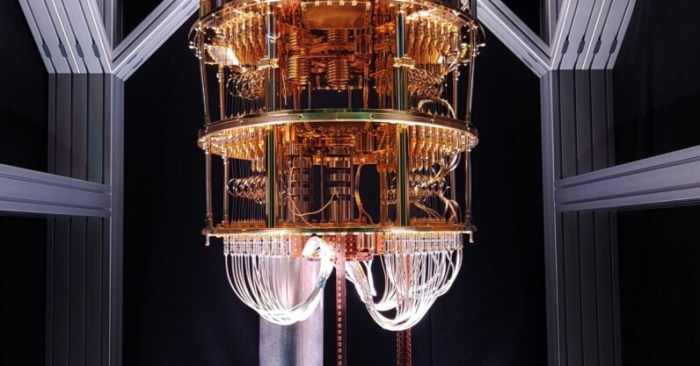
Finland quantum computing hardware ecosystem – Finland’s quantum computing hardware ecosystem is emerging as a powerhouse in the global race for technological dominance. With its strong research base, innovative companies, and government support, Finland is poised to make significant contributions to the development of this transformative technology.
The country’s commitment to quantum computing is evident in the presence of world-class research institutions like Aalto University and VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, which are actively exploring cutting-edge hardware technologies. These institutions are collaborating with private companies like IQM Quantum Computers and Algorithmiq, who are developing and commercializing quantum computers based on superconducting qubits and trapped ions, respectively.
The synergy between academia and industry is fostering a vibrant ecosystem that is attracting talent and investment from around the world.
Introduction: Finland Quantum Computing Hardware Ecosystem
Finland has emerged as a significant player in the global quantum computing landscape, with a growing ecosystem of research institutions, startups, and established companies actively involved in developing quantum computing hardware. The country’s focus on quantum computing hardware is driven by its strong foundation in scientific research, engineering expertise, and a commitment to technological innovation.The development of quantum computing hardware in Finland holds immense potential to contribute to the country’s technological advancement, fostering economic growth and strengthening its position as a global leader in this emerging field.
The Role of Quantum Computing Hardware in Finland’s Technological Advancement
The development of quantum computing hardware in Finland is crucial for the country’s technological advancement. This is due to the potential of quantum computing to revolutionize various industries, including:
- Medicine:Quantum computers can accelerate drug discovery and development by simulating complex molecular interactions, leading to more effective treatments for diseases.
- Materials Science:Quantum simulations can help design new materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity or strength, driving innovation in fields like energy and manufacturing.
- Finance:Quantum algorithms can optimize financial portfolios and risk management strategies, leading to improved investment decisions and increased efficiency in the financial sector.
- Artificial Intelligence:Quantum computing can enhance machine learning algorithms, enabling the development of more powerful and efficient AI systems with applications in areas like autonomous driving and natural language processing.
By investing in quantum computing hardware, Finland can position itself at the forefront of these technological advancements, attracting global talent and investment, and creating new opportunities for economic growth.
Find out further about the benefits of esa solar orbiter sports solar wind source that can provide significant benefits.
Key Players and Organizations
Finland boasts a thriving quantum computing hardware ecosystem, driven by a combination of academic research, industry innovation, and government support. Several prominent companies and research institutions are actively involved in developing quantum computing hardware, contributing to the advancement of this transformative technology.
Key Players in Finland’s Quantum Computing Hardware Ecosystem
| Organization | Specialization | Notable Projects |
|---|---|---|
| IQM Quantum Computers | Superconducting qubit-based quantum computers | IQM’s first commercial quantum computer, installed at the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, is used for research and development. They are also developing a quantum computer for the European Union’s flagship quantum technology project, “Quantum Flagship.” |
| VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland | Quantum computing hardware and software development, research, and applications | VTT has been a pioneer in quantum computing research, developing quantum simulators and contributing to the development of quantum algorithms. They have also collaborated with IQM to build Finland’s first commercial quantum computer. |
| Aalto University | Quantum computing research, including superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and photonic qubits | Aalto University researchers have made significant contributions to the development of quantum computing hardware, particularly in superconducting qubits. They are also involved in developing quantum algorithms and applications. |
| University of Helsinki | Quantum computing research, including quantum communication and quantum information theory | The University of Helsinki has a strong research program in quantum computing, focusing on areas such as quantum cryptography and quantum simulation. They are also involved in the development of quantum algorithms. |
Hardware Technologies and Research
Finland’s quantum computing landscape is characterized by a vibrant research scene exploring various hardware technologies, each with its own strengths and limitations. These endeavors aim to develop cutting-edge quantum computers capable of solving problems beyond the reach of classical computers.
Superconducting Qubits
Superconducting qubits are a leading contender in the race to build practical quantum computers. They leverage the unique properties of superconductors, materials that conduct electricity with zero resistance at extremely low temperatures.
- Quantum Computing Finland (QCF), a national research initiative, focuses on superconducting qubit development, aiming to build a 100-qubit processor by 2025. Their research explores various aspects of qubit design, fabrication, and control.
