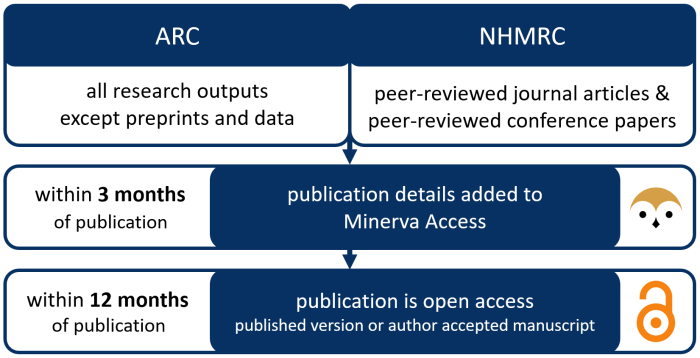
Eu to make open access research default rein in scientific publishing – EU to Make Open Access Research Default: Reining in Scientific Publishing. This bold move by the EU is shaking up the world of scientific research and publishing. For decades, access to scientific knowledge has been limited by paywalls and subscription models.
Now, the EU is leading the charge to make research freely available to everyone, potentially revolutionizing the way we share and advance knowledge.
The EU’s mandate aims to break down these barriers and create a more equitable and collaborative research landscape. This policy shift is driven by a recognition of the immense value of open access research. By removing financial barriers, researchers worldwide can access the latest discoveries, accelerate their own work, and foster greater collaboration.
This shift has far-reaching implications for the scientific publishing industry, researchers, and society as a whole.
The EU’s Open Access Mandate
The European Union (EU) has recently made a bold move towards open access research, mandating that all research funded by the EU be published in open access venues by 2024. This policy shift is a significant development in the ongoing global push for open science, with the potential to reshape the landscape of scientific publishing.
Motivations Behind the Policy Shift
The EU’s decision to mandate open access research is driven by several key motivations. First and foremost, the EU recognizes the immense societal and economic benefits of open access. By making research freely available to everyone, the EU aims to accelerate scientific progress, foster innovation, and stimulate economic growth.
Open access research also promotes transparency and accountability, allowing for greater scrutiny and reproducibility of scientific findings. Additionally, the EU is committed to promoting equality and inclusivity in research, ensuring that everyone has access to the latest scientific knowledge, regardless of their location or financial resources.
Historical Context of the Shift Towards Open Access
The shift towards open access in scientific publishing has been a long and gradual process, with its roots in the early days of the internet. In the 1990s, researchers began to experiment with online platforms for sharing their work, recognizing the potential of the internet to break down traditional barriers to knowledge dissemination.
This early experimentation paved the way for the emergence of open access journals and repositories, which began to gain traction in the early 2000s.The Budapest Open Access Initiative, launched in 2002, was a pivotal moment in the open access movement, outlining a set of principles for promoting open access to research.
This initiative was followed by the development of several other key open access frameworks, including the Berlin Declaration on Open Access to Knowledge in the Sciences and Humanities (2003), the Bethesda Statement on Open Access Publishing (2003), and the Creative Commons licenses (2001).
Comparing the EU’s Approach to Open Access with Other Major Research Regions
The EU’s open access mandate is a significant step forward, but it is not without its challenges. While other major research regions, such as the United States and the United Kingdom, have also implemented open access policies, their approaches differ from the EU’s.The United States, for example, has adopted a more decentralized approach to open access, relying on funding agencies to implement their own open access policies.
This approach has resulted in a patchwork of open access requirements across different research areas and funding agencies. The United Kingdom, on the other hand, has adopted a more centralized approach, with the Research Councils UK (RCUK) mandating open access for all research funded by the UK government.The EU’s approach to open access, which mandates open access for all EU-funded research, is more comprehensive and ambitious than the approaches taken by other major research regions.
However, the EU’s mandate also faces challenges, including the need to ensure that researchers have the necessary support and infrastructure to comply with the new requirements.
Impact on Scientific Publishing
The EU’s Open Access Mandate is poised to significantly reshape the scientific publishing landscape, challenging traditional models and ushering in a new era of accessibility and collaboration. This mandate will have profound implications for both publishers and researchers, presenting both opportunities and challenges.
Implications for Traditional Publishing Models
The mandate’s requirement for open access to publicly funded research will disrupt the traditional model of subscription-based scientific publishing. Publishers, who have long relied on revenue generated from subscriptions, will need to adapt to a new reality where access to research is free and open to all.
This shift will likely lead to a decrease in subscription revenue for publishers, forcing them to explore alternative revenue streams.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for Publishers and Researchers
The mandate’s impact on publishers and researchers can be analyzed from various perspectives. Here’s a table summarizing the key challenges and opportunities for each stakeholder:
| Stakeholder | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Publishers |
|
|
| Researchers |
|
|
Costs and Benefits of Open Access, Eu to make open access research default rein in scientific publishing
The costs and benefits of open access can vary depending on the stakeholder. Here’s a table comparing the costs and benefits for different stakeholders:
| Stakeholder | Costs | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Researchers |
|
|
| Publishers |
|
|
| Society |
|
|
Benefits of Open Access Research: Eu To Make Open Access Research Default Rein In Scientific Publishing
Open access research, where research publications are freely available to anyone with internet access, offers numerous benefits for researchers, institutions, and society as a whole. It promotes knowledge sharing, collaboration, and innovation, ultimately contributing to a more equitable and progressive scientific landscape.
Increased Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Open access research facilitates seamless collaboration and knowledge sharing among researchers worldwide. By eliminating barriers to access, researchers can readily build upon existing work, share their findings with a wider audience, and foster interdisciplinary collaborations. This open exchange of information accelerates scientific progress by eliminating redundancies, encouraging new perspectives, and enabling researchers to leverage the collective knowledge of the global research community.
“Open access allows researchers to build upon the work of others, accelerating the pace of discovery and innovation.”
For example, consider the field of biomedical research. Researchers working on different aspects of a disease can readily access each other’s findings, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the disease and faster development of treatments. This collaborative approach, facilitated by open access, has the potential to significantly impact the fight against diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and infectious diseases.
Increased Research Visibility and Impact
Open access research ensures that research findings are readily available to a wider audience, including researchers, policymakers, and the general public. This increased visibility translates into greater impact, as research can be more effectively disseminated, discussed, and applied to address real-world challenges.
Check launching a startup with friends follow these 4 basic tips to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
“Open access research ensures that research findings reach a wider audience, leading to greater impact and societal benefits.”
For example, open access publications on climate change can inform policymakers and the public about the urgency of the issue and the need for immediate action. This can lead to more informed policy decisions and public engagement in addressing climate change, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Open access research can be more cost-effective than traditional subscription-based models, as it eliminates the need for researchers and institutions to pay for access to published research. This cost-saving can be redirected towards other research activities, such as funding new projects, acquiring equipment, or supporting researchers.
“Open access research can be more cost-effective, freeing up resources for other research activities.”
For instance, imagine a research institution with limited funding. By adopting an open access policy, the institution can save substantial funds on journal subscriptions, allowing it to invest in promising new research projects. This can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and innovations that would otherwise be impossible due to financial constraints.
Enhanced Scientific Progress and Innovation
Open access research fosters a more inclusive and collaborative scientific community, accelerating scientific progress and innovation. By removing barriers to access, it enables researchers to leverage the collective knowledge of the global research community, leading to faster and more efficient breakthroughs.
“Open access research fosters a more inclusive and collaborative scientific community, accelerating scientific progress and innovation.”
Consider the field of renewable energy research. Open access publications on solar energy, wind energy, and other renewable technologies can be accessed by researchers worldwide, fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing. This can lead to faster advancements in renewable energy technologies, contributing to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Broader Societal Benefits
Open access research benefits society as a whole by making knowledge more accessible and empowering individuals to participate in the scientific process. It promotes transparency and accountability in research, ensuring that the public can access and understand research findings. This can lead to more informed decision-making, improved public health, and a more informed citizenry.
“Open access research benefits society as a whole by making knowledge more accessible and empowering individuals to participate in the scientific process.”
For example, open access research on public health issues, such as obesity, can inform individuals about healthy lifestyle choices and empower them to take control of their health. This can lead to a healthier and more productive society, reducing healthcare costs and improving overall well-being.
