Eus ev battery ambitions hang in balance – EU’s EV battery ambitions hang in balance, a delicate dance between ambition and reality. The European Union has set ambitious goals for EV battery production, aiming to establish itself as a global leader in this burgeoning industry. This move is crucial for the region’s automotive industry, which is rapidly transitioning towards electric vehicles.
However, the road to success is paved with challenges, from securing vital raw materials to navigating fierce competition from established players in Asia.
The EU’s success in achieving its ambitious goals will depend on a multifaceted approach. This includes securing a reliable supply chain for critical raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, fostering innovation in battery technology, and creating a supportive regulatory environment.
Furthermore, collaboration between member states, industry players, and research institutions will be paramount in developing a robust and sustainable EV battery ecosystem.
EU’s EV Battery Ambitions

The European Union (EU) has set ambitious goals for becoming a global leader in electric vehicle (EV) battery production. These ambitions are driven by a desire to secure a strategic position in the rapidly growing EV market, reduce reliance on foreign suppliers, and promote sustainable mobility.
The EU’s efforts to establish a robust domestic battery industry are crucial for the future of its automotive sector and the transition to a cleaner energy future.
Current State of EU EV Battery Production
The EU is currently facing significant challenges in its quest to become a major player in EV battery production. Despite progress in recent years, the region’s market share remains relatively small compared to Asia, particularly China. The EU’s dependence on imports for battery components and materials poses a significant risk to its supply chain security and competitiveness.
When investigating detailed guidance, check out 5 out of the box sustainability ideas from gelatinized marine waste to seaweed straws now.
Challenges
- Limited Manufacturing Capacity:The EU currently lacks sufficient manufacturing capacity to meet its ambitious EV battery production targets. The region’s existing battery factories are struggling to keep pace with the rapidly growing demand for EVs.
- High Production Costs:European battery production costs are generally higher than in Asia, due to factors such as labor costs, energy prices, and regulatory requirements. This makes it challenging for European companies to compete on price with Asian rivals.
- Raw Material Dependence:The EU is heavily reliant on imports for key battery materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This dependence on foreign suppliers creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain and exposes the EU to price fluctuations and potential disruptions.
- Lack of Skilled Workforce:The EU faces a shortage of skilled workers in the battery industry, making it difficult to attract and retain talent. This lack of skilled labor is hindering the development of a robust domestic battery ecosystem.
Successes
- Government Support:The EU has implemented a number of initiatives to support the development of its EV battery industry, including financial incentives, research and development funding, and regulatory frameworks. These efforts have helped to attract investments and foster innovation in the battery sector.
- Growing Battery Manufacturing:The EU has witnessed a significant increase in battery manufacturing capacity in recent years, with several new battery factories being built or announced. These investments are expected to contribute to a more robust and competitive battery industry in the region.
- Focus on Sustainability:The EU is prioritizing sustainable battery production, with a strong focus on environmental and social responsibility. This includes promoting the use of recycled materials and ensuring ethical sourcing practices.
Impact of EU’s EV Battery Ambitions on the Global EV Market
The EU’s ambitious EV battery goals are expected to have a significant impact on the global EV market. By increasing its production capacity and developing a competitive battery industry, the EU aims to become a major supplier of batteries to the global market.
This could potentially lead to:
- Increased Competition:The EU’s entry into the global battery market will intensify competition among battery producers, potentially leading to lower prices and improved battery technologies.
- Shift in Global Battery Supply Chain:The EU’s ambitions could lead to a shift in the global battery supply chain, with more production moving to Europe. This could have implications for the automotive industry and other sectors that rely on batteries.
- Promotion of Sustainable Battery Production:The EU’s focus on sustainable battery production could influence global standards and practices, promoting the use of recycled materials and ethical sourcing in the battery industry.
Factors Affecting the Balance
The EU’s ambition to become a global leader in EV battery production faces a complex interplay of factors, both supportive and hindering. Achieving this goal requires navigating a delicate balance between securing raw materials, fostering innovation, and creating a competitive landscape.
Availability of Raw Materials, Eus ev battery ambitions hang in balance
Securing a consistent supply of critical raw materials, particularly lithium, cobalt, and nickel, is paramount for battery production. These materials are essential for the performance and longevity of EV batteries, and their availability directly impacts the feasibility of the EU’s ambitions.
- The EU currently relies heavily on imports for these materials, primarily from China, Australia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. This dependence creates vulnerabilities in the supply chain, making the EU susceptible to price fluctuations and potential disruptions.
- Efforts are underway to diversify sourcing and reduce dependence on specific countries. The EU is investing in exploration and mining projects within its member states and exploring partnerships with other regions, such as Latin America and Africa.
- Recycling and reuse of battery materials are crucial for sustainable battery production. The EU is implementing policies to promote closed-loop recycling systems, aiming to recover valuable materials from end-of-life batteries and reduce reliance on virgin resources.
Government Policies
Government policies play a pivotal role in shaping the EV battery landscape, influencing investment, innovation, and market competitiveness.
