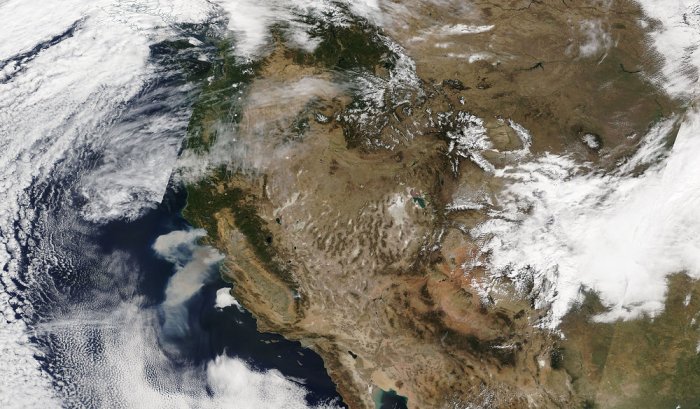
Space satellites europe wildfires – Space Satellites: Europe’s Wildfire Watchdogs – Imagine a network of watchful eyes orbiting Earth, constantly scanning for signs of danger. These aren’t the eyes of mythical creatures, but sophisticated sensors aboard satellites, providing invaluable insights into the ever-growing threat of wildfires in Europe.
These technological guardians play a critical role in monitoring, analyzing, and ultimately, helping to combat these destructive events.
From the moment a wildfire ignites, these space-based sentinels track its progress, measuring its intensity and the spread of smoke plumes. They provide crucial information to firefighters and emergency responders, enabling them to act quickly and effectively. This data is not just a snapshot; it’s a continuous stream of information, allowing for real-time analysis and informed decision-making.
The Role of Satellites in Wildfire Monitoring

Wildfires pose a significant threat to ecosystems, human lives, and property in Europe. Fortunately, advancements in satellite technology have provided valuable tools for monitoring these events and supporting wildfire management efforts. Satellites equipped with various sensors can detect, track, and analyze wildfires, providing crucial information for firefighters, scientists, and policymakers.
Satellite Capabilities in Wildfire Detection and Monitoring
Satellites play a vital role in wildfire monitoring by offering a unique perspective from space. They can cover vast areas, providing near real-time information on wildfire locations, spread, intensity, and smoke plumes.
- Thermal Infrared Sensors:These sensors detect heat radiation emitted by fires, allowing for the identification of active fire fronts even at night or through smoke.
- Visible and Near-Infrared Sensors:These sensors capture images in the visible and near-infrared spectrum, enabling the detection of changes in vegetation and land cover, which can indicate the presence of fire scars or burned areas.
- Multispectral and Hyperspectral Sensors:These sensors collect data at multiple wavelengths, providing information about the chemical composition of smoke and burned areas, which can be used to assess fire severity and potential environmental impacts.
European Space Agency’s (ESA) Contribution: Space Satellites Europe Wildfires

The European Space Agency (ESA) plays a pivotal role in wildfire monitoring and management, leveraging its advanced satellite technology and expertise to support global efforts in mitigating the devastating effects of these natural disasters.
ESA’s Initiatives and Programs
ESA’s commitment to wildfire monitoring is evident in its numerous initiatives and programs. The agency’s efforts are aimed at enhancing our understanding of wildfire dynamics, improving early warning systems, and facilitating efficient response strategies.
- The Copernicus Programme:The Copernicus Programme, a key initiative of the European Union, leverages a constellation of Earth observation satellites, including Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3, to provide near real-time data on wildfire occurrences and their impact. This data is crucial for fire detection, mapping, and assessing the severity of wildfires.
- Fire Risk Assessment and Early Warning Systems:ESA collaborates with various partners to develop and deploy fire risk assessment and early warning systems. These systems use satellite data to identify areas at high risk of wildfires, enabling proactive measures to be taken to prevent or mitigate their impact.
- Post-Fire Monitoring and Damage Assessment:Satellite imagery plays a critical role in assessing the damage caused by wildfires. ESA’s satellites can monitor the extent of burned areas, assess the impact on vegetation and infrastructure, and support post-fire recovery efforts.
ESA’s Satellite Constellations
ESA’s satellite constellations, specifically the Sentinel series, are instrumental in wildfire monitoring.
- Sentinel-2:This satellite provides high-resolution optical imagery, enabling the detection and mapping of wildfires with high accuracy. Its frequent revisit time allows for timely updates on fire progression and intensity.
- Sentinel-3:This satellite carries a suite of instruments, including a thermal infrared sensor, which can detect heat signatures associated with wildfires. This data is crucial for identifying active fires and estimating their intensity.
ESA’s Collaboration with Other Organizations and Countries
ESA recognizes the global nature of wildfire threats and collaborates with various organizations and countries to strengthen wildfire monitoring and management capabilities.
- International Collaboration:ESA works closely with international partners, including the European Union, NASA, and other space agencies, to share data, develop joint initiatives, and foster knowledge exchange.
- National Partnerships:ESA collaborates with national governments and agencies to provide satellite data and expertise to support their wildfire management programs. These collaborations often involve training, capacity building, and the development of customized solutions.
Impact of Wildfires on European Ecosystems

Wildfires, a recurring threat in Europe, have significant consequences for the continent’s ecosystems, biodiversity, and human well-being. The impact of wildfires extends beyond immediate damage, influencing long-term environmental changes and posing challenges to sustainable development.
Environmental Consequences, Space satellites europe wildfires
The impact of wildfires on European forests is multifaceted. Wildfires can destroy vast areas of forest, eliminating trees and undergrowth, and disrupting natural regeneration processes. This loss of forest cover affects biodiversity, as many species rely on these habitats for survival.
Wildfires can alter the composition and structure of forests, favoring fire-resistant species over others. This can lead to a shift in the balance of ecosystems, with potential implications for the long-term health and resilience of forests.
Impact on Air Quality, Water Resources, and Human Health
Wildfires release large quantities of smoke and particulate matter into the atmosphere, significantly impacting air quality. This can lead to respiratory problems, particularly for vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions.
Wildfires also affect water resources. Burned areas are more susceptible to soil erosion, leading to increased sediment runoff into rivers and lakes. This can degrade water quality, impacting aquatic ecosystems and water supplies.
Long-Term Effects
The long-term effects of wildfires on soil erosion are significant. Burned areas are often left with exposed soil, making them more vulnerable to wind and water erosion. This can lead to soil degradation, reduced soil fertility, and the loss of valuable topsoil.
Discover how best google review ever has transformed methods in this topic.
Wildfires also contribute to carbon emissions, as burning vegetation releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This exacerbates climate change, creating a feedback loop where warmer temperatures increase the risk of wildfires, further intensifying the problem.
Wildfire Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Wildfires pose a significant threat to European ecosystems, human health, and infrastructure. A comprehensive approach to wildfire management is essential, encompassing prevention, preparedness, and response. Effective strategies focus on reducing the risk of ignition, minimizing the spread of fires, and enhancing resilience to wildfire impacts.
Forest Management Practices
Sustainable forest management practices play a crucial role in reducing wildfire risk. These practices aim to create healthier and more resilient forests that are less susceptible to fire.
- Prescribed Burning:Controlled burns, conducted under specific conditions, help reduce fuel loads, create firebreaks, and mimic natural fire cycles. This practice can help prevent large, destructive wildfires by removing flammable undergrowth and creating areas resistant to fire spread.
- Thinning and Selective Logging:Removing dense vegetation and trees, particularly in areas with high fire risk, can reduce fuel density and create space for firebreaks. This practice promotes the growth of healthier trees and reduces the likelihood of crown fires, which spread rapidly through tree canopies.
- Fuel Breaks:Creating firebreaks, such as roads, clearings, or strips of land with minimal vegetation, can help contain wildfires by preventing their spread across landscapes. These barriers act as fire lines, allowing firefighters to control the fire’s perimeter.
- Species Diversity:Planting a mix of tree species with varying fire resistance can create a more resilient forest. This diversity helps prevent the spread of fire by reducing the continuity of flammable fuels.
Early Detection Systems and Rapid Response Measures
Early detection and rapid response are critical in wildfire control. Advanced technologies and monitoring systems play a crucial role in identifying fires quickly and deploying resources efficiently.
- Satellite Monitoring:Earth observation satellites equipped with infrared sensors can detect heat signatures from wildfires, providing near real-time information on fire locations and intensity. This information enables rapid deployment of firefighting resources and helps prioritize response efforts.
- Aerial Reconnaissance:Aircraft equipped with infrared cameras and other sensing technologies can survey large areas quickly, providing detailed information on fire perimeters, smoke plumes, and potential fire spread. This information helps guide firefighting strategies and assess the severity of the situation.
- Ground-Based Sensors:Networks of ground-based sensors, such as weather stations and smoke detectors, can provide real-time data on fire activity and environmental conditions. This information helps predict fire behavior and alert authorities to potential fire threats.
- Firefighting Resources:Efficient deployment of firefighting resources, including firefighters, helicopters, and fire engines, is essential for controlling wildfires effectively. Rapid response and coordinated efforts are crucial in minimizing fire damage.
Public Awareness Campaigns and Community Engagement
Public awareness and community engagement are essential in wildfire prevention. Educating the public about wildfire risks, responsible behavior, and fire safety practices can significantly reduce the number of human-caused fires.
- Fire Safety Education:Public awareness campaigns can emphasize the importance of safe campfire practices, proper disposal of cigarettes, and avoiding activities that could spark a fire, such as using machinery during dry periods.
- Community Involvement:Engaging local communities in wildfire prevention efforts can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility. This can involve training residents in fire safety practices, organizing community fire prevention events, and establishing local fire watch programs.
- Communication and Collaboration:Effective communication channels between authorities, emergency responders, and the public are crucial for disseminating wildfire information, issuing warnings, and coordinating response efforts.
Technological Advancements in Wildfire Management
The fight against wildfires is becoming increasingly sophisticated, with technological advancements playing a crucial role in detection, response, and mitigation efforts. From drones to artificial intelligence, new tools are transforming how we monitor, analyze, and combat these devastating events.
Drones for Wildfire Detection and Response
Drones have emerged as a valuable asset in wildfire management, offering several advantages over traditional methods. They can be deployed quickly and efficiently to access remote or hazardous areas, providing real-time aerial imagery and data.
- Enhanced Detection:Drones equipped with thermal cameras can detect heat signatures from smoldering vegetation, allowing for early identification of potential fire outbreaks. This early detection is crucial for prompt response and suppression efforts.
- Real-Time Monitoring:Drones can provide continuous surveillance of active fires, enabling firefighters to monitor fire spread, assess fire behavior, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and firefighting strategies.
- Precise Mapping:Drones can create detailed 3D maps of fire-affected areas, providing valuable information for fire suppression efforts, damage assessment, and post-fire recovery planning.
Examples of successful drone deployments include the use of drones by the French Civil Security in the south of France, where they were deployed to assess fire damage and provide real-time information to firefighters.
Artificial Intelligence for Wildfire Prediction and Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing wildfire management by providing advanced analytical capabilities for prediction, prevention, and response.
- Predictive Modeling:AI algorithms can analyze historical fire data, weather patterns, and environmental factors to predict fire risk and identify areas prone to wildfire ignition. This information can help fire agencies prioritize resources and implement preventive measures in high-risk areas.
- Fire Behavior Simulation:AI models can simulate fire spread under various scenarios, enabling firefighters to anticipate fire behavior and develop effective suppression strategies. This allows for more proactive and efficient fire suppression efforts.
- Data Analysis and Decision Support:AI can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, including satellite imagery, weather reports, and sensor networks, to provide real-time insights into fire conditions and support decision-making in wildfire management.
For instance, the European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS) uses AI algorithms to analyze satellite data and generate fire risk maps, providing valuable information to fire agencies across Europe.