OpenCosmos launches satellite volcano wildlife monitoring is a groundbreaking initiative that’s poised to revolutionize our understanding of how volcanic eruptions impact wildlife. This new satellite, equipped with cutting-edge technology, will provide continuous, real-time data on volcanic activity, allowing scientists to monitor and predict eruptions with unprecedented accuracy.
The information gathered will be crucial for protecting endangered species and preserving delicate ecosystems in volcanic regions.
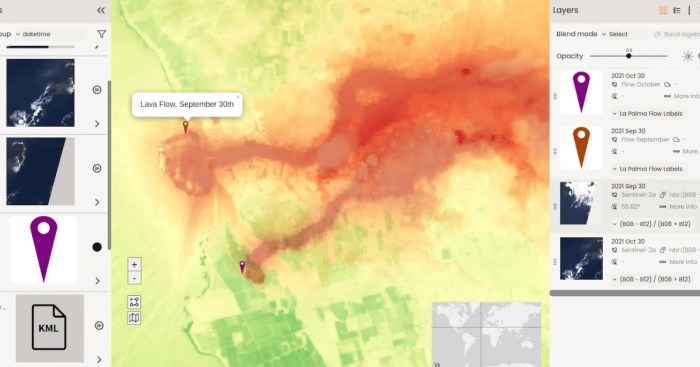
The satellite’s sophisticated sensors will collect data on various volcanic parameters, including heat signatures, gas emissions, and ground deformation. This information will be analyzed to identify potential eruptions and provide valuable insights into the eruption process itself. Furthermore, the satellite’s high-resolution imagery will enable scientists to track the movements of wildlife in volcanic areas, identifying those most at risk and allowing for the implementation of targeted conservation strategies.
OpenCosmos Satellite Launch: Opencosmos Launches Satellite Volcano Wildlife Monitoring
The launch of OpenCosmos’s new satellite marks a significant step forward in wildlife conservation and the understanding of volcanic activity. This dedicated satellite, equipped with cutting-edge technology, will provide valuable data to help protect vulnerable wildlife populations living near active volcanoes.
Satellite Features and Capabilities
This innovative satellite boasts a suite of advanced sensors designed to monitor volcanic activity and its impact on wildlife. The primary features include:
- High-Resolution Imaging:The satellite utilizes a powerful camera capable of capturing detailed images of volcanic landscapes, allowing researchers to track changes in volcanic activity, such as lava flows, ash plumes, and gas emissions.
- Thermal Imaging:Equipped with thermal sensors, the satellite can detect heat signatures, providing insights into volcanic activity and the presence of wildlife. This information is crucial for understanding the impact of volcanic eruptions on animal habitats and migration patterns.
- Multispectral Imaging:The satellite captures images across various wavelengths, enabling researchers to differentiate between various vegetation types and identify potential food sources for wildlife. This information is valuable for assessing the impact of volcanic activity on the local ecosystem.
- Data Transmission:The satellite transmits real-time data to ground stations, providing researchers with continuous updates on volcanic activity and wildlife movements. This enables timely interventions and proactive conservation efforts.
Mission Objectives and Expected Impact, Opencosmos launches satellite volcano wildlife monitoring
The OpenCosmos satellite mission aims to achieve several key objectives:
- Real-time Monitoring of Volcanic Activity:The satellite’s high-resolution imagery and thermal sensors provide constant monitoring of volcanic activity, enabling early warning systems for potential eruptions and helping to protect nearby communities.
- Understanding Wildlife Responses to Volcanic Activity:By tracking animal movements and habitat changes, the satellite provides valuable insights into how wildlife responds to volcanic events. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
- Protecting Endangered Species:The satellite’s data can help identify areas where endangered species are particularly vulnerable to volcanic activity. This information allows conservationists to focus their efforts on protecting these vulnerable populations.
- Supporting Sustainable Development:By providing real-time information on volcanic activity and its impact on the environment, the satellite supports sustainable development in volcanic regions, helping communities mitigate risks and make informed decisions.
Volcano Monitoring Technology
OpenCosmos’s satellite utilizes a suite of cutting-edge technologies to monitor volcanic activity and its impact on wildlife. These technologies enable real-time data collection, analysis, and communication, providing valuable insights into volcanic behavior and its potential consequences.
Data Collection Methods
The satellite employs various methods to collect data on volcanic eruptions and their impact on wildlife.
- Thermal Imaging:The satellite’s infrared sensors detect heat signatures, allowing it to monitor changes in volcanic temperatures. This data is crucial for identifying potential eruptions, tracking lava flows, and assessing the intensity of volcanic activity.
- Multispectral Imaging:By capturing images across multiple wavelengths of light, the satellite can distinguish different materials and land cover changes associated with volcanic eruptions. This data helps researchers analyze the composition of volcanic ash, track the spread of volcanic gases, and assess the impact on vegetation and wildlife habitats.
