Alchemy e waste apple products tradein circularity – Apple’s Trade-In: Alchemy of E-Waste & Circularity – a powerful concept that’s turning the tide on electronic waste. With the growing environmental impact of e-waste, especially from tech giants like Apple, the need for sustainable solutions has become increasingly urgent.
Apple’s Trade-In program offers a unique opportunity to transform discarded Apple products into valuable resources, promoting a circular economy and reducing our footprint on the planet.
This program, which allows users to trade in their old devices for credit towards new ones, has emerged as a catalyst for circularity. It incentivizes responsible disposal and reduces the amount of e-waste ending up in landfills. Apple’s commitment to circularity goes beyond just recycling, as they strive to incorporate recycled materials into their new products.
This initiative is not only a step towards a greener future but also a testament to the potential of technology to drive positive change.
The Alchemy of E-Waste
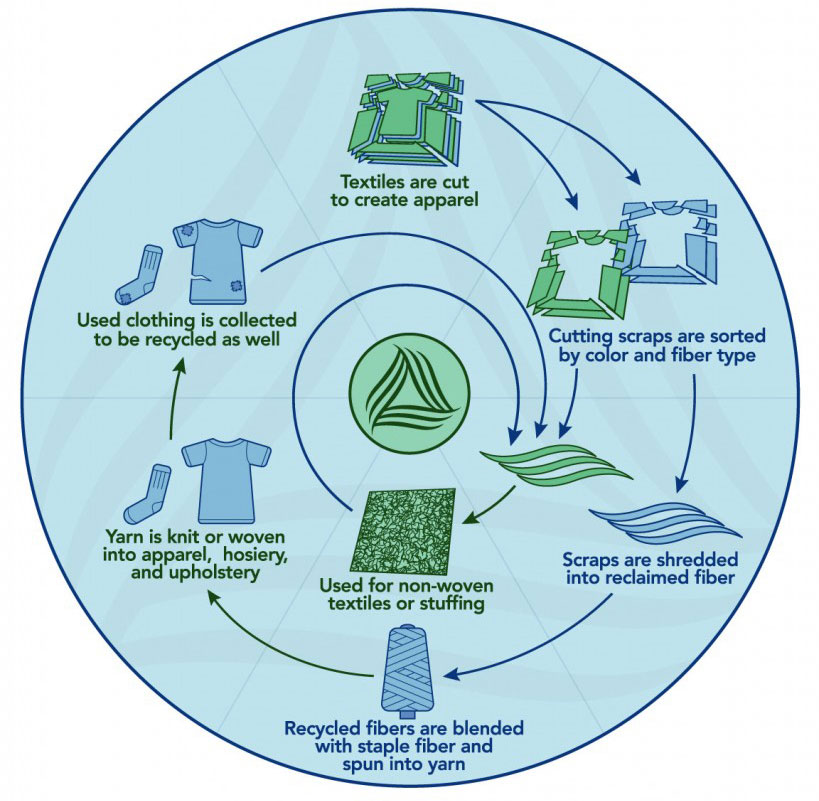
The world is awash in electronic waste, and Apple products, with their sleek designs and rapid obsolescence cycles, contribute significantly to this growing problem. This e-waste poses a serious environmental threat, demanding innovative solutions to transform discarded devices into valuable resources.
Environmental Impact of Apple E-Waste
The environmental impact of e-waste from Apple products is multifaceted and alarming. The extraction of raw materials, such as rare earth metals and precious metals, for manufacturing these devices has devastating consequences for ecosystems and communities. Mining activities often lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and water pollution.
Furthermore, the production of these products requires vast amounts of energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Challenges of Responsible E-Waste Management
Managing e-waste responsibly presents a complex challenge. The sheer volume of e-waste generated globally, coupled with the hazardous materials contained within, necessitates robust systems for collection, sorting, and processing.
- Lack of Infrastructure:Many countries lack the infrastructure and expertise to handle e-waste effectively, leading to improper disposal and illegal dumping.