- Aalto University, a prominent research institution, has a strong track record in superconducting qubit technology. They are actively involved in developing new qubit designs and exploring advanced control techniques.
Superconducting qubits offer advantages like high coherence times and relatively easy scalability, making them a promising technology for building large-scale quantum computers. However, they require extremely low operating temperatures, typically near absolute zero, posing significant engineering challenges.
Trapped Ions, Finland quantum computing hardware ecosystem
Trapped ion quantum computers use individual atoms, known as ions, trapped and manipulated using electric fields. This approach offers high coherence times and the potential for long-range entanglement, making it suitable for specific quantum algorithms.
- University of Helsinkihas a research group dedicated to trapped ion quantum computing. They are investigating novel methods for controlling and manipulating trapped ions, aiming to build a high-fidelity quantum computer.
While trapped ion technology boasts high fidelity and long coherence times, scaling up to large numbers of qubits remains a significant challenge.
Other Emerging Technologies
Beyond superconducting qubits and trapped ions, other quantum computing hardware technologies are being explored in Finland. These include:
- Neutral Atoms: Researchers at the University of Helsinki are investigating the potential of neutral atoms for quantum computing. Neutral atoms offer advantages like long coherence times and the possibility of building large-scale systems.
- Photonic Quantum Computing: Researchers at VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland are exploring photonic quantum computing, which uses photons (light particles) as qubits. This approach offers potential advantages in terms of scalability and integration with existing optical technologies.
These emerging technologies are still in their early stages of development, but they hold promise for the future of quantum computing.
Government Initiatives and Funding
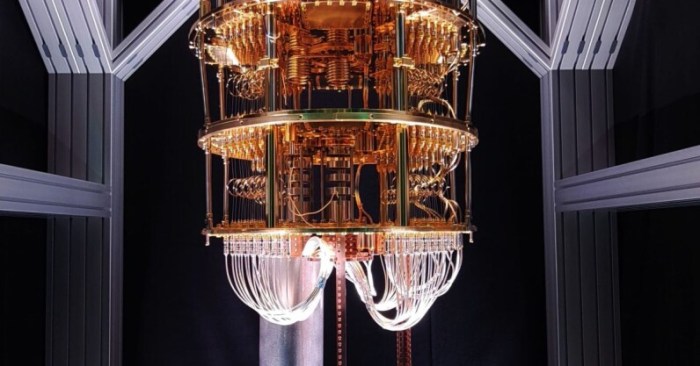
The Finnish government recognizes the strategic importance of quantum computing and has implemented several initiatives and funding programs to support the development of the national quantum computing hardware ecosystem. These initiatives aim to attract talent, foster innovation, and promote collaboration among researchers, businesses, and public institutions.
Funding Programs and Policies
The Finnish government has implemented several funding programs to support research and development in quantum computing hardware. These programs aim to provide financial assistance to universities, research institutes, and startups working on quantum computing technologies.
- The Academy of Finland: This national research funding agency supports research projects in quantum computing hardware through various funding schemes, including the Strategic Research Council, which focuses on funding research projects with significant societal impact. The Academy of Finland also supports the development of national research infrastructures, such as the Finnish Quantum Institute, which plays a crucial role in fostering research and innovation in quantum computing.
- Business Finland: This government agency supports businesses developing quantum computing hardware by providing funding for research and development projects, as well as for market entry and internationalization efforts. Business Finland also offers funding for collaboration projects between universities and businesses, promoting the transfer of research results into practical applications.
- The European Union’s Horizon Europe program: Finland actively participates in this research and innovation program, which provides funding for quantum computing research projects. Through Horizon Europe, Finnish researchers and businesses can collaborate with their European counterparts, contributing to the development of a strong European quantum computing ecosystem.
Impact on Ecosystem Growth
Government funding has played a significant role in the growth of Finland’s quantum computing hardware ecosystem. It has enabled the establishment of research centers, attracted international talent, and facilitated the development of new technologies.
- The Finnish Quantum Institute, established with support from the Academy of Finland, has become a hub for quantum computing research and development in Finland. The institute brings together researchers from various universities and research institutions, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Government funding has attracted international talentto Finland, contributing to the growth of the quantum computing workforce. For example, the Quantum Computing and Artificial Intelligence (QCAI) project, funded by the Academy of Finland, has attracted researchers from various countries, strengthening the Finnish research community in quantum computing.
- Funding programs have also supported the development of new technologies, such as the development of superconducting qubits by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland. This research has led to the creation of spin-off companies, further contributing to the growth of the ecosystem.
Effectiveness of Government Support
The government’s support for quantum computing hardware development has been effective in fostering innovation and building a strong ecosystem in Finland.
- The Finnish government’s commitment to funding research and developmenthas enabled the country to become a leader in quantum computing hardware. Finland’s expertise in superconducting qubit technology, for example, is recognized globally.
- The government’s focus on building a strong research infrastructure, such as the Finnish Quantum Institute, has facilitated collaboration and knowledge sharing, accelerating the pace of innovation.
