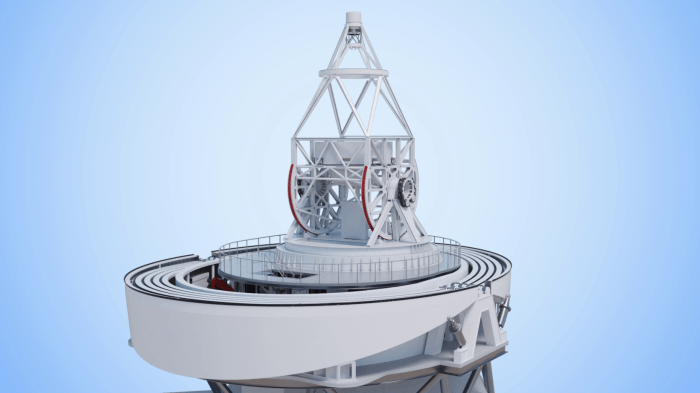
Europes largest ever solar telescope to enter construction phase – Europe’s largest ever solar telescope is entering its construction phase, marking a significant milestone in our quest to understand the Sun. This ambitious project, known as the European Solar Telescope (EST), is poised to revolutionize solar physics by providing unprecedented views of our star.
Located on the Canary Island of La Palma, the EST will boast cutting-edge technology and a prime observing location, making it a powerful tool for unlocking the secrets of the Sun.
The EST is designed to be a world-leading solar observatory, equipped with advanced instruments and a unique design that will allow scientists to study the Sun in greater detail than ever before. The telescope’s advanced capabilities will enable researchers to delve into the Sun’s complex magnetic fields, solar flares, and the processes that drive space weather.
This knowledge will not only deepen our understanding of the Sun but also help us better predict and mitigate the effects of solar activity on Earth.
The European Solar Telescope: A New Era of Solar Research
The European Solar Telescope (EST) is poised to become the largest and most advanced solar telescope in Europe, marking a significant leap forward in our understanding of the Sun. This ambitious project is a testament to the collaborative spirit of European scientists and engineers, who are working together to build a cutting-edge instrument that will revolutionize our study of the Sun.
Project Overview
The EST is a ground-based telescope designed to observe the Sun in unprecedented detail. Its primary mirror, with a diameter of 4 meters, will be the largest ever used for a solar telescope. This size allows the EST to gather significantly more light than existing telescopes, enabling astronomers to study the Sun’s surface and atmosphere with unprecedented resolution.
Location and Timeline
The EST is planned to be located on the island of La Palma in the Canary Islands, a site known for its exceptional astronomical observing conditions. The construction phase is expected to span several years, with the telescope anticipated to be operational by the early 2030s.
Key Features and Capabilities
The European Solar Telescope (EST) is not just another solar observatory; it is a revolutionary leap forward in solar research, designed to unravel the Sun’s mysteries with unprecedented clarity and detail. Its innovative design and cutting-edge technology will enable scientists to study the Sun in ways never before possible.
Design and Technical Specifications
The EST’s unique design features a 4-meter primary mirror, making it the largest solar telescope ever built in Europe. This large aperture will allow the telescope to collect significantly more light than any other solar telescope currently in operation, providing unparalleled resolution and sensitivity for observing the Sun.
The EST will be equipped with a state-of-the-art adaptive optics system to compensate for atmospheric distortions, ensuring crisp and clear images of the Sun’s surface and atmosphere. This advanced system will use deformable mirrors to adjust the telescope’s optics in real-time, effectively eliminating the blurring effects caused by turbulence in the Earth’s atmosphere.
Advanced Instruments and Observation Capabilities
The EST will be equipped with a suite of advanced instruments designed to study various aspects of the Sun. These instruments include:
- Spectrographs: These instruments will analyze the Sun’s light to determine its chemical composition, temperature, and velocity.
- Polarimeters: These instruments will measure the polarization of the Sun’s light, providing information about the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Imaging systems: These systems will capture high-resolution images of the Sun’s surface and atmosphere, revealing intricate details of solar phenomena like sunspots, flares, and prominences.
The EST will be able to observe the Sun in various wavelengths, including visible light, ultraviolet, and infrared. This multi-wavelength capability will provide a comprehensive view of the Sun’s activity and its impact on the Earth’s environment.