Challenges and Concerns
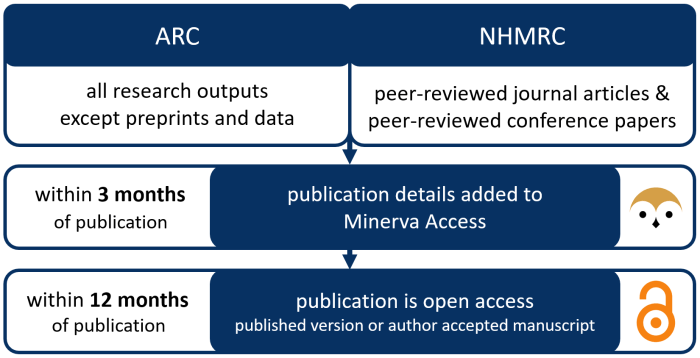
While the vision of open access research is compelling, its implementation presents several challenges and concerns that require careful consideration. The transition to an open access model could potentially disrupt existing funding models and research infrastructure, and there are concerns about unintended consequences and negative impacts.
Impact on Funding Models
The transition to open access research raises concerns about the sustainability of current funding models. Traditionally, scientific publishing has been funded through subscriptions, with institutions paying hefty fees to access journals. Open access models, where research is freely available, necessitate alternative funding mechanisms.
- Author Publication Charges (APCs):Open access journals often charge APCs, requiring authors or their institutions to pay fees for publishing their research. While this model can support the publication process, it can create financial burdens, particularly for researchers in developing countries or with limited funding.
- Open Access Fund:Some institutions and funding agencies are establishing open access funds to cover APCs and other costs associated with open access publishing. However, these funds may not be readily available to all researchers, and their sustainability remains a concern.
- Public Funding Models:Some countries have adopted public funding models where research is funded by public sources, with open access being a requirement for receiving grants. This approach ensures that research funded by taxpayers is freely available, but it also necessitates a shift in how research is funded and managed.
Potential for Unintended Consequences
While the benefits of open access are undeniable, there are concerns about potential unintended consequences.
- Predatory Publishing:The rise of open access has led to an increase in predatory publishers, who exploit the demand for open access by charging exorbitant fees for publishing in journals with low quality control and dubious impact factors. This can undermine the credibility of open access research.
- Quality Control:Concerns exist about maintaining quality control in an open access environment. Without rigorous peer review processes, the risk of publishing flawed or inaccurate research increases.
- Data Security and Privacy:Open access research often involves sharing large datasets, which can raise concerns about data security and privacy. Researchers need to ensure that sensitive data is anonymized and protected to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Solutions to Address Challenges
Addressing the challenges of open access requires a multifaceted approach that involves collaboration between researchers, institutions, funding agencies, and publishers.
- Developing Sustainable Funding Models:Exploring alternative funding models for open access research is crucial. This could involve a combination of public funding, institutional support, and alternative revenue streams, such as author-pays models or subscription-based models that support open access journals.
- Strengthening Quality Control:Ensuring rigorous peer review processes is essential for maintaining the quality of open access research. Initiatives such as the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ) and the Open Access Scholarly Publishing Association (OASPA) play a vital role in promoting quality control and ethical publishing practices.
- Addressing Data Security and Privacy:Establishing clear guidelines and best practices for data sharing and management is essential. This includes ensuring data is anonymized, protected from unauthorized access, and handled in accordance with ethical principles.
The Future of Open Access Research
The EU’s Open Access Mandate has set a bold path for research dissemination, and its impact on scientific publishing is undeniable. As we move forward, it’s crucial to consider the future of open access research and its potential to revolutionize scientific progress.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
The future of open access research is inextricably linked to technological advancements. The development of new platforms, tools, and technologies will play a crucial role in shaping the open access landscape.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can automate tasks like metadata extraction, manuscript processing, and research discovery, improving efficiency and accessibility.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can ensure the integrity and provenance of research data, fostering trust and transparency in the open access ecosystem.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing enables researchers to collaborate and share data more effectively, breaking down geographical barriers and fostering global research collaborations.