- Subsidies and incentives are crucial for stimulating demand for EVs and battery production. The EU has implemented various financial support programs, including tax breaks and subsidies for EV purchases and battery manufacturing facilities.
- Regulations and standards are essential for ensuring safety, performance, and environmental sustainability of EV batteries. The EU has established strict regulations for battery production, recycling, and disposal, aiming to promote responsible practices and consumer confidence.
- Research and development investments are crucial for driving innovation and technological advancements in battery technology. The EU has allocated significant funds for research and development initiatives, focusing on improving battery performance, reducing costs, and enhancing sustainability.
Competitive Landscape
The global EV battery market is highly competitive, with major players from China, South Korea, and Japan vying for market share.
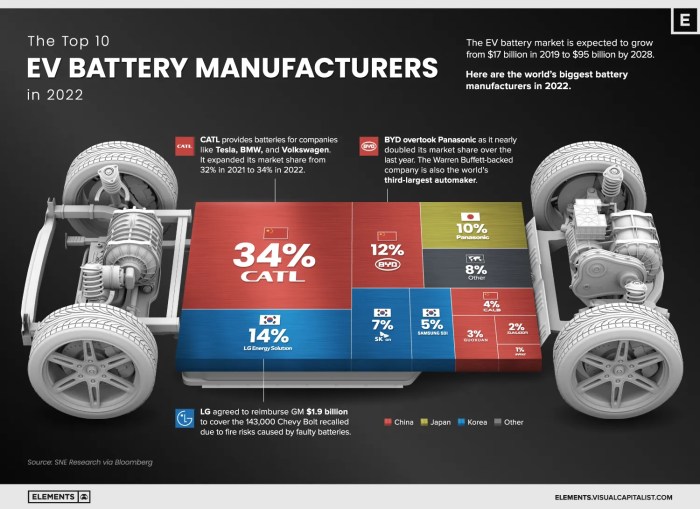
- China dominates the global EV battery market, with significant investments in manufacturing capacity, research and development, and supply chain control. Chinese companies have established strong positions in both domestic and international markets.
- South Korea has emerged as a strong contender, with companies like LG Energy Solution and Samsung SDI making significant contributions to the global EV battery market. South Korean companies are known for their advanced technology and strong manufacturing capabilities.
- The EU faces stiff competition from these established players, requiring a concerted effort to enhance its competitiveness. The EU must leverage its strengths in research, innovation, and manufacturing to create a level playing field and attract investment.
Strategies for Success: Eus Ev Battery Ambitions Hang In Balance

The EU’s ambition to establish a robust and competitive EV battery ecosystem requires a comprehensive strategy that addresses the challenges and opportunities Artikeld previously. This strategy must encompass policy measures, industry collaboration, technological innovation, and environmental sustainability.
A Coordinated Approach
A successful strategy necessitates a coordinated approach involving EU member states, industry players, and research institutions. This collaboration is crucial for achieving the necessary scale and speed of development.
- National Action Plans:Member states should develop and implement national action plans that align with the EU’s overall objectives. These plans should focus on supporting battery production, recycling, and research activities within their respective territories.
- Public-Private Partnerships:Fostering strong public-private partnerships is essential for driving innovation and scaling up production. The EU can leverage its funding programs to incentivize collaborative projects between industry and research institutions.
- Cross-Border Collaboration:Collaboration across borders is crucial for leveraging the strengths of different member states and creating a truly integrated European battery ecosystem. This can involve joint research initiatives, supply chain optimization, and harmonized regulatory frameworks.
Technological Innovation
The EU’s success hinges on developing and deploying innovative battery technologies that can enhance performance, reduce costs, and ensure sustainable production.
- Next-Generation Battery Technologies:Investing in research and development of next-generation battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, is critical for achieving breakthroughs in energy density, charging speed, and lifespan. The EU can support research projects and provide incentives for industry to adopt these technologies.
- Recycling and Second-Life Applications:The EU should prioritize the development of advanced recycling technologies that can recover valuable materials from end-of-life batteries. This will help secure a sustainable supply of critical raw materials and reduce reliance on imports. Moreover, exploring second-life applications for batteries, such as stationary energy storage, can extend their useful lifespan and reduce waste.
- Digitalization and Automation:Embracing digitalization and automation in battery production can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance quality control. The EU can support the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies in the battery sector, fostering innovation and competitiveness.
Environmental Sustainability
Addressing the environmental concerns associated with battery production and recycling is crucial for ensuring the sustainability of the EU’s EV battery ambitions.
- Sustainable Raw Material Sourcing:The EU should prioritize the development of sustainable and responsible sourcing practices for critical raw materials used in battery production. This includes promoting ethical mining practices, reducing reliance on single-source suppliers, and developing alternative materials.
- Low-Carbon Production Processes:The EU should encourage the adoption of low-carbon production processes in the battery industry. This can involve using renewable energy sources, optimizing energy efficiency, and reducing emissions throughout the value chain.
- Responsible Recycling and Waste Management:The EU should implement comprehensive recycling and waste management systems for EV batteries, ensuring that valuable materials are recovered and reused. This requires investing in infrastructure, developing innovative recycling technologies, and promoting responsible disposal practices.