Climate startup help decarbonise construction luxembourg – Climate startups help decarbonize construction luxembourg is a vital issue, particularly in a nation like Luxembourg with a thriving construction sector. This blog post delves into the innovative solutions and collaborative efforts that are transforming the industry, making it more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Luxembourg’s construction industry faces a critical challenge in reducing its carbon footprint. The country is committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, and the construction sector plays a pivotal role in reaching this goal. This blog post will explore the current state of the construction industry in Luxembourg, the emergence of climate startups, and the innovative technologies and sustainable practices that are being implemented to create a greener future for the built environment.
The Construction Industry’s Carbon Footprint in Luxembourg
The construction industry in Luxembourg, like its counterparts globally, significantly contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. This sector’s impact extends across various stages, from material extraction and manufacturing to construction activities and building operation. Understanding the specific challenges and opportunities for decarbonization in Luxembourg’s construction sector is crucial for achieving the country’s ambitious sustainability goals.
Carbon Emissions in Luxembourg’s Construction Sector
The construction sector in Luxembourg is responsible for a substantial portion of the country’s overall carbon footprint. While exact figures can vary depending on the specific methodology used, the sector’s contribution to national emissions is estimated to be around 10%, highlighting the need for targeted decarbonization efforts.
Comparison with Other Developed Nations
Luxembourg’s construction sector’s carbon footprint aligns with trends observed in other developed nations. For example, in the European Union, the construction sector contributes approximately 11% of total greenhouse gas emissions. While Luxembourg’s emissions are comparable to this average, there is room for improvement, especially considering the country’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
Major Contributors to Emissions
The construction lifecycle encompasses multiple stages, each contributing to the sector’s overall carbon footprint. Here are some of the key sources of emissions in Luxembourg’s construction sector:
- Material Production:The extraction and processing of raw materials like cement, steel, and concrete account for a significant portion of emissions. Cement production, in particular, is a major contributor, with its manufacturing process releasing substantial amounts of carbon dioxide.
- Construction Activities:Construction activities, including site preparation, transportation, and on-site operations, generate emissions from fuel consumption, machinery use, and waste generation.
- Building Operations:Once completed, buildings contribute to emissions through energy consumption for heating, cooling, and lighting. Energy efficiency measures and the use of renewable energy sources can significantly reduce these operational emissions.
Challenges and Opportunities for Decarbonization
Decarbonizing Luxembourg’s construction sector presents both challenges and opportunities. The following points highlight some key considerations:
- Policy and Regulation:Implementing robust policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable construction practices, promote the use of low-carbon materials, and enforce energy efficiency standards is essential. This can include carbon pricing mechanisms, tax incentives, and building codes that promote sustainable design.
- Technological Innovation:Investing in and promoting technological innovation in construction materials, building technologies, and energy efficiency solutions is crucial. This can involve developing low-carbon concrete alternatives, implementing smart building technologies, and exploring the potential of renewable energy integration in buildings.
- Collaboration and Partnerships:Fostering collaboration between government agencies, industry stakeholders, research institutions, and construction professionals is vital. This collaboration can facilitate knowledge sharing, promote best practices, and drive innovation in sustainable construction.
- Public Awareness and Education:Raising public awareness about the environmental impact of construction and promoting sustainable building practices among consumers is essential. This can involve educational campaigns, public-private partnerships, and initiatives that highlight the benefits of sustainable construction.
