and ethical considerations. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring responsible and equitable adoption of this transformative technology.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The use of AI in deep medicine relies heavily on vast amounts of patient data, including sensitive information like medical history, genetic data, and personal details. This raises concerns about data privacy and security.
- Data breaches:The collection, storage, and processing of sensitive patient data require robust security measures to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. A breach could compromise patient confidentiality and potentially lead to identity theft or misuse of medical information.
- Data misuse:There are concerns about how patient data might be used for purposes other than intended, such as for commercial gain or profiling without consent. Clear guidelines and regulations are essential to ensure data is used ethically and responsibly.
- Data ownership:Questions arise regarding who owns the data generated through AI-powered deep medicine, especially when it involves data from multiple sources. Clear ownership rights need to be established to prevent exploitation or misuse.
Bias in AI Algorithms, Ai powered deep medicine could transform healthcare in the nhs
AI algorithms are trained on vast datasets, and if these datasets contain biases, the algorithms may perpetuate and even amplify these biases in their outputs. This is a significant concern in healthcare, where biased AI could lead to unfair or discriminatory treatment of patients.
- Data bias:If the training data reflects historical biases, such as underrepresentation of certain demographic groups in medical research, the AI model may learn and perpetuate these biases, leading to inaccurate diagnoses or treatment recommendations.
- Algorithmic bias:Even if the training data is diverse, biases can arise from the design of the algorithm itself. This could lead to the model unfairly favoring certain patient groups over others.
Ethical Considerations Surrounding the Use of AI in Healthcare
The use of AI in healthcare raises numerous ethical considerations, including:
- Transparency and explainability:AI models can be complex and difficult to understand. This lack of transparency can make it challenging to explain the rationale behind their decisions, which is crucial for patient trust and accountability.
- Autonomy and patient consent:Patients need to be fully informed about the use of AI in their care and have the right to choose whether or not to participate. Clear consent processes and safeguards are essential.
- Responsibility and liability:Determining who is responsible when AI-powered deep medicine leads to an adverse outcome is a complex issue. Clear guidelines and frameworks are needed to address liability and ensure patient safety.
- Access and equity:AI-powered deep medicine has the potential to improve healthcare access and equity. However, there are concerns about the potential for exacerbating existing inequalities if the technology is not accessible to all patients, particularly those from disadvantaged communities.
The Future of AI in Deep Medicine: Ai Powered Deep Medicine Could Transform Healthcare In The Nhs

The potential of AI in deep medicine is vast, promising a future where healthcare is personalized, predictive, and proactive. As AI technologies continue to evolve, their impact on the NHS and the healthcare landscape will be profound, leading to a paradigm shift in how we approach health and disease.
A Timeline of Advancements
The future of AI in deep medicine is a journey marked by continuous advancements and breakthroughs. Here’s a timeline outlining key milestones and potential developments:
- Near Future (2023-2028):
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy:AI algorithms will become even more sophisticated in analyzing medical images, lab results, and patient data, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. This will enable early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
For example, AI-powered tools are already being used to detect breast cancer in mammograms with higher accuracy than human radiologists.
- Personalized Treatment Plans:AI will play a crucial role in tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, including genetics, lifestyle, and medical history. This will lead to more effective therapies and reduced side effects. For instance, AI algorithms can predict which patients are most likely to respond to specific cancer treatments, allowing for personalized therapies.
- Improved Drug Discovery:AI will accelerate drug discovery and development by analyzing vast datasets of chemical compounds and biological interactions. This will lead to the creation of new drugs and therapies for currently incurable diseases. For example, AI is already being used to identify potential drug candidates for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy:AI algorithms will become even more sophisticated in analyzing medical images, lab results, and patient data, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses. This will enable early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Mid-Term Future (2029-2035):
- Predictive Healthcare:AI will be able to predict the risk of developing certain diseases based on individual patient data, allowing for proactive interventions and prevention strategies. For example, AI algorithms can predict the risk of heart attacks or strokes based on a patient’s lifestyle, genetic factors, and medical history, enabling early intervention and lifestyle modifications.
- Remote Patient Monitoring:AI-powered devices will continuously monitor patient health remotely, providing real-time data to healthcare professionals. This will allow for early detection of health issues and prompt intervention, improving patient outcomes and reducing hospital admissions. For instance, wearable devices can monitor heart rate, blood pressure, and other vital signs, alerting healthcare providers to potential problems.
- AI-Assisted Surgery:AI will assist surgeons in performing complex procedures with greater precision and accuracy, leading to faster recovery times and reduced complications. For example, AI-powered robotic arms are already being used in minimally invasive surgeries, enabling surgeons to perform delicate procedures with greater control and precision.
- Long-Term Future (2036 onwards):
- Integrated Healthcare Systems:AI will seamlessly integrate into healthcare systems, creating a holistic and personalized approach to patient care. This will involve the use of AI-powered virtual assistants, chatbots, and other technologies to provide patients with 24/7 support and guidance. For example, AI-powered chatbots can answer patient questions, schedule appointments, and provide personalized health advice.
- Breakthroughs in Disease Understanding:AI will revolutionize our understanding of diseases by analyzing massive datasets of genomic, proteomic, and other biological data. This will lead to the development of new diagnostic tools, targeted therapies, and preventative measures. For example, AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets of genomic data to identify genetic mutations associated with specific diseases, leading to personalized therapies and preventative strategies.
- Human-AI Collaboration:The future of healthcare will involve a close collaboration between human doctors and AI systems. AI will enhance the capabilities of healthcare professionals, allowing them to make more informed decisions and provide more personalized care. For example, AI systems can analyze patient data and suggest treatment options, while doctors can leverage their clinical expertise and human judgment to make final decisions.





