Musk might remove x twitter from eu disinformation law – Musk Might Remove Twitter from EU Disinformation Law, a move that could significantly impact the fight against misinformation within the European Union. This decision, if implemented, would see Twitter withdraw from the EU market, potentially leaving a void in the online landscape and raising questions about the future of tech regulation in the region.
The EU’s Disinformation Law, aimed at curbing the spread of false information online, has imposed specific regulations on platforms like Twitter. These regulations require platforms to take measures to address disinformation, including transparency about algorithms and advertising. Musk’s potential removal of Twitter from the EU could be driven by a desire to avoid complying with these regulations, which he might perceive as overly burdensome or restrictive.
The EU’s Disinformation Law
The EU’s Disinformation Law, officially known as the “Regulation on a coordinated approach to combatting disinformation,” is a landmark piece of legislation designed to address the spread of false and misleading information online. Its primary objective is to protect democratic processes and public discourse from the harmful effects of disinformation.
Enhance your insight with the methods and methods of social impact startups joining accelerator.
The law aims to create a more transparent and accountable online environment by imposing obligations on online platforms and empowering users to combat disinformation.
Responsibilities of Online Platforms
The law imposes specific obligations on online platforms, requiring them to take proactive measures to mitigate the spread of disinformation. These responsibilities include:
- Transparency:Platforms must disclose information about their algorithms, including how they rank content and promote certain posts. This transparency aims to increase user understanding of the factors influencing their online experience.
- Content Moderation:Platforms are obligated to develop and implement robust content moderation policies to remove or flag disinformation. This includes taking down false or misleading content, providing users with tools to report disinformation, and labeling potentially harmful content.
- Cooperation with Researchers:Platforms are required to collaborate with independent researchers to facilitate the study of disinformation and its impact. This collaboration aims to enhance the understanding of disinformation and its spread, ultimately leading to more effective countermeasures.
- User Empowerment:The law encourages platforms to provide users with tools and resources to identify and report disinformation. This includes offering educational materials about disinformation and providing mechanisms for users to flag suspicious content.
Examples of Law Application
The EU’s Disinformation Law has been applied in several instances, demonstrating its impact on online platforms and their responses to disinformation.
- Fact-checking Initiatives:The law has spurred platforms like Facebook and Twitter to partner with independent fact-checking organizations to verify the accuracy of information shared on their platforms. These partnerships have led to the labeling of false or misleading content, increasing user awareness of the potential for disinformation.
- Political Advertising Transparency:The law has pushed platforms to introduce more transparency regarding political advertising. Platforms are now required to disclose information about the sources of political ads, including who is paying for them and who they target. This transparency aims to combat the spread of misleading political messages and ensure greater accountability in online campaigning.
- Disinformation Campaigns:The law has been invoked in cases of coordinated disinformation campaigns aimed at influencing public opinion or manipulating elections. Platforms have been required to take down content associated with these campaigns and investigate their origins. These actions demonstrate the law’s potential to combat malicious actors seeking to undermine democratic processes.
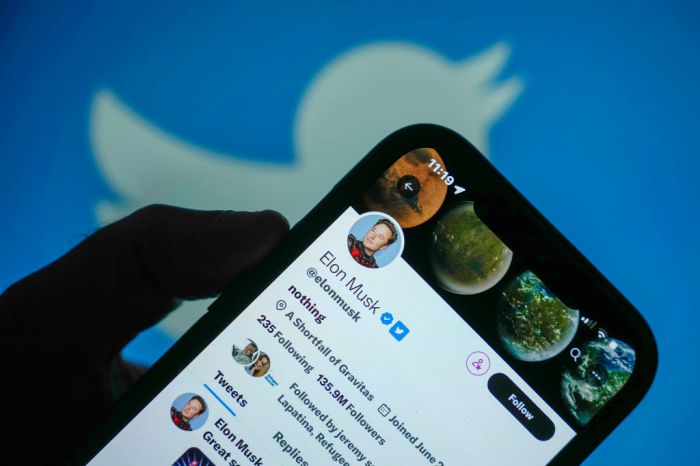
Musk’s Potential Removal of Twitter from the EU

Elon Musk’s acquisition of Twitter has been marked by a series of controversial decisions, including the reinstatement of previously banned accounts and the introduction of a subscription service for verified accounts. These changes have sparked debate about the future of Twitter and its role in the global information ecosystem.
One of the most pressing questions is whether Musk might remove Twitter from the European Union, a move that would have significant implications for users, businesses, and the spread of information within the region.