Climate Startup Landscape in Luxembourg
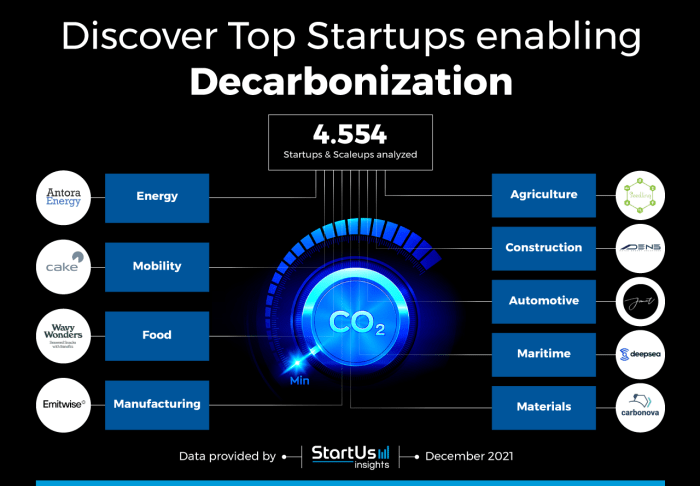
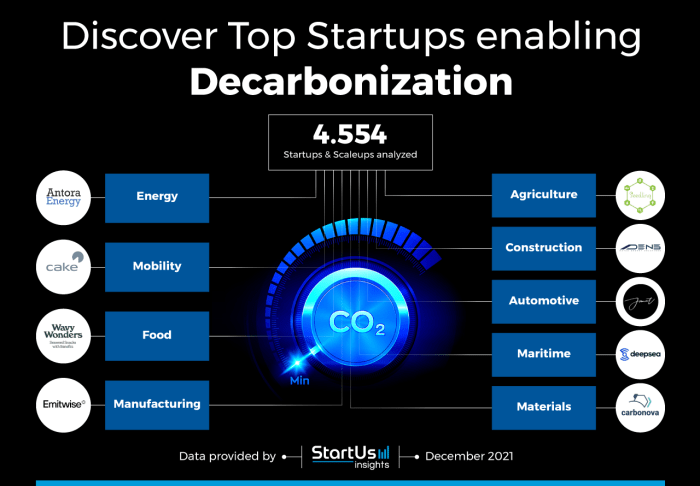
Luxembourg has emerged as a hub for climate startups, attracting entrepreneurs and investors focused on tackling climate change. The country’s commitment to sustainability, coupled with a supportive regulatory environment and access to funding, has fostered a thriving ecosystem for climate innovation.
Key Climate Startups in Luxembourg
Luxembourg is home to a growing number of climate startups operating across various sectors, including renewable energy, sustainable finance, and green technologies. These startups are contributing to the country’s ambitious climate goals and driving innovation in the fight against climate change.
- Green Lighthouse: A company focused on developing and implementing innovative solutions for sustainable construction, including modular buildings and green building materials.
- Envirobat: A startup offering software solutions for environmental impact assessment and reporting, helping businesses track and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Luxinnovation: A public agency supporting innovation and research in Luxembourg, including initiatives to promote climate-friendly technologies and businesses.
Government Support and Initiatives for Climate Startups
The Luxembourg government recognizes the importance of climate startups in driving the country’s transition to a sustainable economy. Several initiatives and programs are in place to support climate startups, including:
- The Climate Fund: A dedicated fund to support climate-related projects and initiatives, including those led by startups.
- The Climate Technology Innovation Platform: A platform connecting climate startups with investors, mentors, and industry partners to accelerate their growth and impact.
- Tax incentives: The government offers tax incentives for companies investing in renewable energy and other climate-friendly technologies.
Potential for Climate Startups to Contribute to Decarbonizing Construction in Luxembourg
Climate startups have the potential to significantly contribute to decarbonizing the construction sector in Luxembourg. By developing innovative solutions for sustainable building materials, energy-efficient construction methods, and carbon capture technologies, these startups can help reduce the sector’s environmental footprint.
- Green Building Materials: Startups developing sustainable alternatives to traditional building materials, such as recycled materials and bio-based materials, can reduce the sector’s reliance on resource-intensive materials.
- Energy-Efficient Construction: Startups focusing on energy-efficient design and construction methods, such as passive house design and smart building technologies, can reduce energy consumption in buildings.
- Carbon Capture Technologies: Startups developing technologies to capture and store carbon emissions from construction activities can help mitigate the sector’s impact on climate change.
Innovative Technologies for Decarbonizing Construction: Climate Startup Help Decarbonise Construction Luxembourg
The construction industry is a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions. This makes it crucial to explore and implement innovative technologies that can reduce the carbon footprint of construction projects. This section will explore some of the most promising technologies for decarbonizing construction, highlighting their potential applications and impact on emissions.