- Difficulties in Recycling:The complex components and materials found in electronic devices make recycling challenging and costly.
- Transboundary Movements:The movement of e-waste across borders, often to countries with weaker environmental regulations, raises ethical and environmental concerns.
Circularity in Apple Products
Circularity is a concept that promotes a closed-loop system, where materials are kept in use for as long as possible, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency. Apple has made significant strides in implementing circularity practices across its product lifecycle, focusing on:
- Design for Disassembly:Apple designs its products with ease of disassembly in mind, facilitating the recovery of valuable materials.
- Recycling Programs:Apple offers comprehensive recycling programs, allowing users to dispose of their old devices responsibly.
- Closed-Loop Manufacturing:Apple is working to increase the use of recycled materials in its products, reducing reliance on virgin resources.
Apple’s Trade-In Program
Apple’s Trade-In program has emerged as a prominent initiative in the tech industry, aimed at promoting circularity and reducing e-waste. This program allows users to trade in their old Apple devices for credit towards new purchases or for cash. By providing a convenient and valuable way to dispose of old devices, Apple aims to encourage responsible recycling and minimize the environmental impact of its products.
Effectiveness of Apple’s Trade-In Program
Apple’s Trade-In program has been instrumental in reducing e-waste by providing a viable alternative to discarding old devices. The program encourages users to responsibly recycle their devices, diverting them from landfills and promoting reuse and refurbishment. According to Apple, its Trade-In program has diverted millions of devices from landfills, demonstrating its significant impact on reducing e-waste.
Comparison with Other Tech Companies
Several other tech companies, including Samsung, Google, and Microsoft, have implemented similar trade-in programs. However, Apple’s Trade-In program stands out for its comprehensive approach and its focus on environmental sustainability.
- Apple’s Trade-In program offers a wider range of eligible devices compared to some competitors.
- Apple also provides a transparent and easy-to-use process for evaluating and trading in devices, enhancing user convenience.
- Apple’s commitment to responsible recycling and refurbishment processes further strengthens the program’s environmental impact.
Potential Improvements to Apple’s Trade-In Program
While Apple’s Trade-In program has been effective, there are potential improvements that could further enhance its impact:
- Expanding the program to include a wider range of devices, including those from other manufacturers, could further encourage recycling and reduce e-waste.
- Increasing the value offered for older or less popular devices could incentivize users to trade in their devices rather than discarding them.
- Implementing a program to incentivize the use of refurbished devices could promote a more sustainable consumption model.
The Role of Technology in Transforming E-Waste
The global e-waste crisis is a pressing issue, demanding innovative solutions. Technology plays a crucial role in tackling this challenge by enabling efficient recycling and repurposing of electronic waste.
Innovative Technologies for E-Waste Recycling and Repurposing
Innovative technologies are being employed to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of e-waste recycling and repurposing processes. These technologies are crucial for addressing the increasing volume of e-waste and extracting valuable materials from discarded electronics.
- Automated Sorting Systems:Advanced robotic systems equipped with sensors and machine learning algorithms can automatically sort e-waste based on material type, size, and other characteristics. This automated sorting process significantly improves efficiency and reduces manual labor, minimizing human error and safety risks.
- Hydrometallurgical Processing:This technology uses water-based solutions to extract valuable metals from e-waste. Hydrometallurgical processing offers a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional smelting methods, reducing emissions and minimizing the generation of hazardous byproducts.
- Bioleaching:This innovative approach utilizes microorganisms to extract valuable metals from e-waste. Bioleaching offers a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional methods, minimizing the use of harsh chemicals and energy consumption.
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in E-Waste Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming e-waste management by providing powerful tools for data analysis, prediction, and optimization.
- Predictive Analytics:AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical data on e-waste generation, composition, and recycling rates to predict future trends and optimize resource allocation. This enables proactive planning and resource management for e-waste collection, processing, and recycling.
- Smart Waste Management Systems:AI-powered sensors and tracking systems can monitor waste collection and processing activities, providing real-time data on waste levels, material composition, and recycling performance. This data can be used to optimize waste collection routes, improve resource utilization, and reduce transportation costs.
- E-Waste Identification and Sorting:AI and ML algorithms can analyze images and data from e-waste streams to identify and sort different types of electronic waste with high accuracy. This automated sorting process improves efficiency, reduces manual labor, and minimizes human error.
Hypothetical System for Automated E-Waste Sorting and Processing
A hypothetical system for automated e-waste sorting and processing could be designed using advanced technologies and AI algorithms.
This system would involve a multi-stage process, starting with the collection of e-waste from various sources, followed by automated sorting and processing.
- E-Waste Collection:A network of collection points equipped with AI-powered sensors could be established to collect e-waste from households, businesses, and other sources. These sensors would identify and track the type and volume of e-waste collected, providing real-time data for efficient resource management.
Finish your research with information from eu media surveillance law journalists.
- Automated Sorting:Once collected, e-waste would be transported to a central processing facility equipped with advanced robotic sorting systems. These systems would utilize AI and ML algorithms to identify and separate different types of e-waste based on material composition, size, and other characteristics.
This automated sorting process would significantly improve efficiency and accuracy compared to manual sorting methods.
- Material Recovery:After sorting, e-waste would be processed using various technologies to recover valuable materials. For example, metals could be extracted using hydrometallurgical or bioleaching processes, while plastics and other materials could be recycled using advanced separation and purification techniques.
- Data Analytics and Optimization:The entire process would be monitored and analyzed using AI and ML algorithms to identify bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and improve overall efficiency. This data-driven approach would ensure continuous improvement and optimization of the e-waste management system.
Consumer Awareness and Behavior: Alchemy E Waste Apple Products Tradein Circularity

The success of Apple’s Trade-In program, and the broader concept of e-waste circularity, hinges on consumer awareness and behavior change. While many consumers are aware of the environmental impact of e-waste, they may not be fully aware of the benefits of recycling or trading in their old devices.
Understanding Consumer Attitudes Towards E-Waste, Alchemy e waste apple products tradein circularity
Consumer attitudes towards e-waste recycling vary significantly. Some individuals are highly motivated by environmental concerns and actively seek out responsible disposal options. Others may be less informed or lack convenient access to recycling programs. A recent study by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) found that only 15% of Americans are very concerned about e-waste, while 40% are somewhat concerned.
This indicates a need for greater public education and awareness campaigns.
Encouraging Participation in Apple’s Trade-In Program
Apple can effectively encourage consumer participation in its Trade-In program through a multifaceted approach:
Marketing Strategies
- Clear and Accessible Information:Apple should provide readily available information on the Trade-In program, highlighting its benefits and simplicity. This information can be disseminated through various channels, including its website, retail stores, social media, and email campaigns.
- Value Proposition:Emphasizing the financial incentives associated with trading in devices, such as discounts on new purchases or gift cards, can motivate consumers to participate. Apple can also highlight the environmental benefits, such as reducing e-waste and contributing to a more sustainable future.
- Convenience:Apple should streamline the Trade-In process, making it easy and convenient for consumers. This can involve offering online trade-in options, convenient drop-off locations, and quick processing times.
Community Engagement
- Partnerships:Collaborating with organizations and initiatives focused on e-waste recycling and environmental sustainability can broaden the reach of Apple’s Trade-In program and promote a collective effort towards responsible e-waste management.
- Educational Campaigns:Apple can conduct educational campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of responsible e-waste disposal and the benefits of its Trade-In program. These campaigns can utilize various mediums, such as social media, videos, and interactive workshops.
Promoting Circularity and Responsible E-Waste Management
A comprehensive marketing campaign can effectively promote the benefits of circularity and responsible e-waste management:
Campaign Theme:
“Reimagine Technology. Reimagine the Future.”
This theme captures the essence of circularity and highlights the positive impact of responsible e-waste management on the future.
Key Messages:
- Environmental Responsibility:Emphasize the environmental impact of e-waste and the role consumers can play in reducing it. Highlight the benefits of recycling and trading in devices, such as reducing pollution, conserving resources, and minimizing landfill waste.
- Economic Value:Promote the financial benefits of trading in devices, such as discounts on new purchases, gift cards, and the ability to recover value from old devices. This can incentivize consumers to participate in the program.
- Technological Innovation:Showcase how Apple is innovating to create products that are more durable, repairable, and recyclable. Highlight the company’s commitment to closed-loop manufacturing and the use of recycled materials.
Campaign Channels:
- Social Media:Leverage social media platforms to share engaging content, stories, and statistics about e-waste and circularity. Encourage user-generated content, such as testimonials from consumers who have participated in the Trade-In program.
- Influencer Marketing:Partner with influential figures in technology, sustainability, and consumer advocacy to promote the benefits of circularity and Apple’s Trade-In program.
- Public Relations:Engage with media outlets and publications to raise awareness about the issue of e-waste and Apple’s commitment to responsible e-waste management. Share positive stories and case studies about the impact of the Trade-In program.
Future Directions

The current state of e-waste management, particularly with Apple’s trade-in program, presents a foundation for further progress. However, achieving true circularity requires a proactive approach, pushing the boundaries of current practices. This involves exploring innovative technologies, adopting responsible sourcing practices, and fostering consumer awareness.
Closed-Loop Manufacturing
Apple’s commitment to sustainability can be further strengthened by adopting a closed-loop manufacturing model. This approach aims to minimize waste by reusing and recycling materials throughout the product lifecycle.
- Material Recovery and Recycling:Apple can invest in advanced recycling technologies to recover valuable materials from e-waste, such as rare earth elements, precious metals, and plastics. This can significantly reduce reliance on virgin materials and minimize environmental impact.
- Design for Disassembly:Designing products for easy disassembly and component reuse is crucial for efficient recycling. Apple can adopt modular designs that allow for the replacement of individual components, extending the lifespan of devices and reducing waste.
- Material Substitution:Exploring alternative materials with lower environmental impact, such as recycled aluminum, bio-based plastics, and sustainable sourcing of rare earth elements, can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of Apple products.
Ethical Sourcing of Materials
The ethical sourcing of materials is paramount for ensuring the sustainability of Apple products. This involves addressing human rights, environmental impact, and responsible mining practices.
- Conflict Minerals:Apple can implement stricter sourcing policies to ensure that the minerals used in its products, such as tantalum, tin, tungsten, and gold, are not sourced from conflict zones or areas with human rights violations.
- Labor Standards:Apple can work with suppliers to ensure fair labor practices, including safe working conditions, fair wages, and the absence of forced labor or child labor. This can be achieved through rigorous audits, transparent supply chains, and partnerships with ethical organizations.
- Environmental Impact:Apple can prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable mining practices that minimize environmental damage, such as reducing water usage, minimizing pollution, and restoring mined land.
Roadmap for Sustainability
Apple can achieve its long-term sustainability goals by implementing a comprehensive roadmap that encompasses various aspects of its operations.
- Setting Ambitious Targets:Apple can set ambitious targets for reducing its environmental footprint, such as achieving carbon neutrality, reducing reliance on virgin materials, and increasing the use of recycled materials.
- Investing in Research and Development:Apple can invest in research and development of innovative technologies, such as advanced recycling processes, renewable energy sources, and sustainable materials, to drive progress in its sustainability efforts.
- Transparency and Reporting:Apple can enhance transparency by providing detailed reports on its environmental performance, including its carbon footprint, material sourcing, and recycling practices. This will allow for greater accountability and stakeholder engagement.
- Collaboration and Partnerships:Apple can collaborate with industry partners, governments, and non-governmental organizations to address the challenges of e-waste management and promote sustainable practices across the value chain.