- Radar Interferometry:This technique uses radar signals to detect subtle changes in ground deformation, which can indicate the buildup of magma beneath the volcano. By analyzing these changes, scientists can predict the likelihood and potential scale of future eruptions.
- Gas Detection:The satellite can detect volcanic gases, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2), which are released during volcanic activity. This information provides insights into the intensity of eruptions, the potential hazards posed by volcanic gases, and the impact on air quality and wildlife health.
Wildlife Impact of Volcanic Eruptions

Volcanic eruptions, while awe-inspiring natural phenomena, can have profound and lasting impacts on wildlife. The severity of these impacts varies greatly depending on the eruption’s intensity, location, and the specific species affected.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of scottish startup found new way to harness power of waves.
Short-Term Impacts on Wildlife
The immediate effects of volcanic eruptions on wildlife are often catastrophic.
- Direct Mortality:Lava flows, pyroclastic flows, and ashfall can directly kill animals through burns, suffocation, or burial. For example, the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens in the United States killed thousands of animals, including deer, elk, and birds.
- Habitat Loss and Fragmentation:Volcanic eruptions can destroy habitats, leaving animals displaced and vulnerable. This can disrupt food chains and create competition for resources.
- Food and Water Contamination:Ashfall can contaminate food and water sources, making them unsafe for consumption. This can lead to starvation or poisoning, especially for herbivores and aquatic species.
Long-Term Impacts on Wildlife
The long-term consequences of volcanic eruptions on wildlife can be equally devastating.
- Ecosystem Alteration:Volcanic eruptions can alter the physical and chemical properties of the soil and water, leading to changes in plant communities and the overall ecosystem structure. This can affect the distribution and abundance of wildlife over time.
- Population Decline:The combined effects of habitat loss, food shortages, and increased competition can lead to significant population declines in affected species. This can disrupt the ecological balance and lead to the extinction of vulnerable species.
- Evolutionary Adaptations:Over time, some species may develop adaptations to survive in volcanic environments. For example, certain plants have evolved to tolerate high levels of sulfur dioxide, a gas released during volcanic eruptions.
Examples of Wildlife Impact
Volcanic eruptions have had a significant impact on wildlife throughout history.
- Mount Pinatubo, Philippines (1991):The eruption of Mount Pinatubo resulted in the deaths of thousands of birds and bats, and caused widespread habitat loss. The ashfall also contaminated water sources, leading to the decline of fish populations.
- Kilauea, Hawaii (2018):The eruption of Kilauea volcano destroyed hundreds of homes and forced the evacuation of thousands of people. It also resulted in the deaths of numerous birds and the displacement of endangered Hawaiian monk seals.
Conservation Applications
The data collected by the OpenCosmos satellite can be a powerful tool for supporting wildlife conservation efforts, especially in areas prone to volcanic eruptions. This data can help us understand how volcanic activity impacts wildlife and their habitats, allowing us to develop effective conservation strategies.
Monitoring Wildlife Movements
The satellite’s advanced imaging capabilities can track the movements of wildlife, both before and after volcanic eruptions. By analyzing satellite imagery, we can identify migration patterns, assess population densities, and monitor the distribution of endangered species. This information is crucial for understanding how wildlife responds to volcanic events and identifying areas where conservation efforts are most needed.
For example, the satellite can help us track the movements of elephants in the Virunga National Park in the Democratic Republic of Congo. This information can be used to predict their movements and minimize human-wildlife conflict during volcanic eruptions.
Future Implications
The successful deployment of satellites for volcano monitoring and wildlife impact assessment paves the way for a future where technology plays a vital role in safeguarding biodiversity and mitigating environmental risks. This technology has the potential to revolutionize how we understand and protect our planet.
Expanding Satellite Capabilities
The current satellite system, while impressive, can be further enhanced to monitor a wider range of environmental threats to wildlife. This involves integrating additional sensors and analyzing data from multiple sources.
- Advanced Imaging:Implementing hyperspectral imaging can provide detailed information about vegetation health, water quality, and the presence of pollutants, allowing for early detection of habitat degradation and potential threats to wildlife.
- Real-time Data Collection:Integrating sensors that can collect real-time data on factors like temperature, humidity, and wind patterns can provide valuable insights into how climate change is impacting wildlife populations and their habitats.
- AI-Powered Analysis:Utilizing artificial intelligence algorithms can automate the analysis of vast amounts of satellite data, enabling faster identification of patterns and anomalies related to wildlife populations and environmental changes.
Benefits and Challenges of Satellite Technology for Wildlife Conservation
The use of satellite technology for wildlife conservation presents both significant benefits and challenges that need to be addressed.