Technologies for Decarbonizing Construction
These technologies offer a wide range of solutions to reduce emissions in various stages of construction, from material production to building operation.
| Technology Name | Description | Applications in Construction | Potential Impact on Carbon Emissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mass Timber Construction | Utilizes large-scale wood panels as structural elements, reducing reliance on concrete and steel. | Multi-story buildings, residential projects, and commercial structures. | Significantly reduces embodied carbon emissions compared to traditional concrete and steel construction. |
| Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) | A type of engineered wood panel composed of layers of lumber glued together, offering high strength and durability. | Floor and wall systems, roof structures, and prefabricated modular units. | Lowers embodied carbon emissions and reduces construction waste. |
| Prefabricated Construction | Off-site manufacturing of building components, reducing on-site construction time and waste. | Residential homes, commercial buildings, and infrastructure projects. | Minimizes construction waste, reduces energy consumption, and improves construction efficiency. |
| 3D Printing Construction | Utilizes digital models to create building structures layer by layer, using concrete, soil, or other materials. | Building prototypes, complex structures, and customized architectural designs. | Reduces waste, minimizes labor requirements, and enables more sustainable building designs. |
| Bio-based Materials | Employs natural materials like hemp, bamboo, and mycelium to create building components. | Insulation, flooring, and structural elements. | Reduces reliance on fossil fuel-based materials, promoting sustainable and renewable resources. |
| Solar-Powered Construction Equipment | Utilizes solar energy to power construction machinery and equipment. | Heavy equipment, cranes, and lighting systems. | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers operational emissions. |
| Building Information Modeling (BIM) | A digital representation of a building project, facilitating efficient planning, design, and construction. | Construction planning, design coordination, and material optimization. | Reduces waste, optimizes material usage, and enhances construction efficiency. |
| Smart Building Technologies | Integrates sensors, automation, and data analytics to optimize building performance and energy consumption. | Lighting systems, HVAC controls, and energy management systems. | Reduces energy consumption and lowers operational carbon emissions. |
Feasibility of Implementing Technologies in Luxembourg
Luxembourg’s construction sector can benefit from the implementation of these technologies. The country has a strong commitment to sustainability and a supportive regulatory environment for green building practices. The adoption of these technologies can be further facilitated by:* Government Incentives:Providing financial incentives and tax breaks for using sustainable construction materials and technologies.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring the dutch commitment to cycling is a challenge to the whole of europe.
Public-Private Partnerships
Encouraging collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private companies to develop and deploy innovative solutions.
Skill Development
Investing in training programs to equip the construction workforce with the skills needed to implement these technologies effectively.
Awareness Campaigns
Raising awareness among stakeholders about the benefits of sustainable construction and the availability of innovative technologies.
Implementing these technologies in Luxembourg’s construction sector presents a significant opportunity to reduce the industry’s carbon footprint and contribute to the country’s sustainability goals.
Sustainable Building Materials and Practices
The construction industry in Luxembourg is actively seeking to reduce its environmental impact. Sustainable building materials and practices are crucial for achieving this goal. By incorporating these elements, the industry can significantly reduce its carbon footprint and promote a more sustainable built environment.
Use of Sustainable Building Materials in Luxembourg’s Construction Sector
The use of sustainable building materials is gaining momentum in Luxembourg’s construction sector. This shift towards environmentally friendly materials is driven by a combination of factors, including:* Environmental Regulations:Luxembourg has implemented strict environmental regulations, including the “Circular Economy Package,” which encourages the use of sustainable building materials and promotes resource efficiency.
Government Incentives
The government provides financial incentives and tax breaks for projects that utilize sustainable building materials and practices.
Growing Awareness
There is a growing awareness among architects, developers, and consumers about the environmental impact of construction materials.
Types of Sustainable Building Materials and their Environmental Benefits
Here is a list of sustainable building materials commonly used in Luxembourg, along with their environmental benefits:
- Wood:Wood is a renewable resource that sequesters carbon dioxide during its growth. Using sustainably harvested wood reduces the need for energy-intensive materials like concrete and steel.
- Bamboo:Bamboo is a rapidly growing, renewable resource that requires minimal water and is naturally strong and durable.
- Recycled Concrete:Recycled concrete aggregates are produced from demolished concrete structures, reducing the need for virgin materials and minimizing landfill waste.