- The government’s efforts to attract international talenthave contributed to the growth of a highly skilled workforce in quantum computing, further strengthening the ecosystem.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Finnish quantum computing hardware ecosystem, while promising, faces several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and development, paving the way for a thriving quantum technology sector in Finland.
Challenges
The Finnish quantum computing hardware ecosystem faces several challenges, including:
- Limited Funding and Investment:Despite government initiatives and funding, the overall investment in quantum computing hardware research and development in Finland remains relatively limited compared to other leading nations. This can hinder the pace of innovation and limit the scale of projects.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention:Attracting and retaining skilled professionals in quantum computing is a significant challenge. The field requires specialized expertise and a deep understanding of complex concepts. Finland needs to invest in education and training programs to develop a robust talent pool.
- Collaboration and Partnerships:Fostering strong collaborations between academia, industry, and government is crucial for accelerating progress. This involves creating a conducive environment for knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and joint research projects.
- Infrastructure Development:Building a robust infrastructure for quantum computing hardware development requires significant investment in specialized equipment, cleanroom facilities, and advanced computing resources. This infrastructure is essential for supporting research, prototyping, and scaling up technologies.
Opportunities
Despite the challenges, the Finnish quantum computing hardware ecosystem presents several opportunities for growth and development:
- Strong Research Base:Finland has a strong foundation in scientific research, particularly in areas related to quantum physics and materials science. This provides a solid base for developing quantum computing technologies.
- Government Support:The Finnish government has recognized the strategic importance of quantum technologies and has committed to supporting research and development initiatives. This includes funding programs, tax incentives, and regulatory frameworks.
- Industry Partnerships:Finnish companies are increasingly engaging in quantum computing research and development, partnering with universities and research institutions. These partnerships can drive innovation and commercialization of quantum technologies.
- Emerging Applications:Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including healthcare, materials science, finance, and cybersecurity. Identifying and developing specific applications in these sectors can create significant economic benefits.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Capitalizing on Opportunities
To overcome the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities, the following strategies can be implemented:
- Increase Funding and Investment:Governments and private investors should increase funding for quantum computing hardware research and development, supporting both fundamental research and applied projects.
- Develop Talent Pipeline:Investing in education and training programs at all levels, from undergraduate to postgraduate, is essential for developing a skilled workforce in quantum computing. This can include scholarships, research grants, and industry internships.
- Promote Collaboration:Encouraging collaboration between academia, industry, and government through joint research projects, technology transfer initiatives, and shared infrastructure can accelerate innovation and commercialization.
- Develop Infrastructure:Investing in specialized equipment, cleanroom facilities, and advanced computing resources is essential for supporting quantum computing hardware development. This can include building national research centers or partnering with existing infrastructure providers.
- Focus on Applications:Identifying and developing specific applications for quantum computing in key industries can drive adoption and create economic value. This can involve supporting startups, incubators, and industry consortia focused on quantum applications.
Future Outlook and Trends
The Finnish quantum computing hardware ecosystem is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years. Several factors, including ongoing research, government support, and the increasing demand for quantum computing solutions, will shape the future trajectory of this sector.
Emerging Trends and Advancements
The Finnish quantum computing hardware ecosystem is witnessing several emerging trends that will significantly impact its development and potential. These trends include:
- Development of Novel Quantum Hardware Platforms:Research institutions and companies in Finland are actively exploring and developing new quantum hardware platforms beyond superconducting qubits. These include trapped ion systems, photonic qubits, and topological qubits. These platforms offer unique advantages and could lead to more robust and scalable quantum computers.
- Integration of Quantum Computing with Existing Technologies:The integration of quantum computing with existing technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC), is gaining momentum. This integration will unlock new possibilities for tackling complex problems in various fields, including drug discovery, materials science, and financial modeling.
- Focus on Quantum Software and Algorithms:Alongside hardware development, there is a growing emphasis on developing quantum software and algorithms. This includes developing programming languages, libraries, and tools that enable users to effectively leverage quantum computers.
- Growing Importance of Quantum Education and Workforce Development:To foster a thriving quantum ecosystem, Finland is investing in education and workforce development programs. These programs aim to equip the next generation of scientists, engineers, and entrepreneurs with the skills and knowledge required to drive quantum innovation.
Impact on Finland’s Technological Landscape
The advancements in Finland’s quantum computing hardware ecosystem will have a profound impact on the country’s technological landscape. This impact can be observed in several areas:
- Strengthening Finland’s Position as a Global Technology Leader:Finland’s strong focus on quantum computing research and development will solidify its position as a global leader in technology innovation. The country’s expertise in quantum technologies will attract investment, talent, and partnerships, further boosting its technological prowess.
- Driving Economic Growth and Innovation:The development and application of quantum computing technologies will create new industries, stimulate economic growth, and foster innovation across various sectors. This includes healthcare, finance, manufacturing, and energy.
- Creating New Job Opportunities:The expansion of the quantum computing ecosystem will lead to the creation of new job opportunities in research, development, engineering, and software development. This will contribute to Finland’s economic prosperity and provide skilled employment opportunities for its workforce.