Enhanced Understanding of the Sun
The EST’s exceptional capabilities will enable scientists to make significant advances in our understanding of the Sun. Some key research areas include:
- Solar magnetism: The Sun’s magnetic field drives many of its most energetic phenomena, including solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). The EST’s advanced polarimeters will allow scientists to study the Sun’s magnetic field in unprecedented detail, providing crucial insights into the processes that generate these powerful events.
- Solar activity: The Sun’s activity varies over time, influencing the Earth’s atmosphere and climate. The EST will provide valuable data to understand the mechanisms behind solar activity and its impact on our planet.
- Solar wind: The Sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. The EST will help scientists study the origin and evolution of the solar wind, understanding its impact on Earth and other planets in the solar system.
- Stellar evolution: By studying the Sun, we can gain insights into the evolution of other stars. The EST will provide data to refine models of stellar evolution and understand the life cycle of stars.
Scientific Objectives: Europes Largest Ever Solar Telescope To Enter Construction Phase
The European Solar Telescope (EST) is designed to revolutionize our understanding of the Sun, addressing some of the most fundamental questions in solar physics. Its advanced capabilities will enable unprecedented observations, paving the way for significant breakthroughs in our comprehension of the Sun’s structure, activity, and influence on the Earth.
Obtain access to 6 ways eu startups can cut spending during the recession to private resources that are additional.
Unraveling the Sun’s Secrets, Europes largest ever solar telescope to enter construction phase
The EST will focus on a wide range of scientific objectives, aiming to answer crucial questions about the Sun’s behavior and its impact on our planet. These include:
- Understanding the Sun’s Magnetic Field:The Sun’s magnetic field is responsible for a variety of phenomena, including sunspots, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections. The EST will provide detailed observations of the magnetic field, allowing scientists to study its evolution and the processes that drive solar activity.
- Investigating the Sun’s Internal Structure:The EST will use helioseismology, the study of solar vibrations, to probe the Sun’s internal structure. This will help scientists understand the processes that occur deep within the Sun and how they influence the surface activity.
- Exploring the Solar Atmosphere:The EST will provide high-resolution images of the Sun’s atmosphere, including the chromosphere and corona. This will allow scientists to study the dynamics of the solar atmosphere, the processes that heat the corona, and the mechanisms that drive solar eruptions.
- Studying the Sun’s Impact on Earth:The EST will provide valuable data on the Sun’s influence on Earth’s atmosphere and climate. This includes studying the effects of solar flares and coronal mass ejections on Earth’s magnetic field, as well as the role of the Sun in climate change.
Potential Breakthroughs in Solar Physics
The EST’s advanced capabilities are expected to lead to significant breakthroughs in solar physics, including:
- Improved Understanding of Magnetic Reconnection:The EST will allow scientists to study magnetic reconnection, a fundamental process that occurs in the Sun’s atmosphere and drives solar flares and coronal mass ejections, with unprecedented detail. This will lead to a better understanding of the mechanisms behind these events and their impact on Earth.
- Unveiling the Secrets of the Solar Corona:The EST will provide detailed observations of the solar corona, the Sun’s outermost layer, allowing scientists to study the processes that heat the corona to millions of degrees and drive the solar wind. This will help us understand the Sun’s influence on the heliosphere, the region of space dominated by the Sun’s magnetic field.
- Predicting Solar Activity:By providing detailed information about the Sun’s magnetic field and activity, the EST will contribute to the development of improved space weather forecasting models. This will help protect critical infrastructure on Earth from the effects of solar storms.
Construction and Engineering
The construction of the European Solar Telescope (EST) is a monumental undertaking, requiring a meticulous blend of engineering prowess and scientific vision. This ambitious project, spanning multiple phases, will culminate in the creation of a cutting-edge observatory capable of unlocking new mysteries of the Sun.The EST’s construction is divided into distinct phases, each focusing on specific aspects of the project.
These phases are meticulously planned and coordinated to ensure a smooth and efficient construction process.
Construction Phases
The construction process is divided into several distinct phases:
- Site Preparation:This initial phase involves preparing the chosen site on the island of La Palma, Canary Islands, for the telescope’s construction. It includes clearing the land, constructing access roads, and laying the foundation for the telescope’s support structure.
- Civil Works:This phase focuses on the construction of the telescope’s main building, including the dome, the control room, and other auxiliary facilities. It also involves the installation of the telescope’s primary mirror and the complex infrastructure required to support its operation.