- Recycled Steel:Using recycled steel in construction reduces the energy required to produce new steel, lowering carbon emissions.
- Bio-based Materials:Materials derived from plants, such as hemp, flax, and straw, offer a sustainable alternative to traditional building materials, providing good insulation and thermal performance.
- Geothermal Energy:Utilizing geothermal energy for heating and cooling systems reduces reliance on fossil fuels and minimizes carbon emissions.
Case Study: Sustainable Construction Project in Luxembourg
“The ‘House of the Future’ project in Luxembourg City showcases the successful implementation of sustainable building practices. The project incorporates a variety of sustainable building materials, including wood, recycled concrete, and geothermal energy. The building is designed to be energy-efficient and has achieved a high level of sustainability certification. The project demonstrates that sustainable construction can be both environmentally friendly and economically viable.”
Impact of Sustainable Building Practices on Carbon Emissions
Adopting sustainable building practices can significantly reduce carbon emissions in the construction industry. Here are some key impacts:* Reduced Material Production:Using recycled and renewable materials reduces the energy and resources needed to produce new materials, minimizing carbon emissions.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Sustainable building designs incorporate features that enhance energy efficiency, such as high-performance insulation and solar panels, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced carbon emissions.
Reduced Waste Generation
Sustainable construction practices emphasize waste reduction and recycling, minimizing the amount of construction waste sent to landfills.
Increased Carbon Sequestration
Using materials like wood and bamboo, which store carbon dioxide during their growth, can help offset carbon emissions.
Collaboration and Partnerships for Decarbonization
Decarbonizing the construction sector in Luxembourg requires a concerted effort from various stakeholders. Collaboration between climate startups, construction companies, and government agencies is crucial for achieving significant progress in reducing emissions.
The Importance of Collaboration
Collaboration is essential for achieving ambitious decarbonization goals. By sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise, stakeholders can:
- Accelerate innovation: Climate startups can develop innovative technologies and solutions, while construction companies can provide real-world testing grounds and feedback. This synergy can lead to faster adoption of sustainable practices.
- Overcome financial barriers: Government agencies can provide funding and incentives to support the development and deployment of decarbonization technologies. This can encourage investment and reduce the risk associated with adopting new solutions.
- Foster a shared vision: Collaborative efforts can align the goals and objectives of different stakeholders, creating a unified vision for a sustainable construction sector. This shared vision can drive collective action and ensure that decarbonization efforts are aligned with broader sustainability goals.
Potential Partnerships in Luxembourg, Climate startup help decarbonise construction luxembourg
Luxembourg has a strong ecosystem for climate startups and a growing construction sector. Potential partnerships could include:
- Climate startups and construction companies: Startups can provide construction companies with innovative technologies for reducing emissions in areas such as energy efficiency, materials, and construction processes. Companies can provide startups with real-world testing opportunities and valuable feedback on their solutions.
- Climate startups and government agencies: Startups can collaborate with government agencies to develop and implement policies and regulations that promote sustainable construction practices. Agencies can also provide funding and support for research and development of new technologies.
- Construction companies and government agencies: Construction companies can work with government agencies to develop and implement sustainable building codes and standards. Agencies can also provide incentives for companies to adopt sustainable practices.
Public-Private Partnerships for Decarbonization
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) can play a significant role in accelerating decarbonization initiatives. PPPs involve collaboration between government agencies and private sector entities to achieve common goals.
- Shared risk and reward: PPPs can distribute the risk and reward associated with implementing decarbonization technologies. This can encourage private sector investment in sustainable solutions.
- Access to expertise: Government agencies can leverage the expertise of private sector companies in areas such as technology development, project management, and financing. Private sector companies can benefit from the government’s policy expertise and regulatory framework.
- Scalability and impact: PPPs can facilitate the scaling up of successful decarbonization initiatives. By combining public and private resources, projects can achieve greater impact and reach.
Collaboration Pathways
The following flowchart illustrates potential collaboration pathways between stakeholders:[Diagram] [Flowchart description]The flowchart demonstrates how climate startups, construction companies, and government agencies can work together to achieve decarbonization goals. Climate startups can develop innovative technologies, while construction companies can provide real-world testing grounds and feedback.