Reasons for Potential Withdrawal
The EU’s Disinformation Law, which aims to combat the spread of false and misleading information online, has been a source of friction between Musk and the European Union. Musk has publicly criticized the law, calling it “unworkable” and arguing that it will stifle free speech.
He has also expressed concerns about the law’s impact on Twitter’s business operations.
- The law requires platforms to proactively identify and remove disinformation, a task that Musk believes is difficult and subjective. He has argued that Twitter is already taking steps to combat disinformation, such as labeling potentially misleading content and providing users with tools to report false information.
- The law imposes fines on platforms that fail to comply with its requirements, which Musk sees as a significant financial risk. He has suggested that Twitter might be better off withdrawing from the EU market altogether than facing potentially crippling penalties.
- Musk’s vision for Twitter emphasizes free speech, even if it means allowing controversial or offensive content. This vision clashes with the EU’s commitment to combating hate speech and other forms of harmful content online. The EU’s Disinformation Law could force Twitter to remove content that Musk believes should be allowed, creating a conflict between his principles and the law.
Potential Consequences of Twitter’s Withdrawal
If Twitter were to withdraw from the EU, it would have significant consequences for users, businesses, and the spread of information within the region.
- Userswould lose access to Twitter, a platform that many use for news, social interaction, and communication. This would be particularly disruptive for users who rely on Twitter for professional or political purposes.
- Businessesthat use Twitter for marketing, customer service, and brand building would have to find alternative platforms or adapt their strategies. This could be costly and time-consuming, especially for businesses that have invested heavily in their Twitter presence.
- The spread of informationwithin the EU could be affected, as Twitter is a major source of news and information for many users. The loss of Twitter could create information silos, making it more difficult for people to access diverse perspectives and stay informed about current events.
The Implications of Twitter’s Absence

The potential withdrawal of Twitter from the EU raises serious concerns about the impact on the bloc’s efforts to combat disinformation. This move could significantly disrupt the EU’s digital landscape and pose challenges to its ongoing efforts to protect its citizens from harmful online content.
The EU’s Regulatory Approach to Disinformation
The EU has adopted a comprehensive approach to tackling disinformation, recognizing its potential to undermine democratic processes and public trust. The EU’s Disinformation Code of Practice, launched in 2018, encourages voluntary commitments from online platforms to address disinformation. The EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA), adopted in 2022, further strengthens the regulatory framework by imposing stricter obligations on large online platforms, including measures to combat disinformation.
Comparison with Other Regions, Musk might remove x twitter from eu disinformation law
The EU’s regulatory approach to disinformation stands out in its comprehensiveness and proactive stance. While other regions, such as the United States, have adopted measures to combat disinformation, the EU’s focus on platform accountability and transparency is more pronounced. The EU’s approach is also characterized by its emphasis on cross-border cooperation and the development of common standards for tackling disinformation.
Potential Advantages and Disadvantages of Twitter’s Withdrawal
The potential withdrawal of Twitter from the EU presents a complex scenario with both advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reduced platform for disinformation spread. | Loss of a valuable tool for communication and information sharing. |
| Potential for increased focus on other platforms. | Reduced reach of EU regulations on a major platform. |
| Opportunity for EU to strengthen its own platforms. | Potential for fragmentation of the digital landscape. |
| Potential for increased transparency and accountability. | Increased difficulty in monitoring disinformation campaigns. |
Potential Responses from the EU
The EU’s response to Twitter’s potential withdrawal from the region would be a complex and multifaceted affair, likely involving a mix of diplomatic pressure, regulatory action, and potential legal challenges. The EU has demonstrated a strong commitment to combating disinformation and protecting online users, and Twitter’s departure would raise significant concerns.
Possible EU Actions
The EU’s response would likely be driven by the desire to protect its citizens from the negative impacts of disinformation and to uphold its regulatory framework. Here are some potential actions the EU might take:
- Negotiations and Dialogue:The EU could attempt to engage in direct negotiations with Twitter to find a compromise that allows the platform to remain in the EU while adhering to its regulations. This might involve discussions about specific aspects of the Disinformation Law that Twitter finds problematic, potential exemptions or modifications, and the establishment of a collaborative framework for addressing concerns.
- Enforcement of Existing Regulations:The EU could leverage existing regulations, such as the Digital Services Act (DSA), to impose penalties on Twitter for non-compliance. The DSA already requires large online platforms to take proactive measures to combat illegal content and misinformation, and Twitter’s withdrawal could be seen as a deliberate attempt to circumvent these obligations.
- Legal Challenges:The EU could initiate legal action against Twitter, arguing that its withdrawal from the region constitutes a violation of EU law. This could involve challenging Twitter’s decision in court, potentially leading to fines or other sanctions.
- Alternative Platforms:The EU could encourage the development and adoption of alternative social media platforms that comply with its regulations and prioritize user safety and responsible content moderation. This could involve providing funding or incentives to European startups or fostering partnerships with existing platforms that are committed to ethical online practices.
Negotiation Scenario
A possible scenario involves the EU engaging in direct negotiations with Twitter, aiming to reach a compromise that allows the platform to remain in the EU. The EU might offer Twitter some concessions, such as clarifying specific aspects of the Disinformation Law or providing more guidance on its implementation.
In exchange, Twitter would need to commit to complying with the EU’s regulations and demonstrate its willingness to work collaboratively to address concerns about disinformation and user safety. This scenario would require both parties to show flexibility and a willingness to find common ground.
The Broader Context of Tech Regulation: Musk Might Remove X Twitter From Eu Disinformation Law
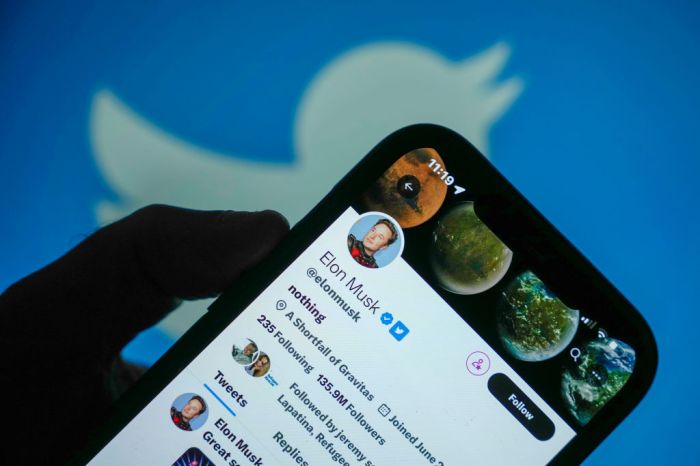
Musk’s potential move to remove Twitter from the EU’s Disinformation Law is not just a single event; it’s a symptom of a larger trend: the increasing friction between tech companies and governments around the world, particularly concerning the regulation of social media platforms.
This tension is shaping the future of the internet, with significant implications for both users and businesses.
Global Approaches to Social Media Regulation
The EU’s approach to regulating social media is becoming increasingly influential globally, as other major countries are grappling with similar challenges. The EU’s approach is characterized by its focus on:
- Content Moderation:The EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA) requires large online platforms to take down illegal content and to be more transparent about their algorithms and content moderation processes.
- Disinformation and Manipulation:The EU’s Disinformation Law aims to curb the spread of false and misleading information online by requiring social media platforms to take steps to combat it.
- User Rights and Data Protection:The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) grants users greater control over their personal data and sets strict rules for how companies can collect and use it.
The US, in contrast, has largely taken a more hands-off approach to regulating social media, relying on existing laws and industry self-regulation. However, the US Congress is increasingly considering legislation to address issues like content moderation and data privacy.China, on the other hand, has adopted a highly centralized approach, with strict controls on online content and social media platforms.
This approach has led to a more fragmented online landscape, with limited access to global platforms and services.
Potential Fragmentation in the Online Landscape
Musk’s potential withdrawal of Twitter from the EU could lead to further fragmentation in the online landscape, creating a “digital Berlin Wall” between different regions. This could have significant consequences for users and businesses:
- Limited Access to Global Platforms:Users in certain regions may lose access to popular social media platforms like Twitter, creating a more fragmented and localized online experience.
- Challenges for Businesses:Businesses may face difficulties operating across different regulatory landscapes, requiring them to tailor their strategies and content to comply with local laws.
- Increased Costs and Complexity:Companies may face higher costs and administrative burdens in managing their online presence across multiple jurisdictions with different regulations.
- Potential for Reduced Innovation:A fragmented online landscape could hinder the development of new technologies and services, as companies may be less inclined to invest in global platforms that face regulatory hurdles.
The implications of Musk’s move are far-reaching and raise critical questions about the future of the internet. As technology continues to evolve and the online world becomes increasingly interconnected, finding a balance between promoting innovation and protecting users will be a crucial challenge for policymakers and tech companies alike.