- Telescope Assembly:Once the civil works are complete, the telescope’s various components are assembled and integrated into a functional unit. This includes the installation of the secondary mirror, the adaptive optics system, and the instruments that will be used to collect and analyze the solar data.
- Testing and Commissioning:Before the telescope is ready for scientific observations, it undergoes a series of rigorous tests and commissioning procedures. These tests ensure that all systems are working correctly and that the telescope is capable of meeting its scientific objectives.
Engineering Challenges
Engineers face numerous challenges during the construction of the EST, stemming from the telescope’s sheer size and the demanding requirements of solar observation:
- Structural Stability:The EST’s massive size and the need for precise pointing accuracy require a robust and stable support structure. Engineers must ensure that the telescope can withstand the forces of wind, gravity, and thermal variations while maintaining its alignment.
- Thermal Control:Observing the Sun generates significant heat, which can distort the telescope’s optics and compromise the quality of the data. Engineers must implement sophisticated thermal control systems to maintain a stable temperature environment within the telescope.
- Adaptive Optics:To compensate for atmospheric turbulence, which distorts the incoming light, the EST will employ adaptive optics. This technology requires precise and rapid adjustments to the telescope’s mirrors, presenting a significant engineering challenge.
- Instrumentation:The EST will be equipped with a suite of advanced instruments to collect and analyze the solar data. These instruments must be designed to operate under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and intense solar radiation.
Innovative Technologies
The EST’s construction incorporates several innovative technologies that will push the boundaries of solar research:
- Segmented Primary Mirror:The EST’s primary mirror is composed of 98 individual segments, which are precisely aligned to form a single reflecting surface. This design reduces the cost and complexity of manufacturing a large mirror and allows for greater flexibility in shaping the mirror’s surface.
- Active Optics:To compensate for the distortions caused by gravity and thermal variations, the EST will employ active optics. This system continuously adjusts the positions of the mirror segments to maintain a perfect optical surface.
- Adaptive Optics:As mentioned earlier, the EST will utilize adaptive optics to correct for atmospheric turbulence. This technology uses a deformable mirror to adjust the telescope’s optics in real time, providing a sharp and undistorted view of the Sun.
- Advanced Instruments:The EST will be equipped with a suite of cutting-edge instruments, including spectrometers, polarimeters, and coronagraphs. These instruments will enable scientists to study the Sun in unprecedented detail, exploring its magnetic fields, its internal structure, and its dynamic atmosphere.
Impact and Collaboration
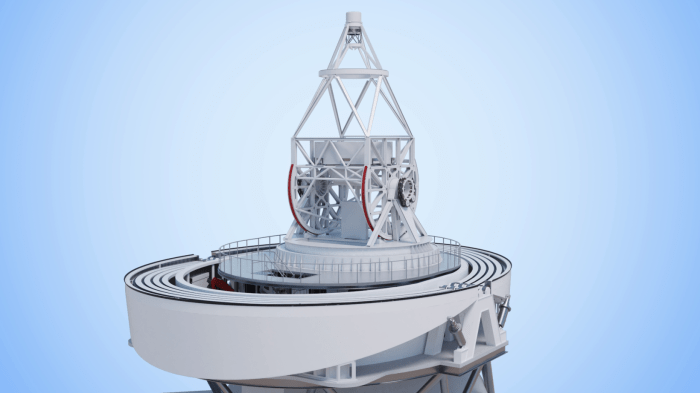
The European Solar Telescope (EST) is poised to revolutionize our understanding of the Sun, its influence on Earth, and its place in the cosmos. This cutting-edge instrument will not only provide unprecedented insights into the Sun’s behavior but also serve as a catalyst for international scientific collaboration and advancements in technology and education.
The EST will create a paradigm shift in solar research by offering unparalleled resolution and sensitivity, enabling scientists to study the Sun in unprecedented detail. Its advanced capabilities will unlock new avenues of exploration, paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries that could reshape our understanding of the Sun and its impact on our planet.
International Collaboration
The EST project is a testament to the power of international collaboration in scientific endeavors. It brings together leading researchers and institutions from across Europe, fostering a vibrant exchange of ideas and expertise. This collaborative spirit extends beyond Europe, with scientists from other continents actively participating in the project, ensuring a global perspective on solar research.
The EST’s construction and operation are a collaborative effort, involving scientists, engineers, and technicians from various European countries. This diverse team brings together a wealth of knowledge and experience, ensuring that the telescope is built to the highest standards and equipped with the latest technologies.
The EST’s scientific program will also be shaped by international collaboration, with scientists from around the world submitting proposals and contributing to the project’s scientific goals.The EST’s success hinges on the ability to attract and retain top talent, and the project’s international scope provides a platform for global collaboration.
The EST will create opportunities for scientists from different countries to work together, share knowledge, and develop new technologies. This exchange of ideas and expertise will not only advance solar research but also foster a global community of scientists dedicated to understanding the Sun.
Education and Outreach
The EST will play a crucial role in promoting science education and public outreach. The project’s innovative technologies and groundbreaking discoveries will inspire future generations of scientists and engineers. The EST will provide a platform for engaging the public in the wonders of solar science.
Through public lectures, workshops, and online resources, the project will showcase the latest discoveries and highlight the importance of solar research. The EST’s data will also be made available to the public, fostering citizen science initiatives and encouraging people to participate in the scientific process.The EST will be a beacon for science education, inspiring young minds to pursue careers in STEM fields.
The project will offer educational programs for students of all ages, providing hands-on experiences and opportunities to learn about the Sun and its impact on our lives. The EST’s educational outreach programs will not only spark interest in science but also equip future generations with the knowledge and skills needed to address the challenges of the 21st century.
Future Prospects
The European Solar Telescope (EST) is not merely a marvel of engineering; it is a gateway to groundbreaking discoveries in solar physics. Its construction marks the beginning of a new era in solar research, one filled with the potential for revolutionary advancements in our understanding of the Sun and its influence on our planet.
The EST’s capabilities are not static; they are poised to evolve and expand over time, fueled by technological innovations and the ever-growing thirst for knowledge.
Future Upgrades and Enhancements
The EST’s design incorporates a modular approach, allowing for future upgrades and enhancements to be seamlessly integrated. This adaptability ensures that the telescope remains at the cutting edge of solar research for decades to come. One key area of focus is the development of advanced instrumentation.
- The EST is expected to benefit from the development of new, more sensitive detectors, capable of capturing a wider range of wavelengths and with improved spatial resolution. These advancements will allow for the observation of fainter features and the study of solar phenomena in unprecedented detail.
- The implementation of adaptive optics will further enhance the telescope’s ability to compensate for atmospheric distortions, leading to sharper images and more accurate measurements.
- The development of novel polarimetric techniques will enable scientists to probe the magnetic fields of the Sun with even greater precision, unlocking new insights into the dynamics of the solar atmosphere.
Long-Term Scientific Contributions
The EST is expected to make significant contributions to our understanding of the Sun’s internal structure, its magnetic field, and the processes that drive solar activity. This knowledge is crucial for predicting space weather events, which can have a profound impact on Earth’s technological infrastructure and human activities in space.
- The EST will provide unprecedented insights into the Sun’s internal dynamics, shedding light on the processes that generate its magnetic field and drive its variability. This knowledge will enhance our ability to predict solar flares and coronal mass ejections, events that can disrupt communication systems, power grids, and satellite operations.
- The EST will allow for the detailed study of the Sun’s magnetic field, which plays a pivotal role in shaping its activity. By unraveling the intricacies of the solar magnetic field, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and other energetic events.
- The EST will contribute to our understanding of the Sun’s influence on the Earth’s climate and atmosphere. By observing the Sun’s output of energy and particles, scientists can gain valuable insights into how solar activity affects the Earth’s climate and weather patterns.
Potential Discoveries
The EST’s advanced capabilities open up a vast realm of possibilities for groundbreaking discoveries. These discoveries could revolutionize our understanding of the Sun and its impact on our planet.
- The EST could potentially detect new types of solar activity, providing further insights into the Sun’s complex behavior and its influence on the solar system.
- The EST could shed light on the origins of the solar wind, the constant stream of charged particles that flows from the Sun and interacts with the Earth’s magnetosphere. This knowledge could lead to improved models of space weather forecasting and a better understanding of the Sun’s influence on the heliosphere.
- The EST could provide evidence for the existence of dark matter in the solar corona, a region of the Sun’s atmosphere that is still poorly understood. This discovery would have profound implications for our understanding of the fundamental nature of the universe.