Government agencies can provide funding, incentives, and policy support. PPPs can facilitate collaboration and leverage the strengths of each stakeholder.
Policy and Regulatory Framework for Sustainable Construction
Luxembourg, a country committed to environmental sustainability, has established a robust policy and regulatory framework to promote sustainable construction practices. This framework aims to minimize the environmental impact of the construction sector while fostering innovation and economic growth.
Current Policies and Regulations
Luxembourg’s sustainable construction policies are driven by national and European Union (EU) directives. The country has implemented several regulations and initiatives, including:
- Building Regulations:The Grand Duchy’s building regulations, enforced by the Ministry of Sustainable Development and Infrastructure, incorporate energy efficiency requirements and promote the use of sustainable materials. These regulations specify minimum energy performance standards for new buildings, encouraging the use of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient building technologies.
- Green Building Certifications:The government actively encourages the use of green building certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method). These certifications provide a framework for assessing the environmental performance of buildings and promote best practices in sustainable construction.
- Financial Incentives:Luxembourg offers various financial incentives to encourage the adoption of sustainable construction practices. These incentives include tax breaks for investments in renewable energy systems, grants for energy-efficient renovations, and subsidies for the use of sustainable building materials.
- Public Procurement:The government has implemented policies that prioritize sustainable construction in public procurement. This includes requiring contractors to adhere to specific environmental standards and using sustainable materials in public projects.
Policy Recommendations to Incentivize Climate-Friendly Construction Practices
While Luxembourg has made significant progress in promoting sustainable construction, there is still room for improvement. Several policy recommendations can further incentivize the adoption of climate-friendly construction practices:
- Strengthening Building Regulations:The government should consider strengthening building regulations by setting more ambitious energy efficiency standards and incorporating stricter requirements for the use of sustainable materials. This can encourage the construction industry to adopt innovative technologies and practices that minimize environmental impact.
- Expanding Financial Incentives:The government can further expand financial incentives to make sustainable construction more financially attractive. This can include increasing the amount of subsidies for renewable energy systems, extending tax breaks for green building investments, and introducing incentives for the use of innovative, low-carbon building materials.
- Promoting Circular Economy Principles:Implementing policies that promote circular economy principles in the construction sector can significantly reduce waste and emissions. This can include promoting the reuse and recycling of construction materials, supporting the development of circular construction models, and establishing infrastructure for material recovery and recycling.
- Supporting Research and Development:Investing in research and development initiatives focused on innovative, climate-friendly construction technologies and materials can drive innovation and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable construction sector. This can include funding research projects, establishing partnerships between universities and industry, and creating incentives for the development of low-carbon construction solutions.
- Promoting Collaboration and Partnerships:Fostering collaboration and partnerships between government, industry, research institutions, and NGOs can create a more supportive ecosystem for sustainable construction. This can involve establishing platforms for knowledge sharing, facilitating joint research projects, and promoting best practices in sustainable construction.
Impact of Regulatory Changes on Climate Startups
Regulatory changes that promote sustainable construction can significantly impact the growth of climate startups in the construction sector. These changes can create new market opportunities for startups developing innovative solutions for decarbonizing construction, such as:
- Demand for Sustainable Building Materials:As regulations become stricter and incentives are offered, the demand for sustainable building materials will increase. This creates opportunities for startups developing new, low-carbon building materials or innovative solutions for reusing and recycling existing materials.
- Adoption of Energy-Efficient Technologies:Regulations and incentives promoting energy efficiency in buildings create demand for innovative technologies that can reduce energy consumption. This opens doors for startups developing smart building systems, renewable energy integration solutions, and energy-efficient building design technologies.
- Digitalization and Data-Driven Construction:Regulatory changes can encourage the adoption of digitalization and data-driven approaches in construction. This can benefit startups developing technologies for building information modeling (BIM), construction management software, and data analytics platforms for optimizing building performance and sustainability.
- Access to Funding and Support:Government support through funding programs, grants, and incentives can provide crucial support for climate startups in the construction sector. This can help them develop their technologies, scale their businesses, and bring their innovative solutions to the market.
Policy Recommendations and Expected Outcomes
The following table Artikels key policy recommendations and their expected outcomes: